
Class 8 Maths NCERT Exemplar Solutions Chapter 7 Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 8 Math Chapter 7 - Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation solved by expert Math teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 7 - Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Every NCERT Solution is provided to make the study simple and interesting on Vedantu. Subjects like Science, Math, English will become easy to study if you have access to NCERT Solution for Class 8 Science, Math solutions, and solutions of other subjects. You can also download NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Math to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Solutions for NCERT, Class 8 Science, Chapter 7, Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation are Now Available for a Free Download at Vedantu
Solved Examples
In examples 1 to 4, there are four options given out of which one is correct. Write the correct answer.
Example 1: Which is the like term as $24{a^2}bc$?
(a) $13 \times 8a \times 2b \times c \times a$
(b) $8 \times 3 \times a \times b \times c$
(c) $3 \times 8 \times a \times b \times c \times c$
(d) $3 \times 8 \times a \times b \times b \times c$
Ans: The correct answer is (a).
$\Rightarrow 13 \times 8 a \times 2 b \times c \times a=(13 \times 8 \times 2)(a \times b \times c \times a)$
$\Rightarrow(208)\left(a^{2} b c\right)$
$\Rightarrow 208 a^{2} b c$, we can see that $24 a^{2} b c$ and $208 a^{2} b c$ are like terms.
Example 2: Which of the following is an identity?
(a) ${(p + q)^2} = {p^2} + {q^2}$
(b) ${p^2} - {q^2} = {(p - q)^2}$
(c) ${p^2} - {q^2} = {p^2} + 2pq - {q^2}$
(d) ${(p + q)^2} = {p^2} + 2pq + {q^2}$
Ans: The correct answer is (d).
$\Rightarrow(p+q)(p+q)=p^{2}+2 p q+q^{2}$
$\Rightarrow p(p+q)+q(p+q)=p^{2}+2 p q+q^{2}$
$\Rightarrow p^{2}+p q+p q+q^{2}=p^{2}+2 p q+q^{2}$
$\Rightarrow p^{2}+2 p q+q^{2}=p^{2}+2 p q+q^{2}$
Example 3: The irreducible factorisation of $3{a^3} + 6a$ is
(a) $3a\left( {{a^2} + 2} \right)$
(b) $3\left( {{a^3} + 2} \right)$
(c) $a\left( {3{a^2} + 6} \right)$
(d) $3 \times a \times a \times a + 2 \times 3 \times a$
Ans: The correct answer is $3a\left( {{a^2} + 2} \right)$
$\Rightarrow 3{{a}^{3}}+6a=3\left( {{a}^{3}}+3a \right)$
$\Rightarrow 3{{a}^{3}}+6a=3a\left( {{a}^{2}}+3 \right)$
Example 4: $a(b + c) = ab + ac$ is
(a)commutative property
(b) distributive property
(c) associative property
(d) closure property
Ans: The correct answer is (b).
Distributive property of multiplication over addition is given by
$\Rightarrow a\times (b+c)=(a\times b)+(a\times c)$
In examples 5 and 6, fill in the blanks to make the statements true.
Example 5: The representation of an expression as the product of its factors is called __________.
Ans: Factorisation.
Examples 6: \[\left( {x + a} \right)\left( {x + b} \right) = {x^2} + \left( {a + b} \right)x + \_\_\_\_\]
Ans: ab.
Because, $\Rightarrow(x+a)(x+b)=x(x+b)+a(x+b)$
$\Rightarrow(x+a)(x+b)=x^{2}+b x+a x+a b$
$\Rightarrow(x+a)(x+b)=x^{2}+x(a+b)+a b$
In examples 7 to 9, state whether the statements are true (T) or false (F).
Example 7: An identity is true for all values of its variables.
Ans: True.
For example we have $(a+b)^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}+2 a b$,
Give the value of $a=1$ and $b=2$ for the above identity.
\[\Rightarrow {{(1+2)}^{2}}={{1}^{2}}+{{2}^{2}}+2(1)(2)\]
\[\Rightarrow {{(3)}^{2}}=1+4+4\]
\[\Rightarrow 9=9\]
Example 8: Common factor of ${x^2}y$ and $ - x{y^2}$ is $x{\kern 1pt} y$.
Ans: True.
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}y=x\times x\times y\]
\[\Rightarrow -x{{y}^{2}}=-1\times x\times y\times y\]
We can see that the common factor is xy.
Examples 9: $\left( {3x + 3{x^2}} \right) \div 3x = 3{x^2}$
Ans: False.
\[\Rightarrow \left( 3x+3{{x}^{2}} \right)\div 3x=\dfrac{3x+3{{x}^{2}}}{3x}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{3x}{3x}+\dfrac{3{{x}^{2}}}{3x}\]
\[\Rightarrow 1+x\]
Examples 10: Simplify
(i) $ - pqr\left( {{p^2} + {q^2} + {r^2}} \right)$
Ans: $ - pqr\left( {{p^2} + {q^2} + {r^2}} \right)$
$ = - (pqr) \times {p^2} - (pqr) \times {q^2} - (pqr) \times {r^2}$
$ = - {p^3}qr - p{q^3}r - pq{r^3}$
(ii) $(px + qy)(ax - by)$
Ans: $(px + qy)(ax - by)$
\[ = px(ax - by) + qy(ax - by)\]
\[ = ap{x^2} - pbxy + aqxy - qb{y^2}\]
Example 11: Find the expansion of the following using suitable identity.
(i) $(3x + 7y)(3x - 7y)$
Ans: $(3x + 7y)(3x - 7y)$
Since $(a + b)(a - b) = {a^2} - {b^2}$, therefore
$(3x + 7y)(3x - 7y) = {(3x)^2} - {(7y)^2}$
$ = 9{x^2} - 49{y^2}$
(ii) $\left( {\dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \dfrac{y}{4}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \dfrac{{3y}}{4}} \right)$
Ans: $\left( {\dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \dfrac{y}{4}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \dfrac{{3y}}{4}} \right)$
Since $(x + a)(x + b) = {x^2} + (a + b)x + ab$, therefore
$ = {\left( {\dfrac{{4x}}{5}} \right)^2} + \left( {\dfrac{y}{4} + \dfrac{{3y}}{4}} \right) \times \dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \dfrac{y}{4} \times \dfrac{{3y}}{4}$
$ = \left[ {{\text{Here, }}x = \dfrac{{4x}}{5},a = \dfrac{y}{4}{\text{ and }}b = \dfrac{{3y}}{4}} \right]$
$ = \dfrac{{16{x^2}}}{{25}} + \dfrac{{4y}}{4} \times \dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \dfrac{{3{y^2}}}{{16}}$
$ = \dfrac{{16{x^2}}}{{25}} + \dfrac{{4xy}}{5} + \dfrac{{3{y^2}}}{{16}}$
Example 12: Factorise the following.
(i) $21{x^2}{y^3} + 27{x^3}{y^2}$
Ans: $21{x^2}{y^3} + 27{x^3}{y^2}$
$ = 3 \times 7 \times x \times x \times y \times y \times y + 3 \times 3 \times 3 \times x \times x \times x \times y \times y$
$ = 3 \times x \times x \times y \times y(7y + 9x){\text{ (Using }}ab + ac = a(b + c))$
$ = 3{x^2}{y^2}(7y + 9x)$
(ii) ${a^3} - 4{a^2} + 12 - 3a$
Ans: ${a^3} - 4{a^2} + 12 - 3a$
$ = {a^2}(a - 4) - 3a + 12$
$ = {a^2}(a - 4) - 3(a - 4)$
$ = (a - 4)\left( {{a^2} - 3} \right)$
(iii) $4{x^2} - 20x + 25$
Ans: $4{x^2} - 20x + 25$
$ = {(2x)^2} - 2 \times 2x \times 5 + {(5)^2} = {(2x - 5)^2}\quad \left( {{\text{ Since }}{a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {{(a - b)}^2}} \right)$
$ = (2x - 5)(2x - 5)$
(iv) $\dfrac{{{y^2}}}{9} - 9$
Ans: \[\dfrac{{{y^2}}}{9} - 9\]
\[ = {\left( {\dfrac{y}{3}} \right)^2} - {3^2}\]
$ = \left( {\dfrac{y}{3} + 3} \right)\left( {\dfrac{y}{3} - 3} \right)\left( {{\text{ Since }}{a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)} \right)$
(v) ${x^4} - 256$
Ans: ${x^4} - 256$
$ = {\left( {{x^2}} \right)^2} - {(16)^2}$
$\left. { = \left( {{x^2} + 16} \right)\left( {{x^2} - 16} \right)\quad {\text{ (using }}{a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)} \right)$
$ = \left( {{x^2} + 16} \right)\left( {{x^2} - {4^2}} \right)$
$ = \left( {{x^2} + 16} \right)(x + 4)(x - 4)\left( {{\text{ using }}{a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)} \right)$
Example 13: Evaluate using suitable identities.
(i)${(48)^2}$
Ans: ${(48)^2}$
$ = {(50 - 2)^2}$
Since ${(a - b)^2} = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}$, therefore
${(50 - 2)^2} = {(50)^2} - 2 \times 50 \times 2 + {(2)^2}$
$ = 2500 - 200 + 4$
$ = 2504 - 200$
$ = 2304$
(ii)${181^2} - {19^2}$
Ans: ${181^2} - {19^2} = (181 - 19)(181 + 19)$
$\left[ {{\text{using}}\,\,{{\text{a}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ - }}{{\text{b}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}({\text{a - b}})({\text{a + b}})} \right]$
$ = 162 \times 200$
$ = 32400$
(iii)$497 \times 505$
Ans: $497 \times 505 = (500 - 3)(500 + 5)$
$ = {500^2} + ( - 3 + 5) \times 500 + ( - 3)(5)$
$\left[ {{\text{using}}\,\,(x + a)(x + b) = {x^2} + (a + b)x + ab} \right]$
$ = 250000 + 1000 - 15$
$ = 250985{\text{ }}$
(iv)$2.07 \times 1.93$
Ans: $2.07 \times 1.93 = (2 + 0.07)(2 - 0.07)$
$ = {2^2} - {(0.07)^2}$
$ = 3.9951$
Example 14: Verify that
${(3x + 5y)^2} - 30xy{\text{ }} = 9{x^2} + 25{y^2}$
Ans: ${\text{L}}{\text{.H}}{\text{.S }} = {(3x + 5y)^2} - 30xy$
$ = {(3x)^2} + 2 \times 3x \times 5y + {(5y)^2} - 30xy$
$\left[ {{\text{ Since }}{{(a + b)}^2} = {a^2} + 2ab + {b^2}} \right]$
$ = 9{x^2} + 30xy + 25{y^2} - 30xy$
$ = 9{x^2} + 25{y^2}$
$ = {\text{R}}{\text{.H}}{\text{.S}}$
Hence, verified.
Example 15: Verify that ${(11pq + 4q)^2} - {(11pq - 4q)^2} = 176p{q^2}$
Ans: $\text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S }={{(11pq+4q)}^{2}}-{{(11pq-4q)}^{2}}$
Using $\text{ }{{(a+b)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab$ and ${{(a-b)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab$
\[=\left[ {{(11pq)}^{2}}+{{(4q)}^{2}}+2(11pq)(4q) \right]-\left[ {{(11pq)}^{2}}+{{(4q)}^{2}}-2(11pq)(4q) \right]\]
\[={{(11pq)}^{2}}+{{(4q)}^{2}}+2(11pq)(4q)-{{(11pq)}^{2}}-{{(4q)}^{2}}+2(11pq)(4q)\]
\[=2(11pq)(4q)+2(11pq)(4q)\]
\[=88p{{q}^{2}}+88p{{q}^{2}}\]
\[=176p{{q}^{2}}\text{ }\]
\[=\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\]
Hence Verified
Example 16: The area of a rectangle is ${x^2} + 12xy + 27{y^2}$ and its length is $(x + 9y)$. Find the breadth of the rectangle.
Ans:
${\text{Breadth = }}\dfrac{{{\text{ Area }}}}{{{\text{ Length }}}}$
$ = \dfrac{{{x^2} + 12xy + 27{y^2}}}{{(x + 9y)}}$
$ = \dfrac{{{x^2} + 9xy + 3xy + 27{y^2}}}{{(x + 9y)}}$
$ = \dfrac{{x(x + 9y) + 3y(x + 9y)}}{{x + 9y}}$
$ = \dfrac{{(x + 9y)(x + 3y)}}{{(x + 9y)}}$
$ = (x + 3y)$
Example 17: Divide $15(y + 3)\left( {{y^2} - 16} \right)$ by $5\left( {{y^2} - y - 12} \right).$
Ans: Factorising $15(y + 3)\left( {{y^2} - 16} \right)$,
we get $5 \times 3 \times (y + 3)(y - 4)(y + 4)$
On factorising $5\left( {{y^2} - y - 12} \right)$, we get $5\left( {{y^2} - 4y + 3y - 12} \right)$
$ = 5[y(y - 4) + 3(y - 4)]$ $ = 5(y - 4)(y + 3)$
Therefore, on dividing the first expression by the second expression, we get $\dfrac{{15(y + 3)\left( {{y^2} - 16} \right)}}{{5\left( {{y^2} - y - 12} \right)}}$
$ = \dfrac{{5 \times 3 \times (y + 3)(y - 4)(y + 4)}}{{5 \times (y - 4)(y + 3)}}$
$ = 3(y + 4)$
Example 18: By using suitable identity, evaluate ${x^2} + \dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}}$, if $x + \dfrac{1}{x} = 5$.
Ans: Given that $x + \dfrac{1}{x} = 5$
So, ${\left( {x + \dfrac{1}{x}} \right)^2} = 25$
Now, ${\left( {x + \dfrac{1}{x}} \right)^2} = {x^2} + 2 \times x \times \dfrac{1}{x} + {\left( {\dfrac{1}{x}} \right)^2}$
[Using identity ${(a + b)^2} = {a^2} + 2ab + {b^2}$, with $a = x$ and $b = \dfrac{1}{x}$]
$ = {x^2} + 2 + \left( {\dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}}} \right)$
$ = {x^2} + \left( {\dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}}} \right) + 2$
Since ${\left( {x + \dfrac{1}{x}} \right)^2} = 25$, therefore ${x^2} + \dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}} + 2 = 25$
or
${x^2} + \dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}} = 25 - 2 = 23$
Example 19: Find the value of $\dfrac{{{{38}^2} - {{22}^2}}}{{16}}$, using a suitable identity.
Ans: Since ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$, therefore
${38^2} - {22^2} = (38 - 22)(38 + 22)$
$ = 16 \times 60$
So, $\dfrac{{{{38}^2} - {{22}^2}}}{{16}} = \dfrac{{16 \times 60}}{{16}}$ $ = 60$
Example 20: Find the value of $x$, if
$10000x = {(9982)^2} - {(18)^2}$
Ans: ${\text{R}}{\text{.H}}{\text{.S}}{\text{.}} = {(9982)^2} - {(18)^2}$
$ = (9982 + 18)(9982 - 18)$
$\left[ {{\text{Since }}{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)} \right]$
$ = (10000) \times (9964)$
${\text{L}}{\text{.H}}{\text{.S}}{\text{.}} = (10000) \times x$
Comparing L.H.S. and R.H.S., we get $(a - b)]$
$10000x = 10000 \times 9964$
Or
$x = \dfrac{{10000 \times 9964}}{{10000}} = 9964$
In questions 1 to 33, there are four options out of which one is correct. Write the correct answer.
1. The product of a monomial and a binomial is a
Monomial
Binomial
Trinomial
None of these
Ans: b) Binomial
For example, take a product of monomials with binomials. That is $x\left( {x + 1} \right) = {x^2} + x$, we can see that the obtained result is binomial.
2. In a polynomial, the exponents of the variables are always
Integers
Positive integers
Non-negative integers
Non-positive integers
Ans: b) positive integers
Because, we will not consider the expression as a polynomial which consists of a variable having negative or fractional exponents.
3. Which of the following is correct?
${(a - b)^2} = {a^2} + 2ab - {b^2}$
${(a - b)^2} = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}$
${(a - b)^2} = {a^2} - {b^2}$
${(a + b)^2} = {a^2} + 2ab - {b^2}$
Ans: b) ${(a - b)^2} = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}$
Because,
$ \Rightarrow (a - b)(a - b) = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}$
$ \Rightarrow a(a - b) - b(a - b) = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {a^2} - ab - ab + {b^2} = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}$
4. The sum of $ - 7pq$ and $2{\kern 1pt} p{\kern 1pt} q$ is
$ - 9{\kern 1pt} p{\kern 1pt} q$
$9{\kern 1pt} p{\kern 1pt} q$
$5{\kern 1pt} p{\kern 1pt} q$
$ - 5{\kern 1pt} p{\kern 1pt} q$.
Ans: d) $ - 5{\kern 1pt} p{\kern 1pt} q$.
We have the sum of two monomials,
$ \Rightarrow - 7pq + 2{\kern 1pt} p{\kern 1pt} q$
$ \Rightarrow - 5pq$
5. If we subtract $ - 3{x^2}{y^2}$ from ${x^2}{y^2}$, then we get
$ - 4{x^2}{y^2}$
$ - 2{x^2}{y^2}$
$2{x^2}{y^2}$
$4{x^2}{y^2}$
Ans: d) $4{x^2}{y^2}$
If we subtract $ - 3{x^2}{y^2}$ from ${x^2}{y^2}$, then we get
$ \Rightarrow {x^2}{y^2} - \left( { - 3{x^2}{y^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2}{y^2} + 3{x^2}{y^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 4{x^2}{y^2}$
6. Like term as $4{m^3}{n^2}$ is
$4{m^2}{n^2}$
$ - 6{m^3}{n^2}$
$6p{m^3}{n^2}$
$4{m^3}n$
Ans: b) $ - 6{m^3}{n^2}$
Like terms are the terms in which a variable and its exponents are the same.
7. Which of the following is a binomial?
$7 \times a + a$
$6{a^2} + 7b + 2c$
$4a \times 3b \times 2c$
$6\left( {{a^2} + b} \right)$
Ans: d) $6\left( {{a^2} + b} \right)$
Binomial is an expression which contains two unlike terms. Only option d) has two terms.
8. Sum of $a - b + ab,b + c - bc$ and $c - a - ac$ is
$2c + ab - ac - bc$
$2c - ab - ac - bc$
$2c + ab + ac + bc$
$2c - ab + ac + bc$
Ans: a) $2c + ab - ac - bc$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {a - b + ab} \right) + \left( {b + c - bc} \right) + \left( {c - a - ac} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow a - b + ab + b + c - bc + c - a - ac$
$ \Rightarrow a - a + b - b + c + c + ab - bc - ac$
$ \Rightarrow 2c + ab - bc - ac$
9. Product of the following monomials $4p, - 7{q^3}, - 7pq$ is
$196{p^2}{q^4}$
$196p{q^4}$
$ - 196{p^2}{q^4}$
$196{p^2}{q^3}$
Ans: a) $196{p^2}{q^4}$
Because, $ \Rightarrow 4p \times - 7{q^3} \times - 7pq$
$ \Rightarrow 196{p^2}{q^4}$
10. Area of a rectangle with length 4ab and breadth $6{b^2}$ is
$24{a^2}{b^2}$
$24a{b^3}$
$24a{b^2}$
$24{\kern 1pt} a{\kern 1pt} b$
Ans: b) $24a{b^3}$
Area of a rectangle is the product of its length and breadth.
That is $ \Rightarrow 4ab \times 6{b^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 24a{b^3}$
11. Volume of a rectangular box (cuboid) with length $ = 2{\kern 1pt} a{\kern 1pt} b$, breadth = $3{\kern 1pt} a{\kern 1pt} c$ and height $ = 2ac$ is
$12{a^3}b{c^2}$
$12{a^3}bc$
$12{a^2}bc$
$2ab + 3ac + 2ac$
Ans: a) $12{a^3}b{c^2}$
Volume of a rectangular box (cuboid) = length\[ \times \]breadth\[ \times \]height
$ \Rightarrow $ Volume of rectangular box (cuboid) $ = 2{\kern 1pt} a{\kern 1pt} b \times 3{\kern 1pt} a{\kern 1pt} c \times 2ac = 12{a^3}b{c^2}$
12. Product of $6{a^2} - 7b + 5ab$ and $2{\kern 1pt} a{\kern 1pt} b$ is
$12{a^3}b - 14a{b^2} + 10ab$
$12{a^3}b - 14a{b^2} + 10{a^2}{b^2}$
$6{a^2} - 7b + 7ab$
$12{a^2}b - 7a{b^2} + 10ab$
Ana: b) $12{a^3}b - 14a{b^2} + 10{a^2}{b^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 2ab\left( {6{a^2} - 7b + 5ab} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 12{a^3}b - 14a{b^2} + 10{a^2}{b^2}$
13. Square of $3x - 4y$ is
$9{x^2} - 16{y^2}$
$6{x^2} - 8{y^2}$
$9{x^2} + 16{y^2} + 24xy$
$9{x^2} + 16{y^2} - 24xy$
Ans: d) $9{x^2} + 16{y^2} - 24xy$
We know that \[ \Rightarrow {\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}\]
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {3x - 4y} \right)^2} = {\left( {3x} \right)^2} + {\left( {4y} \right)^2} - 2\left( {3x} \right)\left( {4y} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {3x - 4y} \right)^2} = 9{x^2} + 16{y^2} - 24xy$
14. Which of the following are like terms?
$5xy{z^2}, - 3x{y^2}z$
$ - 5xy{z^2},7xy{z^2}$
$5xy{z^2},5{x^2}yz$
$5xy{z^2},{x^2}{y^2}{z^2}$
Ans: b) $ - 5xy{z^2},7xy{z^2}$
We know that Like terms are the terms in which a variable and its exponents are the same.
