NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology - Reproduction in Organism - Free PDF Download
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 - Reproduction in Organism solved by expert Biology teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 1 - Reproduction in Organism exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Biology Solutions Chapter 1: Reproduction in Organism is intended to help the students who need to score good in their CBSE NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Biology Board tests. Reproduction in living beings is an extensive topic that includes the course of preparation and the development of new individuals. The NCERT Exemplar Solutions will provide you with a concise outline of the sexual and asexual reproduction in the two: plants and creatures. These NCERT Exemplar problems with solutions will help you in a profound comprehension of the ideas of pre preparation and post-fertilization occasions in plants just as animals.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Biology Solutions Chapter 1 contains 49 Exemplar problems ordered into 4 areas specifically: MCQs, VSA, SA, and long answer types. These NCERT Exemplar problems are outlined according to your CBSE rules and will be advantageous for your test perspective.
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Science (Biology) Chapter 1 - Reproduction in organisms
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS-:
1. A few statements describing certain features of reproduction are given
below:
i. Gametic fusion takes place
ii. Transfer of genetic material takes place
iii. Reduction division takes place
iv. Progeny have some resemblance with parents
Select the options that are true for both asexual and sexual reproduction from the options given below:
(a) i and ii
(b) ii and iii
(c) ii and iv
(d) i and iii.
Ans: The correct answer is option (c) ii & iv
Gametic fusion & reductional division (meiosis) does not occurs in case of asexual reproduction.
2. The term ‘clone’ cannot be applied to offspring formed by sexual reproduction because:
a. Offspring do not possess exact copies of parental DNA
b. DNA of only one parent is copied and passed on to the offspring.
c. Offspring are formed at different times.
d. The DNA of parents and offspring are completely different.
Ans: The correct answer is option (a).
Clone is defined as the photocopy of something or someone. This term does not apply in case of sexual reproduction because in this case an offspring is the result of fusion of gametes that comes from both the parents' side & variation is because of crossing over.
3. Asexual method of reproduction by binary fission is common to which of the following?
i. Some eukaryotes
ii. All eukaryotes
iii. Some prokaryotes
iv. All prokaryotes
Choose the correct option from the following:
(a) i and ii
(b) ii and iii
(c) i and iii
(d) iii and iv
Ans: The correct answer is option (c) Some prokaryotes & some eukaryotes.
There are varieties of methods of asexual reproduction such as binary fission, budding, multiple fission etc. occurs in prokaryotes similarly in case of eukaryotes few can reproduce by sexual , few by asexual means and few can reproduce by both the method.
4. A few statements with regard to sexual reproduction are given below:
i. Sexual reproduction does not always require two individuals
ii. Sexual reproduction generally involves gametic fusion
iii. Meiosis never occurs during sexual reproduction
iv. External fertilization is a rule during sexual reproduction
Choose the correct statements from the options below:
(a) i and iv
(b) i and ii
(c) ii and iii
(d) i and iv
Ans: The correct answer is option (b) i & ii
In case of bisexual individual sexual reproduction can perform by the single individual as this kind of individuals are capable enough for the production of both the type of gametes. Gametic fusion occurs in the sexual mode of reproduction. Meiosis always occurs in sexual reproduction. External fertilization is not the rule of sexual reproduction.
5. A multicellular, filamentous alga exhibits a type of sexual life cycle in which the meiotic division occurs after the formation of zygote. The adult
filament of this alga has
a. haploid vegetative cells and diploid gametangia
b. diploid vegetative cells and diploid gametangia
c. diploid vegetative cells and haploid gametangia
d. haploid vegetative cells and haploid gametangia.
Ans: The correct answer is option (d).
Many species of algae show a haplontic life cycle. In this case the dominant phase is represented by free living gametophyte & sporophytic generation is represented by zygote that undergoes meiosis & results in the formation of spores.
