
Write the function of RNA polymerase II.
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: The polymer means multiple protein units making a complex single unit. And polymerase means an enzyme that speeds up the formation of those complex single units. Catalysis is a major characteristic of a polymerase enzyme. The term RNA polymerase means an enzyme that is employed in forming complex RNA units.
Step by step answer:The RNA (Ribonucleic acid) polymerase II or RNAP II or Pol II is a multi-protein complex enzyme that plays a major role in the transcription process of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). RNA polymerase II is one of the three major RNA polymerase enzymes found in the eukaryotic cell’s nucleus. Usually, all these enzymes work in pairs to synthesize different RNA molecules.
RNA polymerase I transcribe rRNAs and RNA polymerase III functions in transcribing tRNAs.
RNA polymerase II, on the other hand, is the enzyme that transcribes the heterogeneous nuclear RNA or hnRNA which is the precursor of mRNA. It fastens the reaction rate of the transcription process of DNA to synthesize mRNA.
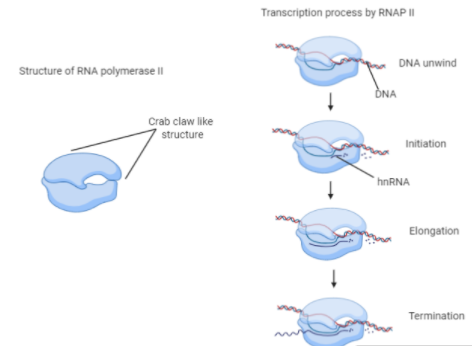
RNAP II has 12 subunits in total, out of which 10 subunits are common to those that are found in other RNA polymerases. Additionally, the RNAP II has extra two subunits that initiate transcription and helps in post-transcriptional modifications.
In general, the RNAP II works in association with five general transcription factors. It binds to the promoter site of DNA with these factors and forms the pre-initiation complex to start the initiation process. It always forms the RNA strand from 5’ to 3’ direction. After the initiation, the RNA strand gets extended and complementary nucleotides are added.
Once the RNAP II reaches the end of the DNA target sequence it recognizes the special type of termination sequence. This sequence commands it to end the process and to stop transcription.
Note: RNA polymerase is different from DNA polymerase. RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA and DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA. Also, the transcription processes carried out by both enzymes are different from each other. The RNA polymerase does not require any starting sequence to initiate polynucleotide chain formation. Thus, the process governs by it is called de novo.
Step by step answer:The RNA (Ribonucleic acid) polymerase II or RNAP II or Pol II is a multi-protein complex enzyme that plays a major role in the transcription process of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). RNA polymerase II is one of the three major RNA polymerase enzymes found in the eukaryotic cell’s nucleus. Usually, all these enzymes work in pairs to synthesize different RNA molecules.
RNA polymerase I transcribe rRNAs and RNA polymerase III functions in transcribing tRNAs.
RNA polymerase II, on the other hand, is the enzyme that transcribes the heterogeneous nuclear RNA or hnRNA which is the precursor of mRNA. It fastens the reaction rate of the transcription process of DNA to synthesize mRNA.

RNAP II has 12 subunits in total, out of which 10 subunits are common to those that are found in other RNA polymerases. Additionally, the RNAP II has extra two subunits that initiate transcription and helps in post-transcriptional modifications.
In general, the RNAP II works in association with five general transcription factors. It binds to the promoter site of DNA with these factors and forms the pre-initiation complex to start the initiation process. It always forms the RNA strand from 5’ to 3’ direction. After the initiation, the RNA strand gets extended and complementary nucleotides are added.
Once the RNAP II reaches the end of the DNA target sequence it recognizes the special type of termination sequence. This sequence commands it to end the process and to stop transcription.
Note: RNA polymerase is different from DNA polymerase. RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA and DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA. Also, the transcription processes carried out by both enzymes are different from each other. The RNA polymerase does not require any starting sequence to initiate polynucleotide chain formation. Thus, the process governs by it is called de novo.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




