An Overview of Cbse Class 12 Micro Economics Notes Chapter 6
FAQs on Cbse Class 12 Micro Economics Notes Chapter 6
1. What is a non-competitive market as per the Class 12 syllabus?
A non-competitive market is a market structure where individual firms possess the power to influence the price of their products. Unlike in perfect competition where firms are price takers, firms in non-competitive markets are price makers due to factors like a small number of sellers, product differentiation, or significant barriers to entry.
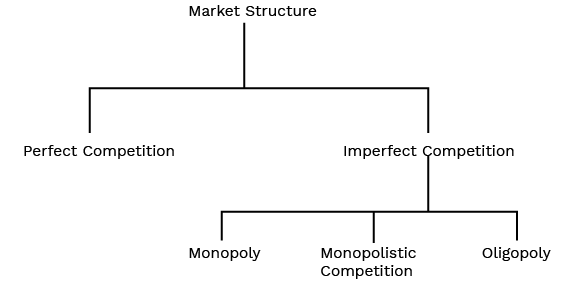
2. What are the main types of non-competitive markets?
The primary types of non-competitive markets studied in Class 12 Microeconomics are:
- Monopoly: A market structure with only one seller and many buyers, offering a product with no close substitutes.
- Monopolistic Competition: A market with a large number of sellers offering differentiated products that are close, but not perfect, substitutes.
- Oligopoly: A market dominated by a few large firms, where each firm's actions significantly impact the others.
3. How does a non-competitive market fundamentally differ from a perfect competition market?
The fundamental difference lies in market power. In perfect competition, numerous firms sell a homogeneous product, and no single firm can influence the price (they are price takers). In a non-competitive market, firms have some control over price because of product differentiation (monopolistic competition), being the sole provider (monopoly), or strategic interdependence (oligopoly).
4. What does it mean for a firm to be a 'price maker'?
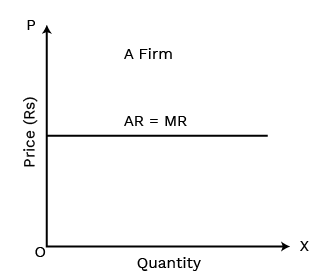
A 'price maker' is a firm that can set or influence the price of its goods or services without losing all its customers. This power arises in non-competitive markets like monopoly and monopolistic competition because the products they offer do not have perfect substitutes. A price maker faces a downward-sloping demand curve, meaning it can sell more by lowering the price.
5. What are the key features to remember for a monopoly market?
For a quick revision of monopoly, remember these key features:
- Single Seller: There is only one firm that constitutes the entire industry.
- No Close Substitutes: The product sold has no readily available alternatives.
- Barriers to Entry: Strong barriers, such as patents, licenses, or control over resources, prevent new firms from entering.
- Price Maker: The monopolist has significant control over the price or output level.
