Download NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 On Vedantu
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids solved by expert Chemistry teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 – Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
1. Addition of water to alkynes occurs in acidic medium and in the presence of $H{g^{2 + }}$ ions as a catalyst. Which of the following products will be formed in addition to water to but-1-yne under these conditions?
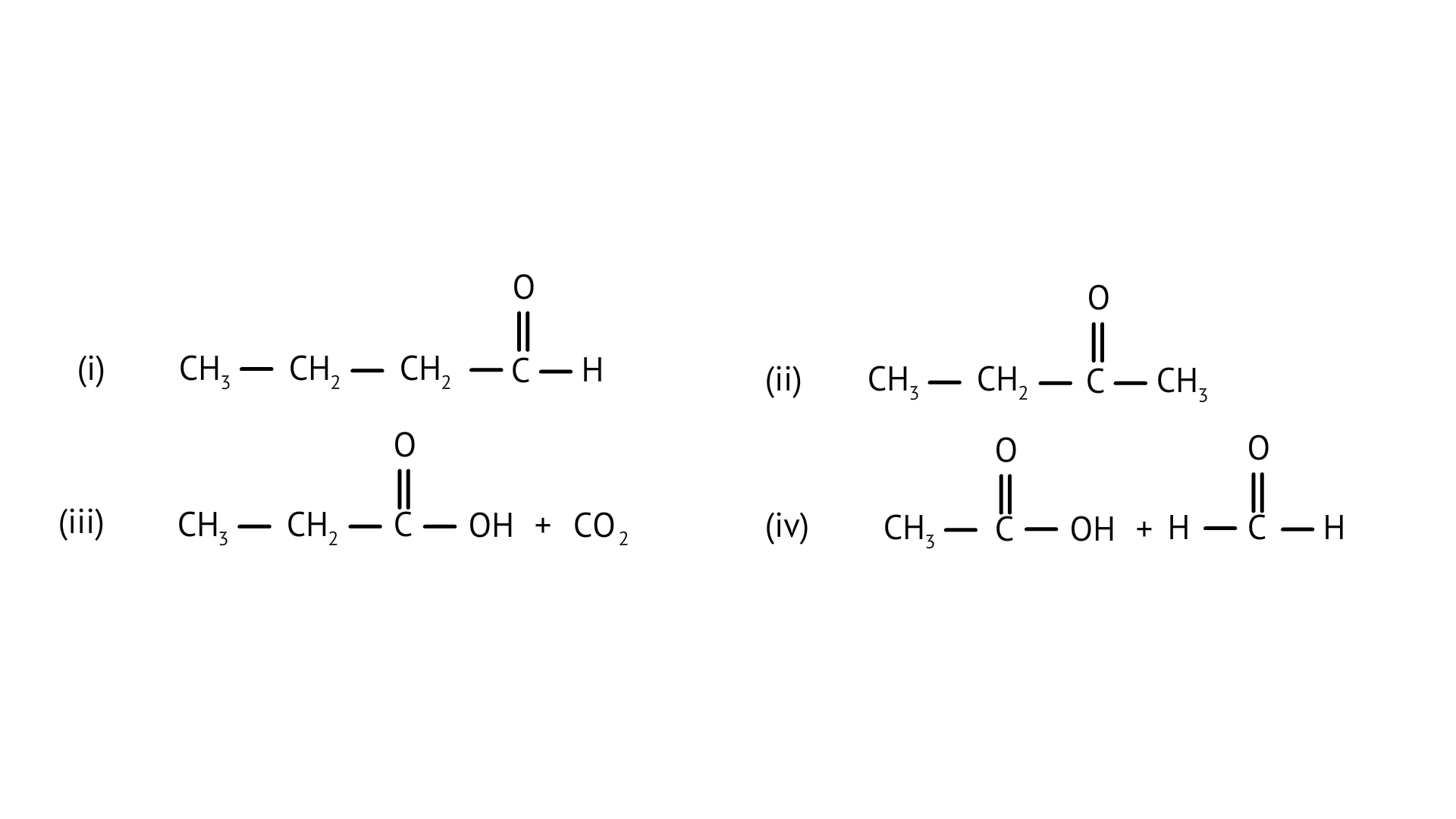
Ans: Correct option: B
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C\equiv CH+{{H}_{2}}O\xrightarrow{(H{{g}^{2\text{ }+\text{ }}}/{{H}^{\text{ }+\text{ }}})+{{H}_{2}}}C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CO-C{{H}_{3}}$
Butan-2-one is produced when butyne is hydrated in the presence of Hg ions as a catalyst. The ketone is the product. After the triple bond is broken, the OH group attaches to the secondary carbocation.
