
Write two examples of molecular solids.

Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Here, we will proceed by defining molecular solids. Then, we will be mentioning any two examples of molecular solids. Finally, we will be individually discussing both of these considered examples.
Complete step by step answer:
Molecular solids are solids that are essentially collections of molecules held together by intermolecular forces. The solid structure is maintained by intermolecular forces rather than bonds (metallic, covalent, or ionic). The forces holding the solids together are much weaker than for other types of solids. As a result, these materials have much lower melting points. Molecular solids also have localized electrons (localized within the bonds in each molecule) and as such do not conduct electricity.
Molecular solids tend to dissolve in organic solvents. Most molecular solids are relatively soft electrical insulators with low density.
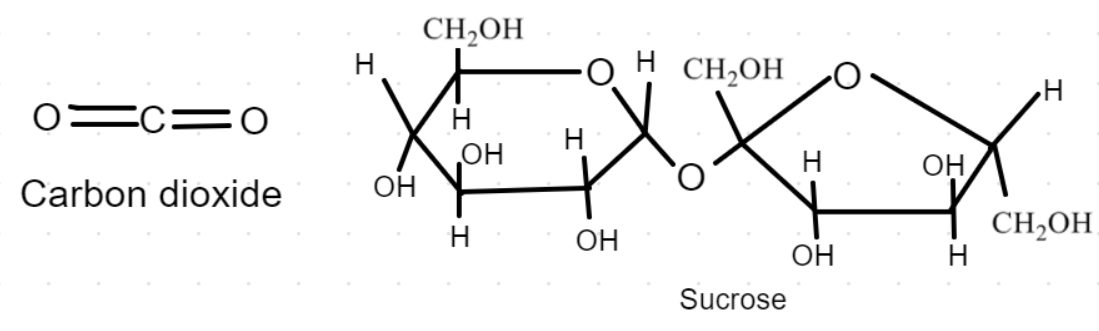
Any two examples of molecular solids are sucrose (or table sugar) and solid carbon dioxide.
Sucrose- Sucrose is a disaccharide sugar, meaning it is made up of two monosaccharide sugar units. In the case of sucrose, the two units are glucose and fructose. Glucose is the simple carbohydrate formed as a result of photosynthesis. Fructose is nearly identical, except for the location of a double-bonded oxygen. They are both six-carbon molecules, but fructose has a slightly different configuration. When the two combine, they become sucrose. Sucrose is commonly known as table sugar or cane sugar. The molecular formula of sucrose is ${{\text{C}}_{12}}{{\text{H}}_{22}}{{\text{O}}_{11}}$.
Solid carbon dioxide (solid ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}$)- Dry Ice is the common name for solid carbon dioxide (${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}$). It gets this name because it does not melt into a liquid when heated instead it changes directly into a gas (a process known as sublimation). This dry ice is used in many areas like hospitals, food processing and distribution, industrial cleaning, etc.
Note: Molecular solids are basically divided into three categories i.e. polar molecular solids (atoms or molecules are held together by stronger dipole-dipole interactions), nonpolar molecular solids (atoms or molecules are held together by weak dispersion forces or London forces) and hydrogen bonded molecular solids (contain polar covalent bonds).
Complete step by step answer:
Molecular solids are solids that are essentially collections of molecules held together by intermolecular forces. The solid structure is maintained by intermolecular forces rather than bonds (metallic, covalent, or ionic). The forces holding the solids together are much weaker than for other types of solids. As a result, these materials have much lower melting points. Molecular solids also have localized electrons (localized within the bonds in each molecule) and as such do not conduct electricity.
Molecular solids tend to dissolve in organic solvents. Most molecular solids are relatively soft electrical insulators with low density.
Any two examples of molecular solids are sucrose (or table sugar) and solid carbon dioxide.
Sucrose- Sucrose is a disaccharide sugar, meaning it is made up of two monosaccharide sugar units. In the case of sucrose, the two units are glucose and fructose. Glucose is the simple carbohydrate formed as a result of photosynthesis. Fructose is nearly identical, except for the location of a double-bonded oxygen. They are both six-carbon molecules, but fructose has a slightly different configuration. When the two combine, they become sucrose. Sucrose is commonly known as table sugar or cane sugar. The molecular formula of sucrose is ${{\text{C}}_{12}}{{\text{H}}_{22}}{{\text{O}}_{11}}$.
Solid carbon dioxide (solid ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}$)- Dry Ice is the common name for solid carbon dioxide (${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}$). It gets this name because it does not melt into a liquid when heated instead it changes directly into a gas (a process known as sublimation). This dry ice is used in many areas like hospitals, food processing and distribution, industrial cleaning, etc.
Note: Molecular solids are basically divided into three categories i.e. polar molecular solids (atoms or molecules are held together by stronger dipole-dipole interactions), nonpolar molecular solids (atoms or molecules are held together by weak dispersion forces or London forces) and hydrogen bonded molecular solids (contain polar covalent bonds).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