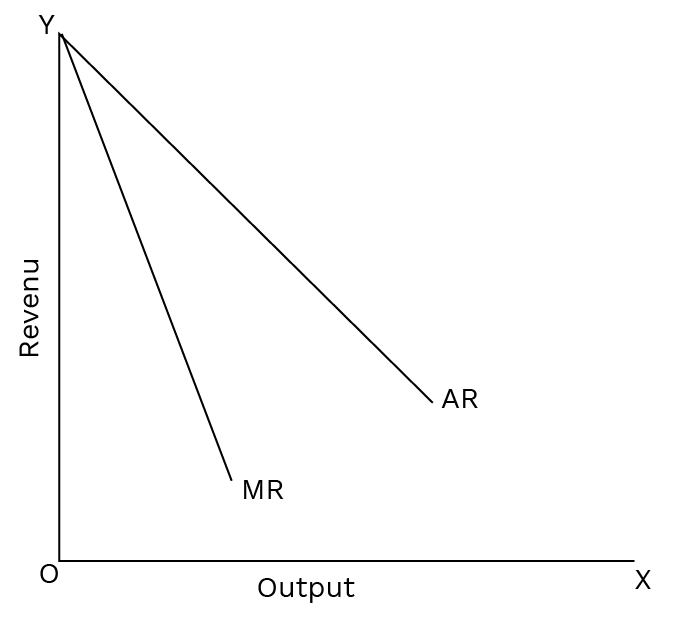
6. Explain the relationship between the Average Revenue (AR) and Marginal Revenue (MR) curves under monopoly.
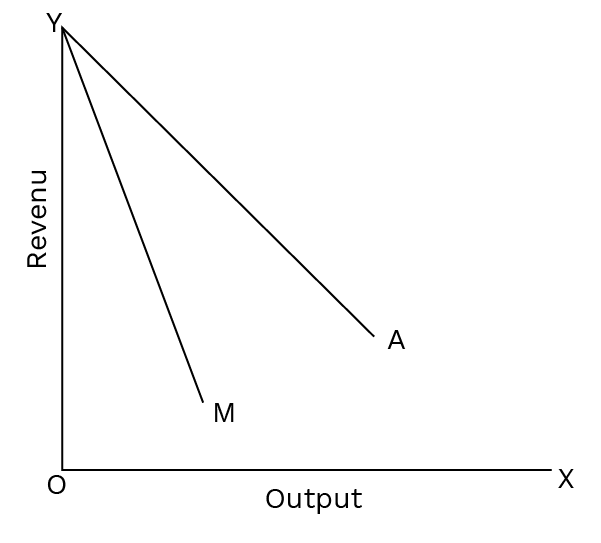
In a monopoly, both the Average Revenue (AR) and Marginal Revenue (MR) curves are downward sloping. Since a monopolist must lower the price to sell more units, the revenue from each additional unit (MR) is less than the average price (AR). Therefore, the MR curve lies below the AR curve, and it declines at a faster rate.
7. What is monopolistic competition and how does it differ from a pure monopoly?
Monopolistic competition is a market with many sellers offering similar but not identical products (e.g., restaurants, salons). It differs from a monopoly in two key ways: there are many firms instead of one, and there are no significant barriers to entry. While a monopolist sells a unique product, firms in monopolistic competition sell differentiated products with many close substitutes.
8. How does product differentiation influence the demand curve in monopolistic competition?
Product differentiation, achieved through branding, quality, or packaging, gives each firm a mini-monopoly over its specific version of the product. This makes the firm's demand curve downward-sloping, as it has some power to set prices. However, because many close substitutes exist, the demand curve is also highly elastic—a small price increase can cause a significant loss of customers to competitors.
9. Why do firms in monopolistic competition typically earn only normal profits in the long run?
Firms in monopolistic competition earn only normal profits in the long run due to the freedom of entry and exit. If existing firms earn super-normal profits, new firms are attracted to the market. This increases the number of substitutes, reduces the demand for existing firms' products, and erodes their profits until they reach the break-even point (normal profit).
10. What is an oligopoly, and what are its main characteristics?
An oligopoly is a market structure dominated by a few large firms. Its key characteristics include a high degree of interdependence (one firm's pricing decisions affect all others), significant barriers to entry, and the sale of either homogeneous (e.g., steel) or differentiated (e.g., cars) products. Firms often engage in non-price competition, like advertising and marketing.
11. Why is the demand curve for a firm in an oligopoly market often considered indeterminate?
The demand curve is considered indeterminate due to the strategic interdependence among firms. A firm cannot predict with certainty how its rivals will react to a price change. If a firm lowers its price, rivals might follow suit, leading to a price war. If it raises its price, rivals might not, causing the firm to lose market share. This unpredictability makes it impossible to define a precise demand curve for an individual oligopolistic firm.
12. Can you give some real-world examples of monopoly and oligopoly in the Indian context?
Certainly. For revision, you can think of these examples:
- Monopoly Example: Indian Railways is a classic example of a monopoly in rail transportation in India.
- Oligopoly Examples: The automobile industry (dominated by firms like Maruti Suzuki, Hyundai, Tata Motors) and the telecommunications sector (with major players like Jio, Airtel, and Vi) are clear examples of oligopoly markets.