15. Coefficient of $y$ in the term $\dfrac{{ - y}}{3}$ is
$ - 1$
$ - 3$
$\dfrac{{ - 1}}{3}$
$\dfrac{1}{3}$
Ans: c) $\dfrac{{ - 1}}{3}$
16. ${a^2} - {b^2}$ is equal to
${(a - b)^2}$
$(a - b)(a - b)$
$(a + b)(a - b)$
$(a + b)(a + b)$
Ans: c) $(a + b)(a - b)$
$ \Rightarrow (a + b)(a - b) = a\left( {a - b} \right) + b\left( {a - b} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow (a + b)(a - b) = {a^2} - ab + ab - {b^2}$
$ \Rightarrow (a + b)(a - b) = {a^2} - {b^2}$
17. Common factor of $17abc,34a{b^2},51{a^2}b$ is
$17{\kern 1pt} a{\kern 1pt} b{\kern 1pt} c$
$17{\kern 1pt} a{\kern 1pt} b$
$17{\kern 1pt} a{\kern 1pt} c$
$17{\kern 1pt} {a^2}{\kern 1pt} {b^2}{\kern 1pt} c$
Ans: b) $17{\kern 1pt} a{\kern 1pt} b$
Because all of the terms are multiples of 17 and all of the terms have ab, we chose 17ab as a common factor.
18. Square of $9x - 7xy$ is
$81{x^2} + 49{x^2}{y^2}$
$81{x^2} - 49{x^2}{y^2}$
$81{x^2} + 49{x^2}{y^2} - 126{x^2}y$
$81{x^2} + 49{x^2}{y^2} - 63{x^2}y$
Ans: c) $81{x^2} + 49{x^2}{y^2} - 126{x^2}y$
We know that \[ \Rightarrow {\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}\]
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {9x - 7xy} \right)^2} = {\left( {9x} \right)^2} + {\left( {7xy} \right)^2} - 2\left( {9x} \right)\left( {7xy} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {9x - 7xy} \right)^2} = 81{x^2} + 49{x^2}{y^2} - 126{x^2}y$
19. Factored form of $23xy - 46x + 54y - 108$ is
$(23x + 54)(y - 2)$
$(23x + 54y)(y - 2)$
$(23xy + 54y)( - 46x - 108)$
$(23x + 54)(y + 2)$
Ans: a) $(23x + 54)(y - 2)$
$ \Rightarrow 23xy - 46x + 54y - 108$
In first two terms take 23x common and in the remaining term take 54 common
$ \Rightarrow 23x\left( {y - 2} \right) + 54\left( {y - 2} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {y - 2} \right)\left( {23x + 54} \right)$
20. Factored form of ${r^2} - 10r + 21$ is
$(r - 1)(r - 4)$
$(r - 7)(r - 3)$
$(r - 7)(r + 3)$
$(r + 7)(r + 3)$
Ans: b) $(r - 7)(r - 3)$
$ \Rightarrow {r^2} - 10r + 21$
Split the middle term,
$ \Rightarrow {r^2} - 7r - 3r + 21$
$ \Rightarrow r\left( {r - 7} \right) - 3\left( {r - 7} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {r - 7} \right)\left( {r - 3} \right)$
21. Factored form of ${p^2} - 17p - 38$ is
$(p - 19)(p + 2)$
$(p - 19)(p - 2)$
$(p + 19)(p + 2)$
$(p + 19)(p - 2)$
Ans: a) $(p - 19)(p + 2)$
$ \Rightarrow {p^2} - 17p - 38$
$ \Rightarrow {p^2} - 19p + 2p - 38$
$ \Rightarrow p\left( {p - 19} \right) + 2\left( {p - 19} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {p - 19} \right)\left( {p + 2} \right)$
22. On dividing $57{p^2}qr$ by $114{\kern 1pt} p{\kern 1pt} q$, we get
$\dfrac{1}{4}pr$
$\dfrac{3}{4}pr$
$\dfrac{1}{2}pr$
$2{\kern 1pt} p{\kern 1pt} r$
Ans: c) $\dfrac{1}{2}pr$
On dividing $57{p^2}qr$ by $114{\kern 1pt} p{\kern 1pt} q$, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{57{p^2}qr}}{{114{\kern 1pt} p{\kern 1pt} q}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{1pr}}{2}$
23. On dividing $p\left( {4{p^2} - 16} \right)$ by $4p(p - 2)$, we get
$2p + 4$
$2p - 4$
$p + 2$
$p - 2$
Ans: c) $p + 2$
On dividing $p\left( {4{p^2} - 16} \right)$ by $4p(p - 2)$, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{p\left( {4{p^2} - 16} \right)}}{{4p(p - 2)}} = \dfrac{{4p\left( {{p^2} - 4} \right)}}{{4p(p - 2)}}$
$ = \dfrac{{4p\left( {{{\left( p \right)}^2} - {2^2}} \right)}}{{4p(p - 2)}}$
We know $ \Rightarrow (a + b)(a - b) = {a^2} - {b^2}$
$ = \dfrac{{\left( {p + 2} \right)\left( {p - 2} \right)}}{{(p - 2)}}$
$ = \left( {p + 2} \right)$
24. The common factor of $3{\kern 1pt} a{\kern 1pt} b$ and $2{\kern 1pt} c{\kern 1pt} d$ is
1
$ - 1$
$a$
$c$
Ans: a) 1
Because in both terms we don’t have any common factors.
25. An irreducible factor of $24{x^2}{y^2}$ is
${x^2}$
${y^2}$
$x$
$24{\kern 1pt} x$
Ans: c) $x$
An irreducible factor is a factor which can not be expressed as a product of factors. Hence option c) is correct. Remaining options can be expressed as a product of factors.
26. Number of factors of ${(a + b)^2}$ is
4
3
2
1
Ans: c) 2
${(a + b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a + b} \right)$
Hence, the factors are $\left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a + b} \right)$
27. The factored form of $3x - 24$ is
$3x \times 24$
$3(x - 8)$
$24(x - 3)$
$3(x - 12)$
Ans: b) $3(x - 8)$
$ \Rightarrow 3x - 24 = 3\left( {x - 8} \right)$
28. The factors of ${x^2} - 4$ are
$(x - 2),(x - 2)$
$(x + 2),(x - 2)$
$(x + 2),(x + 2)$
$(x - 4),(x - 4)$
Ans: b) $(x + 2),(x - 2)$
We know that $(a + b)(a - b) = {a^2} - {b^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 4 = {x^2} - {2^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 4 = \left( {x + 2} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)$
29. The value of $\left( { - 27{x^2}y} \right) \div ( - 9xy)$ is
$3{\kern 1pt} x{\kern 1pt} y$
$ - 3x{\kern 1pt} y$
$ - 3{\kern 1pt} x$
$3{\kern 1pt} x$
Ans: d) $3{\kern 1pt} x$
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - 27{x^2}y} \right) \div ( - 9xy)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - 27{x^2}y}}{{ - 9xy}}$
$ \Rightarrow 3x$
30. The value of $\left( {2{x^2} + 4} \right) \div 2$ is
$2{x^2} + 2$
${x^2} + 2$
${x^2} + 4$
$2{x^2} + 4$
Ans: b) ${x^2} + 2$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {2{x^2} + 4} \right) \div 2 = \dfrac{{2{x^2} + 4}}{2}$
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{2{{x}^{2}}}{2}+\dfrac{4}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+2\]
31. The value of $\left( {3{x^3} + 9{x^2} + 27x} \right) \div 3x$ is
${x^2} + 9 + 27x$
$3{x^3} + 3{x^2} + 27x$
$3{x^3} + 9{x^2} + 9$
${x^2} + 3x + 9$
Ans: d) ${x^2} + 3x + 9$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {3{x^3} + 9{x^2} + 27x} \right) \div 3x = \dfrac{{3{x^3} + 9{x^2} + 27x}}{{3x}}$
$ = \dfrac{{3{x^3}}}{{3x}} + \dfrac{{9{x^2}}}{{3x}} + \dfrac{{27x}}{{3x}}$
$ = {x^2} + 3x + 9$
32. The value of ${(a + b)^2} + {(a - b)^2}$ is
$2a + 2b$
$2a - 2b$
$2{a^2} + 2{b^2}$
$2{a^2} - 2{b^2}$
Ans: c) $2{a^2} + 2{b^2}$
We know ${(a + b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab$ and ${(a - b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab$, then
$ \Rightarrow {(a + b)^2} + {(a - b)^2} = \left( {{a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab} \right) + \left( {{a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(a + b)^2} + {(a - b)^2} = {a^2} + {a^2} + {b^2} + {b^2} + 2ab - 2ab$
${(a + b)^2} + {(a - b)^2} = 2{a^2} + 2{b^2}$
33. The value of ${(a + b)^2} - {(a - b)^2}$ is
$4{\kern 1pt} a{\kern 1pt} b$
$ - 4{\kern 1pt} a{\kern 1pt} b$
$2{a^2} + 2{b^2}$
$2{a^2} - 2{b^2}$.
Ans: a) 4ab
We know ${(a + b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab$ and ${(a - b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab$, then
$ \Rightarrow {(a + b)^2} - {(a - b)^2} = \left( {{a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab} \right) - \left( {{a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(a + b)^2} - {(a - b)^2} = {a^2} - {a^2} + {b^2} - {b^2} + 2ab + 2ab$
${(a + b)^2} - {(a - b)^2} = 4ab$
In questions 34 to 58, fill in the blanks to make the statements true:
34. The product of two terms with like signs is a ________ term.
Ans: The product of two terms with like signs is a positive term.
For example, \[\left( -x \right)\times \left( -x \right)=+{{x}^{2}}\]
35. The product of two terms with unlike signs is a _______ term.
Ans: The product of two terms with unlike signs is a negative term
For example, \[\left( -x \right)\times \left( x \right)=-{{x}^{2}}\]
36. $a(b + c) = a \times \_\_\_\_\_ + a \times \_\_\_\_\_\_$
Ans: \[a(b + c) = a \times b + a \times c\]
37. $(a - b)\_\_\_\_\_\_\_ = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}$
Ans: \[\left( {a - b} \right)\]
Because, \[\left( {a - b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right) = a\left( {a - b} \right) - b\left( {a - b} \right)\]
\[ = {a^2} - ab - ab + {b^2}\]
\[ = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}\]
38. ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)\_\_\_\_\_\_\_$
Ans: \[\left( {a - b} \right)\]
Because \[\left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right) = a\left( {a - b} \right) + b\left( {a - b} \right)\]
\[ = {a^2} - ab + ab - {b^2}\]
\[ = {a^2} - {b^2}\]
39. ${(a - b)^2} + \_\_\_\_\_\_\_ = {a^2} - {b^2}$
Ans: $ - 2{b^2} - 2ab$
Let the required term is M
Then by the question, ${(a - b)^2} + M = {a^2} - {b^2}$
$ \Rightarrow M = {a^2} - {b^2} - {(a - b)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow M = {a^2} - {b^2} - ({a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab)$
$ \Rightarrow M = {a^2} - {b^2} - {a^2} - {b^2} - 2ab$
$ \Rightarrow M = - 2{b^2} - 2ab$
40. ${(a + b)^2} - 2ab = \_\_\_\_\_\_ + \_\_\_\_\_$
Ans: ${a^2} + {b^2}$
${(a + b)^2} - 2ab = \left( {{a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab} \right) - 2ab$
$ = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab - 2ab$
$ = {a^2} + {b^2}$
41. $(x + a)(x + b) = {x^2} + (a + b)x + \_\_\_\_\_$
Ans: $ab$
$ \Rightarrow (x + a)(x + b) = x\left( {x + b} \right) + a\left( {x + b} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow (x + a)(x + b) = {x^2} + bx + ax + ab$
$ \Rightarrow (x + a)(x + b) = {x^2} + \left( {a + b} \right)x + ab$
42. The product of two polynomials is a _____________
Ans: The product of two polynomials is a polynomial.
For example, \[\left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right) = a\left( {a - b} \right) + b\left( {a - b} \right)\]
\[ = {a^2} - ab + ab - {b^2}\]
\[ = {a^2} - {b^2}\]
43. Common factor of $a{x^2} + bx$ is _____________
Ans: Common factor of $a{x^2} + bx$ is x.
$a{x^2} = a \times x \times x$
$bx = b \times x$
We can see that x is the only common factor.
44. Factored form of $18mn + 10mnp$ is ___________
Ans: Factored form of $18mn + 10mnp$ is $2mn\left( {9 + 5p} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 18mn + 10mnp = 2mn\left( {9 + 5p} \right)$
45. Factored form of $4{y^2} - 12y + 9$ is ____________
Ans: Factored form of $4{y^2} - 12y + 9$ is ${\left( {2y - 3} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 4{y^2} - 12y + 9 = 4{y^2} - 6y - 6y + 9$
$ = 2y\left( {2y - 3} \right) - 3\left( {2y - 3} \right)$
$ = \left( {2y - 3} \right)\left( {2y - 3} \right)$
$ = {\left( {2y - 3} \right)^2}$
46. $38{x^3}{y^2}z \div 19x{y^2}$ is equal to _____________
Ans: $38{x^3}{y^2}z \div 19x{y^2}$ is equal to $2 x^{2} z$
$\Rightarrow 38{{x}^{3}}{{y}^{2}}z\div 19x{{y}^{2}}=\dfrac{38{{x}^{3}}{{y}^{2}}z}{19x{{y}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow 38{{x}^{3}}{{y}^{2}}z\div 19x{{y}^{2}}=2{{x}^{2}}z$
$\Rightarrow 38{{x}^{3}}{{y}^{2}}z\div 19x{{y}^{2}}=\dfrac{38{{x}^{2}}z}{19}$
47. Volume of a rectangular box with length $2{\kern 1pt} x$, breadth $3{\kern 1pt} y$ and height $4{\kern 1pt} z$ is
Ans: Volume of a rectangular box with length $2{\kern 1pt} x$, breadth $3{\kern 1pt} y$ and height $4{\kern 1pt} z$ is $24xyz$.
We know that Volume of a rectangular box = length\[ \times \]breadth\[ \times \]height
$ \Rightarrow $ Volume of rectangular box (cuboid) $ = 2{\kern 1pt} x \times 3{\kern 1pt} y \times 4z = 24xyz$
48. ${67^2} - {37^2} = (67 - 37) \times \_\_\_\_\_ = \_\_\_\_\_\_$
Ans: ${67^2} - {37^2} = (67 - 37) \times \left( {67 + 37} \right) = 3120$
Because by using the identity \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\]
${67^2} - {37^2} = (67 - 37) \times \left( {67 + 37} \right)$
${67^2} - {37^2} = 30 \times 104$
${67^2} - {37^2} = 3120$
49. ${103^2} - {102^2} = \_\_\_\_\_\_\_ \times (103 - 102) = \_\_\_\_\_\_$
Ans: ${103^2} - {102^2} = (103 + 102) \times (103 - 102) = 205$
Because by using the identity \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\]
${103^2} - {102^2} = \left( {103 + 102} \right) \times (103 - 102)$
${103^2} - {102^2} = 205 \times 1$
${103^2} - {102^2} = 205$
50. Area of a rectangular plot with sides $4{x^2}$ and $3{y^2}$ is ________
Ans: Area of a rectangular plot with sides $4{x^2}$ and $3{y^2}$ is $12{x^2}{y^2}$.
We know that Area of a rectangle is the product of its length and breadth.
That is \[ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} \times 3{y^2}\]
$ \Rightarrow 12{x^2}{y^2}$
51. Volume of a rectangular box with $l = b = h = 2x$ is ________
Ans: Volume of a rectangular box with $l = b = h = 2x$ is $8{x^3}$
We know that Volume of a rectangular box = length\[ \times \]breadth\[ \times \]height
$ \Rightarrow $ Volume of rectangular box (cuboid) $ = 2{\kern 1pt} x \times 2x \times 2x = 8{x^3}$
52. The coefficient in $ - 37abc$ is _______
Ans: The coefficient in \[ - 37abc\] is $ - 37$.
53. Number of terms in the expression ${a^2} + bc \times d$ is ________
Ans: Number of terms in the expression ${a^2} + bc \times d$ is 2.
Because $ \Rightarrow {a^2} + bc \times d = {a^2} + bcd$.
54. The sum of areas of two squares with sides $4{\kern 1pt} a$ and $4{\kern 1pt} b$ is ________
Ans: The sum of areas of two squares with sides $4{\kern 1pt} a$ and $4{\kern 1pt} b$ is $16\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right)$.
The area of square with side 4a is $ \Rightarrow {\left( {4a} \right)^2} = 16{a^2}$
The area of square with side 4b is $ \Rightarrow {\left( {4b} \right)^2} = 16{b^2}$
Now the sum of areas of two squares with sides $4{\kern 1pt} a$ and $4{\kern 1pt} b$ is $ \Rightarrow 16{a^2} + 16{b^2} = 16\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right)$.
55. The common factor method of factorisation for a polynomial is based on ________ property.
Ans: The common factor method of factorisation for a polynomial is based on distributive property.
56. The side of the square of area $9{y^2}$ is________
Ans: The side of the square of area $9{y^2}$ is 3y.
Because we know that Area of square = (side)2
$ \Rightarrow 9{y^2} = {\left( {{\text{side}}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\text{side}} = \sqrt {9{y^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow {\text{side}} = 3y$
57. On simplification $\dfrac{{3x + 3}}{3} = $ ________
Ans: On simplification $\dfrac{{3x + 3}}{3} = x + 1$
Because,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{3x + 3}}{3} = \dfrac{{3x}}{3} + \dfrac{3}{3}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{3x + 3}}{3} = x + 1$
58. The factorisation of $2x + 4y$ is ________
Ans: The factorisation of $2x + 4y$ is $2(x + 2y)$
\[2x + 4y = \left( {2 \times x} \right) + \left( {2 \times 2 \times y} \right)\]
\[2x + 4y = 2\left( {x + 2y} \right)\]
In questions 59 to 80, state whether the statements are True (T) or False (F):
59. ${(a + b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}$
Ans: False
Because we know the formula, ${(a + b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab$.
60. ${(a - b)^2} = {a^2} - {b^2}$
Ans: False
Because we know the formula, ${(a - b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab$.
61. $(a + b)(a - b) = {a^2} - {b^2}$
Ans: True
Because $ \Rightarrow (a + b)(a - b) = a\left( {a - b} \right) + b\left( {a - b} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow (a + b)(a - b) = {a^2} - ab + ba - {b^2}$
$ \Rightarrow (a + b)(a - b) = {a^2} - {b^2}$
62. The product of two negative terms is a negative term.
Ans: False
Because we know that the product of two negative terms is a positive term.
For example, $ \Rightarrow - x \times - y = \left( { - 1} \right) \times \left( { - 1} \right) \times x \times y$
$ \Rightarrow - x \times y = xy$, as we can see that the product of two negative terms is positive.
63. The product of one negative and one positive term is a negative term.
Ans: True
Because we know that the product of two negative terms is a negative term.
For example, $ \Rightarrow - x \times y = \left( { - 1} \right) \times \left( 1 \right) \times x \times y$
$ \Rightarrow - x \times y = - xy$, as we can see that the product of two negative terms is positive.
64. The coefficient of the term $ - 6{x^2}{y^2}$ is $ - 6$.
Ans: True
Because the coefficient of the term $ - 6{x^2}{y^2}$ is $ - 6$ only.
65. ${p^2}q + {q^2}r + {r^2}q$ is a binomial.
Ans: False.
We can see that the given expression has three unlike terms, hence it is a trinomial not a binomial.
66. The factors of ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}$ are $(a + b)$ and $(a + b)$.
Ans: False.
$ \Rightarrow {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {a^2} - ab - ab + {b^2}$
$ = a(a - b) - b(a - b)$
$ = (a - b)(a - b)$
We can see that the factors are $(a - b)$ and $(a - b)$
67. Is$h$ a factor of $2\pi (h + r)$.
Ans: False.
Because the factors of $2\pi (h + r)$ are $2$, $\pi $ and $(h + r)$.
68. Some of the factors of $\dfrac{{{n^2}}}{2} + \dfrac{n}{2}$ are $\dfrac{1}{2},n$ and $(n + 1)$.
Ans: True.
Because, $ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{n^2}}}{2} + \dfrac{n}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{n^2} + n} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{n^2}}}{2} + \dfrac{n}{2} = n \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {n + 1} \right)$
Hence, some of the factors of $\dfrac{{{n^2}}}{2} + \dfrac{n}{2}$ are $\dfrac{1}{2},n$ and $(n + 1)$.
69. An equation is true for all values of its variables.
Ans: False.
Because, most of the algebraic equations are true when certain values are substituted for the variable and false for all other values.
70. ${x^2} + (a + b)x + ab = (a + b)(x + ab)$
Ans: False.
$\Rightarrow x^{2}+(a+b) x+a b=(a+b)(x+a b)$
$\Rightarrow x^{2}+a x+b x+a b=(a+b)(x+a b)$
$\Rightarrow x(x+a)+b(x+a)=(a+b)(x+a b)$
$\Rightarrow(x+a)(x+b)=(a+b)(x+a b)$
71. Common factor of $11p{q^2},121{p^2}{q^3},1331{p^2}q$ is $11{p^2}{q^2}$.
Ans: False.
$11p{q^2} = 11 \times p \times q \times q$
\[121{p^2}{q^3} = 11 \times 11 \times p \times p \times q \times q \times q\]
$1331{p^2}q = 11 \times 11 \times 11 \times p \times p \times q$
We can see that the common factor is 11pq
72. Common factor of $12{a^2}{b^2} + 4a{b^2} - 32$ is 4.
Ans: True.
$ \Rightarrow 12{a^2}{b^2} + 4a{b^2} - 32 = 4\left( {3{a^2}{b^2} + a{b^2} - 8} \right)$, we can see that each term is a multiple of 4.