2. Which of the following compounds is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions?
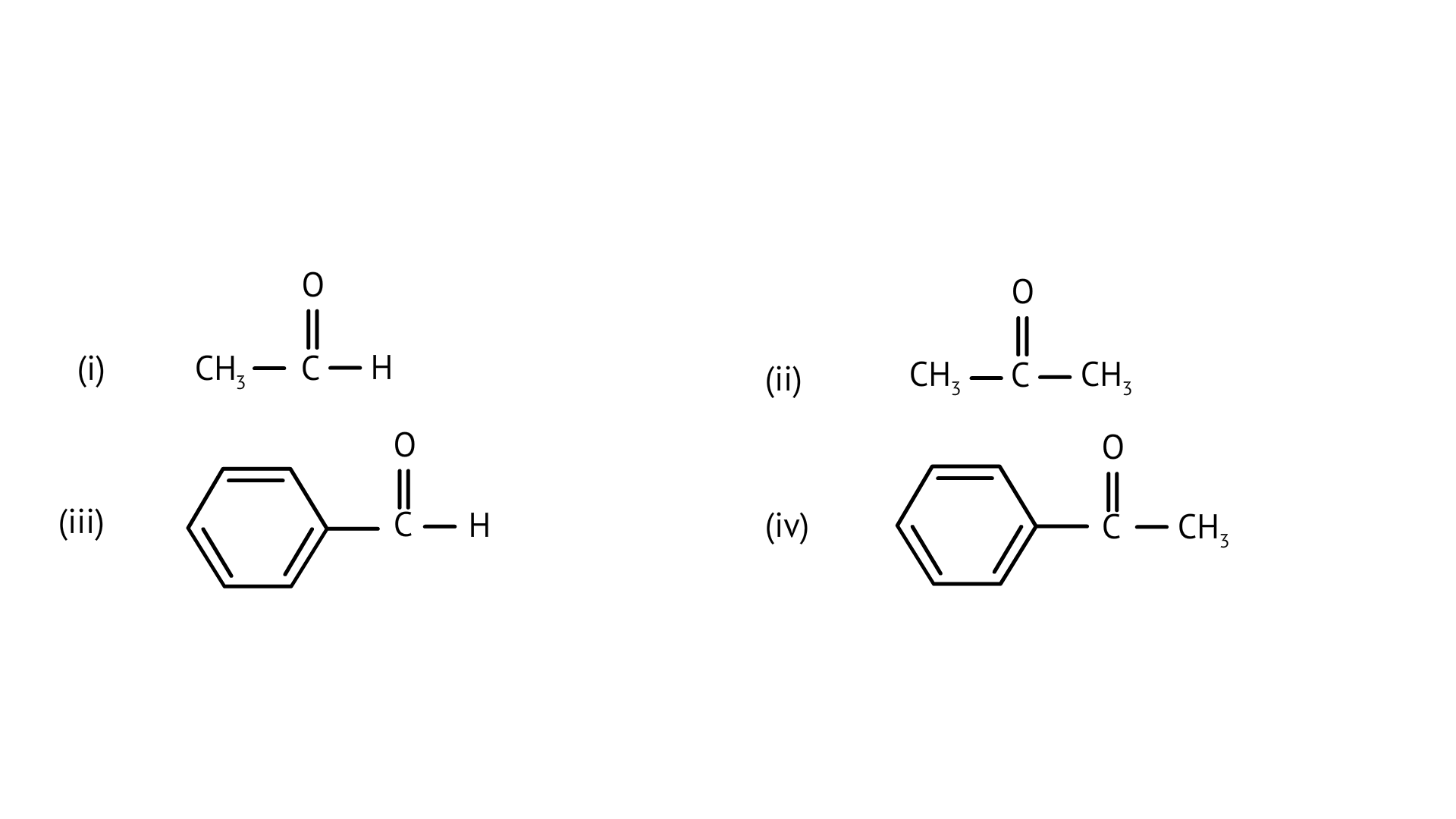
Ans: Correct option: B or (ii)
In nucleophilic addition processes, the reactivity of aldehydes and ketones are steric factors. The carbonyl group with the highest positive charge will be the most reactive, and if these groups have a positive inductive impact, the attack tendency will be reduced.
