Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Summary Notes PDF Download
FAQs on Light Class 8 Science Chapter 13 CBSE Notes - 2025-26
1. What are the essential concepts to revise in the Light chapter for Class 8?
For a quick revision of Class 8 Light, focus on these key concepts: the laws of reflection, the difference between regular and diffused reflection, how a plane mirror forms images, the principle of multiple reflections in a kaleidoscope, the dispersion of white light, and the basic structure and function of the human eye.
2. How can we summarise the laws of reflection for a quick recap?
The two laws of reflection are simple to recap. First, the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection (∠i = ∠r). Second, the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal (the line perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence) all lie in the same plane.
3. Why does a new stainless steel plate act like a mirror, but an old, used one doesn't?
This happens due to the type of reflection. A new plate has a very smooth, polished surface, causing regular reflection where all parallel light rays bounce off in the same direction, creating a clear image. An old plate has scratches and irregularities, causing diffused or irregular reflection. Here, parallel light rays scatter in many different directions, so you don't see a clear reflection.
4. What is a quick summary of the image characteristics formed by a plane mirror?
When revising, remember these key points about an image from a plane mirror. The image is:
- Virtual (it cannot be formed on a screen).
- Erect or upright.
- The same size as the object.
- Formed at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
- Laterally inverted (left appears right and right appears left).
5. If we can see non-luminous objects like a book or a chair, does this mean they produce their own light?
No, this is a common point of confusion. Non-luminous objects do not produce their own light. We see them because they reflect light from a luminous source (like the sun or a lamp) into our eyes. The ability to see an object depends on light travelling from that object to our eye, but the object itself doesn't have to be the source.
6. What is the main takeaway about the dispersion of light in Class 8?
The key concept to remember is that what we see as white light (like sunlight) is actually a mixture of seven different colours. This phenomenon, called dispersion, can be seen when light passes through a prism, splitting it into a spectrum of colours (VIBGYOR). A rainbow is a natural example of dispersion.
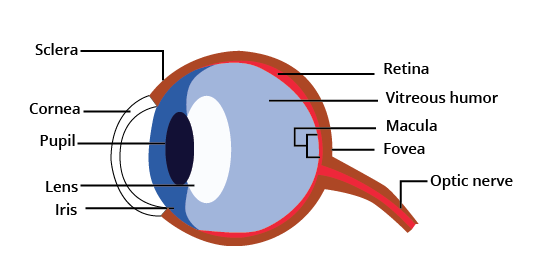
7. What are the key parts of the human eye to remember for revision?
For a summary of the human eye, focus on these main parts and their functions. The cornea is the transparent front part. The iris controls the size of the pupil, which regulates light entry. The lens focuses light onto the retina at the back of the eye. The retina contains light-sensitive cells, and the optic nerve transmits the signals to the brain.
8. How does a kaleidoscope work based on the concepts from this chapter?
A kaleidoscope is a practical application of the concept of multiple reflections. It uses mirrors, typically three, arranged at an angle to each other. When you look through it, the light from the coloured objects at the other end bounces off the mirrors multiple times, creating numerous virtual images that form beautiful, symmetrical patterns.
9. Why is understanding the concept of persistence of vision important when we watch movies?
The concept of persistence of vision is crucial because it explains how we perceive motion from still pictures. The impression of an image stays on our retina for about 1/16th of a second. Movies are a series of still images (frames) shown faster than this rate. Our brain blends these separate images together, creating the illusion of smooth, continuous movement.
10. What is the key concept behind the Braille system for visually challenged persons?
The key concept is that the Braille system is a tactile reading and writing system, not a visual one. It uses raised dots to represent letters and numbers, allowing visually challenged individuals to read through the sense of touch. This is an important topic in the chapter that highlights how people adapt to challenges in perception.