73. Factorisation of $ - 3{a^2} + 3ab + 3ac$ is $3a( - a - b - c)$.
Ans: False.
Because,
$ - 3{a^2} + 3ab + 3ac$
Taking 3 common in each term, we have
$ \Rightarrow - 3{a^2} + 3ab + 3ac = 3\left( { - {a^2} + ab + ac} \right)$
Again, each term contains ‘a’. Taking common we have
$ \Rightarrow - 3{a^2} + 3ab + 3ac = 3a\left( { - a + b + c} \right)$
74. Factored form of ${p^2} + 30p + 216$ is $(p + 18)(p - 12)$.
Ans: False.
Because,
${p^2} + 30p + 216$
$ = {p^2} + 18p + 12p + 216$
$ = p\left( {p + 18} \right) + 12\left( {p + 18} \right)$
$ = \left( {p + 18} \right)\left( {p + 12} \right)$
75. The difference of the squares of two consecutive numbers is their sum.
Ans: True.
Let the two consecutive terms be \[x\] and \[\left( {x + 1} \right)\].
The squares of these numbers are \[{x^2}\] and \[{\left( {x + 1} \right)^2}\].
Difference of the squares of two consecutive numbers \[ = {\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} - {x^2}\]
Applying the identity \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\] we have
\[ = {x^2} + 1 + 2x - {x^2}\]
\[ = 2x + 1\]
\[ = x + x + 1\]
\[ = \left( x \right) + \left( {x + 1} \right)\], that is, it is the sum of their sum.
76. $abc + bca + cab$ is a monomial.
Ans: True.
Because, in the given expression we have 3 like terms and we can add them.
$ \Rightarrow abc + bca + cab = abc + abc + abc = 3abc$
77. On dividing $\dfrac{p}{3}$ by $\dfrac{3}{p}$, the quotient is 9.
Ans: False.
Because,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{p}{3}} \right)}}{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{p}} \right)}} = \dfrac{p}{3} \times \dfrac{3}{p} = 1$
78. The value of $p$ for ${51^2} - {49^2} = 100p$ is 2.
Ans: True.
${51^2} - {49^2} = 100p$
By applying the identity ${a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a - b} \right)\left( {a + b} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {51 + 49} \right)\left( {51 - 49} \right) = 100p$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {51 + 49} \right)\left( {51 - 49} \right) = 100p$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {100} \right)\left( 2 \right) = 100p$
$ \Rightarrow 200 = 100p$
$ \Rightarrow p = \dfrac{{200}}{{100}}$
$ \Rightarrow p = 2$
79. $(9x - 51) \div 9$ is $x - 51$.
Ans: False.
$ \Rightarrow \left( {9x - 51} \right) \div 9 = \dfrac{{\left( {9x - 51} \right)}}{9}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {9x - 51} \right) \div 9 = \dfrac{{9x}}{9} - \dfrac{{51}}{9}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {9x - 51} \right) \div 9 = x - \dfrac{{51}}{9}$
80. The value of $(a + 1)(a - 1)\left( {{a^2} + 1} \right)$ is ${a^4} - 1$.
Ans: True.
$ \Rightarrow (a + 1)(a - 1)\left( {{a^2} + 1} \right)$
By applying the identity ${a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a - b} \right)\left( {a + b} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{a^2} - 1} \right)\left( {{a^2} + 1} \right)$
Again, by applying the identity ${a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a - b} \right)\left( {a + b} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{a^4} - 1} \right)$
81. Add:
$7{a^2}bc, - 3ab{c^2},3{a^2}bc,2ab{c^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {7{a^2}bc} \right) + \left( { - 3ab{c^2}} \right) + \left( {3{a^2}bc} \right) + \left( {2ab{c^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 7{a^2}bc - 3ab{c^2} + 3{a^2}bc + 2ab{c^2}$
Grouping like terms
$ \Rightarrow 7{a^2}bc + 3{a^2}bc - 3ab{c^2} + 2ab{c^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 10{a^2}bc - ab{c^2}$
$9ax, + 3by - cz, - 5by + ax + 3cz$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {9ax} \right) + \left( { + 3by - cz} \right) + \left( { - 5by + ax + 3cz} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 9ax + 3by - cz - 5by + ax + 3cz$
Grouping like terms
$ \Rightarrow 9ax + ax + 3by - 5by - cz + 3cz$
$ \Rightarrow 10ax - 2by + 2cz$
$x{y^2}{z^2} + 3{x^2}{y^2}z - 4{x^2}y{z^2}, - 9{x^2}{y^2}z + 3x{y^2}{z^2} + {x^2}y{z^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {x{y^2}{z^2} + 3{x^2}{y^2}z - 4{x^2}y{z^2}} \right) + \left( { - 9{x^2}{y^2}z + 3x{y^2}{z^2} + {x^2}y{z^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow x{y^2}{z^2} + 3{x^2}{y^2}z - 4{x^2}y{z^2} - 9{x^2}{y^2}z + 3x{y^2}{z^2} + {x^2}y{z^2}$
Grouping like terms
$ \Rightarrow x{y^2}{z^2} + 3x{y^2}{z^2} + 3{x^2}{y^2}z - 9{x^2}{y^2}z - 4{x^2}y{z^2} + {x^2}y{z^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 4x{y^2}{z^2} - 6{x^2}{y^2}z - 3{x^2}y{z^2}$
$5{x^2} - 3xy + 4{y^2} - 9,7{y^2} + 5xy - 2{x^2} + 13$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {5{x^2} - 3xy + 4{y^2} - 9} \right) + \left( {7{y^2} + 5xy - 2{x^2} + 13} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 5{x^2} - 3xy + 4{y^2} - 9 + 7{y^2} + 5xy - 2{x^2} + 13$
Grouping like terms
$ \Rightarrow 5{x^2} - 2{x^2} - 3xy + 5xy + 4{y^2} + 7{y^2} - 9 + 13$
$ \Rightarrow 3{x^2} + 2xy + 11{y^2} + 4$
$2{p^4} - 3{p^3} + {p^2} - 5p + 7, - 3{p^4} - 7{p^3} - 3{p^2} - p - 12$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow 2\left( {{p^4} - 3{p^3} + {p^2} - 5p + 7} \right) + \left( { - 3{p^4} - 7{p^3} - 3{p^2} - p - 12} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {2{p^4} - 6{p^3} + 2{p^2} - 10p + 14} \right) + \left( { - 3{p^4} - 7{p^3} - 3{p^2} - p - 12} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2{p^4} - 6{p^3} + 2{p^2} - 10p + 14 - 3{p^4} - 7{p^3} - 3{p^2} - p - 12\]
Grouping like terms
\[ \Rightarrow 2{p^4} - 3{p^4} - 6{p^3} - 7{p^3} + 2{p^2} - 3{p^2} - 10p - p + 14 - 12\]
\[ \Rightarrow - {p^4} - 13{p^3} - {p^2} - 11p + 2\]
$3a(a - b + c),2\;{\text{b}}(a - b + c)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 3a(a - b + c) + 2b(a - b + c)$
$ \Rightarrow 3{a^2} - 3ab + 3ac + 2ba - 2{b^2} + 2bc$
Grouping like terms
$ \Rightarrow 3{a^2} - 3ab + 2ba + 3ac + 2bc - 2{b^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 3{a^2} - ab + 3ac + 2bc - 2{b^2}$
$3a(2b + 5c),3c(2a + 2b)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 3a(2b + 5c) + 3c(2a + 2b)$
$ \Rightarrow 6ab + 15ac + 6ac + 6bc$
Adding like terms,
$ \Rightarrow 6ab + 21ac + 6bc$
82. Subtract:
$5{a^2}{b^2}{c^2}$ from $ - 7{a^2}{b^2}{c^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow - 7{a^2}{b^2}{c^2} - 5{a^2}{b^2}{c^2}$
$ \Rightarrow - 12{a^2}{b^2}{c^2}$
$6{x^2} - 4xy + 5{y^2}$ from $8{y^2} + 6xy - 3{x^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {8{y^2} + 6xy - 3{x^2}} \right) - \left( {6{x^2} - 4xy + 5{y^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 8{y^2} + 6xy - 3{x^2} - 6{x^2} + 4xy - 5{y^2}$
Grouping like terms,
$ \Rightarrow 8{y^2} - 5{y^2} - 3{x^2} - 6{x^2} + 4xy + 6xy$
$ \Rightarrow 3{y^2} - 9{x^2} + 10xy$
$2a{b^2}{c^2} + 4{a^2}{b^2}c - 5{a^2}b{c^2}$ from $ - 10{a^2}{b^2}c + 4a{b^2}{c^2} + 2{a^2}b{c^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - 10{a^2}{b^2}c + 4a{b^2}{c^2} + 2{a^2}b{c^2}} \right) - \left( {2a{b^2}{c^2} + 4{a^2}{b^2}c - 5{a^2}b{c^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow - 10{a^2}{b^2}c + 4a{b^2}{c^2} + 2{a^2}b{c^2} - 2a{b^2}{c^2} - 4{a^2}{b^2}c + 5{a^2}b{c^2}$
Grouping like terms,
$ \Rightarrow - 10{a^2}{b^2}c - 4{a^2}{b^2}c + 4a{b^2}{c^2} - 2a{b^2}{c^2} + 2{a^2}b{c^2} + 5{a^2}b{c^2}$
$ \Rightarrow - 14{a^2}{b^2}c + 2a{b^2}{c^2} + 7{a^2}b{c^2}$
$3{t^4} - 4{t^3} + 2{t^2} - 6t + 6$ from $ - 4{t^4} + 8{t^3} - 4{t^2} - 2t + 11$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - 4{t^4} + 8{t^3} - 4{t^2} - 2t + 11} \right) - \left( {3{t^4} - 4{t^3} + 2{t^2} - 6t + 6} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow - 4{t^4} + 8{t^3} - 4{t^2} - 2t + 11 - 3{t^4} + 4{t^3} - 2{t^2} + 6t - 6$
Grouping like terms,
$ \Rightarrow - 4{t^4} - 3{t^4} + 8{t^3} + 4{t^3} - 4{t^2} - 2{t^2} - 2t + 6t + 11 - 6$
$ \Rightarrow - 7{t^4} + 12{t^3} - 6{t^2} + 4t + 5$
$2ab + 5bc - 7ac$ from $5ab - 2bc - 2ac + 10abc$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {5ab - 2bc - 2ac + 10abc} \right) - \left( {2ab + 5bc - 7ac} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 5ab - 2bc - 2ac + 10abc - 2ab - 5bc + 7ac$
Grouping like terms,
$ \Rightarrow 5ab - 2ab - 2bc - 5bc + 7ac - 2ac + 10abc$
$ \Rightarrow 3ab - 7bc + 5ac + 10abc$
$7p(3q + 7p)$ from $8p(2p - 7q)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {8p(2p - 7q)} \right) - \left( {7p(3q + 7p)} \right)$
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {16{p^2} - 56pq} \right) - \left( {21pq + 49{p^2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 16{p^2} - 56pq - 21pq - 49{p^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 16{p^2} - 77pq - 49{p^2}\]
$ - 3{p^2} + 3pq + 3px$ from $3p( - p - a - r)$
Ans:
$\Rightarrow(3 p(-p-a-r))-\left(-3 p^{2}+3 p q+3 p x\right)$
$\Rightarrow\left(-3 p^{2}-3 p a-3 p r\right)-\left(-3 p^{2}+3 p q+3 p x\right)$
$\Rightarrow-3 p^{2}-3 p a-3 p r+3 p^{2}-3 p q-3 p x$
$\Rightarrow-3 p^{2}+3 p^{2}-3 p a-3 p r-3 p q-3 p x$
$\Rightarrow-3 p a-3 p r-3 p q-3 p x$
$\Rightarrow-3 p(a+r+q+x)$
83. Multiply the following:
$ - 7p{q^2}{r^3}, - 13{p^3}{q^2}r$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - 7p{q^2}{r^3}} \right) \times \left( { - 13{p^3}{q^2}r} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - 7 \times - 13} \right) \times \left( {p{q^2}{r^3} \times {p^3}{q^2}r} \right)$
$\Rightarrow(91) \times\left(p^{4} q^{4} r^{4}\right)$
$\Rightarrow 91 p^{4} q^{4} r^{4}$
$3{x^2}{y^2}{z^2},17xyz$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {3{x^2}{y^2}{z^2}} \right) \times \left( {17xyz} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {3 \times 17} \right) \times \left( {{x^2}{y^2}{z^2} \times xyz} \right)$
$\Rightarrow(51) \times\left(x^{3} y^{3} z^{3}\right)$
$\Rightarrow 51 x^{3} y^{3} z^{3}$
$15x{y^2},17y{z^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {15x{y^2}} \right) \times \left( {17y{z^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {15 \times 17} \right) \times \left( {x{y^2} \times y{z^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {255} \right) \times \left( {x{y^3}{z^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 255x{y^3}{z^2}$
$ - 5{a^2}bc,11ab,13ab{c^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - 5{a^2}bc} \right) \times \left( {11ab} \right) \times \left( {13ab{c^2}} \right)$
\[ \Rightarrow \left( { - 5 \times 11 \times 13} \right) \times \left( {{a^2}bc \times ab \times ab{c^2}} \right)\]
$\Rightarrow(-715) \times\left(a^{4} b^{3} c^{3}\right)$
$\Rightarrow-715 a^{4} b^{3} c^{3}$
$ - 3{x^2}y,(5y - xy)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - 3{x^2}y} \right) \times \left( {5y - xy} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - 3{x^2}y \times 5y} \right) - \left( { - 3{x^2}y \times xy} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - 15{x^2}{y^2}} \right) - \left( { - 3{x^3}{y^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow - 15{x^2}{y^2} + 3{x^3}{y^2}$
$abc,(bc + ca)$
Ans:
$\begin{gathered}
\Rightarrow abc \times (bc + ca) \hfill \\
\Rightarrow \left( {abc \times bc} \right) + \left( {abc \times ca} \right) \hfill \\
\Rightarrow a{b^2}{c^2} + {a^2}b{c^2} \hfill \\
\end{gathered} $
$7pqr,(p - q + r)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 7pqr \times (p - q + r)$
Multiplying 7pqr to each term we will have,
$ \Rightarrow 7{p^2}qr - 7p{q^2}r + 7pq{r^2}$
${x^2}{y^2}{z^2},(xy - yz + zx)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {x^2}{y^2}{z^2} \times (xy - yz + zx)$
Multiplying ${x^2}{y^2}{z^2}$ to all the three terms we will have
$ \Rightarrow {x^3}{y^3}{z^2} - {x^2}{y^3}{z^3} + {x^3}{y^2}{z^3}$
$(p + 6),(q - 7)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow (p + 6)(q - 7) = p\left( {q - 7} \right) + 6\left( {q - 7} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow (p + 6)(q - 7) = pq - 7p + 6q - 42$
$6{\kern 1pt} m{\kern 1pt} n,0{\kern 1pt} m{\kern 1pt} n$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 6{\kern 1pt} m{\kern 1pt} n \times 0{\kern 1pt} m{\kern 1pt} n$
$ \Rightarrow 0$
$a,{a^5},{a^6}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow a \times {a^5} \times {a^6}$
$ \Rightarrow {a^{1 + 5 + 6}}$
$ \Rightarrow {a^{12}}$
$ - 7st, - 1, - 13s{t^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow - 7st \times - 1 \times - 13s{t^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - 7 \times - 1 \times - 13} \right) \times \left( {st \times s{t^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - 91} \right) \times \left( {{s^2}{t^3}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow - 91{s^2}{t^3}$
${b^3},3{b^2},7a{b^5}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {b^3} \times 3{b^2} \times 7a{b^5}$
$ \Rightarrow 21a{b^{10}}$
$ - \dfrac{{100}}{9}rs;\dfrac{3}{4}{r^3}{s^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - \dfrac{{100}}{9}rs} \right) \times \left( {\dfrac{3}{4}{r^3}{s^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - \dfrac{{100}}{9} \times \dfrac{3}{4}} \right) \times \left( {rs \times {r^3}{s^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - \dfrac{{25}}{3}} \right) \times \left( {{r^4}{s^3}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow - \dfrac{{25}}{3}{r^4}{s^3}$
$\left( {{a^2} - {b^2}} \right),\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{a^2} - {b^2}} \right) \times \left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right)$
\[ \Rightarrow {a^2}\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right) - {b^2}\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {a^4} + {a^2}{b^2} - {a^2}{b^2} - {b^4}\]
Cancelling like terms
\[ \Rightarrow {a^4} - {b^4}\]
$(ab + c),(ab + c)$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow (ab + c)(ab + c) = ab(ab + c) + c(ab + c)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {a^2}{b^2} + abc + abc + {c^2}\]
Adding like terms
\[ \Rightarrow {a^2}{b^2} + 2abc + {c^2}\]
$(pq - 2r),(pq - 2r)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow (pq - 2r)(pq - 2r) = pq(pq - 2r) - 2r(pq - 2r)$
$ \Rightarrow {p^2}{q^2} - 2pqr - 2pqr + 4{r^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {p^2}{q^2} - 4pqr + 4{r^2}$
$\left( {\dfrac{3}{4}x - \dfrac{4}{3}y} \right),\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}x + \dfrac{3}{2}y} \right)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{3}{4}x - \dfrac{4}{3}y} \right) \times \left( {\dfrac{2}{3}x + \dfrac{3}{2}y} \right)$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{4}x\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}x + \dfrac{3}{2}y} \right) - \dfrac{4}{3}y\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}x + \dfrac{3}{2}y} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}{x^2} + \dfrac{9}{8}xy - \dfrac{8}{9}xy - \dfrac{{12}}{6}{y^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}{x^2} + \dfrac{9}{8}xy - \dfrac{8}{9}xy - 2{y^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}{x^2} + \dfrac{9}{8}xy - \dfrac{8}{9}xy - 2{y^2}\]
$\dfrac{3}{2}{p^2} + \dfrac{2}{3}{q^2},\left( {2{p^2} - 3{q^2}} \right)$
Ans:
$\Rightarrow\left(\dfrac{3}{2} p^{2}+\dfrac{2}{3} q^{2}\right) \times\left(2 p^{2}-3 q^{2}\right)$
$\Rightarrow 2 p^{2}\left(\dfrac{3}{2} p^{2}+\dfrac{2}{3} q^{2}\right)-3 q^{2}\left(\dfrac{3}{2} p^{2}+\dfrac{2}{3} q^{2}\right)$
$\Rightarrow\left(3 p^{4}+\dfrac{4}{3} q^{2} p^{2}\right)-\left(\dfrac{9}{2} q^{2} p^{2}+2 q^{4}\right)$
$\Rightarrow 3 p^{4}+\dfrac{4}{3} q^{2} p^{2}-\dfrac{9}{2} q^{2} p^{2}-2 q^{4}$
$\Rightarrow 3 p^{4}-2 q^{4}+\dfrac{4}{3} q^{2} p^{2}-\dfrac{9}{2} q^{2} p^{2}$
$\Rightarrow 3 p^{4}-2 q^{4}+q^{2} p^{2}\left[\dfrac{4}{3}-\dfrac{9}{2}\right]$
$\Rightarrow 3 p^{4}-2 q^{4}+q^{2} p^{2}\left[\dfrac{8-27}{6}\right]$
$\Rightarrow 3 p^{4}-2 q^{4}+q^{2} p^{2}\left[\dfrac{-19}{6}\right]$
$\Rightarrow 3 p^{4}-2 q^{4}-\dfrac{19}{6} q^{2} p^{2}$
$\left( {{x^2} - 5x + 6} \right),(2x + 7)$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} - 5x + 6} \right) \times (2x + 7) = (2x + 7) \times \left( {{x^2} - 5x + 6} \right)\]
$\Rightarrow\left(x^{2}-5 x+6\right) \times(2 x+7)$
$\Rightarrow(2 x+7) \times\left(x^{2}-5 x+6\right)$
\[ \Rightarrow 2x\left( {{x^2} - 5x + 6} \right) + 7\left( {{x^2} - 5x + 6} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2{x^3} - 10{x^2} + 12x + 7{x^2} - 35x + 42\]
Grouping like terms we have,
\[ \Rightarrow 2{x^3} - 10{x^2} + 7{x^2} + 12x - 35x + 42\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2{x^3} - 3{x^2} - 23x + 42\]
$\left( {3{x^2} + 4x - 8} \right),\left( {2{x^2} - 4x + 3} \right)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {3{x^2} + 4x - 8} \right) \times \left( {2{x^2} - 4x + 3} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 3{x^2}\left( {2{x^2} - 4x + 3} \right) + 4x\left( {2{x^2} - 4x + 3} \right) - 8\left( {2{x^2} - 4x + 3} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 6{x^4} - 12{x^3} + 9{x^2} + 8{x^3} - 16{x^2} + 12x - 16{x^2} + 32x - 24$
Grouping like terms we have
$ \Rightarrow 6{x^4} - 12{x^3} + 8{x^3} + 9{x^2} - 16{x^2} - 16{x^2} + 12x + 32x - 24$
$ \Rightarrow 6{x^4} - 4{x^3} - 23{x^2} + 44x - 24$
$(2x - 2y - 3),(x + y + 5)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow (2x - 2y - 3) \times (x + y + 5)$
$ \Rightarrow 2x\left( {x + y + 5} \right) - 2y\left( {x + y + 5} \right) - 3\left( {x + y + 5} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 2{x^2} + 2xy + 10x - 2xy - 2{y^2} - 10y - 3x - 3y - 15$
Grouping like terms
$ \Rightarrow 2{x^2} - 2{y^2} + 2xy - 2xy + 10x - 3x - 10y - 3y - 15$
$ \Rightarrow 2{x^2} - 2{y^2} + 7x - 13y - 15$
84. Simplify
${(3x + 2y)^2} + {(3x - 2y)^2}$
Ans: We know \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\] and \[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\], applying the identity we will have
$ \Rightarrow {(3x + 2y)^2} + {(3x - 2y)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} + 4{y^2} + 12xy + 9{x^2} + 4{y^2} - 12xy$
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} + 4{y^2} + 9{x^2} + 4{y^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 18{x^2} + 8{y^2}$
${(3x + 2y)^2} - {(3x - 2y)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], by comparing it with the given problem and solving we will have
$ \Rightarrow {(3x + 2y)^2} - {(3x - 2y)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {3x + 2y + 3x - 2y} \right)\left( {3x + 2y - 3x + 2y} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {3x + 3x} \right)\left( {2y + 2y} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {6x} \right)\left( {4y} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 24xy$
${\left( {\dfrac{7}{9}a + \dfrac{9}{7}b} \right)^2} - ab$
Ans: We know \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\] , applying this identity we will have
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{7}{9}a + \dfrac{9}{7}b} \right)^2} - ab$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{7}{9}a} \right)^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{9}{7}b} \right)^2} + 2\left( {\dfrac{7}{9}a} \right)\left( {\dfrac{9}{7}b} \right) - ab$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{49}}{{81}}{a^2} + \dfrac{{81}}{{49}}{b^2} + 2ab - ab$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{49}}{{81}}{a^2} + \dfrac{{81}}{{49}}{b^2} + ab$
${\left( {\dfrac{3}{4}x - \dfrac{4}{3}y} \right)^2} + 2xy$
Ans: We know \[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\] , applying this identity we will have
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{3}{4}x - \dfrac{4}{3}y} \right)^2} + 2xy$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{3}{4}x} \right)^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}y} \right)^2} - 2\left( {\dfrac{3}{4}x} \right)\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}y} \right) + 2xy$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{{16}}{x^2} + \dfrac{{16}}{9}{y^2} - 2xy + 2xy$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{{16}}{x^2} + \dfrac{{16}}{9}{y^2}$
${(1.5p + 1.2q)^2} - {(1.5p - 1.2q)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], by comparing it with the given problem and solving we will have
$ \Rightarrow {(1.5p + 1.2q)^2} - {(1.5p - 1.2q)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {1.5p + 1.2q + 1.5p - 1.2q} \right)\left( {1.5p + 1.2q - 1.5p + 1.2q} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {1.5p + 1.5p} \right)\left( {1.2q + 1.2q} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {3p} \right)\left( {2.4q} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 7.2pq$
${(2.5m + 1.5q)^2} + {(2.5m - 1.5q)^2}$
Ans: We know \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\] and \[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\], applying the identity we will have
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {2.5m} \right)^2} + {\left( {1.5q} \right)^2} + 2\left( {2.5m} \right)\left( {1.5q} \right) + {\left( {2.5m} \right)^2} + {\left( {1.5q} \right)^2} - 2\left( {2.5m} \right)\left( {1.5q} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {2.5m} \right)^2} + {\left( {1.5q} \right)^2} + {\left( {2.5m} \right)^2} + {\left( {1.5q} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 6.25{m^2} + 2.25{q^2} + 6.25{m^2} + 2.25{q^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 12.5{m^2} + 4.5{q^2}\]
$\left( {{x^2} - 4} \right) + \left( {{x^2} + 4} \right) + 16$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} - 4} \right) + \left( {{x^2} + 4} \right) + 16$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 4 + {x^2} + 4 + 16$