3. The correct order of increasing acidic strength is _____________.
A: Phenol < Ethanol < Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid
B: Ethanol < Phenol < Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid
C: Ethanol < Phenol < Acetic acid < Chloroacetic acid
D: Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid < Phenol < Ethanol
Ans: Correct option: C
Because the phenoxide ion produced is stabilised by resonance, phenol is more acidic than ethanol. When it comes to ethanol, resonance does not help to stabilise the phenoxide ion. The acidity of chloroacetic acid is higher than that of acetic acid. Alcohols and phenols are less acidic than carboxylic acids.
4. Compound
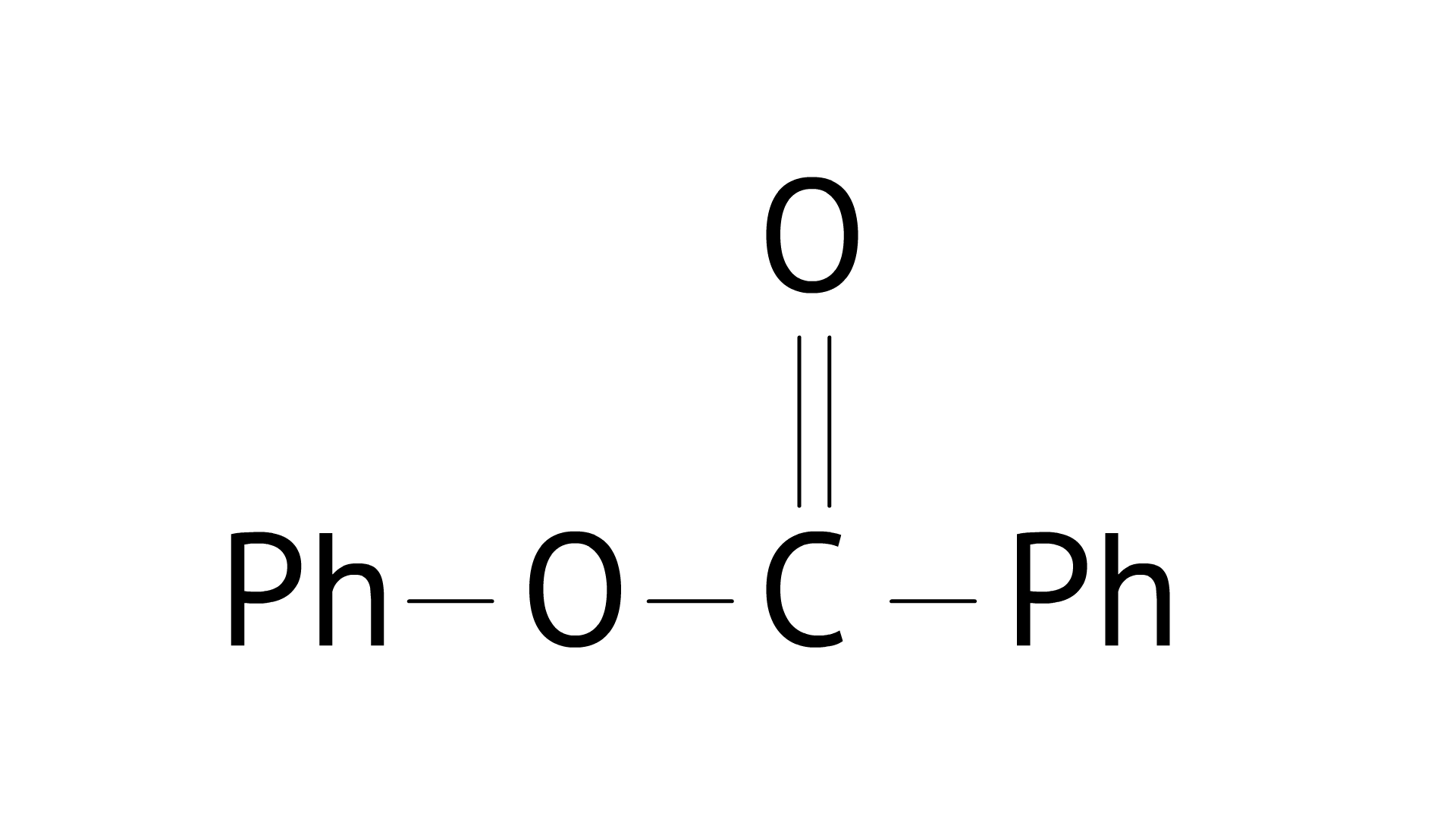
A: Phenol and benzoic acid in the presence of ${\text{NaOH}}$
B: Phenol and benzoyl chloride in the presence of pyridine
C: Phenol and benzoyl chloride in the presence of ${\text{ZnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$
D: Phenol and benzaldehyde in the presence of palladium
Ans: Correct option: B
When phenol reacts with acid chloride in the presence of an alkali, the alkali is pyridine, and the acid chloride is benzoyl chloride, compound ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}OCO{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}$ is formed. During this process, pyridine is utilised to neutralise 4HCl.
