Science Notes for Chapter 12 Magnetic Effect Of Electric Current Class 10 - FREE PDF Download
Magnetic Effect Of Electric Current Class 10 Science Chapter 12 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
FAQs on Magnetic Effect Of Electric Current Class 10 Science Chapter 12 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the core concepts to focus on when revising 'Magnetic Effect of Electric Current' from the notes?
For a focused revision of this chapter, you should concentrate on the following core concepts:
- The relationship between electricity and magnetism, as first demonstrated by Oersted's experiment.
- Properties of magnetic field lines around different current-carrying conductors, including straight wires, circular loops, and solenoids.
- Key rules for determining direction: the Right-Hand Thumb Rule, Fleming's Left-Hand Rule, and Fleming's Right-Hand Rule.
- The principle, construction, and working of electromagnets versus permanent magnets.
- The concept of electromagnetic induction (EMI) and its direct application in electric generators.
- The force experienced by a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field, which is the working principle of an electric motor.
2. What is a good strategy for revising Class 10 Science Chapter 12?
A successful revision strategy for this chapter involves a logical progression of topics. Start with the foundational concepts of magnets and magnetic fields. Next, understand how an electric current produces a magnetic field around it. Then, master the rules that determine direction, such as the Right-Hand Thumb Rule. Finally, connect these principles to their practical applications like the electric motor and electric generator, ensuring you can explain how each device works based on these concepts.
3. What key terms and rules should be prioritised for a quick revision of this chapter?
For a quick and effective revision, memorise these essential terms and rules:
- Magnetic Field: The region around a magnet or a current-carrying conductor where its magnetic influence can be detected.
- Magnetic Field Lines: Imaginary lines used to represent the direction and strength of a magnetic field.
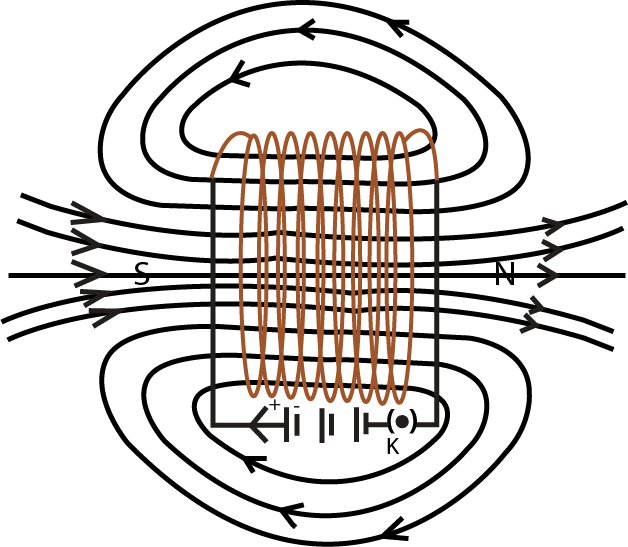
- Solenoid: A cylindrical coil of insulated wire that behaves like a bar magnet when current passes through it, producing a uniform magnetic field inside.
- Electromagnetic Induction: The phenomenon of producing an induced electric current in a coil by changing the magnetic field around it.
- Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule: Used to determine the direction of force on a conductor in a magnetic field (the 'motor rule').
- Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule: Used to find the direction of the induced current (the 'generator rule').
4. How does Oersted's experiment form the foundation for this entire chapter?
Oersted's experiment is the cornerstone of this chapter because it was the first to establish a definitive link between electricity and magnetism. He observed that a compass needle deflected when placed near a wire with an electric current. This simple observation proved that a current-carrying conductor produces a magnetic field, establishing the fundamental principle of electromagnetism upon which all other topics in the chapter, such as motors, generators, and electromagnets, are built.
5. What is the fundamental difference between Fleming's Left-Hand and Right-Hand Rules, and when should each be used during revision?
The key difference lies in their application, which is crucial to remember during revision:
- Fleming's Left-Hand Rule is applied to find the direction of the Force (or motion) on a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field. It is known as the motor rule.
- Fleming's Right-Hand Rule is used to determine the direction of the induced current when a conductor moves through a magnetic field. This is known as the generator rule.
For revision, associate the Left-Hand Rule with devices that use electricity to create motion (motors) and the Right-Hand Rule with devices that use motion to create electricity (generators).
6. What are some common misconceptions about magnetic fields and electromagnets that these revision notes help clarify?
These revision notes help clarify several common misconceptions. For example, some students believe magnetic field lines are physical lines, but the notes clarify they are an imaginary tool for visualisation. Another misconception is that electromagnets are permanent; the notes emphasize that an electromagnet is temporary, with its magnetic properties lasting only as long as current flows. Lastly, it is often assumed that only a stronger current can increase an electromagnet's strength, but the notes highlight that increasing the number of turns in the coil is also a critical factor.
7. How can I quickly revise the concept of a solenoid and its magnetic field using these notes?
To quickly revise the concept of a solenoid, focus on three key takeaways from the notes. First, understand its structure as a long coil with many circular turns of insulated copper wire. Second, memorise the properties of its magnetic field: it is strong and uniform inside the solenoid (shown by parallel field lines) and resembles a bar magnet's field outside. Third, recall its primary application: creating powerful electromagnets by inserting a soft iron core inside it.
8. Why is the magnetic field inside a long solenoid considered uniform, and why is this concept important for revision?
The magnetic field inside a long solenoid is considered uniform because the magnetic field lines are nearly parallel and equally spaced, which indicates that the field has the same strength and direction at almost every point inside. This concept is vital for revision because this uniformity is the main reason solenoids are essential for creating reliable and strong electromagnets. Understanding this property helps explain the functioning of various devices that require a consistent magnetic field, a key application-based topic for exams.
9. How do these revision notes link theoretical concepts like electromagnetic induction to practical devices?
These revision notes effectively bridge theory and practice. They first explain the core principle of electromagnetic induction (EMI), which states that a changing magnetic field can induce an electric current in a nearby coil. The notes then directly apply this theory to explain the working of an electric generator. They illustrate how the mechanical rotation of the coil within a magnetic field causes a continuous change in magnetic flux, thereby generating an induced current according to the principles of EMI and Fleming's Right-Hand Rule.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video