$ \Rightarrow 2{x^2} + 16$
${(ab - c)^2} + 2abc$
Ans: We know \[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\] , applying this identity we will have
$ \Rightarrow {(ab - c)^2} + 2abc$
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{b^2} + {c^2} - 2abc + 2abc$
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{b^2} + {c^2}$
$(a - b)\left( {{a^2} + {b^2} + ab} \right) - (a + b)\left( {{a^2} + {b^2} - ab} \right)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow (a - b){\left( {a + b} \right)^2} - (a + b){\left( {a - b} \right)^2}$
Ans: Given,
$\Rightarrow(a-b)\left(a^{2}+b^{2}+a b\right)-(a+b)\left(a^{2}+b^{2}-a b\right)$
Now we solve $(a-b)\left(a^{2}+b^{2}+a b\right)$ and $(a+b)\left(a^{2}+b^{2}-a b\right)$
Now,
$\Rightarrow(a-b)\left(a^{2}+b^{2}+a b\right)=a\left(a^{2}+b^{2}+a b\right)-b\left(a^{2}+b^{2}+a b\right)$
$\Rightarrow(a-b)\left(a^{2}+b^{2}+a b\right)=a^{3}+a b^{2}+a^{2} b-a^{2} b-b^{3}-a b^{2}$
Grouping like terms,
$\Rightarrow(a-b)\left(a^{2}+b^{2}+a b\right)=a^{3}-b^{3}+a b^{2}-a b^{2}+a^{2} b-a^{2} b$
$\Rightarrow(a-b)\left(a^{2}+b^{2}+a b\right)=a^{3}-b^{3}----(1)$
Now,
$\Rightarrow(a+b)\left(a^{2}+b^{2}-a b\right)=a\left(a^{2}+b^{2}-a b\right)+b\left(a^{2}+b^{2}-a b\right)$
$\Rightarrow(a+b)\left(a^{2}+b^{2}-a b\right)=a^{3}+a b^{2}-a^{2} b+a^{2} b+b^{3}-a b^{2}$$\Rightarrow(a+b)\left(a^{2}+b^{2}-a b\right)=a^{3}+b^{3}+a b^{2}-a b^{2}+a^{2} b-a^{2} b$
Grouping like terms,
$\Rightarrow(a+b)\left(a^{2}+b^{2}-a b\right)=a^{3}+b^{3}----(2)$
Now the given problem becomes
$\Rightarrow(a-b)\left(a^{2}+b^{2}+a b\right)-(a+b)\left(a^{2}+b^{2}-a b\right)$
Using equation 1 and equation 2 we will have,
$\Rightarrow\left(a^{3}-b^{3}\right)-\left(a^{3}+b^{3}\right)$
$\Rightarrow a^{3}-b^{3}-a^{3}-b^{3}$
$\Rightarrow -2{{b}^{3}}$
$\left( {{b^2} - 49} \right)(b + 7) + 343$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{b^2} - 49} \right)\left( {b + 7} \right) + 343$
$ \Rightarrow {b^2}\left( {b + 7} \right) - 49\left( {b + 7} \right) + 343$
$ \Rightarrow {b^3} + 7{b^2} - 49b - 343 + 343$
$ \Rightarrow {b^3} + 7{b^2} - 49b$
${(4.5a + 1.5b)^2} + {(4.5b + 1.5a)^2}$
Ans: We know \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\] and \[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\], applying the identity we will have
$ \Rightarrow {(4.5a + 1.5b)^2} + {(4.5b + 1.5a)^2}$
\[ \Rightarrow 20.25{a^2} + 2.25{b^2} + 13.5ab + 20.25{b^2} + 2.25{a^2} + 13.5ab\]
Now grouping like terms
\[ \Rightarrow 20.25{a^2} + 2.25{a^2} + 2.25{b^2} + 20.25{b^2} + 13.5ab + 13.5ab\]
\[ \Rightarrow 22.5{a^2} + 22.5{b^2} + 27ab\]
${(pq - qr)^2} + 4p{q^2}r$
Ans: We know \[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\] , applying this identity we will have
$ \Rightarrow {p^2}{q^2} + {q^2}{r^2} - 2p{q^2}r + 4p{q^2}r$
$ \Rightarrow {p^2}{q^2} + {q^2}{r^2} + 2p{q^2}r$
${\left( {{s^2}t + t{q^2}} \right)^2} - {(2stq)^2}$
Ans: We know \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\] , applying this identity we will have
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{s^2}t} \right)^2} + {\left( {t{q^2}} \right)^2} + 2\left( {{s^2}t} \right)\left( {t{q^2}} \right) - {(2stq)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {s^4}{t^2} + {t^2}{q^4} + 2{s^2}{t^2}{q^2} - 4{s^2}{t^2}{q^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {s^4}{t^2} + {t^2}{q^4} - 2{s^2}{t^2}{q^2}$
85. Expand the following, using suitable identities.
${(xy + yz)^2}$
Ans: We know \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\], applying this we will have
$ \Rightarrow {(xy + yz)^2} = {\left( {xy} \right)^2} + {\left( {yz} \right)^2} + 2\left( {xy} \right)\left( {yz} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(xy + yz)^2} = {x^2}{y^2} + {y^2}{z^2} + 2x{y^2}z$
${\left( {{x^2}y - x{y^2}} \right)^2}$
Ans: We know \[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\], applying this we will have
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{x^2}y - x{y^2}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{x^2}y} \right)^2} + {\left( {x{y^2}} \right)^2} - 2\left( {{x^2}y} \right)\left( {x{y^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{x^2}y - x{y^2}} \right)^2} = {x^4}{y^2} + {x^2}{y^4} - 2{x^3}{y^3}$
${\left( {\dfrac{4}{5}a + \dfrac{5}{4}b} \right)^2}$
Ans: We know \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\], applying this we will have $ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{4}{5}a + \dfrac{5}{4}b} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{4}{5}a} \right)^2} + \left( {\dfrac{5}{4}b} \right) + 2\left( {\dfrac{4}{5}a} \right)\left( {\dfrac{5}{4}b} \right)$
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{4}{5}a + \dfrac{5}{4}b} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{16}}{{25}}{a^2} + \dfrac{{25}}{{16}}{b^2} + 2ab\]
${\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}x - \dfrac{3}{2}y} \right)^2}$
Ans: We know \[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\], applying this we will have
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}x - \dfrac{3}{2}y} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}x} \right)^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}y} \right)^2} - 2\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}x} \right)\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}y} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}x - \dfrac{3}{2}y} \right)^2} = \dfrac{4}{9}{x^2} + \dfrac{9}{4}{y^2} - 2xy$
${\left( {\dfrac{4}{5}p + \dfrac{5}{3}q} \right)^2}$
Ans: We know \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\], applying this we will have
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{4}{5}p + \dfrac{5}{3}q} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{4}{5}p} \right)^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{5}{3}q} \right)^2} + 2\left( {\dfrac{4}{5}p} \right)\left( {\dfrac{5}{3}q} \right)$
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{4}{5}p + \dfrac{5}{3}q} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{16}}{{25}}{p^2} + \dfrac{{25}}{9}{q^2} + \dfrac{8}{3}pq\]
$(x + 3)(x + 7)$.
Ans: We know \[\left( {x + a} \right)\left( {x + b} \right) = {x^2} + \left( {a + b} \right)x + ab\], then we have
$ \Rightarrow (x + 3)(x + 7) = {x^2} + \left( {3 + 7} \right)x + \left( {7 \times 3} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow (x + 3)(x + 7) = {x^2} + 10x + 21$
$(2x + 9)(2x - 7)$
Ans: We know \[\left( {x + a} \right)\left( {x - b} \right) = {x^2} + \left( {a - b} \right)x - ab\], then we have
$ \Rightarrow (2x + 9)(2x - 7) = {\left( {2x} \right)^2} + \left( {9 - 7} \right)2x - \left( {9 \times 7} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow (2x + 9)(2x - 7) = 2{x^2} + \left( 2 \right)2x - \left( {63} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow (2x + 9)(2x - 7) = 2{x^2} + 4x - 63$
$\left( {\dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \dfrac{y}{4}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \dfrac{{3y}}{4}} \right)$
Ans: We \[\left( {x + a} \right)\left( {x + b} \right) = {x^2} + \left( {a + b} \right)x + ab\], then we have
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \dfrac{y}{4}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \dfrac{{3y}}{4}} \right) = {\left( {\dfrac{{4x}}{5}} \right)^2} + \left( {\dfrac{y}{4} + \dfrac{{3y}}{4}} \right)\dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \left( {\dfrac{y}{4} \times \dfrac{{3y}}{4}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \dfrac{y}{4}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \dfrac{{3y}}{4}} \right) = \dfrac{{16{x^2}}}{{25}} + \left( {\dfrac{{4y}}{4}} \right)\dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \left( {\dfrac{{3{y^2}}}{{16}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \dfrac{y}{4}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{4x}}{5} + \dfrac{{3y}}{4}} \right) = \dfrac{{16{x^2}}}{{25}} + \dfrac{{16xy}}{{20}} + \dfrac{{3{y^2}}}{{16}}$
$\left( {\dfrac{{2x}}{3} - \dfrac{2}{3}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{2x}}{3} + \dfrac{{2a}}{3}} \right)$
Ans: We \[\left( {x - a} \right)\left( {x + b} \right) = {x^2} + \left( {b - a} \right)x - ab\], then we have
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{2x}}{3} - \dfrac{2}{3}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{2x}}{3} + \dfrac{{2a}}{3}} \right) = {\left( {\dfrac{{2x}}{3}} \right)^2} + \left( {\dfrac{{2a}}{3} - \dfrac{2}{3}} \right)\dfrac{{2x}}{3} - \left( {\dfrac{{2a}}{3} \times \dfrac{2}{3}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{2x}}{3} - \dfrac{2}{3}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{2x}}{3} + \dfrac{{2a}}{3}} \right) = \dfrac{{4x}}{9} + \left( {\dfrac{{2a - 2}}{3}} \right)\dfrac{{2x}}{3} - \dfrac{{4a}}{9}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{2x}}{3} - \dfrac{2}{3}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{2x}}{3} + \dfrac{{2a}}{3}} \right) = \dfrac{{4x}}{9} + \dfrac{{4xa}}{9} - \dfrac{{4x}}{9} - \dfrac{{4a}}{9}$
$(2x - 5y)(2x - 5y)$
Ans: $(2x - 5y)(2x - 5y) = {\left( {2x - 5y} \right)^2}$
We know that \[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\]
${\left( {2x - 5y} \right)^2} = {\left( {2x} \right)^2} + {\left( {5y} \right)^2} - 2\left( {2x} \right)\left( {5y} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {2x - 5y} \right)^2} = 4{x^2} + 25{y^2} - 20xy$
$\left( {\dfrac{{2a}}{3} + \dfrac{b}{3}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{2a}}{3} - \dfrac{b}{3}} \right)$
Ans: We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], then we have
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{2a}}{3} + \dfrac{b}{3}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{2a}}{3} - \dfrac{b}{3}} \right) = {\left( {\dfrac{{2a}}{3}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{b}{3}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{2a}}{3} + \dfrac{b}{3}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{2a}}{3} - \dfrac{b}{3}} \right) = \dfrac{{4{a^2}}}{9} - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{9}$
$\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right)$
Ans: We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], then we have
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = {\left( {{x^2}} \right)^2} - {\left( {{y^2}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right) = {x^4} - {y^4}$
${\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\], then we have
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{a^2}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{b^2}} \right)^2} + 2{a^2}{b^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right)^2} = {a^4} + {b^4} + 2{a^2}{b^2}$
${(7x + 5)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\], then we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {7x + 5} \right)^2} = {\left( {7x} \right)^2} + {5^2} + 2\left( {7x} \right)\left( 5 \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {7x + 5} \right)^2} = 49{x^2} + 25 + 70x$
${(0.9p - 0.5q)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\], then we have
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {0.9p - 0.5q} \right)^2} = {\left( {0.9p} \right)^2} + {\left( {0.5q} \right)^2} - 2\left( {0.9p} \right)\left( {0.5q} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {0.9p - 0.5q} \right)^2} = 0.81{p^2} + 0.25{q^2} - 0.9pq$
${x^2}{y^2} = {(xy)^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {x^2}{y^2} = {x^2}{y^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2}{y^2} - {x^2}{y^2} = 0$
86. Using suitable identities, evaluate the following.
${(52)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\], applying this we will have,
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {52} \right)^2} = {\left( {50 + 2} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {52} \right)^2} = {\left( {50} \right)^2} + {\left( 2 \right)^2} + 2\left( {50} \right)\left( 2 \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {52} \right)^2} = 2500 + 4 + 200\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {52} \right)^2} = 2704\]
${(49)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\], applying this we will have,
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {49} \right)^2} = {\left( {50 - 1} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {49} \right)^2} = {\left( {50} \right)^2} + {\left( 1 \right)^2} - 2\left( {50} \right)\left( 1 \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {49} \right)^2} = 2500 + 1 - 100\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {49} \right)^2} = 2401\]
${(103)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\], applying this we will have,
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {103} \right)^2} = {\left( {100 + 3} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {103} \right)^2} = {\left( {100} \right)^2} + {\left( 3 \right)^2} + 2\left( {100} \right)\left( 3 \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {103} \right)^2} = 10000 + 9 + 600\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {103} \right)^2} = 10609\]
${(98)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\], applying this we will have,
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {98} \right)^2} = {\left( {100 - 2} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {98} \right)^2} = {\left( {100} \right)^2} + {\left( 2 \right)^2} - 2\left( {100} \right)\left( 2 \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {98} \right)^2} = 10000 + 4 - 400\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {98} \right)^2} = 9604\]
${(1005)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\], applying this we will have,
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {1005} \right)^2} = {\left( {1000 + 5} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {1005} \right)^2} = {\left( {1000} \right)^2} + {\left( 5 \right)^2} + 2\left( {1000} \right)\left( 5 \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {1005} \right)^2} = 1000000 + 25 + 10000\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {1005} \right)^2} = 1010025\]
${(995)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\], applying this we will have,
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {995} \right)^2} = {\left( {1000 - 5} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {995} \right)^2} = {\left( {1000} \right)^2} + {\left( 5 \right)^2} - 2\left( {1000} \right)\left( 5 \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {995} \right)^2} = 1000000 + 25 - 10000\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {995} \right)^2} = 990025\]
$47 \times 53$
Ans: We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], applying this we will have,
$ \Rightarrow 47 \times 53 = \left( {50 - 3} \right)\left( {50 + 3} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 47 \times 53 = {\left( {50} \right)^2} - {3^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 47 \times 53 = 2500 - 9$
$ \Rightarrow 47 \times 53 = 2491$
$52 \times 53$
Ans: We know that \[\left( {x + a} \right)\left( {x + b} \right) = {x^2} + \left( {a + b} \right)x + ab\], then
$ \Rightarrow 52 \times 53 = \left( {50 + 2} \right)\left( {50 + 3} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 52 \times 53 = {\left( {50} \right)^2} + \left( {2 + 3} \right)50 + \left( {2 \times 3} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 52 \times 53 = 2500 + \left( 5 \right)50 + 6$
$ \Rightarrow 52 \times 53 = 2500 + 250 + 6$
$ \Rightarrow 52 \times 53 = 2756$
$105 \times 95$
Ans: We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], applying this we will have,
$ \Rightarrow 105 \times 95 = \left( {100 + 5} \right)\left( {100 - 5} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 105 \times 95 = {\left( {100} \right)^2} - {5^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 105 \times 95 = 10000 - 25$
$ \Rightarrow 105 \times 95 = 9975$
$104 \times 97$
Ans: We know \[\left( {x + a} \right)\left( {x - b} \right) = {x^2} + \left( {a - b} \right)x - ab\],
$ \Rightarrow 104 \times 97 = \left( {100 + 4} \right)\left( {100 - 3} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 104 \times 97 = {\left( {100} \right)^2} + \left( {4 - 3} \right)100 - \left( {4 \times 3} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 104 \times 97 = 10000 + \left( 1 \right)100 - \left( {12} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 104 \times 97 = 10000 + 100 - 12$
$ \Rightarrow 104 \times 97 = 10088$
$101 \times 103$
Ans: We know that \[\left( {x + a} \right)\left( {x + b} \right) = {x^2} + \left( {a + b} \right)x + ab\], then
$ \Rightarrow 101 \times 103 = \left( {100 + 1} \right)\left( {100 + 3} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 101 \times 103 = {\left( {100} \right)^2} + \left( {1 + 3} \right)100 + \left( {3 \times 1} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 101 \times 103 = 10000 + \left( 4 \right)100 + \left( 3 \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 101 \times 103 = 10000 + 400 + 3$
$ \Rightarrow 101 \times 103 = 10403$
$98 \times 103$
Ans: We know that \[\left( {x - a} \right)\left( {x + b} \right) = {x^2} + \left( {b - a} \right)x - ab\]
$ \Rightarrow 98 \times 103 = \left( {100 - 2} \right)\left( {100 + 3} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 98 \times 103 = {\left( {100} \right)^2} + \left( {3 - 2} \right)100 - \left( {3 \times 2} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 98 \times 103 = 10000 + \left( 1 \right)100 - 6$
$ \Rightarrow 98 \times 103 = 10000 + 100 - 6$
$ \Rightarrow 98 \times 103 = 10094$
${(9.9)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\]
$ \Rightarrow {(9.9)^2} = {\left( {10 - 0.1} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {(9.9)^2} = {\left( {10} \right)^2} + {\left( {0.1} \right)^2} - 2\left( {10} \right)\left( {0.1} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(9.9)^2} = 100 + 0.01 - 2$
$ \Rightarrow {(9.9)^2} = 98.01$
$9.8 \times 10.2$
Ans: We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\],
\[ \Rightarrow 9.8 \times 10.2 = \left( {10 - 0.2} \right)\left( {10 + 0.2} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 9.8 \times 10.2 = {\left( {10} \right)^2} - {\left( {0.2} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 9.8 \times 10.2 = 100 - 0.04\]
\[ \Rightarrow 9.8 \times 10.2 = 99.96\]
$10.1 \times 10.2$
Ans: We know that \[\left( {x + a} \right)\left( {x + b} \right) = {x^2} + \left( {a + b} \right)x + ab\],
$ \Rightarrow 10.1 \times 10.2 = \left( {10 + 0.1} \right)\left( {10 + 0.2} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 10.1 \times 10.2 = {\left( {10} \right)^2} + \left( {0.1 + 0.2} \right)10 + \left( {0.1 \times 0.2} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 10.1 \times 10.2 = 100 + \left( {0.3} \right)10 + \left( {0.02} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 10.1 \times 10.2 = 100 + 3 + 0.02$
$ \Rightarrow 10.1 \times 10.2 = 103.02$
${(35.4)^2} - {(14.6)^2}$
Ans: We know that , then
$\Rightarrow(35.4)^{2}-(14.6)^{2}=(35.4+14.6)(35.4-14.6)$
$\Rightarrow(35.4)^{2}-(14.6)^{2}=(50)(20.8)$
$\Rightarrow(35.4)^{2}-(14.6)^{2}=1040$
$(69.3)^{2}-(30.7)^{2}$
\[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\]
Ans: We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], then
$ \Rightarrow {(69.3)^2} - {(30.7)^2} = \left( {69.3 + 30.7} \right)\left( {69.3 - 30.7} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(69.3)^2} - {(30.7)^2} = \left( {100} \right)\left( {38.6} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(69.3)^2} - {(30.7)^2} = 3860$
${(9.7)^2} - {(0.3)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], then
$ \Rightarrow {(9.7)^2} - {(0.3)^2} = \left( {9.7 + 0.3} \right)\left( {9.7 - 0.3} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(9.7)^2} - {(0.3)^2} = \left( {10} \right)\left( {9.4} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(9.7)^2} - {(0.3)^2} = 94$
${(132)^2} - {(68)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], then
$ \Rightarrow {(132)^2} - {(68)^2} = \left( {132 + 68} \right)\left( {132 - 68} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(132)^2} - {(68)^2} = \left( {200} \right)\left( {64} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(132)^2} - {(68)^2} = 12800$
${(339)^2} - {(161)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], then
$ \Rightarrow {(339)^2} - {(161)^2} = \left( {339 + 161} \right)\left( {339 - 161} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(339)^2} - {(161)^2} = \left( {400} \right)\left( {178} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(339)^2} - {(161)^2} = 71200$
${(729)^2} - {(271)^2}$
Ans: We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], then
$ \Rightarrow {(729)^2} - {(271)^2} = \left( {729 + 271} \right)\left( {729 - 271} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(729)^2} - {(271)^2} = \left( {1000} \right)\left( {458} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(729)^2} - {(271)^2} = 458000$
87. Write the greatest common factor in each of the following terms.
$ - 18{a^2},108a$
Ans:
$ - 18{a^2} = - 1 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 \times a \times a$
$108a = 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 \times 3 \times a$
We can see that the greatest common factor is $2 \times 3 \times 3 \times a = 18a$.