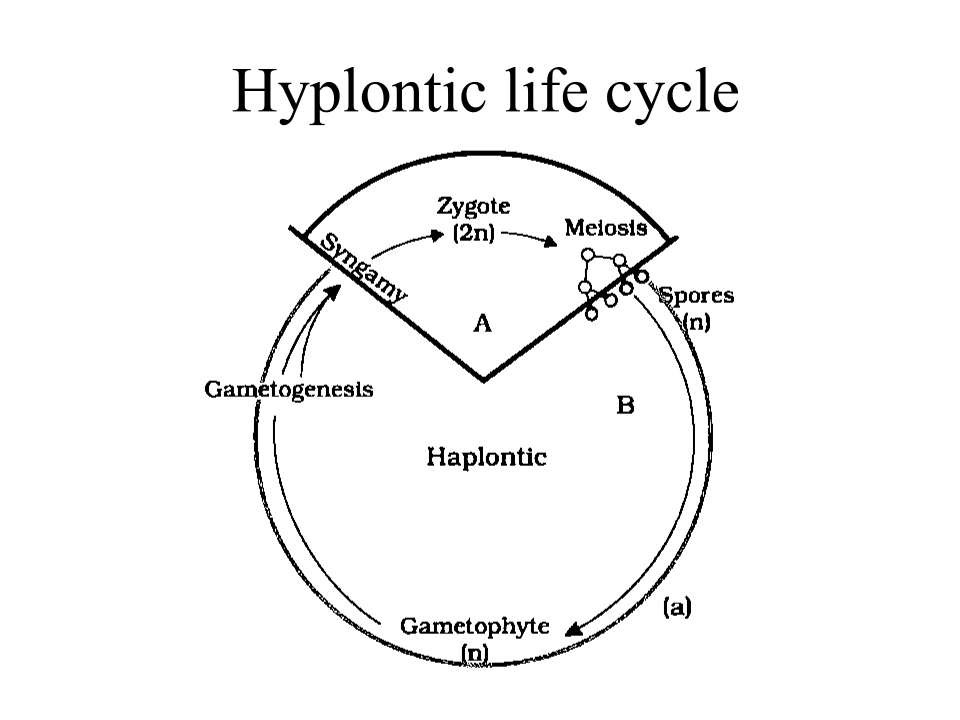
6. The male gametes of rice plants have 12 chromosomes in their nucleus. The chromosome number in the female gamete, zygote and the cells of the seedling will be, respectively,
a. 12, 24, 12
b. 24, 12, 12
c. 12, 24, 24
d. 24, 12, 24.
Ans: The correct answer is option (c) 12, 24, 24.
Gamete-: It is the result of reductional division, that results in reduction of chromosome no. to half.
Zygote-: It is the result of fusion of gametes, hence the chromosome no. becomes double in comparison to gametes.
Seedling-: It is the young plant that develops from seed.
7. Given below are a few statements related to external fertilization. Choose the correct statements.
i. The male and female gametes are formed and released simultaneously
ii. Only a few gametes are released into the medium
iii. Water is the medium in a majority of organisms exhibiting external fertilization
iv. Offspring formed as a result of external fertilization have better chance of survival than those formed inside an organism
(a) iii and iv
(b) i and iii
(c) ii and iv
(d) i and iv
Ans: The correct answer is option (b) i & iii
External fertilization is the process which involves the fusion of gametes outside the body of living organisms. Both the sexes release their gametes outside the body in the external environment that is the water in most of the cases.
All the gametes are released into the medium that increases the chances of fertilization. In case of external fertilization, the chance of survival is very less because the development of the offspring occurs outside the body & chances of predation will be very high.
8. The statements given below describe certain features that are observed in the pistil of flowers.
i. Pistil may produce more than one seed
ii. Each carpel may have more than one ovule
iii. Each carpel has only one ovule
iv. Pistil have only one carpel
Choose the statements that are true from the options below:
(a) i and ii
(b) i and iii
(c) ii and iv
(d) iii and iv
Ans: The correct answer is option (a) i and ii
Gynoecium is the female reproductive part of the flower. The unit of gynoecium is called pistil. A pistil contains one or more carpels & each carpel can be provided with one or more than one ovule.
9. Which of the following situations correctly describe the similarity between an angiosperm egg and a human egg?
i. Eggs of both are formed only once in a lifetime
ii. Both the angiosperm egg and human egg are stationary
iii. Both the angiosperm egg and human egg are mobile
iv. Syngamy in both results in the formation of zygote
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) ii and iv
(b) iv only
(c) iii and iv
(d) i and iv
Ans: The correct answer is option (b) iv only
Both the humans & angiospermic plants are active throughout their reproductive phase, hence eggs are formed many times in their lifetime. In case of human’s eggs travel from ovary to the fallopian tubes. In case of angiospermic plants eggs are stationary.
10. Appearance of vegetative propagules from the nodes of plants such as sugarcane and ginger is mainly because:
a. Nodes are shorter than internodes
b. Nodes have meristematic cells
c. Nodes are located near the soil
d. Nodes have non-photosynthetic cells
Ans: The correct answer is option (b).
Meristematic cells have the ability to control the growth, development of tissues & the organs in plants. As soon as the nodes come in contact with the damp soil, they produce roots that ultimately give rise to new plants.
11. Which of the following statements, support the view that elaborate sexual the reproductive process appeared much later in organic evolution.
i. Lower groups of organisms have simpler body design
ii. Asexual reproduction is common in lower groups
iii. Asexual reproduction is common in higher groups of organisms
iv. The high incidence of sexual reproduction in angiosperms and vertebrates
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) i, ii and iii
(b) i, iii and iv
(c) i, ii and iv
(d) ii, iii and iv
Ans: The correct answer is option (c) i, ii and iv
Asexual reproduction is the kind of reproduction in which fusion of gametes is not there. In this kind of reproduction only one parent is involved. It mainly occurs in lower organisms & is very less efficient in terms of survival. Hence, statement (iii) will be incorrect.
