Lakhmir Singh for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flames - Download Free PDF with Solution
One of the crucial topics in Chemistry is combustion. It is an important chemical reaction that explains how things burn in the presence of oxygen. This is why Class 8 Science Chapter 6 is an important chapter that develops the basic foundation of Combustion Chemistry in students.
To understand the scientific principles and concepts of combustion and flames, refer to the Chapter 6 Science Class 8 Lakhmir Singh Solutions PDF. Find the accurate answers to all the exercise questions with proper explanations. Develop your answering skills by following the formats used by the subject experts of Vedantu.
Access Lakhmir Singh Solutions for Class 8 Science (Chemistry) Chapter 6: Combustion and Flame
Very Short Answer Type Questions
1. Define the ignition temperature of a substance.
Ans: The lowest temperature at which a combustible substance catches fire when heated in the air is called the ignition temperature of a substance.
2. Which of the two has a lower ignition temperature: petrol or kerosene?
Ans: Petrol has a lower ignition temperature.
3. Name the most common fire extinguisher.
Ans: The most common fire extinguisher is water.
4. Which is the best fire extinguisher for fires involving electrical equipment and inflammable materials like petrol?
Ans: The best fire extinguisher for fires involving electrical equipment and inflammable materials like petrol is carbon dioxide.
5. Name one substance which undergoes spontaneous combustion (or burns in air at room temperature)?
Ans: White phosphorus undergoes spontaneous combustion (or burns in air at room temperature).
6. Name the unit in which the calorific value is expressed.
Ans: Flame Calorific value is expressed in energy per unit mass of the substance. Example KJ/Kg
7. Which of the following fuels has the lowest calorific value?
Diesel, Methane, Coal, CNG, Petrol
Ans: Coal has the lowest calorific value.
8. Which of the following fuels has the highest calorific value?
Diesel, Methane, CNG, Coal, Petrol
Ans: CNG and Methane have the highest calorific value.
9. Name the term which is used to express the efficiency of a fuel.
Ans: Calorific value is used to express the efficiency of fuel.
10. Name one solid, one liquid and one gas which burns by producing a flame.
Ans: Solid: Molten wax Liquid: Kerosene Gas: Liquified Petroleum Gas
11. Which of the following does not produce a flame on burning? Camphor, Charcoal, Kerosene
Ans: Charcoal does not produce flame on burning
12. Name one fuel which burns without producing a flame.
Ans: Charcoal burns without producing flame.
13. How many zones are there in a flame?
Ans: There are three zones in a flame. Namely, the innermost, middle, and outer zone.
14. Which zone of a candle flame is the hottest?
Ans: The outermost zone of the candle is the hottest.
And in a candle flame, what is the colour of:
(a) Innermost zone
Ans: Dark or black
(b) Middle zone and
Ans: Yellow
(c) Outer zone?
Ans: Blue
15. Name any harmful product released by the burning of fuels?
Ans: Carbon monoxide is one of the most harmful products released by the burning of fuels.
16. Name the very poisonous gas produced by the incomplete combustion of fuels?
Ans: Incomplete combustion of fuels produces poisonous gas called carbon monoxide.
17. Name the fuel which is gradually replacing petrol and diesel in automobiles?
Ans: CNG is gradually replacing petrol and diesel in automobiles.
18. Name two substances having low ignition temperatures and two having high ignition temperatures.
Ans: Substances having low ignition temperature: LPG and Petrol Substances having high ignition temperature: Coal and wood.
19. Fill in the blanks with suitable words
(a) A fuel must be heated to its_________ before it starts burning.
Ans: ignition temperature
(b) The most common supporter of combustion around us is _________
Ans: air
(c) Fire produced by burning oil cannot be controlled by_________
Ans: water
(d) A liquid fuel used in homes is_________
Ans: kerosene
(e) The amount of heat evolved when 1kg of a fuel is burnt completely is called its _________
Ans: calorific value
(f) The substance which vaporises during, give_________
Ans: flames
(g) Burning of wood and coal causes_________ of air.
Ans: pollution
Short Answer Type Questions
20. (a) What are fuels? Name any two common fuels.