$3{x^2}y,18x{y^2}, - 6xy$
Ans:
$3{x^2}y = 3 \times x \times x \times y$
$18x{y^2} = 2 \times 3 \times 3 \times x \times y \times y$
$ - 6xy = - 2 \times 3 \times x \times y$
We can see that the greatest common factor is $3 \times x \times y = 3xy$.
$2xy, - {y^2},2{x^2}y$
Ans:
$2xy = 2 \times x \times y$
$ - {y^2} = - 1 \times y \times y$
We can see that the greatest common factor is
${{l}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}n,l{{m}^{2}}{{n}^{2}},{{l}^{2}}m{{n}^{2}}$
Ans:
$l \times m \times n = lmn$$2{x^2}y = 2 \times x \times x \times y$ ${l^2}{m^2}n = l \times l \times m \times m \times n$
$l{m^2}{n^2} = l \times m \times m \times n \times n$
${l^2}m{n^2} = l \times l \times m \times n \times n$
We can see that the greatest common factor is
$21pqr, - 7{p^2}{q^2}{r^2},49{p^2}qr$
Ans:
$21pqr = 3 \times 7 \times p \times q \times r$
$ - 7{p^2}{q^2}{r^2} = - 1 \times 7 \times p \times p \times q \times q \times r \times r$
$49{p^2}qr = 7 \times 7 \times p \times p \times q \times r$
We can see that the greatest common factor is \[7 \times p \times q \times r = 7pqr\]
qrxy, pryz, rxyz
Ans: As we can see that in all the three terms, the greatest common factor is ry.
$3{x^3}{y^2}z, - 6x{y^3}{z^2},12{x^2}y{z^3}$
Ans:
$3{x^3}{y^2}z = 3 \times x \times x \times x \times y \times y \times z$
$ - 6x{y^3}{z^2} = - 1 \times 2 \times 3 \times x \times y \times y \times y \times z \times z$
$12{x^2}y{z^3} = 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times x \times x \times y \times z \times z \times z$
We can see that the greatest common factor is \[3 \times x \times y \times z = 3xyz\]
$63{p^2}{a^2}{r^2}s, - 9p{q^2}{r^2}{s^2},15{p^2}q{r^2}{s^2}, - 60{p^2}{a^2}r{s^2}$
Ans:
$63{p^2}{a^2}{r^2}s = 3 \times 3 \times 7 \times p \times p \times a \times a \times r \times r \times s$
$ - 9p{q^2}{r^2}{s^2} = - 1 \times 3 \times 3 \times p \times q \times q \times r \times r \times s \times s$
$15{p^2}q{r^2}{s^2} = 3 \times 5 \times p \times p \times q \times r \times r \times s \times s$
$ - 60{p^2}{a^2}r{s^2} = - 1 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 5 \times p \times p \times a \times a \times r \times s \times s$
We can see that the greatest common factor is \[3 \times p \times r \times s = 3prs\]
$13{x^2}y,169xy$
Ans:
$13{x^2}y = 13 \times x \times x \times y$
$169xy = 13 \times 13 \times x \times y$
We can see that the greatest common factor is \[13 \times x \times y = 13xy\]
$11{x^2},12{y^2}$
Ans:
\[11{x^2} = 11 \times x \times x\]
\[12{y^2} = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times y \times y\]
We can see that the greatest common factor is \[1\]
88. Factorise the following expressions.
$6ab + 12bc$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow 6ab + 12bc\]
\[ \Rightarrow 6b\left( {a + 2c} \right)\]
$ - xy - ay$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow - xy - ay$
$ \Rightarrow - y\left( {x + a} \right)$
$a{x^3} - b{x^2} + cx$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow a{x^3} - b{x^2} + cx$
$ \Rightarrow x\left( {a{x^2} - bx + c} \right)$
${l^2}{m^2}n - l{m^2}{n^2} - {l^2}m{n^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {l^2}{m^2}n - l{m^2}{n^2} - {l^2}m{n^2}$
$ \Rightarrow lmn\left( {lm - mn - \ln } \right)$
$3pqr - 6{p^2}{q^2}{r^2} - 15{r^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 3pqr - 6{p^2}{q^2}{r^2} - 15{r^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 3r\left( {pq - 2{p^2}{q^2}r - 5r} \right)$
${x^3}{y^2} + {x^2}{y^3} - x{y^4} + xy$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {x^3}{y^2} + {x^2}{y^3} - x{y^4} + xy$
$ \Rightarrow xy\left( {{x^2}y + x{y^2} - {y^3} + 1} \right)$
$4x{y^2} - 10{x^2}y + 16{x^2}{y^2} + 2xy$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 4x{y^2} - 10{x^2}y + 16{x^2}{y^2} + 2xy$
$ \Rightarrow 2xy\left( {2y - 5x + 8xy + 1} \right)$
$2{a^3} - 3{a^2}b + 5a{b^2} - ab$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 2{a^3} - 3{a^2}b + 5a{b^2} - ab$
$ \Rightarrow a\left( {2{a^2} - 3ab + 5{b^2} - b} \right)$
$63{p^2}{q^2}{r^2}s - 9p{q^2}{r^2}{s^2} + 15{p^2}q{r^2}{s^2} - 60{p^2}{q^2}r{s^2}$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow 63{p^2}{q^2}{r^2}s - 9p{q^2}{r^2}{s^2} + 15{p^2}q{r^2}{s^2} - 60{p^2}{q^2}r{s^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 3pqrs\left( {21pqr - 3qrs + 5prs - 20pqs} \right)\]
$24{x^2}y{z^3} - 6x{y^3}{z^2} + 15{x^2}{y^2}z - 5xyz$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 24{x^2}y{z^3} - 6x{y^3}{z^2} + 15{x^2}{y^2}z - 5xyz$
$ \Rightarrow xyz\left( {24x{z^2} - 6{y^2}z + 15xy - 5} \right)$
${a^3} + {a^2} + a + 1$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {a^3} + {a^2} + a + 1$
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}\left( {a + 1} \right) + 1\left( {a + 1} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {a + 1} \right)\left( {{a^2} + 1} \right)$
$lx + my + mx + ly$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow lx + my + mx + ly$
$ \Rightarrow my + mx + ly + lx$
$ \Rightarrow m\left( {x + y} \right) + l\left( {x + y} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {x + y} \right)\left( {m + l} \right)$
${a^3}x - {x^4} + {a^2}{x^2} - a{x^3}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {a^3}x - {x^4} + {a^2}{x^2} - a{x^3}$
$ \Rightarrow {a^3}x + {a^2}{x^2} - {x^4} - a{x^3}$
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}x\left( {a + x} \right) - {x^3}\left( {x + a} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {a + x} \right)\left( {{a^2}x - {x^3}} \right)$
$2{x^2} - 2y + 4xy - x$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 2{x^2} - 2y + 4xy - x$
\[ \Rightarrow 2{x^2} - x - 2y + 4xy\]
\[ \Rightarrow x\left( {2x - 1} \right) + 2y\left( { - 1 + 2x} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow x\left( {2x - 1} \right) + 2y\left( {2x - 1} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {2x - 1} \right)\left( {x + 2y} \right)\]
${y^2} + 8zx - 2xy - 4yz$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} - 2xy + 8zx - 4yz$
$ \Rightarrow y\left( {y - 2x} \right) - 4z\left( { - 2x + y} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow y\left( {y - 2x} \right) - 4z\left( {y - 2x} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {y - 2x} \right)\left( {y - 4z} \right)$
$a{x^2}y - bxyz - a{x^2}z + bx{y^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow a{x^2}y - a{x^2}z - bxyz + bx{y^2}$
$ \Rightarrow a{x^2}\left( {y - z} \right) + bxy\left( { - z + y} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow a{x^2}\left( {y - z} \right) + bxy\left( {y - z} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {a{x^2} + bxy} \right)\left( {y - z} \right)$
${a^2}b + {a^2}c + ab + ac + {b^2}c + {c^2}b$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}b + {a^2}c + ab + ac + {b^2}c + {c^2}b$
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}\left( {b + c} \right) + a\left( {b + c} \right) + bc\left( {b + c} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {b + c} \right)\left( {{a^2} + a + bc} \right)$
$2a{x^2} + 4axy + 3b{x^2} + 2a{y^2} + 6bxy + 3b{y^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 2a{x^2} + 4axy + 3b{x^2} + 2a{y^2} + 6bxy + 3b{y^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 2a{x^2} + 4axy + 3b{x^2} + 6bxy + 2a{y^2} + 3b{y^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 2ax\left( {x + 2y} \right) + 3bx\left( {x + 2y} \right) + 2{y^2}\left( {2a + 3b} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow x\left( {x + 2y} \right)\left( {2a + 3b} \right) + 2{y^2}\left( {2a + 3b} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {2a + 3b} \right)\left[ {x\left( {x + 2y} \right) + 2{y^2}} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {2a + 3b} \right)\left[ {{x^2} + 2yx + 2{y^2}} \right]$
89. Factorise the following, using the identity ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$
\[{x^2} + 6x + 9\]
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 6x + 9 = {x^2} + 2\left( 3 \right)\left( x \right) + {3^2}$
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 6x + 9 = {\left( {x + 3} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 6x + 9 = \left( {x + 3} \right)\left( {x + 3} \right)$
${x^2} + 12x + 36$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 12x + 36 = {x^2} + 2\left( 6 \right)\left( x \right) + {6^2}$
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 12x + 36 = {\left( {x + 6} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 12x + 36 = \left( {x + 6} \right)\left( {x + 6} \right)$
${x^2} + 14x + 49$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 14x + 49 = {x^2} + 2\left( 7 \right)\left( x \right) + {7^2}$
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 14x + 49 = {\left( {x + 7} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 14x + 49 = \left( {x + 7} \right)\left( {x + 7} \right)$
${x^2} + 2x + 1$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 2x + 1 = {x^2} + 2\left( 1 \right)\left( x \right) + {1^2}$
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 2x + 1 = {\left( {x + 1} \right)^2}$
$4{x^2} + 4x + 1$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} + 4x + 1 = {\left( {2x} \right)^2} + 2\left( {2x} \right)\left( 1 \right) + {1^2}$
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
\[ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} + 4x + 1 = {\left( {2x + 1} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} + 4x + 1 = \left( {2x + 1} \right)\left( {2x + 1} \right)\]
${a^2}{x^2} + 2ax + 1$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow {a^2}{x^2} + 2ax + {1^2} = {\left( {ax} \right)^2} + 2\left( {ax} \right)\left( 1 \right) + {1^2}\]
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{x^2} + 2ax + 1 = {\left( {ax + 1} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{x^2} + 2ax + 1 = \left( {ax + 1} \right)\left( {ax + 1} \right)$
${a^2}{x^2} + 2abx + {b^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{x^2} + 2abx + {b^2} = {\left( {ax} \right)^2} + 2\left( {ax} \right)\left( b \right) + {b^2}$
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{x^2} + 2abx + {b^2} = {\left( {ax + b} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{x^2} + 2abx + {b^2} = \left( {ax + b} \right)\left( {ax + b} \right)$
${a^2}{x^2} + 2abxy + {b^2}{y^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{x^2} + 2abxy + {b^2}{y^2} = {\left( {ax} \right)^2} + 2\left( {ax} \right)\left( {by} \right) + {\left( {by} \right)^2}$
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{x^2} + 2abxy + {b^2}{y^2} = {\left( {ax + by} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{x^2} + 2abxy + {b^2}{y^2} = \left( {ax + by} \right)\left( {ax + by} \right)$
$4{x^2} + 12x + 9$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} + 12x + 9 = {\left( {2x} \right)^2} + 2\left( {2x} \right)\left( 3 \right) + {3^2}$
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
$ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} + 12x + 9 = {\left( {2x + 3} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} + 12x + 9 = \left( {2x + 3} \right)\left( {2x + 3} \right)$
$16{x^2} + 40x + 25$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 16{x^2} + 40x + 25 = {\left( {4x} \right)^2} + 2\left( {4x} \right)\left( 5 \right) + {5^2}$
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
$ \Rightarrow 16{x^2} + 40x + 25 = {\left( {4x + 5} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 16{x^2} + 40x + 25 = \left( {4x + 5} \right)\left( {4x + 5} \right)$
$9{x^2} + 24x + 16$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} + 24x + 16 = {\left( {3x} \right)^2} + 2\left( {3x} \right)\left( 4 \right) + {4^2}$
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} + 24x + 16 = {\left( {3x + 4} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} + 24x + 16 = \left( {3x + 4} \right)\left( {3x + 4} \right)$
$9{x^2} + 30x + 25$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} + 30x + 25 = {\left( {3x} \right)^2} + 2\left( {3x} \right)\left( 5 \right) + {5^2}$
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} + 30x + 25 = {\left( {3x + 5} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} + 30x + 25 = \left( {3x + 5} \right)\left( {3x + 5} \right)$
$2{x^3} + 24{x^2} + 72x$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow 2{x^3} + 24{x^2} + 72x = 2x\left( {{x^2} + 12x + 36} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2{x^3} + 24{x^2} + 72x = 2x\left( {{x^2} + 2\left( x \right)\left( 6 \right) + {6^2}} \right)\]
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
\[ \Rightarrow 2{x^3} + 24{x^2} + 72x = 2x{\left( {x + 6} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2{x^3} + 24{x^2} + 72x = 2x\left( {x + 6} \right)\left( {x + 6} \right)\]
${a^2}{x^3} + 2ab{x^2} + {b^2}x$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{x^3} + 2ab{x^2} + {b^2}x = x\left( {{a^2}{x^2} + 2abx + {b^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{x^3} + 2ab{x^2} + {b^2}x = x\left( {{{\left( {ax} \right)}^2} + 2\left( {ax} \right)\left( b \right) + {b^2}} \right)$
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{x^3} + 2ab{x^2} + {b^2}x = x{\left( {ax + b} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{x^3} + 2ab{x^2} + {b^2}x = x\left( {ax + b} \right)\left( {ax + b} \right)$
$4{x^4} + 12{x^3} + 9{x^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 4{x^4} + 12{x^3} + 9{x^2} = {x^2}\left( {4{x^2} + 12x + 9} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 4{x^4} + 12{x^3} + 9{x^2} = {x^2}\left( {{{\left( {2x} \right)}^2} + 2\left( {2x} \right)\left( 3 \right) + {3^2}} \right)$
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
$ \Rightarrow 4{x^4} + 12{x^3} + 9{x^2} = {x^2}{\left( {2x + 3} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 4{x^4} + 12{x^3} + 9{x^2} = {x^2}\left( {2x + 3} \right)\left( {2x + 3} \right)$
$\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{4} + 2x + 4$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{4} + 2x + 4 = {\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)^2} + 2\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)(2) + {2^2}$
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{4} + 2x + 4 = {\left( {\dfrac{x}{2} + 2} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{4} + 2x + 4 = \left( {\dfrac{x}{2} + 2} \right)\left( {\dfrac{x}{2} + 2} \right)$
$9{x^2} + 2xy + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{9}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} + 2xy + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{9} = {\left( {3x} \right)^2} + 2\left( {\dfrac{y}{3}} \right)\left( {3x} \right) + {\left( {\dfrac{y}{3}} \right)^2}$
By comparing with ${a^2} + 2ab + {b^2} = {(a + b)^2}$, we will have
\[ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} + 2xy + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{9} = {\left( {3x + \dfrac{y}{3}} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} + 2xy + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{9} = \left( {3x + \dfrac{y}{3}} \right)\left( {3x + \dfrac{y}{3}} \right)\]
90. Factorise the following, using the identity ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {(a - b)^2}$.
${x^2} - 8x + 16$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 8x + 16 = {x^2} - 2\left( x \right)\left( 4 \right) + {4^2}\]
By comparing with ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {(a - b)^2}$, we will have
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 8x + 16 = {\left( {x - 4} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 8x + 16 = \left( {x - 4} \right)\left( {x - 4} \right)\]
${x^2} - 10x + 25$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 10x + 25 = {x^2} - 2\left( x \right)\left( 5 \right) + {5^2}\]
By comparing with ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {(a - b)^2}$, we will have
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 10x + 25 = {\left( {x - 5} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 10x + 25 = \left( {x - 5} \right)\left( {x - 5} \right)\]
${y^2} - 14y + 49$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow {y^2} - 14y + 49 = {y^2} - 2\left( 7 \right)\left( y \right) + {7^2}\]
By comparing with ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {(a - b)^2}$, we will have
\[ \Rightarrow {y^2} - 14y + 49 = {\left( {y - 7} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {y^2} - 14y + 49 = \left( {y - 7} \right)\left( {y - 7} \right)\]
${p^2} - 2p + 1$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow {p^2} - 2p + 1 = {p^2} - 2\left( p \right)\left( 1 \right) + {1^2}\]
By comparing with ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {(a - b)^2}$, we will have
\[ \Rightarrow {p^2} - 2p + 1 = {\left( {p - 1} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {p^2} - 2p + 1 = \left( {p - 1} \right)\left( {p - 1} \right)\]
$4{a^2} - 4ab + {b^2}$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow 4{a^2} - 4ab + {b^2} = {\left( {2a} \right)^2} - 2\left( {2a} \right)\left( b \right) + {b^2}\]
By comparing with ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {(a - b)^2}$, we will have
\[ \Rightarrow 4{a^2} - 4ab + {b^2} = {\left( {2a - b} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 4{a^2} - 4ab + {b^2} = \left( {2a - b} \right)\left( {2a - b} \right)\]
${p^2}{y^2} - 2py + 1$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow {p^2}{y^2} - 2py + 1 = {\left( {py} \right)^2} - 2\left( {py} \right)\left( 1 \right) + {1^2}\]
By comparing with ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {(a - b)^2}$, we will have
\[ \Rightarrow {p^2}{y^2} - 2py + 1 = {\left( {py - 1} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {p^2}{y^2} - 2py + 1 = \left( {py - 1} \right)\left( {py - 1} \right)\]
${a^2}{y^2} - 2aby + {b^2}$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow {a^2}{y^2} - 2aby + {b^2} = {\left( {ay} \right)^2} - 2\left( {ay} \right)\left( b \right) + {b^2}\]
By comparing with ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {(a - b)^2}$, we will have
\[ \Rightarrow {a^2}{y^2} - 2aby + {b^2} = {\left( {ay - b} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {a^2}{y^2} - 2aby + {b^2} = \left( {ay - b} \right)\left( {ay - b} \right)\]
$9{x^2} - 12x + 4$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} - 12x + 4 = {\left( {3x} \right)^2} - 2\left( {3x} \right)\left( 2 \right) + {2^2}\]
By comparing with ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {(a - b)^2}$, we will have
\[ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} - 12x + 4 = {\left( {3x - 2} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} - 12x + 4 = \left( {3x - 2} \right)\left( {3x - 2} \right)\]
$4{y^2} - 12y + 9$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow 4{y^2} - 12y + 9 = {\left( {2y} \right)^2} - 2\left( {2y} \right)\left( 3 \right) + {3^2}\]
By comparing with ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {(a - b)^2}$, we will have
\[ \Rightarrow 4{y^2} - 12y + 9 = {\left( {2y - 3} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 4{y^2} - 12y + 9 = \left( {2y - 3} \right)\left( {2y - 3} \right)\]
$\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{4} - 2x + 4$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{4} - 2x + 4 = {\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)^2} - 2\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)\left( 2 \right) + {2^2}\]
By comparing with ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {(a - b)^2}$, we will have
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{4} - 2x + 4 = {\left( {\dfrac{x}{2} - 2} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{4} - 2x + 4 = \left( {\dfrac{x}{2} - 2} \right)\left( {\dfrac{x}{2} - 2} \right)\]
${a^2}{y^3} - 2ab{y^2} + {b^2}y$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow {a^2}{y^3} - 2ab{y^2} + {b^2}y = y\left( {{a^2}{y^2} - 2aby + {b^2}} \right)\]\[ \Rightarrow {a^2}{y^3} - 2ab{y^2} + {b^2}y = y\left( {{{\left( {ay} \right)}^2} - 2\left( {ay} \right)\left( b \right) + {b^2}} \right)\]
By comparing with ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {(a - b)^2}$, we will have
\[ \Rightarrow {a^2}{y^3} - 2ab{y^2} + {b^2}y = y{\left( {ay - b} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {a^2}{y^3} - 2ab{y^2} + {b^2}y = y\left( {ay - b} \right)\left( {ay - b} \right)\]
$9{y^2} - 4xy + \dfrac{{4{x^2}}}{9}$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow 9{y^2} - 4xy + \dfrac{{4{x^2}}}{9} = {\left( {3y} \right)^2} - 2\left( {\dfrac{{2x}}{3}} \right)\left( {3y} \right) + {\left( {\dfrac{{2x}}{3}} \right)^2}\]
By comparing with ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {(a - b)^2}$, we will have
\[ \Rightarrow 9{y^2} - 4xy + \dfrac{{4{x^2}}}{9} = {\left( {3y - \dfrac{{2x}}{3}} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 9{y^2} - 4xy + \dfrac{{4{x^2}}}{9} = \left( {3y - \dfrac{{2x}}{3}} \right)\left( {3y - \dfrac{{2x}}{3}} \right)\]