12. Offspring formed by sexual reproduction exhibit more variation than those formed by Asexual reproduction because:
a. Sexual reproduction is a lengthy process
b. Gametes of parents have qualitatively different genetic composition
c. Genetic material comes from parents of two different species
d. Greater amount of DNA is involved in sexual reproduction.
Ans: The correct answer is option (b).
During gamete formation the no. of chromosomes become half due to the meiosis (reductional division). Both the parents contribute 50% each in the form of gamete ultimately give rise to offspring that is provided with the same no. of chromosomes as the parents have & also with variation which are due to the crossing over.
13. Choose the correct statement from amongst the following:
a. Dioecious organisms are seen only in animals
b. Dioecious organisms are seen only in plants
c. Dioecious organisms are seen in both plants and animals
d. Dioecious organisms are seen only in vertebrates
Ans: The correct answer is option (c).
Dioecious organisms are those in which male and female reproductive parts are present in different organisms whereas monoecious organisms are those in which male and female reproductive parts are present in the same organism. Monoecious organisms are also called hermaphrodites. The example of dioecious organisms & plants are mammals, birds & insects, mulberry, sago & kiwi fruit respectively.
14. There is no natural death in single celled organisms like Amoeba and bacteria because:
a. They cannot reproduce sexually
b. They reproduce by binary fission
c. Parental body is distributed among the offspring
d. They are microscopic
Ans: The correct answer is option (c)
Amoeba is the unicellular organism that reproduces by the process of binary fission (asexual reproduction). During this parent cell divides into two daughter cells that later on acts as an individual amoeba. Hence, there is no natural death in single celled organisms like Amoeba and bacteria.
15. There are various types of reproduction. The type of reproduction adopted by an organism depends on-:
a. The habitat and morphology of the organism
b. Morphology of the organism
c. Morphology and physiology of the organism
d. The organism’s habitat, physiology, and genetic makeup
Ans: The correct answer is option (d).
The type of reproduction adopted by an organism depends upon the organism’s habitat, physiology, and its genetic makeup.
16. Identify the incorrect statement.
a. In asexual reproduction, the offspring produced are morphologically and genetically identical to the parent
b. Zoospores are sexual reproductive structures
c. In asexual reproduction, a single parent produces offspring with
or without the formation of gametes
d. Conidia are asexual structures in Penicillium
Ans: The correct answer is option (b).
Zoospores are the asexual structure that produces in some algae & certain protozoans such as Phytophthora. These are motile in nature due to the presence of flagella in them.
17. Which of the following is a post-fertilization event in flowering plants?
a. Transfer of pollen grains
b. Embryo development
c. Formation of flower
d. Formation of pollen grains
Ans: The correct answer is option (b) embryo development.
Post-fertilization events are those that occur after fertilization (fusion of gametes). The correct sequence of sexual reproduction in flowering plants are -:
Gametogenesis→ Pollination→ Fertilization→ Embryo development
←Pre-Fertilization event→ ←Post fertilization→
18. The number of chromosomes in the shoot tip cells of a maize plant is 20. The number of chromosomes in the microspore mother cells of the same plant shall be:
a. 20
b. 10
c. 40
d. 15
Ans: The correct answer is option (a) 20.
This is because microspore mother cells have the same ploidy as that of the somatic vegetative cells.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS-:
1. Mention two inherent characteristics of Amoeba and yeast that enable them to reproduce asexually.
Ans: Inherent characteristics of Amoeba and yeast that enable them to reproduce asexually are-:
1. They are unicellular in nature.
2. They are provided with simple body organization.
2. Why do we refer to offspring formed by asexual method of reproduction as clones?
Ans: Clone is defined as the photocopy of anything or any individual.
Asexual reproduction is the kind of reproduction which does not involves the fusion of gametes. In this kind of reproduction only one parent is involved. There is no event of variation or the crossing-over that creates the differences among the offsprings. Hence, offsprings formed by asexual reproduction referred as clones.
3. Although potato tuber is an underground part, it is considered as a stem. Give two reasons.
Ans: Although potato tuber is an underground part but still it is considered as a stem because-:
1. Presence of nodes (eyes).
2. Presence of scaly leaves.
4. Between an annual and a perennial plant, which one has a shorter juvenile phase? Give one reason.
Ans: Perineal plants are those that regrow every season while annual plants are those that grow for one season only & then die off. The annual plant has to complete their life cycle in the single season hence, annual plants have a shorter juvenile phase in comparison to perennial plants.
5. Rearrange the following events of sexual reproduction in the sequence in which they occur in a flowering plant:
embryogenesis, fertilization, gametogenesis, pollination.
