
Write the IUPAC name for the given compound:
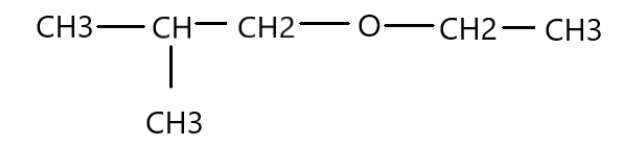
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: The oxygen atom in between the compounds means that it is an ether. The general formula of ether is “alkoxy alkane”. We need to name two sides of the oxygen atom and then combine them to get the IUPAC name.
Complete step by step answer:
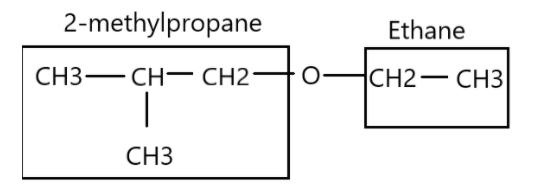
The presence of -O- atom means that the compound is an ether. Nomenclature of an ether has general formula “alkoxyalkane”. Therefore, the left side of oxygen atom is a propane due to three carbon atoms and the -methyl group position at second position makes it 2-methylpropane. The right side of oxygen atom is ethane because of presence of two carbon atoms. Combining both the sides we get 1-ethoxy-2-methylpropane.
Therefore, the IUPAC name of this compound is 1-ethoxy-2-methylpropane.
Additional Information:
1-ethoxy-2-methylpropane is also known as Ethyl isobutyl ether and Isobutyl ethyl ether. It is a chemical compound from the group of ethers, more precisely dialkyl ether. The compound is in the form of a liquid at room temperature and is relatively inert.
There are various IUPAC rules for naming organic compounds. The base part of the name reflects the number of carbons in the parent chain. The suffix of the name reflects the type of functional group present on the parent chain. Other groups which are attached to the parent chain are called substituents.
For alkanes, prefix is used based on the number of carbons. They are meth, eth, prop, but, pent, hex, hept, oct, non, dec, undec and dode for number of carbons from 1 to 12.
For ethers, the two alkyl groups attached to the oxygen are put in alphabetical order with spaces between the names and they are followed by the word ether.
Note:
IUPAC naming rules are different for compounds with different suffixes and prefixes to identify them. Alcohols, alkanes, alkyl halides, Alkenes and alkynes, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters and amines are different categories with different prefixes and suffixes to identify them.
Complete step by step answer:
The presence of -O- atom means that the compound is an ether. Nomenclature of an ether has general formula “alkoxyalkane”. Therefore, the left side of oxygen atom is a propane due to three carbon atoms and the -methyl group position at second position makes it 2-methylpropane. The right side of oxygen atom is ethane because of presence of two carbon atoms. Combining both the sides we get 1-ethoxy-2-methylpropane.

Therefore, the IUPAC name of this compound is 1-ethoxy-2-methylpropane.
Additional Information:
1-ethoxy-2-methylpropane is also known as Ethyl isobutyl ether and Isobutyl ethyl ether. It is a chemical compound from the group of ethers, more precisely dialkyl ether. The compound is in the form of a liquid at room temperature and is relatively inert.
There are various IUPAC rules for naming organic compounds. The base part of the name reflects the number of carbons in the parent chain. The suffix of the name reflects the type of functional group present on the parent chain. Other groups which are attached to the parent chain are called substituents.
For alkanes, prefix is used based on the number of carbons. They are meth, eth, prop, but, pent, hex, hept, oct, non, dec, undec and dode for number of carbons from 1 to 12.
For ethers, the two alkyl groups attached to the oxygen are put in alphabetical order with spaces between the names and they are followed by the word ether.
Note:
IUPAC naming rules are different for compounds with different suffixes and prefixes to identify them. Alcohols, alkanes, alkyl halides, Alkenes and alkynes, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters and amines are different categories with different prefixes and suffixes to identify them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