Ans: Any substance that produces a usable amount of energy is known as fuel upon combustion. For example, fossil fuels, biogas, nuclear energy, etc.
(b) State any four characteristics of an ideal fuel (or good fuel).
Ans: Characteristics of an ideal fuel (or good fuel) are:
Fuel is easily available and cheaper
Burns easily in the air at a moderate rate
Releases a large amount of energy
No harmful substances must be emitted from fuel
Eco friendly
21. (a) Define the calorific value of a fuel.
Ans: The amount of heat energy produced on complete combustion of 1 kg of a fuel is called its calorific value. The calorific value of a fuel is expressed in a unit called kilojoule per kg (kJ/kg).
(b) “The calorific value of LPG is 55000 KJ/kg”. What does it mean?
Ans: The calorific value of LPG is 55000 KJ/kg means 1 kilogram of LPG is burned entirely and 55000 KJ/kg of heat energy is produced.
22. Can you burn a piece of wood by bringing a lighted matchstick near it? Explain.
Ans: No, we cannot burn a piece of wood by bringing a lighted matchstick near it. When a lighted matchstick is brought near a piece of wood it does not start burning because the ignition temperature of the wood is higher than a piece of paper. A matchstick can light a tiny splinter of wood but not a big log of wood. A burning matchstick can produce sufficient heat to reach the ignition temperature of the splinter of wood therefore a matchstick can light a splinter of wood directly.
23. Why do you have to use paper or kerosene oil to start a fire in wood or coal?
Ans: The ignition temperature of wood or coal is higher and it requires more heat to start burning. This is the reason that to start a fire in wood or coal paper or kerosene oil is used as the ignition temperature of paper or kerosene oil is lower than that of wood or coal.
24. What is meant by rapid combustion? Give one example of rapid combustion.
Ans: When a substance burns rapidly, with the aid of an external source and produces heat within a short period of time is called rapid combustion. Example: Burning of LPG.
25. What is meant by spontaneous combustion? Give one example of spontaneous combustion.
Ans: The type of combustion in which material suddenly bursts into flames, without the application of any apparent cause is called spontaneous combustion. Eg., Burning of phosphorus.
26. What is meant by explosive combustion (or explosion)? Give one example of explosive combustion (or explosion).
Ans: A sudden reaction takes place with the release of heat and light and the evolution of a large amount of gas takes place; it is called an explosion. Eg., firecrackers.
27. How will you show that air is necessary for combustion?
Ans: Air helps in combustion. Air contains about twenty-one percent of oxygen and this oxygen present in the air helps in the process of combustion. Without oxygen, combustion will not take place.
28. Can the process of rusting be called combustion? Give a reason for your answer.
Ans: No, because rusting is an exothermic process as heat is liberated during rusting. On the other hand, combustion is a chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen to release energy in the form of heat or light.
29. Why are fires produced by burning oil not extinguished by pouring water?
Ans: Water is heavier than oil. So when it is poured on an oil fire, it sinks to the bottom where it evaporates due to the heat of the fire and thus expands rapidly which may push and splatter fire in all directions. Fire due to oil can be extinguished by using a dry chemical fire extinguisher.
30. Explain why fires caused by electricity should not be extinguished by pouring water.
Ans: The most common fire extinguisher is water. But water works only when things like wood and paper are on fire. If electrical equipment is on fire, water may conduct electricity and harm those trying to douse the fire. For fires involving electrical equipment and inflammable materials like petrol, carbon dioxide ($\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$) is the best extinguisher $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ , being heavier than oxygen, covers the fire like a blanket. Since the contact between the fuel and oxygen is cut off, the fire is controlled. The added advantage of $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is that in most cases it does not harm the electrical equipment.
31. How is the fire caused by electricity extinguished?
Ans: The fire is caused by electricity extinguished by petrol or by carbon dioxide. For fires involving electrical equipment and inflammable materials like petrol, carbon dioxide ($\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$) is the best extinguisher. $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$, being heavier than oxygen, covers the fire like a blanket. Since the contact between the fuel and oxygen is cut off, the fire is controlled. The added advantage of $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is that in most cases it does not harm the electrical equipment.