Ans: The correct sequence of the events in flowering plants are-:
Gametogenesis→ Pollination→ Fertilization→ Embryogenesis
Gametogenesis-: It is the event which involves the formation of gametes.
Pollination-: It is the event which involves the dispersal of pollens (male gametes).
Fertilization-: It is defined as the fusion of gametes.
Embryogenesis-: It is defined as the development of an embryo.
6. The probability of fruit set in a self-pollinated bisexual flower of a plant is far greater than a dioecious plant. Explain.
Ans: This is because in the case of a self-pollinated flower a plant does not depend upon pollinating agents to carry out the process of pollination while a dioecious depends upon pollinating agents that may be some time not available.
7. Is the presence of large number of chromosomes in an organism a hindrance to sexual reproduction? Justify your answer by giving suitable reasons.
Ans: No, this is not true. The no. of chromosomes never decides the mode of reproduction. For example, there are 8 chromosomes in the somatic cells of fruit fly while there are 360 chromosomes in case of butterflies, but both the organisms reproduce by the sexual mode only.
8. Is there a relationship between the size of an organism and its life span? Give two examples in support of your answer.
Ans: No, there is no relationship between the size of an organism and its life span. This thing can be clear by following table-:
Name of Plant | Life span | Name of animal | Life span |
Banyan tree | 200-300 yrs. | Elephant | 70 yrs. |
Peepal | 2000-3000yrs. | Giant Tortoise | 152 yrs. |
Both banyan tree & peepal tree are approximately the same in size, still there is the huge difference between their life span similarly there is the huge difference in the size of elephant & tortoise but if we observe carefully the life span of tortoise is much longer than the elephant.
9. In the figure given below the plant bears two different types of flowers marked ‘A’ and ‘B’. Identify the types of flowers and state the type of pollination that will occur in them.
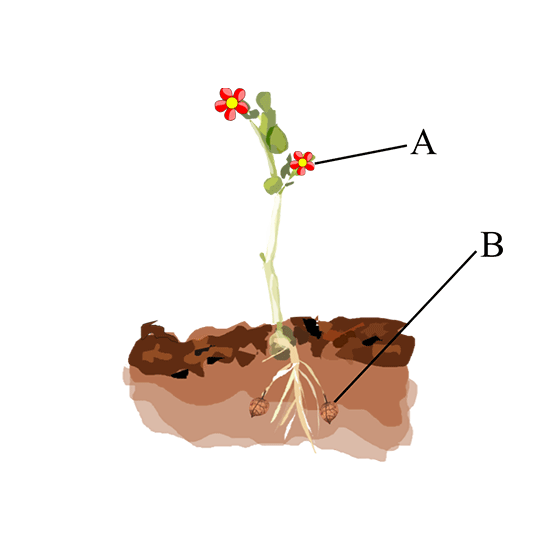
Ans: ‘A’ represents the chasmogamous flower while ‘B’ represents the cleistogamous flower.
Chasmogamous flower | Cleistogamous flower. |
1.This kind of flowers are open type. Anther & stigma are exposed. | 1. These kinds of flowers are closed. |
2.This kind of flowers can go either for self-pollination or cross pollination. | 2. This kind of flower undergoes self-pollination only. |
3.External agencies are required to carry out the process of pollination. | 3. No external agencies are required because the flowers are bisexual in nature. |
10. Give reasons as to why cell division cannot be a type of reproduction in multicellular organisms.
Ans: Multicellular organisms are provided with complex body organization. There is the division of labor. One cannot produce the different types of tissues by mitosis only. Hence, cell division cannot be a type of reproduction in multicellular organisms.
11. In the figure given below, mark the ovule and pericarp.

Ans: The figure below marks the ovule & pericarp.
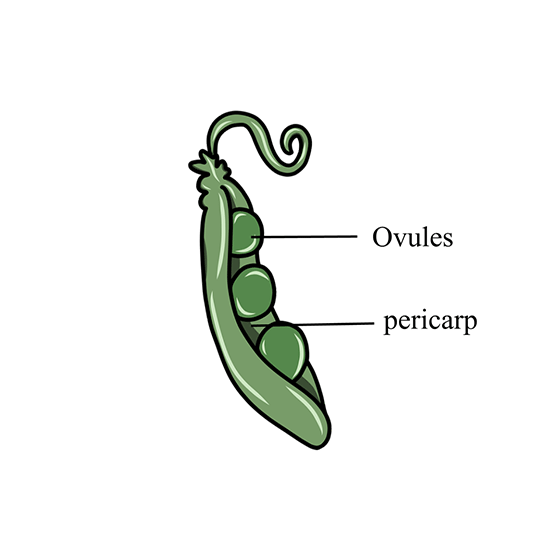
Ovule-: It is the plant structure that develops into the seeds.
Pericarp-: It is the protective covering of seeds that develops from the ovary.
