
Write two examples of metallic solids.
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Solid is one of the fundamental states of matter. The molecules in solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. They are rigid and generally harder than liquid and gas. Metallic solids generally possess cubic crystal structures.
Complete Step by step answer: metallic solids are solid composed of metal atoms that are held together by metallic bonds. In these solids positive ions are surrounded by mobile free electrons and are evenly spread all over the crystal. The electrons in the metallic solids are delocalized. They are not just held between a couple of atoms in a sigma bond. Rather there is a sea of electrons everywhere.
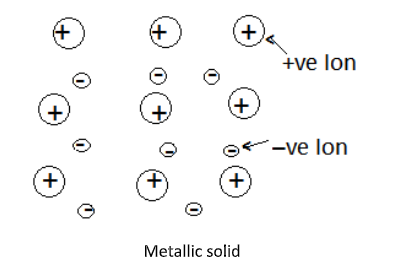
Each metal atom donates one or more electrons to the group of mobile electrons which increases the electrical and thermal conductivity of the metallic elements.
Application of electric fields makes these electrons flow through the linkage of positive ions, hence they are good conductors of electricity. Whereas application of heat to one portion of metal makes the thermal energy spread uniformly throughout by free electrons.
Metals are malleable which means they can be pounded into sheets. They are also ductile, which means they can be pulled into wires. The main idea is that unlike covalent solids, they are stiff or brittle. That is because the cations in the sea of electrons can slide around without needing to break any very strong bond.
Examples of metallic solids – copper, gold, zinc etc.
Note: We generally think metallic solids as pure metals, but they can also be the combinations of metals that are alloys like bronze which is a mixture of copper and tin. Metallic solids because of the free electrons, are good conductors of electricity.
Complete Step by step answer: metallic solids are solid composed of metal atoms that are held together by metallic bonds. In these solids positive ions are surrounded by mobile free electrons and are evenly spread all over the crystal. The electrons in the metallic solids are delocalized. They are not just held between a couple of atoms in a sigma bond. Rather there is a sea of electrons everywhere.

Each metal atom donates one or more electrons to the group of mobile electrons which increases the electrical and thermal conductivity of the metallic elements.
Application of electric fields makes these electrons flow through the linkage of positive ions, hence they are good conductors of electricity. Whereas application of heat to one portion of metal makes the thermal energy spread uniformly throughout by free electrons.
Metals are malleable which means they can be pounded into sheets. They are also ductile, which means they can be pulled into wires. The main idea is that unlike covalent solids, they are stiff or brittle. That is because the cations in the sea of electrons can slide around without needing to break any very strong bond.
Examples of metallic solids – copper, gold, zinc etc.
Note: We generally think metallic solids as pure metals, but they can also be the combinations of metals that are alloys like bronze which is a mixture of copper and tin. Metallic solids because of the free electrons, are good conductors of electricity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




