
Write the method to determine the value of an unknown resistance by meter bridge and derive the necessary formula. Draw a circuit diagram.
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: When no current flows through the coil or, the potential difference across the galvanometer is zero the bridge is said to be in a balanced condition.
Complete answer:
The Meter bridge is the modification of Wheatstone’s network used to determine the value of unknown resistance.
The meter bridge consists of a thin, uniform, and homogenous conducting wire AC, rectangular wooden board between two thick L shaped metal strips C1 and C2 as shown in the diagram.
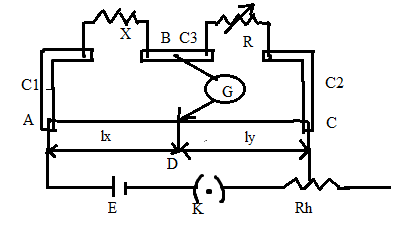
In the diagram AC- conducting wire
C1, C2, and C3- metal strips
E- cell
X- unknown resistance
R- resistance box
D- null point
K’- jockey
G- galvanometer
Rh- rheostat
To determine the unknown resistance, the circuit is connected as shown in the diagram. The unknown resistance X is connected in one gap (left gap) and a resistance box (known variable resistor) is connected in another gap (right gap).
A cell of emf E, key K, and rheostat Rh are connected to junction B of X and R also other terminal connected to the jockey.
The jockey is placed at points A and C and the deflection is checked in the galvanometer. This deflection must be on opposite sides otherwise rheostat and the value of resistance from the resistance box should be adjusted.
A suitable value of resistance R is taken in the resistance box and by touching the jockey at different points of the wire AC, a point D is obtained for which the galvanometer shows zero deflection, point D is called the null point.
Let $l_x$ and $l_y$ be the distances of the null point D (balancing lengths) measured in centimeters from end A and C of the wire AC respectively and σ be the resistance per unit length of wire AC.
Here X, R, and resistances of wire AD and wire CD from arms of Wheatstone’s network.
Therefore from balancing condition,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\text{X}}}{{\text{R}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{Resistance of wire AD}}}}{{{\text{Resistance of wire CD}}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\text{X}}}{{\text{R}}} = \dfrac{{\sigma {l_X}}}{{\sigma {l_y}}} = \dfrac{{{l_X}}}{{{l_y}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{X = R}}\left( {\dfrac{{{l_X}}}{{{l_y}}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{X = R}}\left( {\dfrac{{{l_X}}}{{100 - {l_x}}}} \right)\]
$\therefore$ Hence the unknown resistance X can be determined by using the formula \[{\text{X = R}}\left( {\dfrac{{{l_X}}}{{100 - {l_x}}}} \right)\].
Note:
Slide wire is known as a meter bridge. The meter bridge is an instrument that works on the principle of the Wheatstone bridge. A meter bridge is also a simple type of the potentiometer that is used to measure the resistance and it is being used in the school laboratories.
Complete answer:
The Meter bridge is the modification of Wheatstone’s network used to determine the value of unknown resistance.
The meter bridge consists of a thin, uniform, and homogenous conducting wire AC, rectangular wooden board between two thick L shaped metal strips C1 and C2 as shown in the diagram.

In the diagram AC- conducting wire
C1, C2, and C3- metal strips
E- cell
X- unknown resistance
R- resistance box
D- null point
K’- jockey
G- galvanometer
Rh- rheostat
To determine the unknown resistance, the circuit is connected as shown in the diagram. The unknown resistance X is connected in one gap (left gap) and a resistance box (known variable resistor) is connected in another gap (right gap).
A cell of emf E, key K, and rheostat Rh are connected to junction B of X and R also other terminal connected to the jockey.
The jockey is placed at points A and C and the deflection is checked in the galvanometer. This deflection must be on opposite sides otherwise rheostat and the value of resistance from the resistance box should be adjusted.
A suitable value of resistance R is taken in the resistance box and by touching the jockey at different points of the wire AC, a point D is obtained for which the galvanometer shows zero deflection, point D is called the null point.
Let $l_x$ and $l_y$ be the distances of the null point D (balancing lengths) measured in centimeters from end A and C of the wire AC respectively and σ be the resistance per unit length of wire AC.
Here X, R, and resistances of wire AD and wire CD from arms of Wheatstone’s network.
Therefore from balancing condition,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\text{X}}}{{\text{R}}} = \dfrac{{{\text{Resistance of wire AD}}}}{{{\text{Resistance of wire CD}}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\text{X}}}{{\text{R}}} = \dfrac{{\sigma {l_X}}}{{\sigma {l_y}}} = \dfrac{{{l_X}}}{{{l_y}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{X = R}}\left( {\dfrac{{{l_X}}}{{{l_y}}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{X = R}}\left( {\dfrac{{{l_X}}}{{100 - {l_x}}}} \right)\]
$\therefore$ Hence the unknown resistance X can be determined by using the formula \[{\text{X = R}}\left( {\dfrac{{{l_X}}}{{100 - {l_x}}}} \right)\].
Note:
Slide wire is known as a meter bridge. The meter bridge is an instrument that works on the principle of the Wheatstone bridge. A meter bridge is also a simple type of the potentiometer that is used to measure the resistance and it is being used in the school laboratories.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