5. The reagent which does not react with both acetone and benzaldehyde.
A: Sodium hydrogen sulphite
B: Phenyl hydrazine
C: Fehling’s solution
D: Grignard reagent
Ans: Correct option: C
Acetones belong to the ketonic functional category. To distinguish between aldehyde and ketone, utilise Fehling's solution. Carbonyl groups are found in sodium hydrogen sulphite, phenyl hydrazine, and Grignard reagent. Ketones and aromatic aldehydes do not react with Fehling's solution.
6. Cannizaro’s reaction is not given by _____________.
A:
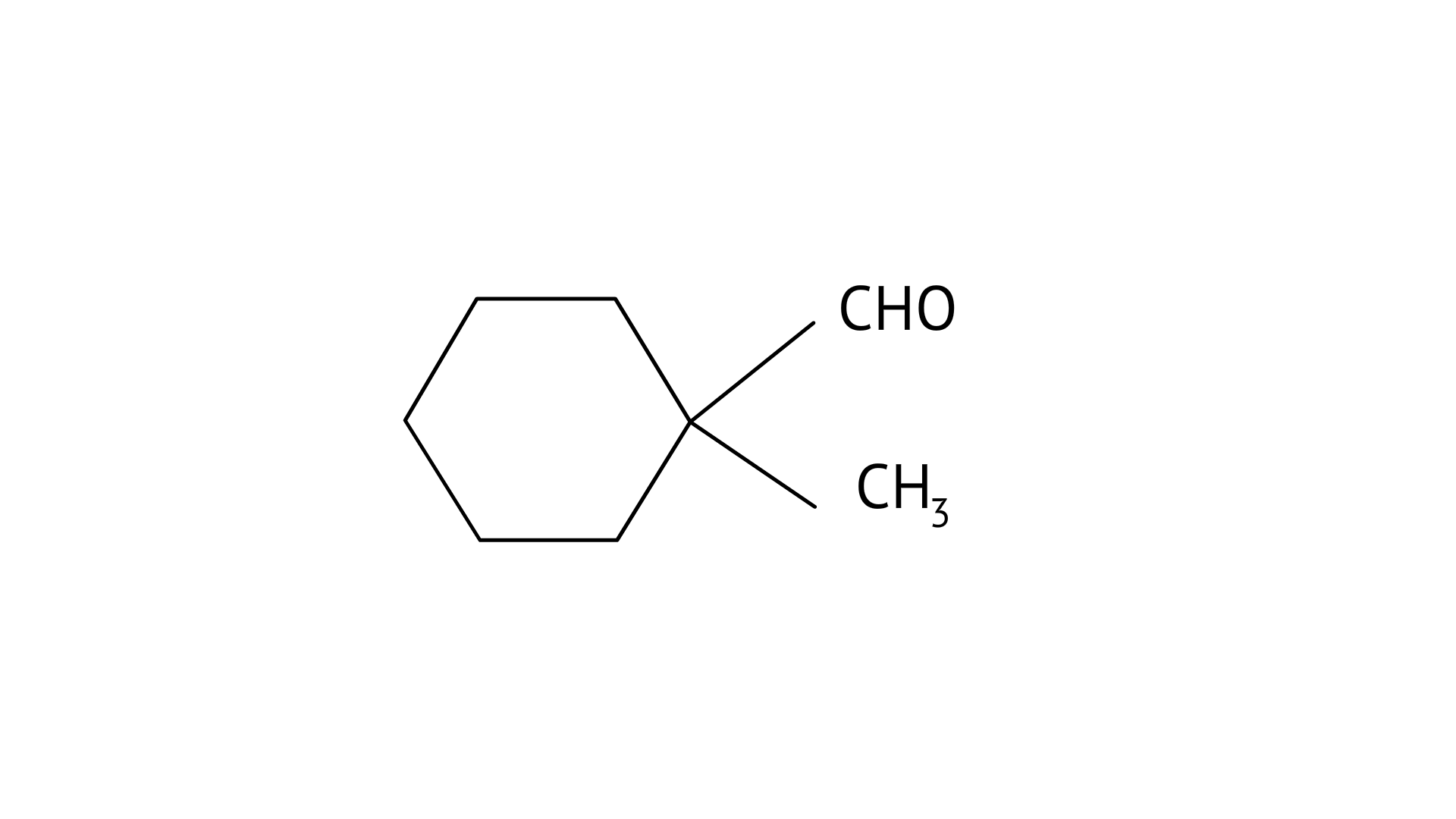
B:
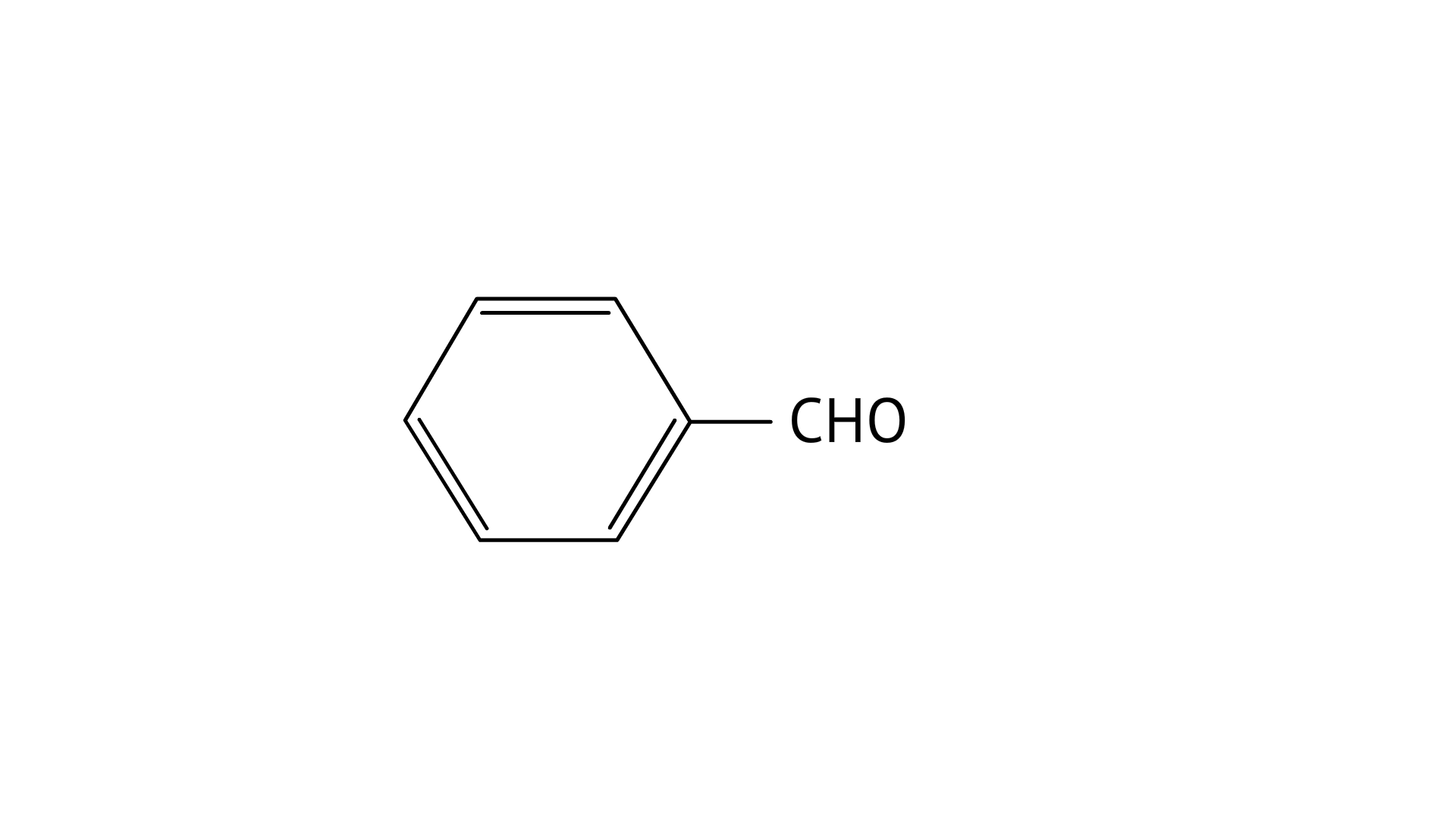
C: $\mathrm{H} \mathrm{CHO}$
D: ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHO}}$
Ans: Correct options: D
Aldehydes without a - hydrogen atom are the subject of Cannizaro's reaction.
