An Overview of Cbse Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 14
FAQs on Cbse Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 14
1. What are the main sources of water summarised in the Class 6 Science Chapter 14 revision notes?
These revision notes cover the primary sources of water as per the Class 6 syllabus. The key sources discussed are:
- Oceans and Seas: The largest bodies of water, though the water is saline and not directly usable for drinking.
- Rivers and Lakes: Major sources of fresh water for cities and towns.
- Groundwater: Water stored beneath the ground, accessed through wells, tube wells, and hand pumps.
- Rain: The purest form of natural water and a crucial part of the water cycle that replenishes other sources.
- Ice and Glaciers: Large masses of frozen fresh water found in polar regions and on high mountains.
2. How can I quickly revise the main stages of the water cycle from these notes?
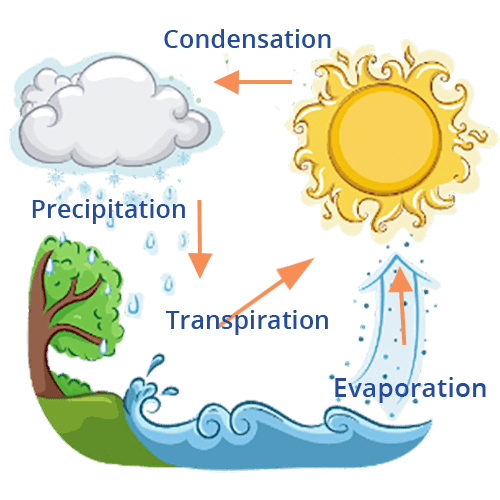
For a quick revision of the water cycle, focus on the four main processes explained in the notes. The continuous circulation of water from the Earth's surface to the atmosphere and back is driven by these stages:
- Evaporation: The process where the sun's heat changes water from rivers, lakes, and oceans into water vapour.
- Condensation: As the water vapour rises, it cools down and changes back into tiny water droplets, which come together to form clouds.
- Precipitation: When the clouds become too heavy, they release the water in the form of rain, snow, or hail.
- Collection: The rainwater collects in rivers, lakes, and oceans, and also seeps into the ground, replenishing the groundwater.
3. How do these revision notes explain the role of plants in the water cycle?
The notes summarise the important role of plants through a process called transpiration. Plants absorb water from the soil through their roots. While they use some of this water to make food, they release the excess water into the atmosphere as water vapour through tiny pores on their leaves. This process contributes a significant amount of water vapour to the air, which then helps in the formation of clouds.
4. If ocean water is salty, why is the rain that comes from it fresh?
This is a key concept explained by the process of evaporation. When the sun heats the ocean, only the water turns into vapour and rises into the atmosphere. The salts and other impurities are heavier and are left behind in the ocean. This fresh water vapour then cools to form clouds and eventually falls as fresh rainwater. This is why rain is a source of fresh water, even though much of it originates from salty seas.
5. What is the difference between a flood and a drought as explained in Chapter 14?
Floods and droughts are two opposite effects related to the amount of rainfall. The notes clarify this difference:
- A flood is a situation caused by excessive rainfall. When it rains too heavily for a long time, rivers and lakes overflow their banks, and the water submerges surrounding land, causing damage to crops, homes, and life.
- A drought is a condition caused by a lack of rainfall for a very long period. Without rain, the soil dries up, water levels in ponds and wells drop, and groundwater becomes scarce, leading to a severe water shortage.
6. How does rainwater harvesting help in conserving water?
Rainwater harvesting is a key method for water conservation summarised in these notes. It is the process of collecting and storing rainwater instead of letting it run off. The two main techniques are:
- Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting: Collecting rainwater from rooftops and directing it into a storage tank or a pit in the ground.
- Recharging Groundwater: Allowing the collected rainwater to seep deep into the soil to raise the level of the groundwater table. This makes more water available for future use through wells and tube wells.
7. Why is it important to conserve water even though most of the Earth is covered with it?
While about two-thirds of the Earth is covered by water, most of it is in oceans and seas, which is saline (salty) and not fit for drinking, cooking, or farming. The amount of usable fresh water is very limited—less than 1% is easily accessible. As the human population grows, the demand for this limited fresh water increases. Therefore, conserving water is crucial to ensure that this precious resource is used wisely and remains available for everyone's needs now and in the future.