
Write the reaction involved in the extraction of copper from its ore by electrolytic refining.
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Electrolytic refining is the final step of purification in the whole process of obtaining copper metal from its ore. In this process purification is done using copper sulfate solution and deposition of pure copper takes place at cathode and overall a redox reaction takes place.
Complete step by step answer:
In an electrolytic cell, anode is made of impure copper and cathode is made of pure copper and they are dipped in the solution of copper sulphate.
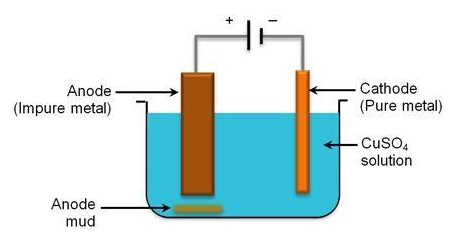
When current passed through the solution, copper ions from solution moved towards cathode and sulphate ions move towards anode.
Copper ions get reduced and get deposited on cathode.
At cathode: $C{{u}^{2+}}(aq)+2{{e}^{-}}\to Cu(s)$
Sulfate ions make sure that the copper atoms present in anode rod get oxidized and come into the solution.
At canode: $Cu(s)\to Cu(aq)+2{{e}^{-}}$
So overall copper ions from the solution are getting deposited on the cathode and copper atoms from the anode are coming into the solution. Therefore we are getting pure copper at cathode. With time, the cathode rod will get thicker because of deposition and the anode rod gets thinner because of dissolution.
Any metal in the impure anode which is below copper in the electrochemical series (reactivity series) does not go into solution as ions. It stays as a metal and falls to the bottom of the cell as "anode sludge" together with any unreactive material left over from the ore. The anode sludge will contain valuable metals such as silver and gold.
Additional information:
Chalcopyrite, chalcocite, covellite, bornite are the major sulfide ores of copper from which copper is usually obtained.
Note: when copper is obtained from its ore chalcopyrite, first of all froth flotation is done to increase the concentration of ore. After this, copper is heated in bassemerisar along with silica in presence of air. From this we get blister copper that we take for electrolytic refining.
Complete step by step answer:
In an electrolytic cell, anode is made of impure copper and cathode is made of pure copper and they are dipped in the solution of copper sulphate.

When current passed through the solution, copper ions from solution moved towards cathode and sulphate ions move towards anode.
Copper ions get reduced and get deposited on cathode.
At cathode: $C{{u}^{2+}}(aq)+2{{e}^{-}}\to Cu(s)$
Sulfate ions make sure that the copper atoms present in anode rod get oxidized and come into the solution.
At canode: $Cu(s)\to Cu(aq)+2{{e}^{-}}$
So overall copper ions from the solution are getting deposited on the cathode and copper atoms from the anode are coming into the solution. Therefore we are getting pure copper at cathode. With time, the cathode rod will get thicker because of deposition and the anode rod gets thinner because of dissolution.
Any metal in the impure anode which is below copper in the electrochemical series (reactivity series) does not go into solution as ions. It stays as a metal and falls to the bottom of the cell as "anode sludge" together with any unreactive material left over from the ore. The anode sludge will contain valuable metals such as silver and gold.
Additional information:
Chalcopyrite, chalcocite, covellite, bornite are the major sulfide ores of copper from which copper is usually obtained.
Note: when copper is obtained from its ore chalcopyrite, first of all froth flotation is done to increase the concentration of ore. After this, copper is heated in bassemerisar along with silica in presence of air. From this we get blister copper that we take for electrolytic refining.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