12. Why do gametes produced in large numbers in organisms exhibit external fertilization?
Ans: External fertilization is the process which involves the fusion of gametes outside the body of living organisms. In case of external fertilization, the chances of fertilization is very less because gametes can either get blown off by the wind or can be eaten by the predator. Hence, to ensure the fertilization large no. of gametes are produced.
13. Which of the following are monoecious and dioecious organisms.
a. Earthworm | ______________ |
b. Chara | ______________ |
c. Marchantia | ______________ |
d. Cockroach | ______________ |
Ans:
a. Earthworm | Monoecious animal |
b. Chara | Monoecious plant |
c. Marchantia | Dioecious plant |
d. Cockroach | Dioecious animal |
14.Match the organisms given in Column-’A’ with the vegetative propagules given in column ‘B’.
Column A | Column B |
i. Bryophyllum | (a) Offset |
ii. Agave | (b) Eyes |
iii. Potato | (c) Leaf buds |
iv. Water hyacinth | (d) Bulbils |
Ans:
Column A | Column B |
i. Bryophyllum | (c) Leaf buds |
ii. Agave | (d) Bulbils |
iii. Potato | (b) Eyes |
iv. Water hyacinth | (a) Offset |
15.What do the following parts of a flower develop into after fertilization?
a. Ovary ______________
Ans: Fruits
b. Ovules ____________
Ans: Seeds
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS-:
1. In haploid organisms that undergo sexual reproduction, name the stage in the life cycle when meiosis occurs. Give reasons for your answer.
Ans: The stage in which meiosis occurs in haploid organisms is the sporophytic stage. During this stage zygote undergoes meiosis & results in production of spores. This type of life cycle is called haplontic life cycle that occurs in certain organisms such as Volvox, Spirogyra etc. The gametophytic generation is dominant in this kind of life cycle.
2. The number of taxa exhibiting asexual reproduction is drastically reduced in higher plants (angiosperms) and higher animals (vertebrates) as compared with lower groups of plants and animals. Analyze the possible reasons for this situation.
Ans: Asexual reproduction is the kind of reproduction in which there is the involvement of mitosis only. In the case of organisms that are provided with complex body organization, mitosis alone is not enough to differentiate the different kinds of tissues. This method of reproduction is frequently seen in lower plants & the animals only that are quite simpler in their body organization.
3. Honeybees produce their young ones only by sexual reproduction. In Spite of this, in a colony of bees we find both haploid and diploid individuals. Name the haploid and diploid individuals in the colony and analyse the reasons behind their formation.
Ans: Honeybees are social insects. In the colony of honeybees, workers & females are diploid in nature while drones are haploid in nature. Drones are produced by the process of parthenogenesis (production of offspring by the unfertilized eggs). All the three members of the colony perform different functions & there is the division of labour in them.
Name of member | Functions |
Worker bee | Nest building, food collection etc. |
Female (queen) | Perform mating & lay eggs. |
Drone | Perform mating & lay eggs. |
4. With which type of reproduction do we associate the reduction division? Analyse the reasons for it.
Ans: The term reduction division is associated with sexual reproduction. This is because in sexual reproduction during gamete formation the no. of chromosomes become half due to the meiosis (reductional division).Both the parents contribute 50% each in the form of gametes ultimately give rise to offspring that is provided with the same no. of chromosomes as the parents have also the variation because of the crossing over.
5. Is it possible to consider vegetative propagation observed in certain plants like Bryophyllum, water hyacinth, ginger etc., as a type of asexual reproduction? Give two/three reasons.
Ans: Vegetative propagation in certain plants like Bryophyllum, water hyacinth, ginger etc. considered as a type of asexual reproduction because of following reasons-:
1. It involves single parents.
2. Meiosis or reduction division does not occur.
3. Fusion of gametes is not there.
6. 'Fertilization is not an obligatory event for fruit production in certain plants. Explain the statement.
Ans: Many plants have the ability to produce the fruits without the process of fertilization. Such kinds of fruits that are produced by this process are called parthenocarpic fruits, The example includes Banana. One can induce the artificial parthenocarpy in certain plants such as papaya & watermelon. The fruits produced by this method do not carry seeds as they can’t be produced without fertilization. Hence, it is said that fertilization is not a mandatory event for fruit production in certain plants.
7. In a developing embryo, analyse the consequences if cell divisions are not followed by cell differentiation.
Ans: Cell differentiation is an essential event because it allows the development of different tissues that ultimately give rise to different organs & organ systems. If there is no differentiation after the cell division then it leads to the production of mass of undifferentiated identical cells that is unable to survive.