91. Factorise the following.
${x^2} + 15x + 26$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 15x + 26 = {x^2} + 13x + 2x + 26\]
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 15x + 26 = x\left( {x + 13} \right) + 2\left( {x + 13} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 15x + 26 = \left( {x + 13} \right)\left( {x + 2} \right)\]
${x^2} + 9x + 20$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 9x + 20 = {x^2} + 4x + 5x + 20$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 9x + 20 = x\left( {x + 4} \right) + 5\left( {x + 4} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 9x + 20 = \left( {x + 4} \right)\left( {x + 5} \right)$
${y^2} + 18x + 65$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} + 18y + 65 = {y^2} + 5y + 13y + 65$
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} + 18y + 65 = y\left( {y + 5} \right) + 13\left( {y + 5} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} + 18y + 65 = \left( {y + 5} \right)\left( {y + 13} \right)$
${p^2} + 14p + 13$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {p^2} + 14p + 13 = {p^2} + 13p + 1p + 13$
$ \Rightarrow {p^2} + 14p + 13 = p\left( {p + 13} \right) + 1\left( {p + 13} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {p^2} + 14p + 13 = \left( {p + 13} \right)\left( {p + 1} \right)$
${y^2} + 4y - 21$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} + 4y - 21 = {y^2} + 7y - 3y - 21$
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} + 4y - 21 = y\left( {y + 7} \right) - 3\left( {y + 7} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} + 4y - 21 = \left( {y + 7} \right)\left( {y - 3} \right)$
${y^2} - 2y - 15$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} - 2y - 15 = {y^2} - 5y + 3y - 15$
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} - 2y - 15 = y\left( {y - 5} \right) + 3\left( {y - 5} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} - 2y - 15 = \left( {y - 5} \right)\left( {y + 3} \right)$
$18 + 11x + {x^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 18 + 11x + {x^2} = {x^2} + 11x + 18$
$ \Rightarrow 18 + 11x + {x^2} = {x^2} + 9x + 2x + 18$
$ \Rightarrow 18 + 11x + {x^2} = x\left( {x + 9} \right) + 2\left( {x + 9} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 18 + 11x + {x^2} = \left( {x + 9} \right)\left( {x + 2} \right)$
${x^2} - 10x + 21$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 10x + 21 = {x^2} - 7x - 3x + 21$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 10x + 21 = x\left( {x - 7} \right) - 3\left( {x - 7} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 10x + 21 = \left( {x - 7} \right)\left( {x - 3} \right)$
${x^2} = 17x + 60$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 17x - 60 = {x^2} - 20x + 3x - 60$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 17x - 60 = x\left( {x - 20} \right) + 3\left( {x - 20} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 17x - 60 = \left( {x - 20} \right)\left( {x + 3} \right)$
${x^2} + 4x - 77$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 4x - 77 = {x^2} + 11x - 7x - 77$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 4x - 77 = x\left( {x + 11} \right) - 7\left( {x + 11} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 4x - 77 = \left( {x + 11} \right)\left( {x - 7} \right)$
${y^2} + 7y + 12$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} + 7y + 12 = {y^2} + 3y + 4y + 12$
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} + 7y + 12 = y\left( {y + 3} \right) + 4\left( {y + 3} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} + 7y + 12 = \left( {y + 3} \right)\left( {y + 4} \right)$
${p^2} - 13p - 30$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {p^2} - 13p - 30 = {p^2} - 15p + 2p - 30$
$ \Rightarrow {p^2} - 13p - 30 = p\left( {p - 15} \right) + 2\left( {p - 15} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {p^2} - 13p - 30 = \left( {p - 15} \right)\left( {p + 2} \right)$
${a^2} - 16p - 80$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {a^2} - 16p - 80 = {a^2} - 16\left( {p + 5} \right)$
As we can see that we cannot factor further.
92. Factorise the following using the identity ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$.
${x^2} - 9$
Ans:
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-9={{x}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}}\]
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 9 = \left( {x + 3} \right)\left( {x - 3} \right)$
$4{x^2} - 25{y^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} - 25{y^2} = {\left( {2x} \right)^2} - {\left( {5y} \right)^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} - 25{y^2} = \left( {2x + 5y} \right)\left( {2x - 5y} \right)$
$4{x^2} - 49{y^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} - 49{y^2} = {\left( {2x} \right)^2} - {\left( {7y} \right)^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} - 49{y^2} = \left( {2x + 7y} \right)\left( {2x - 7y} \right)$
$3{a^2}{b^3} - 27{a^4}b$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 3{a^2}{b^3} - 27{a^4}b = 3{a^2}b\left( {{b^2} - 9{a^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 3{a^2}{b^3} - 27{a^4}b = 3{a^2}b\left( {{b^2} - {{\left( {3a} \right)}^2}} \right)$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
\[ \Rightarrow 3{a^2}{b^3} - 27{a^4}b = 3{a^2}b\left( {b + 3a} \right)\left( {b - 3a} \right)\]
$28a{y^2} - 175a{x^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 28a{y^2} - 175a{x^2} = 7a\left( {4{y^2} - 25{x^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 28a{y^2} - 175a{x^2} = 7a\left( {{{\left( {2y} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {5x} \right)}^2}} \right)$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow 28a{y^2} - 175a{x^2} = 7a\left( {2y + 5x} \right)\left( {2y - 5x} \right)$
$9{x^2} - 1$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} - 1 = {\left( {3x} \right)^2} - {1^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} - 1 = \left( {3x + 1} \right)\left( {3x - 1} \right)$
$25a{x^2} - 25a$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 25a{x^2} - 25a = a\left( {25{x^2} - 25} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 25a{x^2} - 25a = a\left( {{{\left( {5x} \right)}^2} - {5^2}} \right)$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow 25a{x^2} - 25a = a\left( {5x + 5} \right)\left( {5x - 5} \right)$
$\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{9} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{25}}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{9} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{25}} = {\left( {\dfrac{x}{3}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{y}{5}} \right)^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{9} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{25}} = \left( {\dfrac{x}{3} + \dfrac{y}{5}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{x}{3} - \dfrac{y}{5}} \right)$
$\dfrac{{2{p^2}}}{{25}} - 32{q^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2{p^2}}}{{25}} - 32{q^2} = 2\left( {\dfrac{{{p^2}}}{{25}} - 16{q^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2{p^2}}}{{25}} - 32{q^2} = 2\left( {{{\left( {\dfrac{p}{5}} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {4q} \right)}^2}} \right)$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2{p^2}}}{{25}} - 32{q^2} = 2\left( {\dfrac{p}{5} + 4q} \right)\left( {\dfrac{p}{5} - 4q} \right)$
$49{x^2} - 36{y^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 49{x^2} - 36{y^2} = {\left( {7x} \right)^2} - {\left( {6y} \right)^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
\[ \Rightarrow 49{x^2} - 36{y^2} = \left( {7x + 6y} \right)\left( {7x - 6y} \right)\]
${y^3} - \dfrac{y}{9}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {y^3} - \dfrac{y}{9} = y\left( {{y^2} - \dfrac{1}{9}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {y^3} - \dfrac{y}{9} = y\left( {{y^2} - {{\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}} \right)}^2}} \right)$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow {y^3} - \dfrac{y}{9} = y\left( {y + \dfrac{1}{3}} \right)\left( {y - \dfrac{1}{3}} \right)$
$\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{25}} - 625$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{25}} - 625 = {\left( {\dfrac{x}{5}} \right)^2} - {\left( {25} \right)^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{25}} - 625 = \left( {\dfrac{x}{5} + 25} \right)\left( {\dfrac{x}{5} - 25} \right)$
$\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{8} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{18}}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{8} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{18}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{4} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{9}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{8} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{18}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{{\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {\dfrac{y}{3}} \right)}^2}} \right)$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{8} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{18}} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {\dfrac{x}{2} + \dfrac{y}{3}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{x}{2} - \dfrac{y}{3}} \right)$
$\dfrac{{4{x^2}}}{9} - \dfrac{{9{y^2}}}{{16}}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{4{x^2}}}{9} - \dfrac{{9{y^2}}}{{16}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{2x}}{3}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{{3y}}{4}} \right)^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{4{x^2}}}{9} - \dfrac{{9{y^2}}}{{16}} = \left( {\dfrac{{2x}}{3} + \dfrac{{3y}}{4}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{2x}}{3} - \dfrac{{3y}}{4}} \right)$
$\dfrac{{{x^3}y}}{9} - \dfrac{{x{y^3}}}{{16}}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3}y}}{9} - \dfrac{{x{y^3}}}{{16}} = xy\left( {\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{9} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{16}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3}y}}{9} - \dfrac{{x{y^3}}}{{16}} = xy\left( {{{\left( {\dfrac{x}{3}} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {\dfrac{y}{4}} \right)}^2}} \right)$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3}y}}{9} - \dfrac{{x{y^3}}}{{16}} = xy\left( {\dfrac{x}{3} + \dfrac{y}{4}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{x}{3} - \dfrac{y}{4}} \right)$
$1331{x^3}y - 11{y^3}x$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow 1331{x^3}y - 11{y^3}x = 11xy\left( {121{x^2} - {y^2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 1331{x^3}y - 11{y^3}x = 11xy\left( {{{\left( {11x} \right)}^2} - {y^2}} \right)\]
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
\[ \Rightarrow 1331{x^3}y - 11{y^3}x = 11xy\left( {11x + y} \right)\left( {11x - y} \right)\]
$\dfrac{1}{{36}}{a^2}{b^2} - \dfrac{{16}}{{49}}{b^2}{c^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{36}}{a^2}{b^2} - \dfrac{{16}}{{49}}{b^2}{c^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{1}{6}ab} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{4}{7}bc} \right)^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{36}}{a^2}{b^2} - \dfrac{{16}}{{49}}{b^2}{c^2} = \left( {\dfrac{1}{6}ab + \dfrac{4}{7}bc} \right)\left( {\dfrac{1}{6}ab - \dfrac{4}{7}bc} \right)$
${a^4} - {(a - b)^4}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {a^4} - {(a - b)^4} = {\left( {{a^2}} \right)^2} - {\left( {{{(a - b)}^2}} \right)^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow {a^4} - {(a - b)^4} = \left( {{a^2} + {{(a - b)}^2}} \right)\left( {{a^2} - {{(a - b)}^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {a^4} - {(a - b)^4} = \left( {{a^2} + {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab} \right)\left( {{a^2} - {a^2} - {b^2} + 2ab} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {a^4} - {(a - b)^4} = \left( {2{a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab} \right)\left( { - {b^2} + 2ab} \right)$
${x^4} - 1$
Ans:
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{4}}-1={{\left( {{x}^{2}} \right)}^{2}}-{{1}^{2}}\]
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow {x^4} - 1 = \left( {{x^2} + 1} \right)\left( {{x^2} - 1} \right)$
${y^4} - 625$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {y^4} - 625 = {\left( {{y^2}} \right)^2} - {\left( {25} \right)^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow {y^4} - 625 = \left( {{y^2} + 25} \right)\left( {{y^2} - 25} \right)$
${p^5} - 16p$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {p^5} - 16p = p\left( {{p^4} - 16} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {p^5} - 16p = p\left( {{{\left( {{p^2}} \right)}^2} - {4^2}} \right)$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow {p^5} - 16p = p\left( {{p^2} + 4} \right)\left( {{p^2} - 4} \right)$
$16{x^4} - 81$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 16{x^4} - 81 = {\left( {4{x^2}} \right)^2} - {9^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow 16{x^4} - 81 = \left( {4{x^2} + 9} \right)\left( {4{x^2} - 9} \right)$
${x^4} - {y^4}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {x^4} - {y^4} = {\left( {{x^2}} \right)^2} - {\left( {{y^2}} \right)^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow {x^4} - {y^4} = \left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right)$
${y^4} - 81$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {y^4} - 81 = {\left( {{y^2}} \right)^2} - {9^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow {y^4} - 81 = \left( {{y^2} + 9} \right)\left( {{y^2} - 9} \right)$
$16{x^4} - 625{y^4}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 16{x^4} - 625{y^4} = {\left( {4{x^2}} \right)^2} - {\left( {25{y^2}} \right)^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
\[ \Rightarrow 16{x^4} - 625{y^4} = \left( {4{x^2} + 25{y^2}} \right)\left( {4{x^2} - 25{y^2}} \right)\]
${(a - b)^2} - {(b - c)^2}$
Ans:
${(a - b)^2} - {(b - c)^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow {(a - b)^2} - {(b - c)^2} = \left( {a - b + \left( {b - c} \right)} \right)\left( {a - b - \left( {b - c} \right)} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(a - b)^2} - {(b - c)^2} = \left( {a - b + b - c} \right)\left( {a - b - b + c} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(a - b)^2} - {(b - c)^2} = \left( {a - c} \right)\left( {a - 2b + c} \right)$
${(x + y)^4} - {(x - y)^4}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {(x + y)^4} - {(x - y)^4} = {\left( {{{(x + y)}^2}} \right)^2} - {\left( {{{(x - y)}^2}} \right)^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow {(x + y)^4} - {(x - y)^4} = \left( {{{(x + y)}^2} + {{(x - y)}^2}} \right)\left( {{{(x + y)}^2} - {{(x - y)}^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {(x + y)^4} - {(x - y)^4} = \left( {2{x^2} + 2{y^2}} \right)\left( {4xy} \right)$
${x^4} - {y^4} + {x^2} - {y^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {x^4} - {y^4} + {x^2} - {y^2} = \left( {{x^4} - {y^4}} \right) + \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {x^4} - {y^4} + {x^2} - {y^2} = \left( {{{\left( {{x^2}} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {{y^2}} \right)}^2}} \right) + \left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right)$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
\[ \Rightarrow {x^4} - {y^4} + {x^2} - {y^2} = \left[ {\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left( {{x^2} - {y^2}} \right)} \right] + \left[ {\left( {x + y} \right)\left( {x - y} \right)} \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow {x^4} - {y^4} + {x^2} - {y^2} = \left[ {\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right)\left( {x + y} \right)\left( {x - y} \right)} \right] + \left[ {\left( {x + y} \right)\left( {x - y} \right)} \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow {x^4} - {y^4} + {x^2} - {y^2} = \left( {x + y} \right)\left( {x - y} \right)\left[ {\left( {{x^2} + {y^2}} \right) + 1} \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow {x^4} - {y^4} + {x^2} - {y^2} = \left( {x + y} \right)\left( {x - y} \right)\left[ {{x^2} + {y^2} + 1} \right]\]
$8{a^3} - 2a$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 8{a^3} - 2a = 2a\left( {4{a^2} - 1} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 8{a^3} - 2a = 2a\left( {{{\left( {2a} \right)}^2} - {1^2}} \right)$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
\[ \Rightarrow 8{a^3} - 2a = 2a\left( {2a + 1} \right)\left( {2a - 1} \right)\]
${x^2} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{100}}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{100}} = {x^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{y}{{10}}} \right)^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{100}} = \left( {x + \dfrac{y}{{10}}} \right)\left( {x - \dfrac{y}{{10}}} \right)$
$9{x^2} - {(3y + z)^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} - {(3y + z)^2} = {\left( {3x} \right)^2} - {(3y + z)^2}$
By comparing it with ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$ we have,
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} - {(3y + z)^2} = \left( {3x + \left( {3y + z} \right)} \right)\left( {3x - \left( {3y + z} \right)} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} - {(3y + z)^2} = \left( {3x + 3y + z} \right)\left( {3x - 3y - z} \right)$
93. The following expressions are the areas of rectangles. Find the possible lengths and breadths of these rectangles.
${x^2} - 6x + 8$
Ans: We know that Area of a rectangle = length \[ \times \] breadth.
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 6x + 8 = {x^2} - 4x - 2x + 8$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 6x + 8 = x\left( {x - 4} \right) - 2\left( {x - 4} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 6x + 8 = \left( {x - 4} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)$
Thus, we have expressed area as a multiple of length and breadth.
Hence, length and breadth is $\left( {x - 4} \right)$ and $\left( {x - 2} \right)$.
${x^2} - 3x + 2$
Ans: We know that Area of a rectangle = length \[ \times \] breadth.
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 3x + 2 = {x^2} - 2x - x + 2$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 3x + 2 = x\left( {x - 2} \right) - 1\left( {x - 2} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 3x + 2 = \left( {x - 2} \right)\left( {x - 1} \right)$
Thus, we have expressed area as a multiple of length and breadth.
Hence, length and breadth is $\left( {x - 2} \right)$ and $\left( {x - 1} \right)$.
${x^2} - 7x + 10$
Ans: We know that Area of a rectangle = length \[ \times \] breadth.
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 7x + 10 = {x^2} - 5x - 2x + 10$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 7x + 10 = x\left( {x - 5} \right) - 2\left( {x - 5} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 7x + 10 = \left( {x - 5} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)$
Thus, we have expressed area as a multiple of length and breadth.
Hence, length and breadth is $\left( {x - 5} \right)$ and $\left( {x - 2} \right)$.
${x^2} + 19x - 20$
Ans: We know that Area of a rectangle = length \[ \times \] breadth.
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 19x - 20 = {x^2} + 20x - x - 20$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 19x - 20 = x\left( {x + 20} \right) - 1\left( {x + 20} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 19x - 20 = \left( {x + 20} \right)\left( {x - 1} \right)$
Thus, we have expressed area as a multiple of length and breadth.
Hence, length and breadth is $\left( {x + 20} \right)$ and $\left( {x - 1} \right)$.
${x^2} + 9x + 20$
Ans: We know that Area of a rectangle = length \[ \times \] breadth.
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 9x + 20 = {x^2} + 5x + 4x + 20$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 9x + 20 = x\left( {x + 5} \right) + 4\left( {x + 5} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 9x + 20 = \left( {x + 5} \right)\left( {x + 4} \right)$
Thus, we have expressed area as a multiple of length and breadth.