32. How is the fire produced by burning oil (or petrol) extinguished?
Ans: The fires caused by the burning of inflammable materials like oil or petrol are also extinguished by using carbon dioxide fire extinguishers. The carbon dioxide used for extinguishing the fire can be stored as a liquid at high pressure in cylinders.
33. A drum full of kerosene catches fire. What is the simplest way to put off this fire?
Ans: A small fire like a drum of kerosene on fire can be extinguished by throwing sand or soil over it. When sand is thrown over burning kerosene oil, the sand covers it like a blanket. The sand cuts off the air supply to the burning kerosene oil due to which the fire gets extinguished.
34. What is the first thing you should do if a fire is caused by burning wood or paper?
Ans: Water extinguishes heat by cooling down the burning substance such as wood and paper. When water is thrown on these substances, it gets cooled below its ignition temperature and also stops burning.
35. (a) What does a Fire Brigade do when it arrives at a place where a building is on fire?
Ans: When the fire brigade arrives at the rescue, the fireman throws a strong stream of water at the building on fire, the burning material gets cooled down to below its ignition temperature and the fire is extinguished.
(b) Describe one method of putting out a fire caused by burning wood or paper.
Ans: Water extinguishes heat by cooling down the burning substance such as wood and paper. When water is thrown on these substances, it gets cooled below its ignition temperature and also stops burning.
36. Explain why, we are advised not to sleep in a room having closed doors and windows, with a coal fire burning inside.
Ans: Due to the burning of coal, the available oxygen gets depleted and it leads to the incomplete burning of coal. Incomplete combustion of coal gives carbon monoxide gas. It is a very poisonous gas. It is dangerous to burn coal in a closed room. The carbon monoxide gas produced can kill persons sleeping in that closed room.
37. (a) What is a flame? What type of substance, on burning, gives a flame?
Ans: A hot glowing body of ignited gas that is generated by something on fire is called Flame. Kerosene oil and molten wax are substances that give a flame while burning.
(b) What is the difference between the burning of a candle and the burning of a fuel like coal?
Ans: Substances that vapourize during burning produce flames, such as wax in the candle, and Kerosene. Substances that do not vapourize during burning do not produce flames. Example - coal and charcoal.
38. How does pouring water extinguish a fire?
Ans: Water lowers the temperature of the burning substance. When the temperature goes down below the ignition temperature of the burning substance the fire is extinguished. The water here acts as a cooling agent.
39. Explain how carbon dioxide is able to control fires?
Ans: Carbon dioxide is heavier than oxygen, covering the fire like a blanket. Since the contact between the fuel and oxygen is cut off, the fire is controlled. The added advantage of $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is that in most cases it does not harm the electrical equipment.
40. Explain how carbon dioxide is able to control fires?
Ans: Carbon dioxide is heavier than oxygen, covering the fire like a blanket. Since the contact between the fuel and oxygen is cut off, the fire is controlled. The added advantage of $\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is that in most cases it does not harm the electrical equipment.
41. If you see a person whose clothes are on fire, how will you extinguish the fire? Give a reason for your answer.
Ans: The person whose clothes are on fire should be immediately covered with a blanket. When the burning clothes of a person are covered with a blanket, the supply of air to the burning clothes is cut off, and hence the burning stops.
42. Give two examples each:
(a) solid fuels
Ans: A hot glowing body of ignited gas that is generated by something on fire is called Flame. Kerosene oil and molten wax are substances that give a flame while burning.
(b) liquid fuels
Ans: Petrol- Used to run small automobiles like bikes and cars.
Kerosene- Used for domestic heating purposes and jet engines as fuel.
(c) gaseous fuels
Ans: CNG- CNG is used to run automobiles.
Natural Gas- It is used for industrial purposes
43. Name the various zones of a candle flame. Which zone(or part) of a candle flame is the least hot(or coldest)?
Ans: A candle flame consists of three different zones. Each zone has different temperatures. Every zone has a different colour and this will help us in understanding the temperatures of each zone.
1. The first zone is called the Outer zone
2. The second zone is called the Middle zone
3. The third zone is called as Inner zone
The least hot region of the flame is present innermost. This inner zone is black in colour due to the presence of unburnt wax vapours.
