
Write the structure of 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde.
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde is also known as Salicylic aldehyde has the chemical formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\].
Complete step by step answer: From the 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde name, we can get into conclusion that a hydroxyl group is situated to the benzaldehyde at second position.
The structure of 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde is:
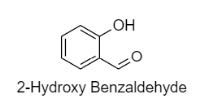
The other common names for this compound is Salicylaldehyde or Salicylic aldehyde. The chemical formula of this structure is \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\].
Additional Information: Salicylaldehyde whose IUPAC name is 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde is an organic compound with wide applications. Along with 3-hydroxybenzaldehyde and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, it is one of the three isomers of hydroxybenzaldehyde. It is a colourless or pale-yellow liquid with a bitter almond odour and a burning taste. It is soluble in alcohol, benzene, and ether, and very slightly soluble in water. Salicylaldehyde is found in shrubs of the genus Spiraea and is usually produced from phenol by the action of chloroform in the presence of an alkali base. It is used in the production of coumarin, saligenin, and salicylaldoxime (an important analytical reagent), and also in analytical chemistry. For example, to detect hydrazine. Besides, salicylaldehyde is a key precursor to various chelating agents and a flavouring ingredient.
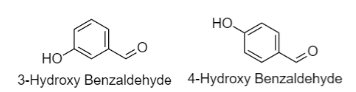
Note: 3-hydroxybenzaldehyde and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde are also available which are position isomers of 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde.
Salicylaldehyde is synthesized from phenol, chloroform, and alkali according to the Reimer–Tiemman method, which was developed in 1876. The major uses of this chemical compound are perfumes, fumigants, flavour ingredients in foods, and medicinal chemicals.
Complete step by step answer: From the 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde name, we can get into conclusion that a hydroxyl group is situated to the benzaldehyde at second position.
The structure of 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde is:

The other common names for this compound is Salicylaldehyde or Salicylic aldehyde. The chemical formula of this structure is \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\].
Additional Information: Salicylaldehyde whose IUPAC name is 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde is an organic compound with wide applications. Along with 3-hydroxybenzaldehyde and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, it is one of the three isomers of hydroxybenzaldehyde. It is a colourless or pale-yellow liquid with a bitter almond odour and a burning taste. It is soluble in alcohol, benzene, and ether, and very slightly soluble in water. Salicylaldehyde is found in shrubs of the genus Spiraea and is usually produced from phenol by the action of chloroform in the presence of an alkali base. It is used in the production of coumarin, saligenin, and salicylaldoxime (an important analytical reagent), and also in analytical chemistry. For example, to detect hydrazine. Besides, salicylaldehyde is a key precursor to various chelating agents and a flavouring ingredient.
Note: 3-hydroxybenzaldehyde and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde are also available which are position isomers of 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde.

Salicylaldehyde is synthesized from phenol, chloroform, and alkali according to the Reimer–Tiemman method, which was developed in 1876. The major uses of this chemical compound are perfumes, fumigants, flavour ingredients in foods, and medicinal chemicals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