Hence, length and breadth is $\left( {x + 5} \right)$ and $\left( {x + 4} \right)$
94. Carry out the following divisions:
$51{x^3}{y^2}z \div 17xyz$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow 51{x^3}{y^2}z \div 17xyz = \dfrac{{51{x^3}{y^2}z}}{{17xyz}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 51{x^3}{y^2}z \div 17xyz = 3{x^2}y\]
$76{x^3}y{z^3} \div 19{x^2}{y^2}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 76{x^3}y{z^3} \div 19{x^2}{y^2} = \dfrac{{76{x^3}y{z^3}}}{{19{x^2}{y^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow 76{x^3}y{z^3} \div 19{x^2}{y^2} = \dfrac{{4x{z^3}}}{y}$
$17a{b^2}{c^3} \div \left( { - ab{c^2}} \right)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 17a{b^2}{c^3} \div \left( { - ab{c^2}} \right) = \dfrac{{17a{b^2}{c^3}}}{{ - ab{c^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow 17a{b^2}{c^3} \div \left( { - ab{c^2}} \right) = - 17bc$
$ - 121{p^3}{q^3}{r^3} \div \left( { - 11x{y^2}{z^3}} \right)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow - 121{p^3}{q^3}{r^3} \div \left( { - 11x{y^2}{z^3}} \right) = \dfrac{{ - 121{p^3}{q^3}{r^3}}}{{ - 11x{y^2}{z^3}}}$
$ \Rightarrow - 121{p^3}{q^3}{r^3} \div \left( { - 11x{y^2}{z^3}} \right) = \dfrac{{11{p^3}{q^3}{r^3}}}{{x{y^2}{z^3}}}$
95. Perform the following divisions:
$\left( {3pqr - 6{p^2}{q^2}{r^2}} \right) \div 3pq$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {3pqr - 6{p^2}{q^2}{r^2}} \right) \div 3pq = \dfrac{{3pqr - 6{p^2}{q^2}{r^2}}}{{3pq}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {3pqr - 6{p^2}{q^2}{r^2}} \right) \div 3pq = \dfrac{{3pqr}}{{3pq}} - \dfrac{{6{p^2}{q^2}{r^2}}}{{3pq}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {3pqr - 6{p^2}{q^2}{r^2}} \right) \div 3pq = r - 2pq{r^2}$
$\left( {a{x^3} - b{x^2} + cx} \right) \div ( - dx)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {a{x^3} - b{x^2} + cx} \right) \div ( - dx) = \dfrac{{a{x^3} - b{x^2} + cx}}{{ - dx}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {a{x^3} - b{x^2} + cx} \right) \div ( - dx) = \dfrac{{x\left( {a{x^2} - bx + c} \right)}}{{ - dx}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {a{x^3} - b{x^2} + cx} \right) \div ( - dx) = \dfrac{{\left( {a{x^2} - bx + c} \right)}}{{ - d}}$
$\left( {{x^3}{y^3} + {x^2}{y^3} - x{y^4} + xy} \right) \div xy$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^3}{y^3} + {x^2}{y^3} - x{y^4} + xy} \right) \div xy = \dfrac{{{x^3}{y^3} + {x^2}{y^3} - x{y^4} + xy}}{{xy}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^3}{y^3} + {x^2}{y^3} - x{y^4} + xy} \right) \div xy = \dfrac{{xy\left( {{x^2}{y^2} + x{y^2} - {y^3} + 1} \right)}}{{xy}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^3}{y^3} + {x^2}{y^3} - x{y^4} + xy} \right) \div xy = \left( {{x^2}{y^2} + x{y^2} - {y^3} + 1} \right)$
$( - qrxy + pryz - rxyz) \div ( - xyz)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - qrxy + pryz - rxyz} \right) \div ( - xyz) = \dfrac{{ - qrxy + pryz - rxyz}}{{ - xyz}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - qrxy + pryz - rxyz} \right) \div ( - xyz) = \dfrac{{y\left( { - qrx + prz - rxz} \right)}}{{ - xyz}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( { - qrxy + pryz - rxyz} \right) \div ( - xyz) = \dfrac{{ - qrx + prz - rxz}}{{ - xz}}$
96. Factorise the expressions and divide them as directed:
$\left( {{x^2} - 22x + 117} \right) \div (x - 13)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} - 22x + 117} \right) \div (x - 13) = \dfrac{{{x^2} - 22x + 117}}{{x - 13}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} - 22x + 117} \right) \div (x - 13) = \dfrac{{{x^2} - 9x - 13x + 117}}{{x - 13}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} - 22x + 117} \right) \div (x - 13) = \dfrac{{x\left( {x - 9} \right) - 13\left( {x - 9} \right)}}{{x - 13}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} - 22x + 117} \right) \div (x - 13) = \dfrac{{\left( {x - 9} \right)\left( {x - 13} \right)}}{{x - 13}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} - 22x + 117} \right) \div (x - 13) = \left( {x - 9} \right)$
$\left( {{x^3} + {x^2} - 132x} \right) \div x(x - 11)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^3} + {x^2} - 132x} \right) \div x(x - 11) = \dfrac{{{x^3} + {x^2} - 132x}}{{x(x - 11)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^3} + {x^2} - 132x} \right) \div x(x - 11) = \dfrac{{x\left( {{x^2} + x - 132} \right)}}{{x(x - 11)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^3} + {x^2} - 132x} \right) \div x(x - 11) = \dfrac{{{x^2} + 12x - 11x - 132}}{{(x - 11)}}$
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^3} + {x^2} - 132x} \right) \div x(x - 11) = \dfrac{{x\left( {x + 12} \right) - 11\left( {x + 12} \right)}}{{(x - 11)}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^3} + {x^2} - 132x} \right) \div x(x - 11) = \dfrac{{\left( {x + 12} \right)\left( {x - 11} \right)}}{{(x - 11)}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^3} + {x^2} - 132x} \right) \div x(x - 11) = \left( {x + 12} \right)\]
$\left( {2{x^3} - 12{x^2} + 16x} \right) \div (x - 2)(x - 4)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {2{x^3} - 12{x^2} + 16x} \right) \div (x - 2)(x - 4) = \dfrac{{2{x^3} - 12{x^2} + 16x}}{{(x - 2)(x - 4)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {2{x^3} - 12{x^2} + 16x} \right) \div (x - 2)(x - 4) = \dfrac{{2x\left( {{x^2} - 6x + 8} \right)}}{{(x - 2)(x - 4)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {2{x^3} - 12{x^2} + 16x} \right) \div (x - 2)(x - 4) = \dfrac{{2x\left( {{x^2} - 2x - 4x + 8} \right)}}{{(x - 2)(x - 4)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {2{x^3} - 12{x^2} + 16x} \right) \div (x - 2)(x - 4) = \dfrac{{2x\left( {x\left( {x - 2} \right) - 4\left( {x - 2} \right)} \right)}}{{(x - 2)(x - 4)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {2{x^3} - 12{x^2} + 16x} \right) \div (x - 2)(x - 4) = \dfrac{{2x\left( {x - 4} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}{{(x - 2)(x - 4)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {2{x^3} - 12{x^2} + 16x} \right) \div (x - 2)(x - 4) = 2x$
$\left( {9{x^2} - 4} \right) \div (3x + 2)$
Ans:
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {9{x^2} - 4} \right) \div (3x + 2) = \dfrac{{9{x^2} - 4}}{{3x + 2}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {9{x^2} - 4} \right) \div (3x + 2) = \dfrac{{{{\left( {3x} \right)}^2} - {2^2}}}{{3x + 2}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {9{x^2} - 4} \right) \div (3x + 2) = \dfrac{{\left( {3x + 2} \right)\left( {3x - 2} \right)}}{{3x + 2}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {9{x^2} - 4} \right) \div (3x + 2) = \left( {3x - 2} \right)\]
$\left( {3{x^2} - 48} \right) \div (x - 4)$
Ans:
$\left( {3{x^2} - 48} \right) \div (x - 4) = \dfrac{{3{x^2} - 48}}{{x - 4}}$
$\left( {3{x^2} - 48} \right) \div (x - 4) = \dfrac{{3\left( {{x^2} - 16} \right)}}{{x - 4}}$
$\left( {3{x^2} - 48} \right) \div (x - 4) = \dfrac{{3\left( {{x^2} - {4^2}} \right)}}{{x - 4}}$
$\left( {3{x^2} - 48} \right) \div (x - 4) = \dfrac{{3\left( {x + 4} \right)\left( {x - 4} \right)}}{{x - 4}}$
$\left( {3{x^2} - 48} \right) \div (x - 4) = 3\left( {x + 4} \right)$
$\left( {{x^4} - 16} \right) \div {x^3} + 2{x^2} + 4x + 8$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^4} - 16} \right) \div {x^3} + 2{x^2} + 4x + 8 = \dfrac{{{x^4} - 16}}{{{x^3} + 2{x^2} + 4x + 8}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^4} - 16} \right) \div {x^3} + 2{x^2} + 4x + 8 = \dfrac{{{{\left( {{x^2}} \right)}^2} - {4^2}}}{{{x^2}\left( {x + 2} \right) + 4\left( {x + 2} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^4} - 16} \right) \div {x^3} + 2{x^2} + 4x + 8 = \dfrac{{\left( {{x^2} + 4} \right)\left( {{x^2} - 4} \right)}}{{\left( {x + 2} \right)\left( {{x^2} + 4} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^4} - 16} \right) \div {x^3} + 2{x^2} + 4x + 8 = \dfrac{{\left( {{x^2} - 4} \right)}}{{\left( {x + 2} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^4} - 16} \right) \div {x^3} + 2{x^2} + 4x + 8 = \dfrac{{\left( {{x^2} - {2^2}} \right)}}{{\left( {x + 2} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^4} - 16} \right) \div {x^3} + 2{x^2} + 4x + 8 = \dfrac{{\left( {x + 2} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}{{\left( {x + 2} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^4} - 16} \right) \div {x^3} + 2{x^2} + 4x + 8 = \left( {x - 2} \right)$
$\left( {3{x^4} - 1875} \right) \div \left( {3{x^2} - 75} \right)$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {3{x^4} - 1875} \right) \div \left( {3{x^2} - 75} \right) = \dfrac{{3{x^4} - 1875}}{{3{x^2} - 75}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {3{x^4} - 1875} \right) \div \left( {3{x^2} - 75} \right) = \dfrac{{3\left( {{x^4} - 625} \right)}}{{3\left( {{x^2} - 25} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {3{x^4} - 1875} \right) \div \left( {3{x^2} - 75} \right) = \dfrac{{3\left( {{{\left( {{x^2}} \right)}^2} - {{25}^2}} \right)}}{{3\left( {{x^2} - 25} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {3{x^4} - 1875} \right) \div \left( {3{x^2} - 75} \right) = \dfrac{{3\left( {{x^2} + 25} \right)\left( {{x^2} - 25} \right)}}{{3\left( {{x^2} - 25} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {3{x^4} - 1875} \right) \div \left( {3{x^2} - 75} \right) = 3\left( {{x^2} + 25} \right)$
97. The area of a square is given by $4{x^2} + 12xy + 9{y^2}$. Find the side of the square.
Ans: We know that the area of the square = (Side)2
Now
$ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} + 12xy + 9{y^2} = {\left( {2x} \right)^2} + 2\left( {2x} \right)\left( {3y} \right) + {\left( {3y} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} + 12xy + 9{y^2} = {\left( {2x + 3y} \right)^2}$
That is Area of the square is $\left( {2x + 3y} \right)$
98. The area of a square is $9{x^2} + 24xy + 16{y^2}$. Find the side of the square.
Ans: We know that the area of the square = (Side)2
Now,
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} + 24xy + 16{y^2} = {\left( {3x} \right)^2} + 2\left( {3x} \right)\left( {4y} \right) + {\left( {4y} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 9{x^2} + 24xy + 16{y^2} = {\left( {3x + 4y} \right)^2}$
That is Area of the square is $\left( {3x + 4y} \right)$
99. The area of a rectangle is ${x^2} + 7x + 12$. If its breadth is $(x + 3)$, then find its length.
Ans: We know that the area of rectangle is the product of its length and breadth.
\[A = Length \times Breadth\]
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 7x + 12 = Length \times (x + 3)$
$ \Rightarrow Length = \dfrac{{{x^2} + 7x + 12}}{{(x + 3)}}$
$ \Rightarrow Length = \dfrac{{{x^2} + 3x + 4x + 12}}{{(x + 3)}}$
$ \Rightarrow Length = \dfrac{{x\left( {x + 3} \right) + 4\left( {x + 3} \right)}}{{(x + 3)}}$
$ \Rightarrow Length = \dfrac{{\left( {x + 3} \right)\left( {x + 4} \right)}}{{(x + 3)}}$
$ \Rightarrow Length = \left( {x + 4} \right)$
100. The curved surface area of a cylinder is $2\pi \left( {{y^2} - 7y + 12} \right)$ and its radius is $(y - 3)$. Find the height of the cylinder (C.S.A. of cylinder = $2\pi rh$).
Ans:
Given C.S.A. of cylinder = $2\pi rh$, Where h is height and r is the radius.
Then,
$2\pi \left( {{y^2} - 7y + 12} \right) = 2\pi \left( {y - 3} \right)h$
\[ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{2\pi \left( {{y^2} - 7y + 12} \right)}}{{2\pi \left( {y - 3} \right)}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{2\pi \left( {{y^2} - 3y - 4y + 12} \right)}}{{2\pi \left( {y - 3} \right)}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{2\pi \left( {y\left( {y - 3} \right) - 4\left( {y - 4} \right)} \right)}}{{2\pi \left( {y - 3} \right)}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{2\pi \left( {\left( {y - 3} \right)\left( {y - 4} \right)} \right)}}{{2\pi \left( {y - 3} \right)}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow h = \left( {y - 4} \right)\]
101. The area of a circle is given by the expression $\pi {x^2} + 6\pi x + 9\pi $. Find the radius of the circle.
Ans: We know that the area of the circle is \[\pi {r^2}\], where r is the radius.
Then,
$ \Rightarrow \pi {x^2} + 6\pi x + 9\pi = \pi {r^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \pi \left( {{x^2} + 6x + 9} \right) = \pi {r^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {r^2} = \left( {{x^2} + 6x + 9} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {r^2} = \left( {{x^2} + 2\left( x \right)\left( 3 \right) + {3^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {r^2} = {\left( {x + 3} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow r = \left( {x + 3} \right)$
102. The sum of the first $n$ natural numbers is given by the expression $\dfrac{{{n^2}}}{2} + \dfrac{n}{2}.$ Factorise this expression.
Ans: Given,
The sum of first n natural number is $\dfrac{{{n^2}}}{2} + \dfrac{n}{2}.$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{n^2}}}{2} + \dfrac{n}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{n^2} + n} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{n^2}}}{2} + \dfrac{n}{2} = \dfrac{n}{2}\left( {n + 1} \right)\]
103. The sum of $(x + 5)$ observations is ${x^4} - 625$. Find the mean of the observations.
Ans: We know that
\[Mean = \dfrac{{Sum{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}observation}}{{number{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}observation}}\]
\[Mean = \dfrac{{{x^4} - 625}}{{\left( {x + 5} \right)}}\]
\[Mean = \dfrac{{{{\left( {{x^2}} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {25} \right)}^2}}}{{\left( {x + 5} \right)}}\]
\[Mean = \dfrac{{\left( {{x^2} + 25} \right)\left( {{x^2} - 25} \right)}}{{\left( {x + 5} \right)}}\]
\[Mean = \dfrac{{\left( {{x^2} + 25} \right)\left( {{x^2} - {5^2}} \right)}}{{\left( {x + 5} \right)}}\]
\[Mean = \dfrac{{\left( {{x^2} + 25} \right)\left( {x + 5} \right)\left( {x - 5} \right)}}{{\left( {x + 5} \right)}}\]
\[Mean = \left( {{x^2} + 25} \right)\left( {x - 5} \right)\]
104. The height of a triangle is ${x^4} + {y^4}$ and its base is $14{\kern 1pt} x{\kern 1pt} y$. Find the area of the triangle.
Ans: We know that the area of triangle,
\[ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times height \times base\]
\[ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left( {{x^4} + {y^4}} \right) \times \left( {14{\kern 1pt} x{\kern 1pt} y} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow A = 7xy\left( {{x^4} + {y^4}} \right)\]
105. The cost of a chocolate is Rs $(x + y)$ and Rohit bought $(x + y)$ chocolates. Find the total amount paid by him in terms of $x$. If x = 10, find the amount paid by him.
Ans:
The cost of chocolate is Rs $(x + y)$.
Rohit bought $(x + y)$ chocolates.
The total amount paid by him will be,
$ \Rightarrow (x + y) \times (x + y)$
$ \Rightarrow {(x + y)^2}$
If x = 10 then,
$ \Rightarrow {(10 + y)^2}$
106. The base of a parallelogram is (2x+3 units) and the corresponding height is ( 2x-3 units). Find the area of the parallelogram in terms of $x$. What will be the area of the parallelogram of x = 30 units?
Ans:
We know that the area of parallelogram is
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{A}} = Base \times Height\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{A}} = \left( {2x + 3} \right) \times \left( {2x - 3} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{A}} = {\left( {2x} \right)^2} - {\left( 3 \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{A}} = 4{x^2} - 9\]
Here, x = 30,
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{A}} = 4{\left( {30} \right)^2} - 9\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{A}} = 4\left( {900} \right) - 9\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{A}} = 3600 - 9\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{A}} = 3591\,\]
Area is 3591 square units.
107. The radius of a circle is $7ab - 7bc - 14ac$. Find the circumference of the circle. $\left( {\pi = \dfrac{{22}}{7}} \right)$
Ans:
The circumference of the circle is
\[ \Rightarrow C = 2\pi \left( {7ab - 7bc - 14ac} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow C = 2 \times \dfrac{{22}}{7}\left( {7ab - 7bc - 14ac} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow C = 2 \times \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 7\left( {ab - bc - 2ac} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow C = 2 \times 22\left( {ab - bc - 2ac} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow C = 44\left( {ab - bc - 2ac} \right)\]
108. If $p + q = 12$ and $pq = 22$, then find ${p^2} + {q^2}$.
Ans: Given,
$p + q = 12 - - - \left( 1 \right)$ and $pq = 22 - - - \left( 2 \right)$.
Squaring on both sides on the equation (1)
${\left( {p + q} \right)^2} = {\left( {12} \right)^2}$
Using the identity \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\],
$ \Rightarrow {p^2} + {q^2} + 2pq = {\left( {12} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {p^2} + {q^2} = {\left( {12} \right)^2} - 2pq$
Using equation 2 we have
$ \Rightarrow {p^2} + {q^2} = {\left( {12} \right)^2} - 2\left( {22} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {p^2} + {q^2} = 144 - 44$
$ \Rightarrow {p^2} + {q^2} = 100$
109. If $a + b = 25$ and ${a^2} + {b^2} = 225$, then find $a{\kern 1pt} b$.
Ans: Given $a + b = 25 - - - (1)$ and ${a^2} + {b^2} = 225 - - - (2)$
Squaring Equation 1 on both sides we have,
${\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {\left( {25} \right)^2}$
${a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab = 625$
Using equation 2 we have,
$ \Rightarrow 225 + 2ab = 625$
$ \Rightarrow 2ab = 625 - 225$
$ \Rightarrow 2ab = 400$
$ \Rightarrow ab = \dfrac{{400}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow ab = 200$
110. If $x - y = 13$ and $xy = 28$, then find ${x^2} + {y^2}$.
Ans: Given, $x - y = 13 - - - (1)$ and $xy = 28 - - - (2)$
Squaring Equation 1 on both sides we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - y} \right)^2} = {\left( {13} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 2xy = {\left( {13} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 2xy = 169$
Using equation 2 we will have
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 2\left( {28} \right) = 169$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 56 = 169$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} = 169 + 56$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} = 225$
111. If $m - n = 16$ and ${m^2} + {n^2} = 400$, then find $m{\mkern 1mu} n$.
Ans: Given $m - n = 16 - - - (1)$ and ${m^2} + {n^2} = 400 - - - (2)$ then
Squaring Equation 1 on both sides we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {m - n} \right)^2} = {\left( {16} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {m^2} + {n^2} - 2mn = {\left( {16} \right)^2}$
Using equation 2 we will have
$ \Rightarrow 400 - 2mn = 256$
$ \Rightarrow - 2mn = 256 - 400$
$ \Rightarrow - 2mn = - 144$
$ \Rightarrow mn = \dfrac{{ - 144}}{{ - 2}}$
$ \Rightarrow mn = 72$
112. If ${a^2} + {b^2} = 74$ and $ab = 35$, then find $a + b$.
Ans: Given ${a^2} + {b^2} = 74 - - - (1)$ and $ab = 35 - - - (2)$.
We know that
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab$
Using equation 1 and using equation 2 we will have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = 74 + 2\left( {35} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = 74 + 70$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = 144$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {a + b} \right) = \pm \sqrt {144} $
$ \Rightarrow a + b = \pm 12$.
113. Verify the following:
(i) $(ab + bc)(ab - bc) + (bc + ca)(bc - ca) + (ca + ab)(ca - ab) = 0$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow (ab + bc)(ab - bc) + (bc + ca)(bc - ca) + (ca + ab)(ca - ab) = 0$
Now we know the identity \[\left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right) = {a^2} - {b^2}\], applying this we will have
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {ab} \right)^2} - {\left( {bc} \right)^2} + {\left( {bc} \right)^2} - {\left( {ca} \right)^2} + {\left( {ca} \right)^2} - {\left( {ab} \right)^2} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{b^2} - {b^2}{c^2} + {b^2}{c^2} - {c^2}{a^2} + {c^2}{a^2} - {a^2}{b^2} = 0$
Grouping the like terms,
$ \Rightarrow {a^2}{b^2} - {a^2}{b^2} - {b^2}{c^2} + {b^2}{c^2} - {c^2}{a^2} + {c^2}{a^2} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow 0 = 0$
Hence, proved.
(ii) $(a + b + c)\left( {{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2} - ab - bc - ca} \right) = {a^3} + {b^3} + {c^3} - 3abc$
Ans: $(a+b+c)\left( {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-ab-bc-ca \right)={{a}^{3}}+{{b}^{3}}+{{c}^{3}}-3abc$
Now, $LHS=(a+b+c)\left( {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-ab-bc-ca \right)$ and $RHS={{a}^{3}}+{{b}^{3}}+{{c}^{3}}-3abc$.
Take LHS.
$\Rightarrow LHS=(a+b+c)\left( {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-ab-bc-ca \right)$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow LHS=a\left( {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-ab-bc-ca \right)+b\left( {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-ab-bc-ca \right) \\
& +c\left( {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-ab-bc-ca \right) \\
\end{align}$
\[\begin{align}
& LHS={{a}^{3}}+a{{b}^{2}}+a{{c}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}b-abc-c{{a}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}b+{{b}^{2}}+b{{c}^{2}}-a{{b}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}c-bca \\
& +{{a}^{2}}c+{{b}^{2}}c+{{c}^{3}}-abc-b{{c}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}a \\
\end{align}\]
Grouping like terms,
\[\begin{align}
& LHS={{a}^{3}}+{{b}^{3}}+{{c}^{3}}+a{{b}^{2}}-a{{b}^{2}}+a{{c}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}a-{{a}^{2}}b+{{a}^{2}}b-c{{a}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}c \\
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,+b{{c}^{2}}-b{{c}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}c+{{b}^{2}}c-abc-abc-bca \\
\end{align}\]
\[LHS={{a}^{3}}+{{b}^{3}}+{{c}^{3}}-3abc\]
That is
\[\Rightarrow LHS=RHS\]
Hence, proved.