44. Why does a goldsmith blow air into the kerosene lamp flame with a blow-pipe?
Ans: A goldsmith blows air into the kerosene lamp flame with a blowpipe to ensure that the combustion of fuel takes place and the temperature of the flame increases. The goldsmith mainly uses a non-luminous flame which is termed to be the outermost part of the flame. This part of the flame is used because the outermost flame undergoes complete combustion and is considered the hottest part of the flame.
45. In which zone of a candle flame:
(a) partial combustion of fuel takes place, and
Ans: Middle Zone
(b) complete combustion of fuel takes place?
Ans: Outer Zone
46. Explain how the use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in cities.
Ans: CNG played an important role in reducing pollution among automobiles for the following reasons;
CNG is comparatively a cleaner fuel.
The CNG can be an alternative to diesel, petrol, and propane/LPG.
It usually contains fewer undesirable gases than the other fuels mentioned above.
The combustion of fuels like petroleum causes many unburnt carbon particles along with carbon monoxide which leads to respiratory diseases.
47. What are the disadvantages of burning wood as fuel?
Ans: The burning of fuels like wood as fuel releases unburnt carbon particles in the air which causes respiratory problems. Incomplete combustion of fuels produces a very poisonous gas called carbon monoxide.
48. Give reason for the following: LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood.
Ans: LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood due to the following reasons:
It doesn’t release smoke and other pollutants
It is a cleaner fuels
The fuel efficiency of LPG is more than that of wood.
The calorific value of LPG is 55000 kJ/kg
49. Explain why, when a burning candle is covered with an inverted gas jar, the candle gets extinguished after some time.
Ans: A burning candle is covered with an inverted gas jar, the candle gets extinguished after some time because it does not get sufficient oxygen. Oxygen is one of the necessary conditions for combustion.
50. It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves but dry leaves catch fire easily. Explain?
Ans: A heap of green leaves contains a lot of moisture in it, hence its ignition temperature is high. Therefore it does not catch fire easily. But dry leaves have no moisture content in them, hence their ignition temperature is low. Therefore it catches fire easily.
Long Answer Type Questions
51. (a) What are combustible substances? Name three combustible substances.
Ans: Those substances which can burn are called combustible substances. For Ex: Cloth, straw, cooking gas, kerosene oil, wood, coal, charcoal, etc. A combustible substance is called fuel.
(b) What are non-combustible substances? Name three non-combustible substances.
Ans: Those substances which do not burn are called non-combustible substances. For Ex: Stone, cement, glass, bricks, soil, sand, water, iron nails, and copper objects.
52 (a) What is meant by ‘combustion’? Explain with an example.
Ans: A chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen to give heat and light is called combustion. The light which is given off during combustion can be in the form of flame or a glow. The substance which undergoes combustion is said to be combustible. It is called fuel.
(b) What are the conditions necessary for combustion to take place?
Ans: There are three conditions which are necessary for combustion to take place:
Presence of combustible substance.
Presence of supporters of combustion.
Heating the combustible substance to its ignition temperature.
53. (a) Make a labelled diagram of a candle flame.