Option D, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHO}}$ has 3 alpha hydrogen atoms and it does not give Cannizaro’s reaction
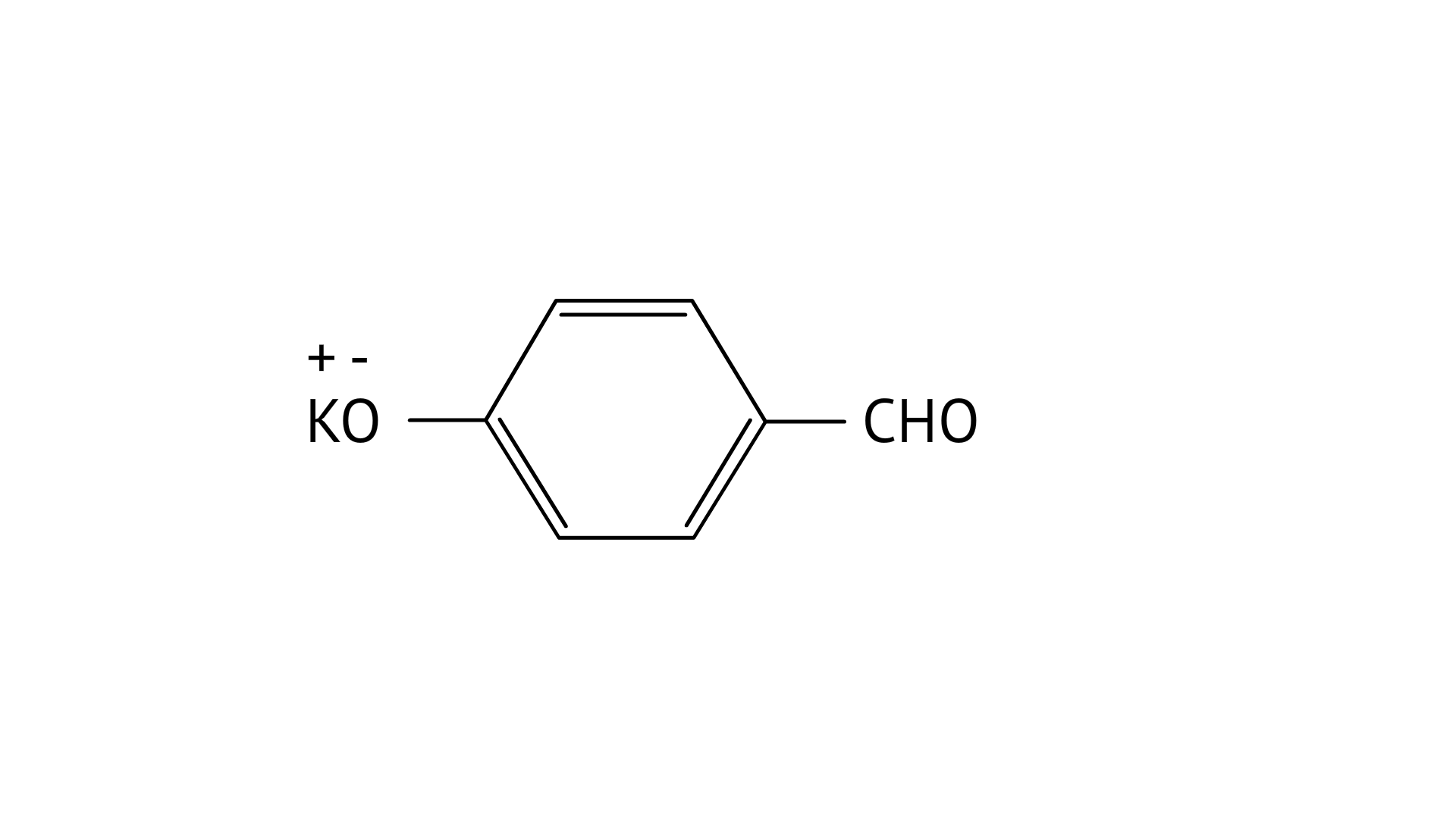
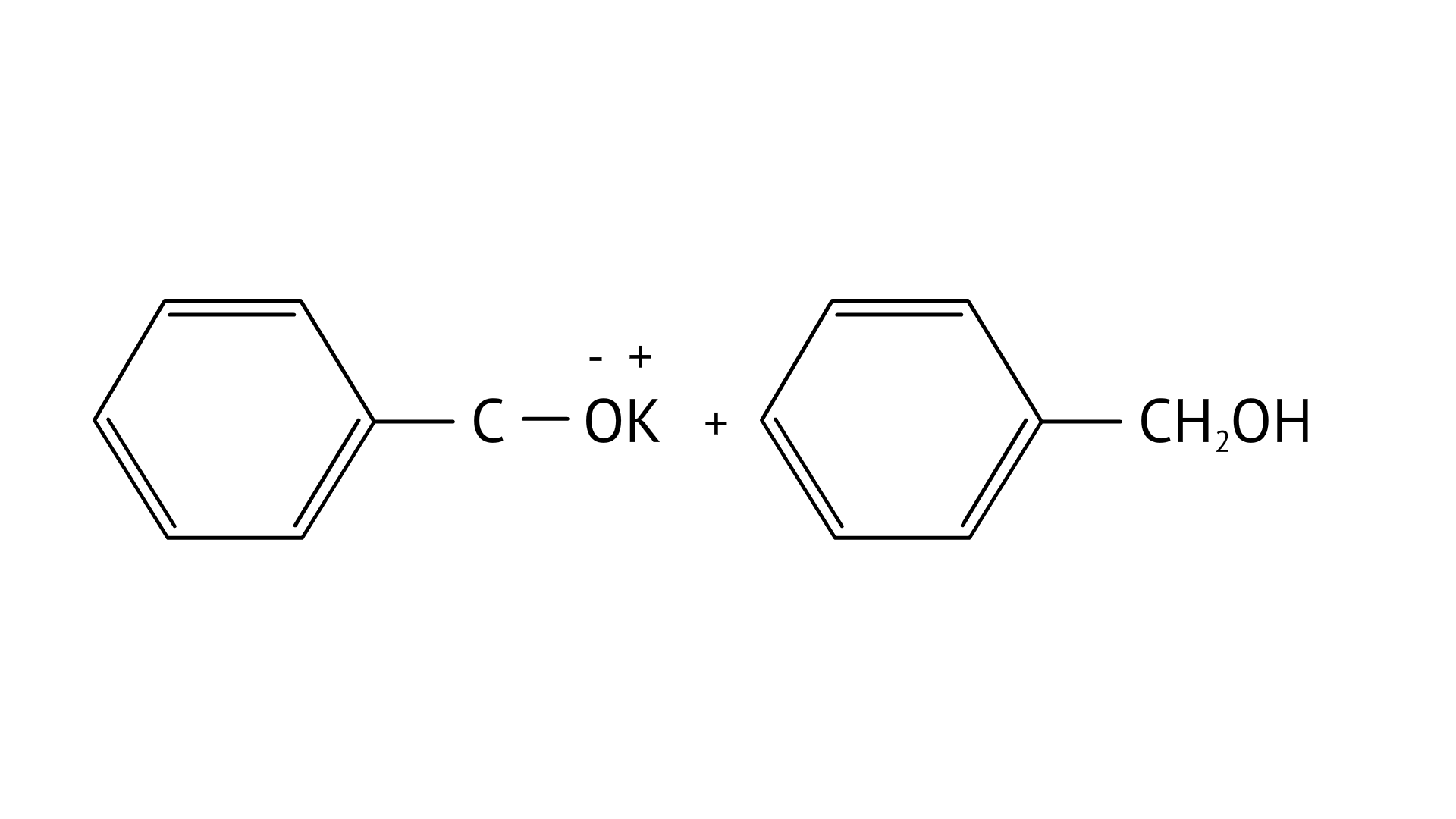
