Class 6 Social Science Chapter 10 Summary Notes PDF Download
Vedantu’s Revision notes for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 10 Grassroots Democracy – Part 1 Governance introduces you to the concept of local governance and its role in our communities. You'll learn about how local leaders are chosen, their responsibilities, and how they help improve everyday life.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentIn these notes, we'll cover key points from the Class 6 Social Science Syllabus, including the importance of grassroots democracy and how it impacts local decision-making. Use these Class 6 Social Science Revision Notes to get a clear and simple overview, helping you understand and remember the chapter's main ideas for your exams.
Access Class 6 Social Science Chapter 10 Grassroots Democracy – Part 1 Governance Notes
1. Introduction to Governance
Governance is the process of creating and enforcing rules to maintain order in society.
It ensures that people follow the same rules to live together harmoniously.
Without governance, there would be disorder and confusion, making society difficult to manage.
2. Importance of Government
Governments are responsible for making laws, ensuring law and order, and resolving conflicts.
They manage public resources and provide essential services like education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
Governments ensure fairness and help protect people’s rights and responsibilities.
3. Democracy
Democracy allows citizens to participate in decision-making by electing representatives.
These elected representatives discuss and create laws on behalf of the people.
In a democracy, power is in the hands of the people, making it a government of the people, by the people, and for the people.
4. Role of Panchayats
Panchayats are local governing bodies in villages, responsible for handling community-level issues.
They manage resources, improve local infrastructure, and address the needs of the people.
Panchayats allow villagers to directly participate in governance, making decisions that affect their daily lives.
5. Functions of the Sarpanch
The Sarpanch is the elected leader of the Panchayat, responsible for leading local governance.
The Sarpanch works to solve village problems, manage resources, and ensure the well-being of the community.
They play a vital role in making decisions about village development and addressing public concerns.
6. Three Organs of Government
Legislature: Makes and updates laws, ensuring they reflect the needs of the society.
Executive: Implements and enforces the laws made by the legislature.
Judiciary: Interprets laws, resolves disputes, and ensures justice is served.
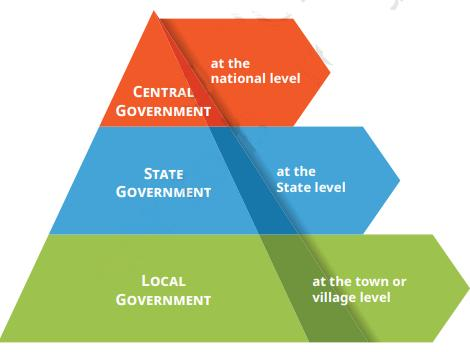
7. Three Levels of Government
Local Government: Manages issues at the village or town level, such as water supply and sanitation.
State Government: Handles matters within a state, like law enforcement, education, and healthcare.
Central Government: Manages national-level issues, including defence, foreign policy, and economic planning.
8. Role of Elections
Elections allow people to choose their representatives at local, state, and national levels.
Representatives are responsible for making decisions that benefit their communities.
Through elections, citizens have a say in how they are governed and who represents them.
9. Local Governance in Action
Panchayats and Gram Sabhas (village assemblies) ensure that decisions are made with community involvement.
Local governance addresses the specific needs of the village, making it a key aspect of grassroots democracy.
Issues like local development, water management, and public services are discussed and decided at the village level.
10. Importance of Grassroots Democracy
Grassroots democracy empowers ordinary people to participate in local governance.
It ensures that decisions impacting daily life are made with input from the community.
This type of democracy strengthens the connection between citizens and their government by involving them directly in the decision-making process.
Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam: It is mentioned that A.P.J.Abdul kalam was a great leader who had a significant impact on India’s development. Known as the "Missile Man of India," he contributed immensely to India’s space and missile programs. He served as the 11th President of India from 2002 to 2007, and despite holding such a high position, he remained humble and deeply connected with the people, especially the youth.
Dr. Kalam believed in the power of education and innovation and encouraged young Indians to dream big and work hard. His life and work are an inspiration to millions, and he is remembered for his dedication to the nation and his vision for a developed India.
5 Important Topics of Class 6 Social Science Chapter 10 Grassroots Democracy – Part 1 Governance
S.No. | Important Topics |
1 | Local Governance Structures |
2 | Panchayats and Their Functions |
3 | Role of the Sarpanch |
4 | Importance of Grassroots Democracy |
5 | Election Process in Local Governance |
Importance of Social Science Class 6 Chapter 10 Grassroots Democracy – Part 1 Governance Notes
Revision notes help us quickly understand and remember key concepts before exams.
They save time by focusing on essential information and skipping unnecessary details.
These notes simplify complex topics, making them easier to understand and use.
They provide practical examples that show how theoretical knowledge is used in real-life situations.
Revision notes ensure thorough preparation by covering all important topics in a structured manner.
They increase confidence by clearly understanding what to expect in exams.
Accessible formats like PDFs allow for easy studying anytime and anywhere.
Tips for Learning the Class 6 Social Science Chapter 10 Grassroots Democracy – Part 1 Governance Notes
Focus on how local leaders, like the Sarpanch, help in your community. Knowing their roles will make the topic clearer.
Understand key terms like Panchayat and election process. These are important for understanding how local governance works.
Study the specific functions and duties of different Panchayat members to understand their roles in local governance.
Learn terms like Gram Sabha, Panchayat Samiti, and Zila Parishad. Knowing these terms will help you understand the structure of local governance.
Think about real-life examples of local governance in your area. This will help you relate the chapter content to everyday life.
Conclusion
Vedantu’s Revision Notes for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 10 Grassroots Democracy – Part 1, helps us understand how local governance works and why it's important. We've learned about the roles of Panchayats, the Sarpanch, and the election process. By using these notes, you can see how local leaders are chosen and how they contribute to our community. Remember, understanding grassroots democracy helps us appreciate how decisions are made close to home and how we can be involved in our local communities.
Related Study Materials for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 10 - Grassroots Democracy – Part 1 Governance
S.No. | Study Materials for Class 6 Chapter 10 |
1. | Class 6 Social Science Grassroots Democracy – Part 1 Governance NCERT Solutions |
2. | Class 6 Social Science Grassroots Democracy – Part 1 Governance Important Questions |
Chapter-wise Revision Notes Links for Class 6 Social Science
S.No. | Revision Notes Links for Class 6 Social Science |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 | Chapter 11 Grassroots Democracy — Part 2: Local Government 163 in Rural Areas Notes |
11 | Chapter 12 Grassroots Democracy — Part 3: Local Government 173 in Urban Areas Notes |
12 | |
13 |
Important Study Materials for Class 6 Social Science:
S.No. | Study Material for Class 6 Social Science |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | CBSE Class 6 Social Science MCQs |
5. |


