Ans: It is given in the following picture:
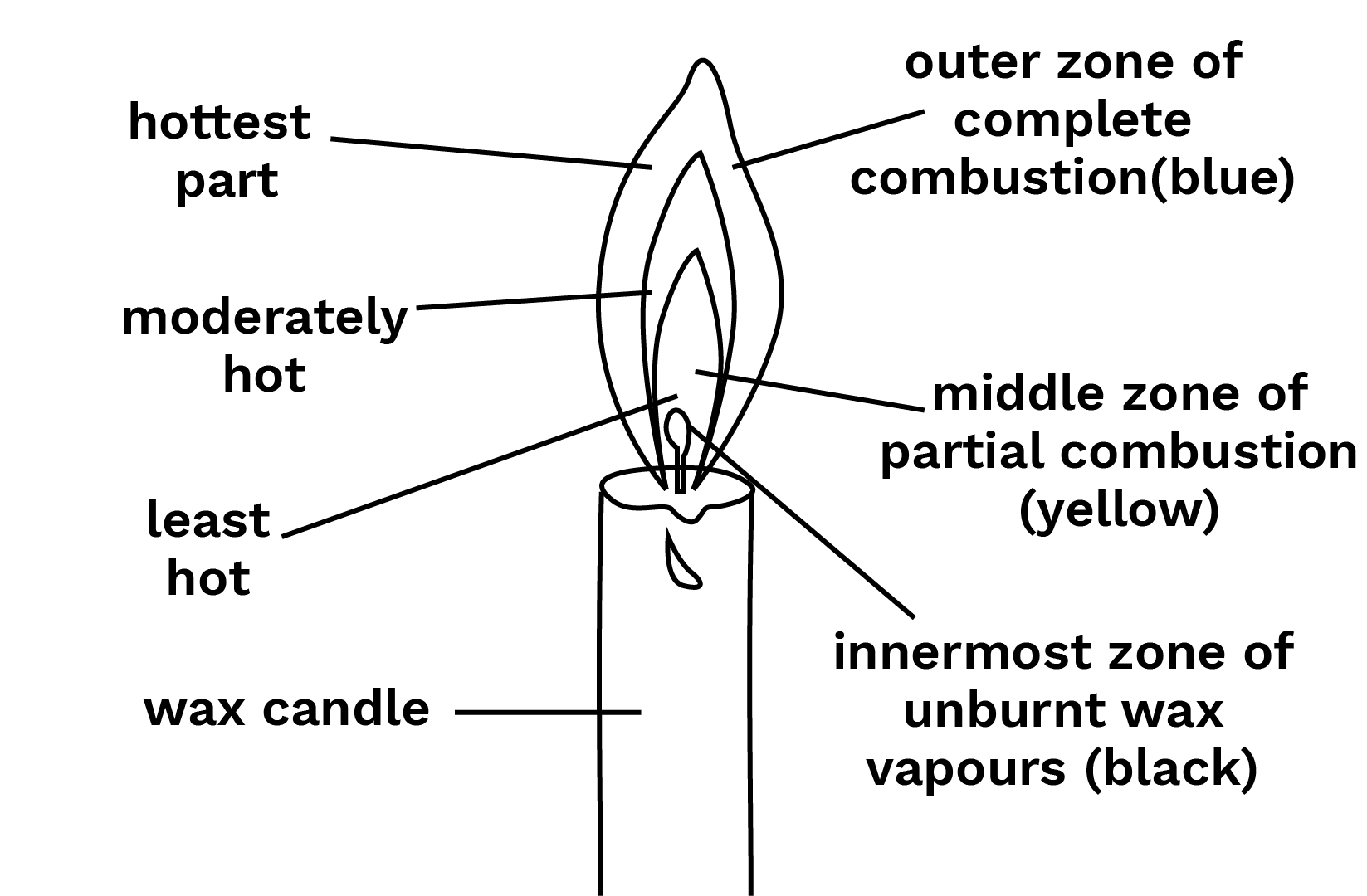
Labelled Diagram of a Candle Flame
(b) What makes the middle zone of a candle flame luminous(or light–giving)?
Ans: The middle zone, partial combustion of the fuel takes place, so the colour of the flame is yellow and it is a moderately hot part of the flame. It is the luminous part of the flame. It is given in the below picture:

The Given Figure Represents the Various Zones of a Candle Flame
54. What is global warming? Name the gas whose increasing percentage in air is leading to global warming. State a harmful effect which can be caused by global warming.
Ans: Global warming is the rise in temperature of the earth's atmosphere caused by the excessive amount of carbon dioxide in the air. Due to the rise in the temperature of the atmosphere, the ice in polar regions will melt very fast, producing a lot of water. The burning of fuels releases carbon dioxide into the air in the environment. The increased percentage of carbon dioxide in the air is causing global warming. Carbon dioxide gas in the air traps the sun’s heat rays by producing a greenhouse effect. The rise in water may cause a rise in the sea level leading to floods in coastal areas. The low-lying areas may be completely submerged under water leading to loss of life and property
55. Explain how burning fuels such as coal, petrol and diesel leads to acid rain. How is acid rain harmful?
Ans: The burning of coal, petrol, and diesel produces sulfur dioxide which goes into the air. It is an extremely suffocating and corrosive gas. It may damage our lungs. The burning of petrol and diesel in the engines of vehicles also releases nitrogen oxides into the air. These oxides produced by the burning of fuels dissolve in rainwater and form acids. The rainwater containing acid is called acid rain. It is harmful to crops, soil and damages buildings.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
56. Which of the following substances has the lowest ignition temperature?
A. Kerosene
B. Spirit
C. Diesel
D. Mustard oil
Ans: (B) Spirit
Minimum or least temperature at which a substance undergoes combination is called ignition temperature. Spirit/petrol has the lowest ignition temperature and can catch fire easily.