8. List the changes observed in an angiosperm flower subsequent to pollination and fertilization.
Ans: Changes that took place in an angiosperm flower after the pollination and fertilization are-:
1. Sepals, Petals & Stamens fall off.
2. Zygote develops into embryo, ovary develops into fruit & ovules develop into seeds.
3. Fruit develops a thick covering, named pericarp (protective covering of seeds).
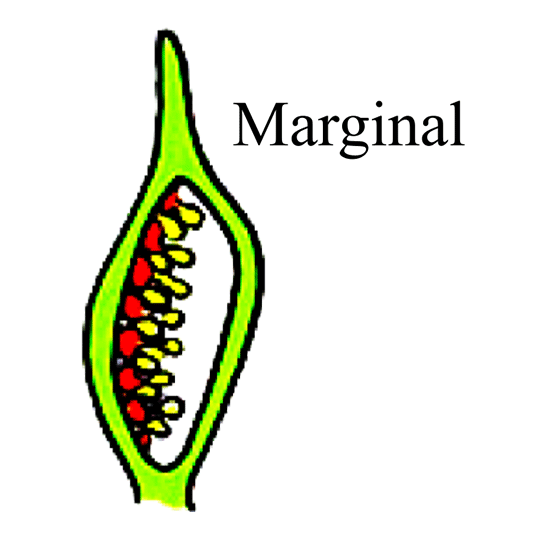
9. Suggest a possible explanation why the seeds in a pea pod are arranged in a row, whereas those in tomatoes are scattered in the juicy pulp.
Ans: This is because of different types of placentation that is responsible for the arrangement of seeds. A pea plant shows marginal placentation while the tomatoes show axial placentation.
Marginal placentation -: In this kind of placentation placenta forms a ridge along the ventral suture of the ovary and the ovules develop in two separate rows.
Axial placentation-: It is the type of placentation in which carpal folds inward with ovules (future seeds) placed along the central axis of the ovary (future fruit).

10. Draw the sketches of a zoospore and a conidium. Mention two dissimilarities between them and at least one feature common to both structures.
Ans:
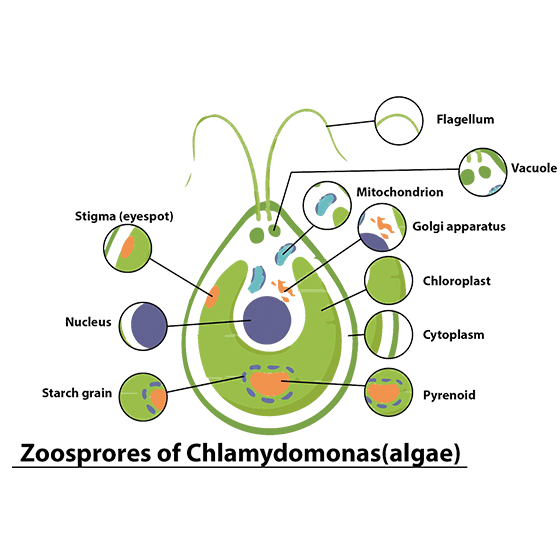
Zoospores | Conidium |
1. It is flagellated in nature. | 1. It is non- flagellated in nature. |
2. It is motile in nature. | 2. It is non-motile in nature. |
Similarities-:
1.Both are produced in asexual mode of reproduction.
2.Both are haploid (n) in nature.
11. Justify the statement ‘Vegetative reproduction is also a type of asexual reproduction’.
Ans: Vegetative reproduction is also a type of asexual reproduction because-:
1. Only one parent is involved.
2. Gametogenesis is not there.
3. Fusion of gametes is not there.
4. Meiosis or reductional division is not there.
5. The offspring is the exact copy (clone) of the parent.
All the features that are mentioned above are of asexual mode of reproduction.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS-:
1. Enumerate the differences between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Ans:
Asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
1. A single parent is involved in this kind of reproduction. | 1. Two parents of opposite sex are involved in this kind of reproduction. |
2. Gamete’s production does not occur. | 2. Gamete’s production occurs. |
3. Reductional division or meiosis does not occur. | 3. Reductional division or meiosis occurs. |
4. Fusion of gametes is not there. | 4. Fusion of gametes is there. |
5. It is the less efficient method of reproduction. | 5.It is the most efficient method of reproduction. |
2. Describe the types of asexual reproduction exhibited by unicellular organisms?
Ans: Asexual reproduction is the kind of reproduction which does not involves the fusion of gametes. This type of reproduction involves only one parent & the offspring is the exact copy of them. There are different types of asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms such as-:
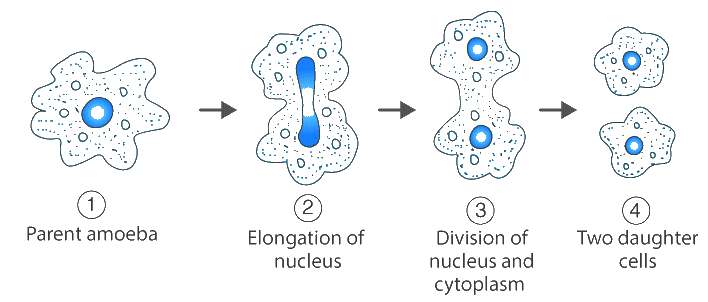
1. Binary fission-: In this kind of reproduction the parental cell divides into two daughter cells that can act as the individual organism in future. The example includes Amoeba.
