
What is Zener diode? How is it used as a voltage regulator?
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: The word diode can be broken into two parts where di means two and ode comes from an electrode. It allows the passage of current in one direction only. Zener diode can be used as a voltage regulator because when it is operated in the reverse region, the voltage across it remains practically constant which is equal to its breakdown voltage.
Complete step by step answer:
A junction diode specially designed to operate in the reverse region of breakdown continuously without getting damaged is called Zener diode. This diode can be obtained by changing the doping concentration of p- and n- sides which, in turn, change the width of the depletion layer and also the barrier field across the junction.
Its electrical symbol is shown below:
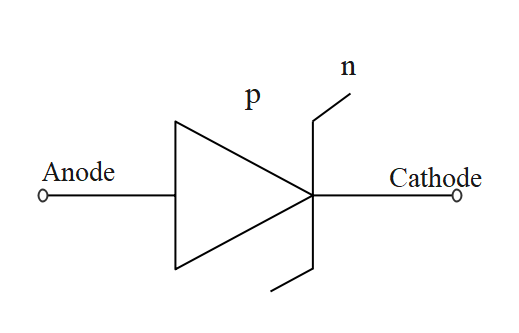
When a Zener diode is operated in the reverse breakdown region, the voltage across it remains practically constant which is equal to its breakdown voltage ${{V}_{Z}}$for a large charge in the reverse direction. The use of Zener diode as a D.C. voltage regulator is based on this fact.
The figure below shows the circuit diagram for using a Zener diode as a voltage regulator. Here the Zener diode is connected in reverse bias to a source of fluctuating D.C. through a dropping resistor${{R}_{S}}$ and Zener diode. The output is obtained across the load resistance${{R}_{L}}$, connected in parallel with the Zener diode.
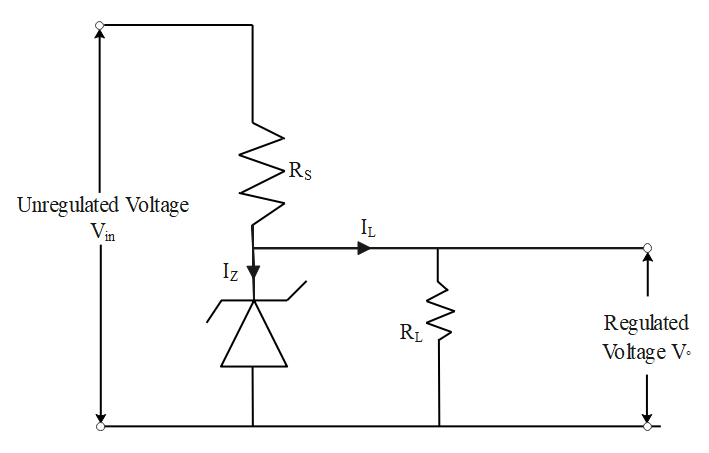
If the input voltage also increases, the current through${{R}_{S}}$ and Zener diode also increases. This increases the voltage drop across ${{R}_{S}}$ without any change in the voltage drop across Zener diode. This happens due to the fact that in the breakdown region, Zener voltage remains constant even though the current through Zener diode changes.
Similarly, if the input voltage decreases, the voltage across ${{R}_{S}}$decreases without any change in the voltage across the Zener diode. Thus any increase/decrease of the input voltage results in, increase/ decrease of the voltage drop across ${R_S}$ without any change in voltage across Zener diode.
Hence Zener diode acts as a voltage regulator.
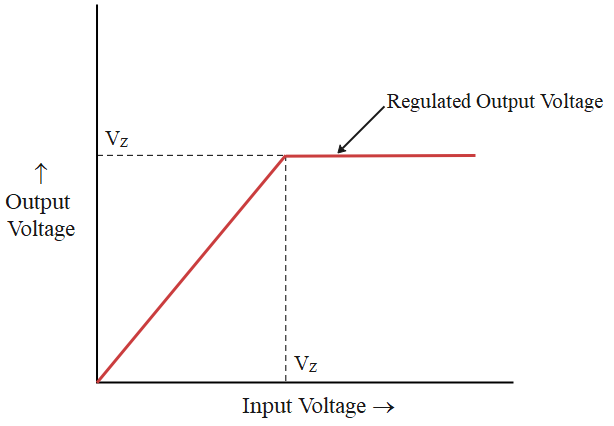
The following graph shows the output voltage versus the input voltage for a Zener diode. Clearly, the output voltage remains constant after the reverse breakdown voltage${V_Z}$.
Note: The internal field emission takes place beyond a certain reverse voltage which is known as Zener breakdown voltage. It results in a large reverse current or a breakdown current. The breakdown in a diode due to the band to band tunneling is called Zener breakdown.
Complete step by step answer:
A junction diode specially designed to operate in the reverse region of breakdown continuously without getting damaged is called Zener diode. This diode can be obtained by changing the doping concentration of p- and n- sides which, in turn, change the width of the depletion layer and also the barrier field across the junction.
Its electrical symbol is shown below:

When a Zener diode is operated in the reverse breakdown region, the voltage across it remains practically constant which is equal to its breakdown voltage ${{V}_{Z}}$for a large charge in the reverse direction. The use of Zener diode as a D.C. voltage regulator is based on this fact.
The figure below shows the circuit diagram for using a Zener diode as a voltage regulator. Here the Zener diode is connected in reverse bias to a source of fluctuating D.C. through a dropping resistor${{R}_{S}}$ and Zener diode. The output is obtained across the load resistance${{R}_{L}}$, connected in parallel with the Zener diode.

If the input voltage also increases, the current through${{R}_{S}}$ and Zener diode also increases. This increases the voltage drop across ${{R}_{S}}$ without any change in the voltage drop across Zener diode. This happens due to the fact that in the breakdown region, Zener voltage remains constant even though the current through Zener diode changes.
Similarly, if the input voltage decreases, the voltage across ${{R}_{S}}$decreases without any change in the voltage across the Zener diode. Thus any increase/decrease of the input voltage results in, increase/ decrease of the voltage drop across ${R_S}$ without any change in voltage across Zener diode.
Hence Zener diode acts as a voltage regulator.
The following graph shows the output voltage versus the input voltage for a Zener diode. Clearly, the output voltage remains constant after the reverse breakdown voltage${V_Z}$.

Note: The internal field emission takes place beyond a certain reverse voltage which is known as Zener breakdown voltage. It results in a large reverse current or a breakdown current. The breakdown in a diode due to the band to band tunneling is called Zener breakdown.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