57. One of the following is not a combustible substance. This one is:
A. Alcohol
B. Hydrogen
C. Asbestos
D. Chaff
Ans: (C) Asbestos
Asbestos is a noncombustible substance and cannot catch fire on its own.
58. Which of the following is not used in making matchsticks these days?
A. Potassium chlorate
B. White phosphorus
C. Antimony trisulfide
D. Red phosphorus
Ans: (B) White phosphorus
White phosphorus undergoes spontaneous combustion. Hence it is not used in making matchsticks nowadays.
59. Which of the following undergoes spontaneous combustion?
A. Yellow sulphur
B. Red phosphorus
C. White phosphorus
D. Brown sulphur
Ans: (C) White phosphorus
White phosphorus undergoes spontaneous combustion. It catches fire on its own at room temperature.
60. Which of the following statements is not correct about carbon dioxide acting as a fire extinguisher for electrical fires?
A. It is heavier than air
B. It is lighter than air
C. It is not combustion
D. It does not support combustion
Ans: (B) it is lighter than air
Carbon dioxide is lighter than air and forms a layer around the burning substance. It covers the fire like a blanket due to which fresh air cannot reach the burning substance.
61. Fires in underground coal mines usually occur due to the:
A. Explosive combustion
B. Deliberate combustion
C. Spontaneous combustion
D. Rapid combustion
Ans: (C) Spontaneous combustion
fires in underground coal mines occur due to spontaneous combustion of coal dust.
62. The calorific value of a fuel is 40000 KJ/kg. This fuel is most likely to be:
A. Biogas
B. Methane
C. Hydrogen gas
D. Liquefied petroleum gas
Ans: (A) Biogas
Biogas has a calorific value of 40000 Kj/Kg.
63. Which of the following fuels has the highest calorific value?
A. Natural gas
B. Liquefied petroleum gas
C. Coal gas
D. Hydrogen gas
Ans: (D) Hydrogen gas
Hydrogen gas has the highest calorific value.
64. On a cold winter night, the person sleeping in a room with closed door and windows with a coal fire burning inside may die due to the excessive accumulation of:
A. Nitrogen monoxide
B. Nitrogen dioxide
C. Carbon dioxide
D. Carbon monoxide
Ans: (D) Carbon monoxide
Due to the burning of coal, the available oxygen gets depleted and it leads to the incomplete burning of coal. Incomplete combustion of coal gives carbon monoxide gas. It is a very poisonous gas. It is dangerous to burn coal in a closed room. The carbon monoxide gas produced can kill persons sleeping in that closed room
65. Which of the following burns without producing a flame?
A. Camphor
B. Coke
C. Cooking gas
D. Kerosene
Ans: (B) Coke
Coke does not evaporate during burning and hence does not produce a flame.
66. On a cold winter night, the persons sleeping in a room with closed doors and windows with a coal fire burning inside may die to the excessive accumulation of:
A. Kerosene
B. CNG
C. biogas
D. LPG
Ans: (B) CNG
CNG has small “nano-carbon” particles which can cause lung cancer.
67. Which of the following is the main cause of global warming?
A. Nitrogen dioxide
B. Sulphur dioxide
C. Carbon dioxide
D. Carbon monoxide
Ans: (C) Carbon dioxide
Burning of fuels releases carbon dioxide into the air in the environment. The increased percentage of carbon dioxide in air is causing global warming. Carbon dioxide gas in the air traps the sun’s heat rays by producing a greenhouse effect.
68. Which of the following gases does not contribute to the formation of acid rain?
A. Nitrogen monoxide
B. Carbon monoxide
C. Sulphur dioxide
D. Nitrogen dioxide
Ans: (B) Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide does not contribute to the formation of acid rain.