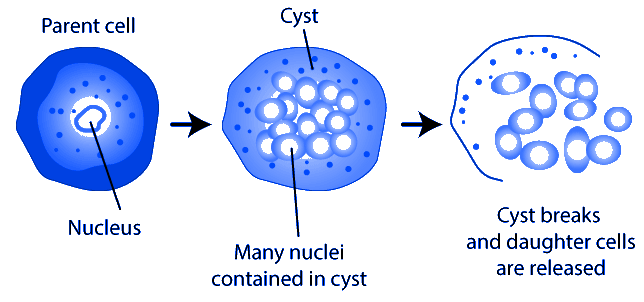
2. Multiple fission-: In this kind of reproduction the parent cell's nucleus divides into multiple nuclei & forms the cyst around the mother cell. The cyst helps the mother cell to survive in unfavorable conditions & as soon as the favorable conditions arrives the cyst degenerates & each nuclei acts as the daughter individual. The example includes Plasmodium.
3. Budding-: In this reproduction a bud is developed on the parental cell surface. As the time passes the bud grows in size & ultimately detached from the parental body that acts as the new individual in the upcoming future.

3. Do all the gametes formed from a parent organism have the same genetic composition (identical DNA copies of the parental genome)? Analyze the situation with the background of gametogenesis and provide or give suitable explanation.
Ans: No, all the gametes formed from a parent organism does have the same genetic composition. This is because sexual reproduction involves the fusion of gametes that comes either from two different individuals of opposite sexes or the same individual provided with both the sexes. The process of formation of gametes is called gametogenesis.
1. The haploid parents such as Monera, fungi, algae and bryophytes produce gametes by mitotic division. The gametes, despite being formed from a single parent, do not have the same genetic composition due to error in DNA copying or mutation.
2. In diploid organisms like pteridophytes, gymnosperms, angiosperms and most of the animals including human beings produce gametes by meiosis. Each individual has a 50% genome contribution from both the parents. During meiosis the no. of chromosomes become half (haploid) in the gametes, so there is random distribution of chromosomes so that each gametes receives a unique combination of chromosomes from the parent. In addition, crossing over in meiosis results in exchange of genetic material between the homologous chromosomes and creates recombined chromosomes that are not found in the parents.
4. Although sexual reproduction is a long drawn, energy-intensive complex form of reproduction, many groups of organisms in Kingdom Animalia and Plantae prefer this mode of reproduction. Give at least three reasons for this.
Ans: Sexual reproduction is the process of reproduction which involves the fusion of gametes that comes either from two different individuals of opposite sexes or the same individual provided with both the sexes. Most of the animals specially the higher animals prefer sexual mode of reproduction because-:
1. Sexual reproduction contributes to the variation in the gene pool thus ensures the survival of fittest.
2. The offspring that are produced by this method contain the characteristics of both the parents. In most of the cases the offspring is superior to the parental generation in terms of adaptation & survival.
3. The chances of survival in this kind of reproduction is more because of the presence of variations that acts as the source of evolution.
5. Differentiate between & site an example for each type.
(a) Oestrus and Menstrual cycles
Ans:
Oestrus cycle | Menstrual cycle |
1. Females show irresistible sexual urges. | 1. Females do not show irresistible sexual urges. |
2. Bleeding does not occur in this case. | 2. Bleeding occurs in this case. |
3. This cycle is comparatively simpler in nature. | 3. This cycle is very complex in nature and consists of various stages such as menstrual phase, proliferative phase & secretory phase. |
4. It occurs in cows, pigs, sheep etc. | 4. It occurs in monkeys, apes & humans. |
(b) Oviparity and Vivipary
Ans:
Oviparity | Viviparity |
1. In this mode an animal lays eggs. | 1. In this mode an animal gives birth to young ones. |
2. The eggs are protected by a hard calcareous shell. | 2. The eggs are not protected by a hard calcareous shell. |
3. In this mode the development of offspring occurs outside the female body. | 3. In this mode the development of offspring occurs inside the female body. |
4. The chances of survival are less in this mode. | 4. The chances of survival are more in this mode. |
5. The example includes birds & most of the reptiles. | 5. The example includes mostly mammals except few like monotremes egg laying mammals. |
6. Rose plants produce large, attractive bisexual flowers but they seldom produce fruits. On the other hand, a tomato plant produces plenty of fruits though they have small flowers. Analyse the reasons for failure of fruit formation in rose. Both these plants - rose and tomato - both selected by human beings for different characteristics, the rose for its flower and tomato for its fruit. Roses, being vegetatively propagated, do not need to produce seeds.
