Biology Notes for Chapter 13 Plant Growth And Development Class 11 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on Plant Growth And Development Class 11 Biology Chapter 13 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the key concepts to focus on for quick revision of Plant Growth and Development in Class 11 Biology?
For efficient revision, students should focus on types of growth (primary, secondary), plant hormones and growth regulators, major developmental stages (germination, vegetative growth, flowering, seed formation), and the impact of environmental factors. Understanding the sigmoid growth curve and the role of meristems are also essential for CBSE exams.
2. How should I structure my revision to cover Class 11 Chapter 13 Plant Growth and Development effectively?
Begin your revision by reading through summary notes and concept maps. Break the chapter into logical sections:
- Plant growth principles
- Types of growth and meristematic activity
- Differentiation, dedifferentiation, and redifferentiation
- Plant hormones and regulators
- Developmental stages and environmental factors
3. Which plant hormones are most important to remember during revision for Chapter 13?
The key plant hormones to focus on are:
- Auxins (cell elongation, apical dominance)
- Gibberellins (stem elongation, seed germination)
- Cytokinins (cell division, delay senescence)
- Abscisic acid (stress response, seed dormancy)
- Ethylene (fruit ripening, leaf abscission)
4. What is the difference between arithmetic and geometric growth in plants?
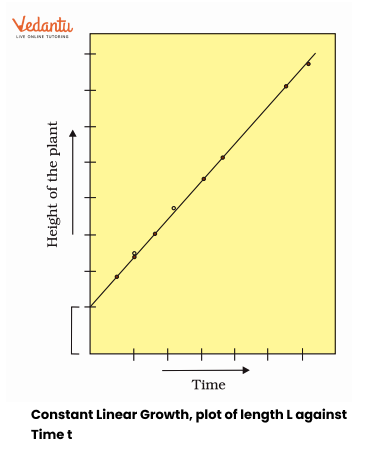
Arithmetic growth involves a constant increase per unit time (e.g., 2, 4, 6...), commonly observed in root and shoot elongation. In contrast, geometric growth is exponential, where each cell divides, resulting in rapid increase (as seen in the early stages of many plants). Understanding this distinction is crucial for questions related to growth patterns.
5. How do plant growth and developmental stages connect to revision strategies?
Revision should connect each stage of plant growth—from germination, vegetative phase, flowering, to seed formation and senescence—with their underlying hormonal and environmental controls. Making concept maps or timelines can help visualize and memorise these connections for exams.
6. How can you quickly recall the physiological effects of plant growth regulators for CBSE short answer questions?
Use mnemonics or summary tables to remember key functions:
- Auxins = elongation (‘A’ for Ascend)
- Gibberellins = germination & growth (‘G’ for Grow)
- Cytokinins = cell division (‘C’ for Cell)
- Abscisic acid = abscission & dormancy
- Ethylene = fruit ripening (think of ‘e’ for eatable ripe fruit)
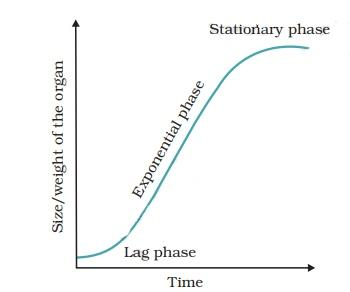
7. What is the significance of the sigmoid growth curve in plant development, and how can you represent it in revision?
The sigmoid (S-shaped) growth curve represents typical plant growth:
- Lag phase — slow growth after germination
- Log (exponential) phase — rapid increase
- Stationary phase — growth plateaus as resources deplete
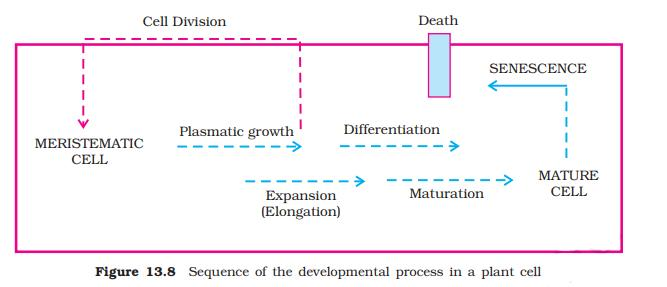
8. Why is understanding differentiation, dedifferentiation, and redifferentiation crucial for effective revision notes?
These processes explain how plants produce varied, specialized tissues and how they can regenerate or adapt after injury. Recognizing these terms and their sequence is key to connecting concepts of growth and development during revision and for answering higher-order thinking skills (HOTS) questions in the exam.
9. How do environmental factors like light and temperature influence the revision focus of Chapter 13?
Environmental factors such as light (photoperiodism) and temperature (vernalisation) regulate flowering and seasonal growth patterns. Students should focus their revision on examples of short day, long day, and day-neutral plants, and the significance of environmental triggers in development.
10. What revision techniques work best for memorising diagrams and cycles in Plant Growth and Development?
For diagrams like the growth curve or hormone pathways, practice by drawing them from memory and labelling all parts. Use colour coding and legends in your notes to visually link steps or factors. Repetition and self-testing are effective revision habits for ensuring clarity and recall during exams.
11. Why should students refer to concept maps along with revision notes for Chapter 13?
Concept maps highlight relationships between different topics in the chapter, such as the interactions between hormones and stages of development. They make it easier to visualise big-picture connections and answer application-based CBSE questions efficiently.
12. How do revision notes simplify complex topics in Plant Growth and Development for last-minute preparation?
Well-prepared revision notes break down complex mechanisms into simple, structured summaries, highlight key terms, and include essential diagrams. This approach helps students quickly review and understand major concepts, aiding in high retention and better performance in Board exams.