
Zener diode is used as-
A. Half wave rectifier
B. Full wave rectifier
C. A.C. voltage stabilizer
D. D.C. voltage stabilizer
Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint:Zener diode is defined as a properly doped $p - n$ junction diode which works in the breakdown region without damaging itself. A Zener diode is also known as a breakdown diode and it is mainly used as a voltage regulator.
Complete step by step answer:
The basic symbol of a Zener diode is given by
A Zener diode can be used as a voltage regulator or voltage stabilizer to provide a constant voltage from a source whose voltage may fluctuate over a wide range. The circuit diagram using a Zener diode as a voltage stabilizer is shown below.
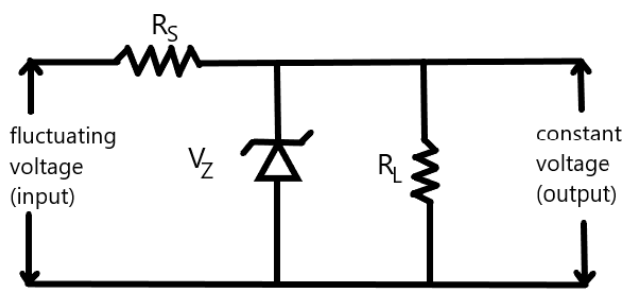
The Zener diode is connected across the fluctuating voltage source through a dropping resistor of resistance ${R_S}$ . The constant voltage supply is obtained across the load resistance ${R_L}$.When the input voltage increases, the resistance of the zener diode decreases, and hence the current through the diode increases to a high value. As a result of this, a large voltage drop occurs across the dropping resistance ${R_S}$. Hence, the output voltage drop across ${R_L}$ is maintained to the desired value.
When the input value decreases, the current through the diode also increases. So now a small voltage drop takes place across the resistance ${R_S}$ and the output voltage across ${R_L}$ is maintained at the desired constant value.Thus, we get a constant voltage in spite of fluctuating input voltage. Hence, the Zener diode acts as a voltage regulator. Therefore, the Zener diode is used as an A.C. voltage regulator.
Hence, option C is the correct option.
Note:The breakdown voltage of zener voltage ${V_Z}$ depends on the concentration of doping. Both $n$ and $p$ regions of the Zener diode are heavily doped.The depletion layer of a heavily doped $p - n$ junction diode is very thin.
Complete step by step answer:
The basic symbol of a Zener diode is given by

A Zener diode can be used as a voltage regulator or voltage stabilizer to provide a constant voltage from a source whose voltage may fluctuate over a wide range. The circuit diagram using a Zener diode as a voltage stabilizer is shown below.

The Zener diode is connected across the fluctuating voltage source through a dropping resistor of resistance ${R_S}$ . The constant voltage supply is obtained across the load resistance ${R_L}$.When the input voltage increases, the resistance of the zener diode decreases, and hence the current through the diode increases to a high value. As a result of this, a large voltage drop occurs across the dropping resistance ${R_S}$. Hence, the output voltage drop across ${R_L}$ is maintained to the desired value.
When the input value decreases, the current through the diode also increases. So now a small voltage drop takes place across the resistance ${R_S}$ and the output voltage across ${R_L}$ is maintained at the desired constant value.Thus, we get a constant voltage in spite of fluctuating input voltage. Hence, the Zener diode acts as a voltage regulator. Therefore, the Zener diode is used as an A.C. voltage regulator.
Hence, option C is the correct option.
Note:The breakdown voltage of zener voltage ${V_Z}$ depends on the concentration of doping. Both $n$ and $p$ regions of the Zener diode are heavily doped.The depletion layer of a heavily doped $p - n$ junction diode is very thin.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




