Science Notes for Chapter 5 Measurement of Length and Motion Class 6 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on Measurement of Length and Motion Class 6 Science Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What key topics are covered in the Class 6 Science Chapter 5 revision notes on Measurement and Motion?
The revision notes provide a quick summary of essential concepts for the 2025-26 syllabus, including the need for standard units, how to measure length accurately, and the different types of motion (rectilinear, circular, and periodic). They are designed for a fast and effective review before exams.
2. According to the revision notes, what is the SI unit of length and why is it important?
The revision notes state that the standard or SI (International System of Units) unit of length is the metre (m). Using standard units like the metre is crucial because it ensures that measurements are consistent and understood by everyone, everywhere, avoiding the confusion caused by non-standard units like hand spans or foot steps.
3. How do the notes summarise the main types of motion for quick revision?
For quick revision, the notes classify motion into three main types, with examples:
Rectilinear motion: Movement in a straight line, like a car on a straight road.
Circular motion: Movement along a circular path, like the hands of a clock.
Periodic motion: Motion that repeats itself after a fixed time, like a swinging pendulum.
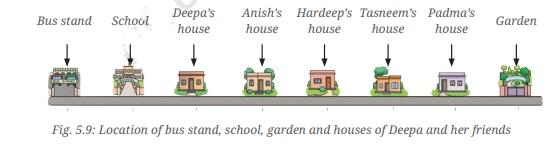
4. What is the concept of a 'reference point' as explained in the Chapter 5 summary?
A reference point is a fixed object or location used to determine if another object is in motion or at rest. The notes clarify that motion is always relative; an object's position is described as changing with respect to this fixed reference point.
5. How can an object have more than one type of motion at the same time? How do the notes help clarify this?
Yes, an object can exhibit multiple types of motion simultaneously. For example, a bicycle wheel has both rectilinear motion (as it moves forward) and circular motion (as it spins). The revision notes help clarify this by providing distinct definitions for each motion type, allowing you to identify them even when they occur together.
6. How do the revision notes explain the method for measuring a curved line?
The revision notes explain a simple method for this task. You can place a thread along the entire curved line, from one end to the other. Then, you straighten the thread without stretching it and measure its length against a standard ruler or scale to find the accurate length of the curved line.
7. While revising, what is a common mistake to avoid when measuring length with a scale?
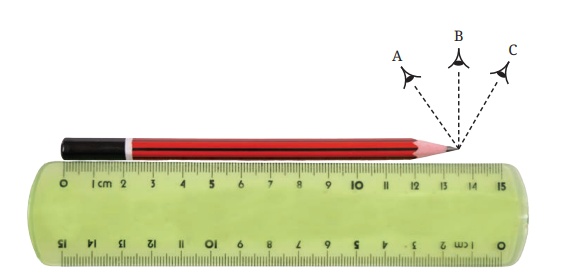
A common mistake highlighted for revision is the error of parallax. You must always ensure your eye is positioned directly above the mark on the scale you are reading. Viewing it from an angle can lead to an incorrect measurement. Also, make sure the measurement starts from the zero mark of the scale.
8. What is the best way to use these revision notes to prepare for the Measurement and Motion chapter?
To use these notes effectively, start by reading the summary to refresh your memory of the core concepts. Then, focus on the definitions of key terms like 'rectilinear motion', 'periodic motion', and 'standard unit'. Finally, try to recall the real-life examples provided for each type of motion to solidify your understanding for the exam.
9. For revision, what is the key difference between periodic and circular motion?
The key difference to remember for revision is that while circular motion at a constant speed is periodic, not all periodic motion is circular. For instance, a pendulum's swing is periodic but follows a to-and-fro path (oscillatory motion), not a full circle. The revision notes help distinguish these by focusing on the path of movement.
10. How are the concepts of measurement and motion connected in this chapter, as per the revision notes?
The revision notes show that measurement and motion are fundamentally linked. To describe motion accurately, you must measure the change in an object's position over time. This requires understanding how to measure length (distance). Therefore, accurate measurement is the first and most crucial step to quantifying and understanding motion.