
Write the Haworth structure of maltose.
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: Haworth structure is a way of representing monosaccharides or disaccharides in a 3D manner. Maltose is an example of disaccharide. It is a combination of two glucose molecules.
Complete step by step solution:
Carbohydrates are the most abundant organic compounds of plants. They serve as the major source of chemical energy for living organisms and of supporting tissues. Simple carbohydrates are called saccharides or sugars. E.g. Glucose, fructose, maltose, sucrose. They are classified into simple and complex carbohydrates based on the number of sugar molecules. Simple carbohydrates include monosaccharides and disaccharides. Complex carbohydrates include oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, glycogen, starch, fibers.
Disaccharides can be broken down to two monosaccharides by hydrolysis.
E.g. Glucose + galactose gives lactose
Glucose + fructose gives sucrose
Glucose + glucose gives maltose which is given below:
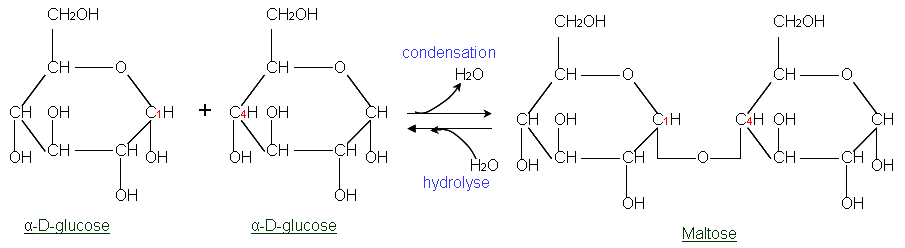
It is joined by the first carbon of one glucose and fourth carbon of another glucose. It reduces sugar. Maltose can be broken down to glucose with the help of maltase enzyme. There is a free aldehyde group remaining. Maltose is also known as malt sugar.
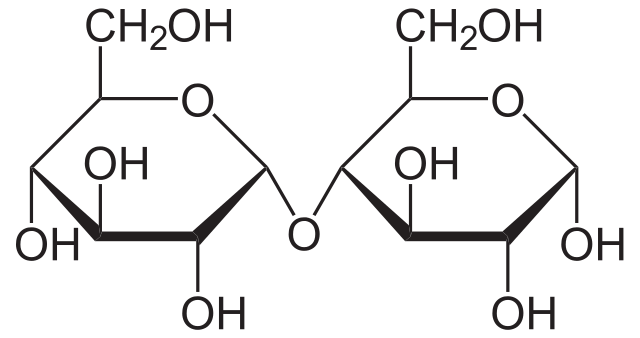
This is the Haworth structure of maltose. It is the common way of representing the structural formula in a cyclic 3D manner. Thick line represents that the atoms are closer and the thinner lines are far from the observer. The groups below the ring plane are the groups which are on the left side of carbon in Fischer projection.
Additional information:
Lactose is also known as milk sugar. The sugar in sugar cane is called sucrose. Disaccharides are formed by combining monosaccharides with removal of water which is called dehydration reaction.
Note: Maltose is produced commercially by hydrolysis of starch. It is also used in alcohol production. When converted to glucose, it is used as an energy source for growing embryos in seed.
Complete step by step solution:
Carbohydrates are the most abundant organic compounds of plants. They serve as the major source of chemical energy for living organisms and of supporting tissues. Simple carbohydrates are called saccharides or sugars. E.g. Glucose, fructose, maltose, sucrose. They are classified into simple and complex carbohydrates based on the number of sugar molecules. Simple carbohydrates include monosaccharides and disaccharides. Complex carbohydrates include oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, glycogen, starch, fibers.
Disaccharides can be broken down to two monosaccharides by hydrolysis.
E.g. Glucose + galactose gives lactose
Glucose + fructose gives sucrose
Glucose + glucose gives maltose which is given below:

It is joined by the first carbon of one glucose and fourth carbon of another glucose. It reduces sugar. Maltose can be broken down to glucose with the help of maltase enzyme. There is a free aldehyde group remaining. Maltose is also known as malt sugar.

This is the Haworth structure of maltose. It is the common way of representing the structural formula in a cyclic 3D manner. Thick line represents that the atoms are closer and the thinner lines are far from the observer. The groups below the ring plane are the groups which are on the left side of carbon in Fischer projection.
Additional information:
Lactose is also known as milk sugar. The sugar in sugar cane is called sucrose. Disaccharides are formed by combining monosaccharides with removal of water which is called dehydration reaction.
Note: Maltose is produced commercially by hydrolysis of starch. It is also used in alcohol production. When converted to glucose, it is used as an energy source for growing embryos in seed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