69. Which of the following is the most environmentally friendly fuel to be used in automobiles?
A. Petrol
B. Diesel
C. Natural gas
D. Petroleum gas
Ans: (C) Natural gas
The use of petrol and diesel as fuels in automobiles is being replaced by CNG because it produces very small amounts of harmful gases.
70. Which of the following does not involve a combustion reaction?
A. Production of heat and light from kerosene in a rocket
B. Production of heat and light from hydrogen in a rocket.
C. Production of heat and light from hydrogen in the sun
D. Production of heat and light from wood in a bonfire.
Ans: (C) Production of heat and light from hydrogen in the sun
production of heat and light from hydrogen in the sun is a nuclear reaction.
71. A heap of green leaves is lying in one corner of a park. The green leaves in the heap burn with difficulty because:
A. They contain a tough material called cellulose.
B. They contain a lot of water.
C. They contain a green pigment chlorophyll.
D. They do not get sufficient oxygen for burning
Ans: (B) they contain a lot of water.
The green leaves contain a lot of water. This water does not allow the green leaves to get heated to their ignition temperature and makes burning of green leaves difficult.
72. If the clothes of a person working in the kitchen catch fire, then to extinguish the fire:
A. Sand should be thrown over the burning clothes
B. Water should be thrown over the burning clothes.
C. Polyester blanket should be used to cover the burning clothes
D. Woollen blanket should be used to cover the burning clothes
Ans: (D) woollen blanket should be used to cover the burning clothes
If the clothes of a person working in the kitchen catch fire, the person is immediately covered with a blanket. When the burning clothes of a person are covered with a blanket, the supply of air to the burning clothes is cut off, and hence the burning stops.
73. The outermost zone of a candle flame is the:
A. Least hot part
B. Coldest part
C. Hottest part
D. Moderately hot part
Ans: (C) hottest part
In the outer zone, complete combustion of the fuel takes place and the colour of the flame is blue and is the hottest part of the flame.
74. The flame of a kerosene oil lamp (or lantern) has:
A. Single zone
B. Two zones
C. Three zones
D. Four zones
Ans: (C) three zones
It has three zones. Each zone has different temperatures and different colours. Due to complete combustion, the outer zone is blue in colour and it is the hottest. The yellow colour region which is the bright part of the flame is the middle zone. It is moderately hot and partial combustion of fuel takes place. The least hot region of the flame is present innermost. This inner zone is black in colour due to the presence of unburnt wax vapours.
75. A lot of dry powder of one of the following chemicals can be released over a fire to extinguish it. This chemical is:
A. Plaster of Paris
B. Baking soda
C. Washing soda
D. Bitumen
Ans: (B) baking soda
To obtain carbon dioxide for extinguishing a fire is to release a lot of dry powder of chemicals like sodium bicarbonate(baking soda) or potassium bicarbonate over the fire.
High Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)
76. An electric spark is struck between two electrodes placed near each other in a closed tank full of petrol. Will the petrol catch fire? Explain your answer.
Ans: As it is a closed tank full of petrol, there will be no supply of air. Hence the petrol will not catch fire as air is necessary for the combustion of petrol.
77. Give reason for the following:
Paper by itself catches fire easily whereas a piece of paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe does not.
Ans: A piece of paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe does not catch fire easily. This is because aluminium, being a metal, is a good conductor of heat and hence heat is conducted away. Also, the ignition temperature of paper is lower compared to that of aluminium. When paper is wrapped around an aluminium pipe; the ignition temperature increases. That is why paper itself catches fire easily whereas a piece of paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe does not.
78. Abida and Ramesh want to heat water taken in separate beakers. Abida kept the beaker near the wick in the yellow part of the candle flame. Ramesh kept the beaker in the outermost part of the flame. Whose water will get heated in a shorter time? Why?
Ans: The yellow part of the flame is the middlemost part where Abida has kept the beaker. The fuel vapours burn partially in the middle zone because there is not enough air of burning in this zone. The partial burning of fuel in the middle zone produces carbon particles. It has a moderate temperature. Hence, Abida’s beaker will take time to heat up.