(iii) $(p - q)\left( {{p^2} + pq + {q^2}} \right) = {p^3} - {q^3}$
Ans: $(p - q)\left( {{p^2} + pq + {q^2}} \right) = {p^3} - {q^3}$
$LHS = (p - q)\left( {{p^2} + pq + {q^2}} \right)$ and $RHS = {p^3} - {q^3}$
Now take LHS,
$ \Rightarrow LHS = p\left( {{p^2} + pq + {q^2}} \right) - q\left( {{p^2} + pq + {q^2}} \right)$
\[ \Rightarrow LHS = \left( {{p^3} + {p^2}q + p{q^2}} \right) - \left( {q{p^2} + p{q^2} + {q^3}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow LHS = {p^3} + {p^2}q + p{q^2} - q{p^2} - p{q^2} - {q^3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow LHS = {p^3} + {p^2}q - q{p^2} + p{q^2} - p{q^2} - {q^3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow LHS = {p^3} - {q^3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow LHS = RHS\]
Hence, proved.
(iv) $(m + n)\left( {{m^2} - mn + {n^2}} \right) = {m^3} + {n^3}$
Ans: $(m + n)\left( {{m^2} - mn + {n^2}} \right) = {m^3} + {n^3}$
$LHS = (m + n)\left( {{m^2} - mn + {n^2}} \right)$ and $RHS = {m^3} + {n^3}$
Now take LHS,
$ \Rightarrow LHS = m\left( {{m^2} - mn + {n^2}} \right) + n\left( {{m^2} - mn + {n^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = \left( {{m^3} - {m^2}n + m{n^2}} \right) + \left( {n{m^2} - m{n^2} + {n^3}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {m^3} - {m^2}n + m{n^2} + n{m^2} - m{n^2} + {n^3}$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {m^3} + n{m^2} - {m^2}n + m{n^2} - m{n^2} + {n^3}$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {m^3} + {n^3}$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = RHS$
Hence, proved.
(v) $(a + b)(a + b)(a + b) = {a^3} + 3{a^2}b + 3a{b^2} + {b^3}$
Ans: $(a + b)(a + b)(a + b) = {a^3} + 3{a^2}b + 3a{b^2} + {b^3}$
$LHS = (a + b)(a + b)(a + b)$ and $RHS = {a^3} + 3{a^2}b + 3a{b^2} + {b^3}$.
Now take,
$ \Rightarrow LHS = (a + b)(a + b)(a + b)$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {(a + b)^2}(a + b)$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = \left( {{a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab} \right)(a + b)$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = a\left( {{a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab} \right) + b\left( {{a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {a^3} + a{b^2} + 2{a^2}b + {a^2}b + {b^3} + 2a{b^2}$
Grouping like terms,
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {a^3} + {b^3} + 2a{b^2} + a{b^2} + 2{a^2}b + {a^2}b$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {a^3} + 3a{b^2} + 3{a^2}b + {b^3}$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = RHS$
Hence, proved.
(vi) $(a - b)(a - b)(a - b) = {a^3} - 3{a^2}b + 3a{b^2} - {b^3}$
Ans: Given,
$LHS = (a - b)(a - b)(a - b)$ and $RHS = {a^3} - 3{a^2}b + 3a{b^2} - {b^3}$.
Take LHS,
$ \Rightarrow LHS = (a - b)(a - b)(a - b)$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = (a - b){(a - b)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = (a - b)\left( {{a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = a\left( {{a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab} \right) - b\left( {{a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = \left( {{a^3} + a{b^2} - 2{a^2}b} \right) - \left( {{a^2}b + {b^3} - 2a{b^2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {a^3} + a{b^2} - 2{a^2}b - {a^2}b - {b^3} + 2a{b^2}$
Grouping like terms,
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {a^3} - {b^3} + 3a{b^2} - 3{a^2}b$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = RHS$
Hence, proved.
(vii) $\left( {{a^2} - {b^2}} \right)\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right) + \left( {{b^2} - {c^2}} \right)\left( {{b^2} + {c^2}} \right) + \left( {{c^2} - {a^2}} \right)\left( {{c^2} + {a^2}} \right) = 0$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{a^2} - {b^2}} \right)\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right) + \left( {{b^2} - {c^2}} \right)\left( {{b^2} + {c^2}} \right) + \left( {{c^2} - {a^2}} \right)\left( {{c^2} + {a^2}} \right) = 0$
Now we know the identity \[\left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right) = {a^2} - {b^2}\], applying this we will have
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{a^2}} \right)^2} - {\left( {{b^2}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{b^2}} \right)^2} - {\left( {{c^2}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{c^2}} \right)^2} - {\left( {{a^2}} \right)^2} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow {a^4} - {b^4} + {b^4} - {c^4} + {c^4} - {a^4} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow {a^4} - {a^4} - {b^4} + {b^4} - {c^4} + {c^4} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow 0 = 0$
Hence, proved.
(viii) ${(5x + 8)^2} - 160x = {(5x - 8)^2}$
Ans:
$LHS = {(5x + 8)^2} - 160x$ and $RHS = {(5x - 8)^2}$
Take LHS,
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {\left( {5x} \right)^2} + {8^2} + 2\left( {5x} \right)\left( 8 \right) - 160x$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = 25{x^2} + 64 + 80x - 160x$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = 25{x^2} + 64 - 80x$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {\left( {5x} \right)^2} + {8^2} - 2\left( {5x} \right)\left( 8 \right)$
It is of the form \[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\]
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {\left( {5x - 8} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = RHS$
Hence, proved.
(ix) ${(7p - 13q)^2} + 364pq = {(7p + 13q)^2}$
Ans:
$LHS = {(7p - 13q)^2} + 364pq$ and $RHS = {(7p + 13q)^2}$.
Now taking LHS,
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {(7p - 13q)^2} + 364pq$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {\left( {7p} \right)^2} + {\left( {13q} \right)^2} - 2\left( {7p} \right)\left( {13q} \right) + 364pq$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = 49{p^2} + 169{q^2} - 182pq + 364pq$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = 49{p^2} + 169{q^2} + 182pq$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {\left( {7p} \right)^2} + {\left( {13q} \right)^2} + 2\left( {7p} \right)\left( {13q} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = {\left( {7p + 13q} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow LHS = RHS$
Hence proved.
(x) ${\left( {\dfrac{{3p}}{7} + \dfrac{7}{{6p}}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{3}{7}p - \dfrac{7}{{6p}}} \right)^2} = 2$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{{3p}}{7} + \dfrac{7}{{6p}}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{3}{7}p - \dfrac{7}{{6p}}} \right)^2} = 2$
It is of the form \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\]
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{3p}}{7} + \dfrac{7}{{6p}} + \dfrac{3}{7}p - \dfrac{7}{{6p}}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{3p}}{7} + \dfrac{7}{{6p}} - \dfrac{3}{7}p + \dfrac{7}{{6p}}} \right) = 2$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{3p}}{7} + \dfrac{3}{7}p} \right)\left( {\dfrac{7}{{6p}} + \dfrac{7}{{6p}}} \right) = 2$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{6p}}{7}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{14}}{{6p}}} \right) = 2$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{6p \times 14}}{{7 \times 6p}} = 2$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{14}}{7} = 2$
$ \Rightarrow 2 = 2$
Hence, proved.
114. Find the value of $a$, if
(i) $8a = {35^2} - {27^2}$
Ans:
We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], then
\[ \Rightarrow 8a = \left( {35 + 27} \right)\left( {35 - 27} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 8a = 62 \times 8\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{62 \times 8}}{8}\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = 62\]
(ii) $9a = {76^2} - {67^2}$
Ans:
We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], then
\[ \Rightarrow 9a = {76^2} - {67^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 9a = \left( {76 - 67} \right)\left( {76 + 67} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 9a = 9 \times 143\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{9 \times 143}}{9}\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = 143\]
(iii) $pqa = {(3p + q)^2} - {(3p - q)^2}$
Ans:
We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], then
$ \Rightarrow pqa = \left( {3p + q + 3p - q} \right)\left( {3p + q - 3p + q} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow pqa = \left( {3p + 3p} \right)\left( {q + q} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow pqa = \left( {6p} \right)\left( {2q} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow pqa = 12pq$
$ \Rightarrow a = 12$
(iv) $p{q^2}a = {(4pq + 3q)^2} - {(4pq - 3q)^2}$
Ans:
We know that \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], then
\[ \Rightarrow p{q^2}a = \left( {4pq + 3q + 4pq - 3q} \right)\left( {4pq + 3q - 4pq + 3q} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow p{q^2}a = \left( {4pq + 4pq} \right)\left( {3q + 3q} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow p{q^2}a = \left( {8pq} \right)\left( {6q} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow p{q^2}a = 48p{q^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = 48\]
115. What should be added to $4c( - a + b + c)$ to obtain $3a(a + b + c) - 2b(a - b + c)$ ?
Ans: Let M be added to $4c( - a + b + c)$ to obtain $3a(a + b + c) - 2b(a - b + c)$.
$ \Rightarrow M + 4c( - a + b + c) = 3a(a + b + c) - 2b(a - b + c)$
$ \Rightarrow M - 4ac + 4bc + 4{c^2} = 3{a^2} + 3ab + 3ac - 2ab + 2{b^2} - 2bc$
$ \Rightarrow M = 3{a^2} + 3ab + 3ac - 2ab + 2{b^2} - 2bc + 4ac - 4bc - 4{c^2}$
\[ \Rightarrow M = 3{a^2} + 2{b^2} - 4{c^2} + 3ab - 2ab + 3ac + 4ac - 2bc - 4bc\]
\[ \Rightarrow M = 3{a^2} + 2{b^2} - 4{c^2} + ab + 7ac - 6bc\]
116. Subtract $b\left( {{b^2} + b - 7} \right) + 5$ from $3{b^2} - 8$ and find the value of expression obtained for $b = - 3$.
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow 3{b^2} - 8 - \left( {b\left( {{b^2} + b - 7} \right) + 5} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 3{b^2} - 8 - \left( {{b^3} + {b^2} - 7b + 5} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow 3{b^2} - 8 - {b^3} - {b^2} + 7b - 5$
$ \Rightarrow 2{b^2} - {b^3} + 7b - 13$
Now, put $b = - 3$
Then
$ \Rightarrow 2{\left( { - 3} \right)^2} - {\left( { - 3} \right)^3} + 7\left( { - 3} \right) - 13$
$ \Rightarrow 2\left( 9 \right) - \left( { - 27} \right) + 7\left( { - 3} \right) - 13$
$ \Rightarrow 18 + 27 - 21 - 13$
$ \Rightarrow 11$
117. If $x - \dfrac{1}{x} = 7$ then find the value of ${x^2} + \dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}}$.
Ans: Given,
$x - \dfrac{1}{x} = 7$
Squaring on both sides,
${\left( {x - \dfrac{1}{x}} \right)^2} = {7^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + \dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}} - 2 = 49$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + \dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}} = 49 + 2$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + \dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}} = 51$
118. Factorise ${x^2} + \dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}} + 2 - 3x - \dfrac{3}{x}$.
Ans: Given
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + \dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}} + 2 - 3x - \dfrac{3}{x} = {x^2} + \dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}} + 2 - 3\left( {x - \dfrac{1}{x}} \right)$
If we compare the first three terms with the \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\], we will have’
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + \dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}} + 2 - 3x - \dfrac{3}{x} = {\left( {x + \dfrac{1}{x}} \right)^2} - 3\left( {x - \dfrac{1}{x}} \right)$
Taking $\left( {x - \dfrac{1}{x}} \right)$ common we will have
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + \dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}} + 2 - 3x - \dfrac{3}{x} = \left( {x - \dfrac{1}{x}} \right)\left( {x + \dfrac{1}{x} - 3} \right)$
119. Factorise ${p^4} + {q^4} + {p^2}{q^2}$.
Ans: Given, ${p^4} + {q^4} + {p^2}{q^2}$.
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{p^2}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{q^2}} \right)^2} + 2{p^2}{q^2} - {p^2}{q^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{p^2} + {q^2}} \right)^2} - {\left( {pq} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{p^2} + {q^2} + pq} \right)\left( {{p^2} + {q^2} - pq} \right)$
120. Find the value of
(i) $\dfrac{{6.25 \times 6.25 - 1.75 \times 1.75}}{{4.5}}$
Ans:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{6.25 \times 6.25 - 1.75 \times 1.75}}{{4.5}}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {6.25} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {1.75} \right)}^2}}}{{4.5}}\]
Applying the \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {6.25 + 1.75} \right)\left( {6.25 - 1.75} \right)}}{{4.5}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( 8 \right) \times \left( {4.5} \right)}}{{4.5}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 8\]
(ii) $\dfrac{{198 \times 198 - 102 \times 102}}{{96}}$
Ans: Given
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{198 \times 198 - 102 \times 102}}{{96}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {198} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {102} \right)}^2}}}{{96}}$
Applying the \[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\]
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {198 + 102} \right)\left( {198 - 102} \right)}}{{96}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {300} \right)\left( {96} \right)}}{{96}}$
$ \Rightarrow 300$
121. The product of two expressions is ${x^5} + {x^3} + x$. If one of them is ${x^2} + x + 1$ , find the other.
Ans: Let the unknown expression be Y.
Then by the given condition we will have,
\[ \Rightarrow y \times \left( {{x^2} + x + 1} \right) = {x^5} + {x^3} + x\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{{x^5} + {x^3} + x}}{{{x^2} + x + 1}}\]
Then using the long division method,
\[\begin{align}
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{{x}^{3}}-{{x}^{2}}+x \\
& {{x}^{2}}+x+1\left| \!{\overline {\,
\begin{align}
& {{x}^{5}}+{{x}^{3}}+x \\
& \underline{{{x}^{5}}+{{x}^{4}}+{{x}^{3}}} \\
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,-{{x}^{4}}+x \\
& \underline{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,-{{x}^{4}}-{{x}^{3}}-{{x}^{2}}} \\
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{{x}^{3}}+{{x}^{2}}+x \\
& \underline{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{{x}^{3}}+{{x}^{2}}+x} \\
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,0 \\
\end{align} \,}} \right. \\
\end{align}\]
Hence the unknown algebraic expression is \[{x^3} - {x^2} + x\].
122. Find the length of the side of the given square if area of the square is 625 square units and then find the value of $x$.
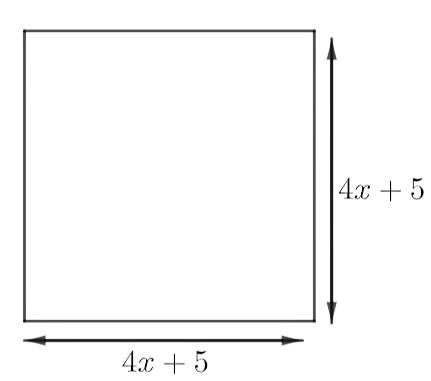
Ans:
We have 7a square. That is all sides are equal.
We know that the area of the square is side2
That is,
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {4x + 5} \right)^2} = 625\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {4x + 5} \right)^2} = {\left( {25} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 4x + 5 = 25\]
\[ \Rightarrow 4x = 25 - 5\]
\[ \Rightarrow 4x = 20\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 5\]
Hence, side is
\[ \Rightarrow 4x + 5 = 4\left( 5 \right) + 5 = 20 + 5 = 25\,\,\,units.\]
123. Take suitable number of cards given in the adjoining diagram [G $(x \times $ $x$ ) representing ${x^2},{\text{R}}(x \times 1)$ representing $x$ and ${\text{Y}}(1 \times 1)$ representing 1] to factorise the following expressions, by arranging the cards in the form of rectangles: (i) $2{x^2} + 6x + 4$ (ii) ${x^2} + 4x + 4$. Factorise $2{x^2} + $ $6x + 4$ by using the figure.
Calculate the area of the figure.
Ans: Given, $[g(x\times x)]$ representing $x^{2}, R(x \times 1)$ representing
Given equation is $2x^2+6x+4$
$={{x}^{2}}+3x+2$
$={{x}^{2}}+2x+x+2$
$=x(x+2)+1(x+2)$
The above steps are shown in figures, see below,
For the box G, the area $\Rightarrow x \times x=x^{2}$
For box R, the area $\Rightarrow x \times 1=x$
For box Y, Area $\Rightarrow 1 \times 1=1$
So the area of the figure representing $2 x^{2}+6 x+4$ is
$\Rightarrow 2[\text{ Area }(G)]+6[\text{ Area }(R)]+4[\text{ Area }(Y)]$
$\begin{aligned}
&\Rightarrow 2[\text { Area }(G)]+6[\text { Area }(R)]+4[\text { Area }(Y)] \\
&\Rightarrow 2 x^{2}+6 x+4
\end{aligned}$
124. The figure shows the dimensions of a wall having a window and a door of a room. Write an algebraic expression for the area of the wall to be painted.
Ans: We have the wall dimensions that is \[5x \times \left( {5x + 2} \right)\] having a window and a door of dimension \[\left( {2x \times x} \right)\] and \[\left( {3x \times x} \right)\] respectively.
Then, the area of the window is \[2x \times x = 2{x^2}\,\,sq.\,units\]
Area of the door \[3x \times x = 3{x^2}\,sq.\,units\]
Area of the wall is \[5x \times \left( {5x + 2} \right) = \left( {25{x^2} + 10x} \right)\,sq.\,\,units\]
Now,
Area of the required part of the wall to be painted = area of the wall + (area of the window + area of the door)
\[ \Rightarrow 25{x^2} + 10x - \left( {2{x^2} + 3{x^2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 25{x^2} + 10x - \left( {5{x^2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 25{x^2} + 10x - 5{x^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 20{x^2} + 10x\,\,sq.\,\,units\]
125. Match the expressions of column I with that of column II:
Column I | Column II |
${(21x + 13y)^2}$ | $441{x^2} - 169{y^2}$ |
${(21x - 13y)^2}$ | $441{x^2} + 169{y^2} + 546xy$ |
$(21x - 13y)(21x + 13y)$ | $441{x^2} + 169{y^2} - 546xy$ |
$441{x^2} - 169{y^2} + 546xy$ |
Ans:
Using the identity,
\[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\]
\[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\]
\[{a^2} - {b^2} = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)\], will have
Column I | |
${(21x + 13y)^2}$ | $441{x^2} + 169{y^2} + 546xy$ |
${(21x - 13y)^2}$ | $441{x^2} + 169{y^2} - 546xy$ |
$(21x - 13y)(21x + 13y)$ | $441{x^2} - 169{y^2}$ |
Maths is the subject that requires so much practice from the students, because, unlike other subjects which are based on the theory, Maths requires the students to practice solving the problem. And For example for the NCERT Class 8, students can find so many questions to practice from for the 7th chapter which is Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation.
But only solving the questions is not enough because students always want to know whether they have properly solved the problem or not, otherwise, the whole practice becomes useless and in vain.
Hence, Vedantu has brought to the students of Class 8 the complete solutions for the Exemplar of the Math, chapter 7, which is Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation.
Benefits of Solving the Exemplar of the Chapter Class 8, Math, Chapter 7 Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation.
Since Math is a practical subject, there are many benefits of solving the exemplar of it, a few of which are as under: -
It provides the students with enough practice for the chapter on Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation.
It helps the students in understanding their weaknesses and their strengths.
It gives a good idea to the students in regards to tackling the chapter on Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation in the exam.
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 8 Maths Solutions Chapter 7 Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation
1. How can I make myself better in Class 8, chapter 7, Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation?
You may find the following steps useful for making yourself better in Class 8, Chapter 7 Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation.
Understand all the concepts of Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation. This revision note can help you in clearing your concepts: CBSE Class 8 Math Chapter 9 - Algebraic Expressions and Identities Revision Notes (vedantu.com)
Find your weak spot and revise those topics.
After that practice as many questions of the Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation as possible. And you can do this by solving the Exemplar questions.
Lastly, match your answers with the solutions, to be sure about your understanding.
2. How many questions are there in the Exemplar of the Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation?
There are many questions given in the Exemplar of the Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation, for the students to practice. A total of 114 questions are there, which are divided in the following manner: -
Question 1 to 33 are multiple-choice type questions.
Questions 34 to 58 fill in the blank question.
The next 21 questions, i.e. 59 to 80 are true and false type questions. Which requires the students to first solve the given expression to determine whether it is true or false.
The remaining questions are the solving the expression and Simplification type.
3. Should I solve all the questions of the Exemplar for the Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation?
Yes, you must solve all the questions given in the example of Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation. Because Math is the subject that demands so much practice from the students and therefore practicing the questions of the Math is of utmost importance for the students. Solving all the questions of the exemplar for the Class 8, chapter Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation gives students the practice that makes them understand how to approach a particular question as soon as they see it.
4. I have solved all the questions for the Exemplar for Class 8, Math chapter Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation, but how can I make sure my solutions are correct?
First of all, you have done a great job by solving all the questions given in the Exemplar for the Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation. Now for the part of making sure that you have got all the answers right, all you have to do is to compare your answers with the answers provided in the solution of the same chapter. And for the solution, you do not have to worry much, because Vedantu provides the complete solutions for the Exemplar of Class 8, chapter 7, which is Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation, which you can download for free.
5. Why should I follow the solutions given by the Vedantu for the Math Exemplar of the Class 8 Algebraic Expression, Identities & Factorisation?
To answer this question let us first see the qualities of a good solution briefly: -
It has to be solved by an expert.
It must be easy to understand and comprehend.
It must include an explanation of all the questions.
All these three essential qualities are fulfilled by the solutions that Vedantu provides.
It is solved by expert teachers, highly qualified in the field of Mathematics.
Everything is written clearly and concisely, hence easy to understand.
It explains all the questions, including the multiple-choice questions.