Ans: Rose plants produce large, attractive bisexual flowers, but they seldom produce fruits. The reasons for failure of fruit formation in rose can be-:
(i) They may not produce viable pollen, hence, fertilization can’t take place.
(ii) They may have non-functional eggs.
(iii) They may have defective and non-functional ovules, which act as the female gametophyte generator.
(iv) They may be genetically self-incompatible that fails them to produce seed.
(v) Internal barrier which restricts the pollen tube growth or fertilization.
Therefore, due to its distinct characteristics in flower and fruit formation ability, humans select rose plants for flower and propagate by vegetative methods. On the other hand, tomatoes are selected to utilize the fruits as vegetables and propagated by seeds only.
Importance of NCERT Class 12 Biology Chapter 1- Reproduction in Organisms
In the present time, we frequently get to see Class 12 students that are stressed about their future and to take on great universities. For CBSE board assessment as well they need to beat in the different competitions like NEET and AIIMS.
Concepts that are involved in the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 - Reproduction in Organism:
The important concepts that are involved in the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter 1 - Reproduction in Organism can be provided as follows:
Sexual Reproduction: Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves the combination of male and female gametes. These gametes are formed by two individual organisms of opposite sex and are then fused together in order to form the zygote. This type of reproduction is considered to be slower than that of the asexual reproduction.
Asexual Reproduction: This is the type of reprodcution where even a single organism can give rise to another offspring. These organisms are not so different from their parents and are hence identical to each other. Cloning is only possible in this type of reproduction. This is a faster process than the sexual reproduction.
Conclusion:
Vedantu comprehends the circumstance, our experts cover these NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Biology Solutions by making them accessible to you in an all around organized way. Rehearsing these model problems by Vedantu will help you. You can easily access the free PDFs from the Website and get a hang of all the answers.
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter-1 (Book Solutions)
1. What is Sexual and Asexual reproduction mentioned in NCERT Class 12 Biology Chapter 1?
Sexual reproduction – Sexual reproduction is the kind of reproduction that includes the development of male and female gametes. This formation happens by the same individual or by the different people of the other gender. Further, these gametes fuse to shape a zygote which creates to frame another posterity. This is a slow cycle contrasted with asexual generation.
Asexual reproduction – Asexual reproduction is the kind of reproduction at which a single animal varieties is capable for shaping a life form. These living beings are like each other. These living beings are also named as a copy of their parent individual. There is a term Clone utilized for depicting the indistinguishable idea of these asexually framed species. This is a quick process contrasted with sexual generation.
2. What is the pre-fertilization stage mentioned in NCERT Exemplar class 12 Biology Chapter 1?
Pre-fertilization Event – Pre-fertilization event incorporate every one of the occasions of sexual generation, which is identified with the arrangement of gametes (male and female). The two kinds of Pre-fertilization event are seen in sexual generation are:
Gametogenesis
Gamete transfer
Gametogenesis includes the development of gametes in sexual regeneration. These gametes are male and female gametes.
Then again, Gamete transfer is supposed to be the course of gametes move. In this interaction, male gamete and female gamete are actually fused together for combination.
3. What are fertilization and post-fertilization events in Chapter 1 Class 12 Biology?
Fertilization Event – This occasion is an imperative occasion of sexual reproduction. Fertilization event is the course of the arrangement of gametes. In this cycle, the male gametes and female gametes fused prompts the formation of new individuals.
For example – Like in creatures, when a sperm combines with an ovum to frame another individual named embryo.
Post- Fertilization – Post- fertilization occasions are the significant occasion in sexual propagation events. This event happens after fertilization in people. This prompts the improvement of seed from an ovule and a fruit from the ovary.
4. What types of questions are there in NCERT Class 12 Biology chapter 1?
The first set of questions are MCQs. This part comprises 18 NCERT Exemplar problems. You should not stress to settle these questions. They are basic questions contrasted with different segments. These questions by and large utilize the ideas of sexual reproduction and its subtopics. The other arrangement of NCERT model problems are exceptionally short answer types. It contains 15 questions which will judge you on the ideas like embryogenesis, preparation, fertilization, self-fertilization, gametogenesis, and so on. These are reason-based where you have to reply in a couple of lines.
5. What are the benefits of using Vedantu to prepare for NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Biology chapter 1?
Addressing NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Biology Solutions Chapter 1 by Vedantu can be an extreme aid for the students seeking their professional objectives in the clinical field. On occasion, students stalled out while solving Exemplar problems. In such a period you have no clue about how to address it. Accordingly, you can take help of Vedantu. It is not difficult to get to and in particular liberated from cost arrangements. Their experts have tried sincerely and adhered to every one of the guidelines and rules of the CBSE, outlined questions in such a way that will help you.
It will also assist you with dealing with the time viably and in this way supports your certainty to pro any aggressive tests.




