Ramesh’s beaker is kept in the outermost part of the flame. In this zone, complete combustion of the fuel takes place because there is plenty of air around it. The outermost zone has the highest temperature in the flame. It is the hottest part of the flame. Hence Ramesh’s beaker gets heated in a shorter time.
79. When a lot of dry powder of a substance X is released over a fire, the fire gets extinguished.
(a) Name the substance X.
And. Sodium Bicarbonate (sodium hydrogen carbonate)
(b) How does this substance extinguish the fire?
Ans: The heat of fire decomposes sodium bicarbonate to produce carbon dioxide gas. This carbon dioxide covers the fire like a blanket and cuts off the supply of fresh air to the burning substance. Due to this, the fire gets extinguished
(c) Name another substance which behaves like X.
Ans: Potassium bicarbonate(or Potassium hydrogen carbonate)
80. What type of combustion is represented by:
(a) burning of white phosphorus in air at room temperature?
Ans: The burning of white phosphorus in the air at room temperature is spontaneous combustion. The type of combustion in which a material suddenly bursts into flames, without the application of any apparent cause is called spontaneous combustion.
(b) burning of LPG in a gas stove?
Ans: The burning of LPG is combustion in which a substance burns rapidly and produces heat and light with the help of external heat.
(c) ignition of a cracker?
Ans: Ignition of a cracker is combustion in which a substance burns suddenly and produces heat, light, and sound with the help of heat or pressure.
(d) burning of coal dust in a coal mine?
Ans: The burning of coal dust in a coalmine is spontaneous combustion. The type of combustion in which a material suddenly bursts into flames, without the application of any apparent cause is called spontaneous combustion.
Importance of Lakhmir Singh Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flames
Class 8 Science Chapter 6 is all about combustion and the flames produced from this chemical reaction. It is a fundamental chapter in the Class 8 ICSE syllabus that introduces the students to combustion, one of the most crucial chemical reactions they will study in other chapters related to chemistry and the next classes.
Combustion is a chemical process where a substance burns and reacts with oxygen to produce products such as oxides, gases, etc. In this reaction, light and heat are produced to form flames. Different substances have different flames in terms of colour and heat produced. By studying this chapter, students will be able to define extinguish. It is a process that puts down a combustion reaction.
Students will also learn what combustible and non-combustible substances are and how to identify them. They will learn the different features of these types of substances. This chapter will explain what a candle is and how it produces a flame.
The chapter will then explain what ignition temperature is and how it is important to reach that temperature to start combustion. Students will also learn what fire and a fire triangle are.
This is just a glimpse of what the students will learn in this chapter of Combustion And Flames Class 8 PDF.
Benefits of Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flames
The solutions have been framed by following the latest ICSE Class 8 syllabus. The experts have also followed the standard formats for answering such fundamental questions. By following these formats, you will be able to write your answers perfectly and score more in the exams.
Resolving doubts will not be a problem when you have the Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 6. This chapter solution will be able to help you find the right answers in no time and assist you in completing preparing this chapter on your own. Practice answering fundamental questions such as naming one fuel which burns without producing a flame and the others in the exercise to check your preparation level. Find out where you need to work more to make it better.
Download Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flames PDF
Get the free PDF version of these solutions and find the accurate answers to HOTS questions on combustion and flame. Make your study sessions more productive by resolving doubts faster and learning to answer fundamental questions in the best way possible.
FAQs on Lakhmir Singh Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flames - PDF
1. What is a flame?
The visible portion of a combustion reaction emitting light is called a flame.
2. What is ignition temperature?
The temperature at which a substance starts burning is called its ignition temperature.
3. What is a non-combustible substance?
A non-combustible substance is a substance that does not catch fire readily.
Example: Sand. Sand does not catch fire that easily. It rather melts when the temperature is very high.
4. What are fuels?
Fuels are combustible substances that readily catch fire and promote burning or combustion.
Example: Kerosene. They are used for creating controlled combustions in engines and appliances for various purposes.
5. What is smoke?
The unburnt dispersed particles arising from a flame together are called smoke. The colour of smoke is determined by the particles in it.
























