
Write the relation between focal length and radius of curvature of a spherical mirror.
Answer
526.6k+ views
Hint: Before stating the relation, derive the relation between radius of curvature and the focal length of a mirror. This will help you understand better. Use the fact that when a parallel ray of light falls on a concave mirror, it passes through the focus of the mirror after reflection.
Complete step by step answer:
The relation between focal length (f) and radius of curvature (R) of a spherical mirror is that the focal length is equal to half of the radius of curvature i.e. $f=\dfrac{R}{2}$.
Let us derive this relation.
Consider a concave mirror such that its radius of curvature is very much larger than the diameter of its aperture.
We can take help from the figure given.
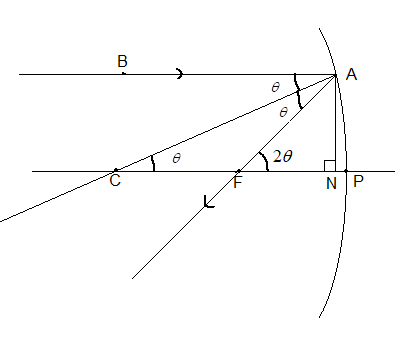
Suppose a parallel ray of light is incident on the mirror as shown in the figure. Let this incident ray make an angle $\theta $ with normal to the surface of the mirror. Since this mirror is part of a circle, the normal drawn to the surface of the circle passes through the centre (C) of the mirror.
We know that rays of light parallel to the principal axis passing through the focus (F) of a concave mirror, after reflection.
According to the law of reflections, the angle of incidence and angle of reflection are equal. Therefore, $\angle BAC=\angle FAC=\theta $ as shown in the given figure.
Since BA and PC are parallel, $\angle BAC=\angle ACF=\theta $.
Therefore, from exterior angle theorem $\angle AFN=\angle ACF+\angle CAF=2\theta $.
Now drop a normal CP from point A. Let the foot of this normal be N.
Here, $\tan \theta =\dfrac{AN}{CN}\Rightarrow AN=CN\tan \theta $ ……. (i).
$\tan 2\theta =\dfrac{AN}{FN}\Rightarrow AN=FN\tan 2\theta $ ….. (ii).
From equation (i) and equation (ii) we get,
$CN\tan \theta =FN\tan 2\theta $
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{CN}{FN}=\dfrac{\tan 2\theta }{\tan \theta }$ …… (iii).
Since the radius of curvature is very much larger than the diameter of its aperture, NP is very small compared to CN and CP and $\theta $ will be a small angle .
Therefore, $CN\approx CP$ and $FN\approx FP$.
For small angles $\tan \theta =\theta $ and $\tan 2\theta =2\theta $.
Therefore, equation (iii) can be written as
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{CP}{FP}=\dfrac{2\theta }{\theta }\Rightarrow FP=\dfrac{CP}{2}$
And CP=R and FP=f.
Hence, $f=\dfrac{R}{2}$
Note: Note that this relation between the radius of curvature (R) of a concave mirror and the focal length (f) of the mirror, which is $f=\dfrac{R}{2}$, is true only when the R is very much larger than the diameter of its aperture.
Complete step by step answer:
The relation between focal length (f) and radius of curvature (R) of a spherical mirror is that the focal length is equal to half of the radius of curvature i.e. $f=\dfrac{R}{2}$.
Let us derive this relation.
Consider a concave mirror such that its radius of curvature is very much larger than the diameter of its aperture.
We can take help from the figure given.

Suppose a parallel ray of light is incident on the mirror as shown in the figure. Let this incident ray make an angle $\theta $ with normal to the surface of the mirror. Since this mirror is part of a circle, the normal drawn to the surface of the circle passes through the centre (C) of the mirror.
We know that rays of light parallel to the principal axis passing through the focus (F) of a concave mirror, after reflection.
According to the law of reflections, the angle of incidence and angle of reflection are equal. Therefore, $\angle BAC=\angle FAC=\theta $ as shown in the given figure.
Since BA and PC are parallel, $\angle BAC=\angle ACF=\theta $.
Therefore, from exterior angle theorem $\angle AFN=\angle ACF+\angle CAF=2\theta $.
Now drop a normal CP from point A. Let the foot of this normal be N.
Here, $\tan \theta =\dfrac{AN}{CN}\Rightarrow AN=CN\tan \theta $ ……. (i).
$\tan 2\theta =\dfrac{AN}{FN}\Rightarrow AN=FN\tan 2\theta $ ….. (ii).
From equation (i) and equation (ii) we get,
$CN\tan \theta =FN\tan 2\theta $
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{CN}{FN}=\dfrac{\tan 2\theta }{\tan \theta }$ …… (iii).
Since the radius of curvature is very much larger than the diameter of its aperture, NP is very small compared to CN and CP and $\theta $ will be a small angle .
Therefore, $CN\approx CP$ and $FN\approx FP$.
For small angles $\tan \theta =\theta $ and $\tan 2\theta =2\theta $.
Therefore, equation (iii) can be written as
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{CP}{FP}=\dfrac{2\theta }{\theta }\Rightarrow FP=\dfrac{CP}{2}$
And CP=R and FP=f.
Hence, $f=\dfrac{R}{2}$
Note: Note that this relation between the radius of curvature (R) of a concave mirror and the focal length (f) of the mirror, which is $f=\dfrac{R}{2}$, is true only when the R is very much larger than the diameter of its aperture.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