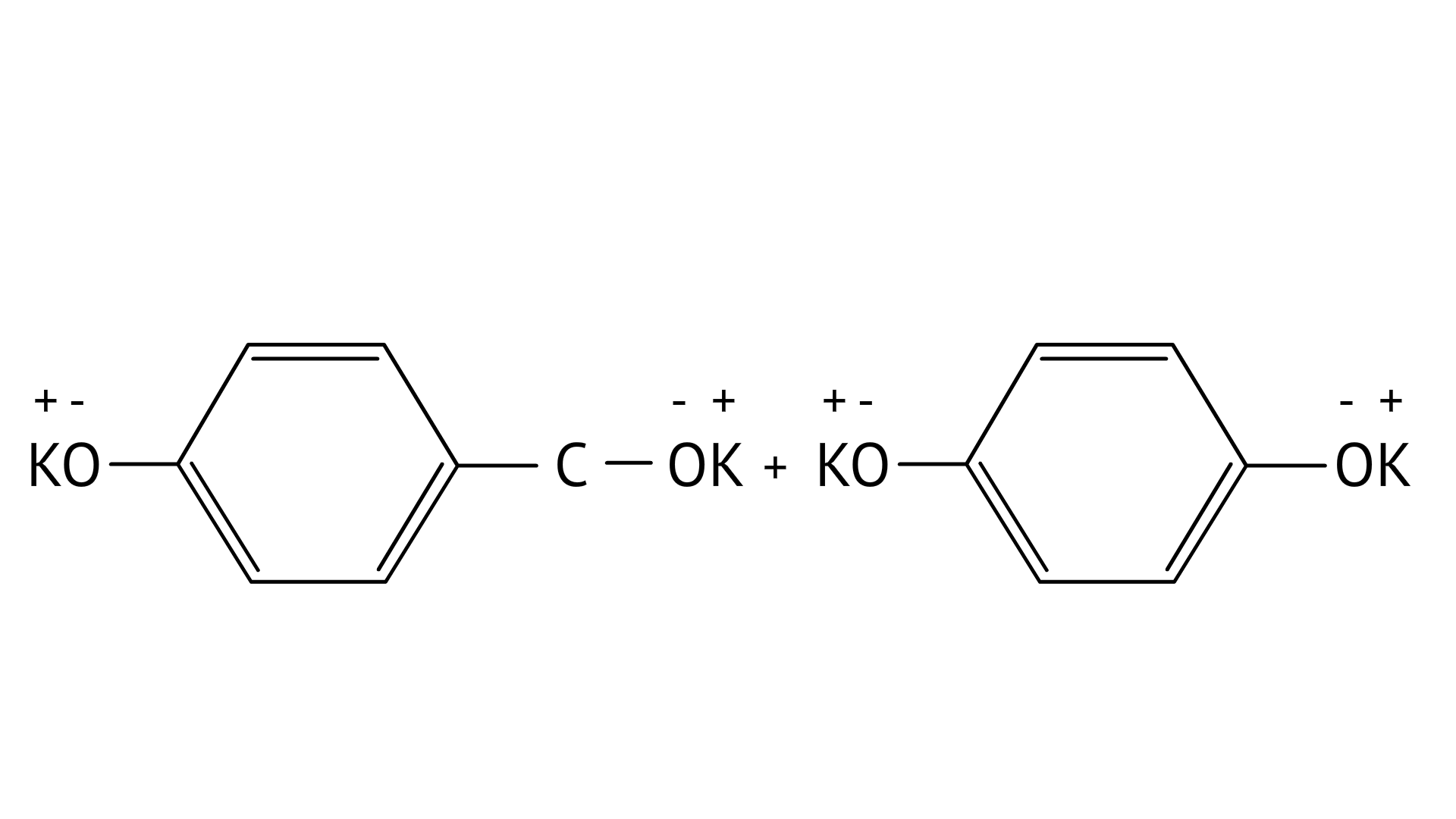
7. Which product is formed when the compound

A:
B:
C:
D:
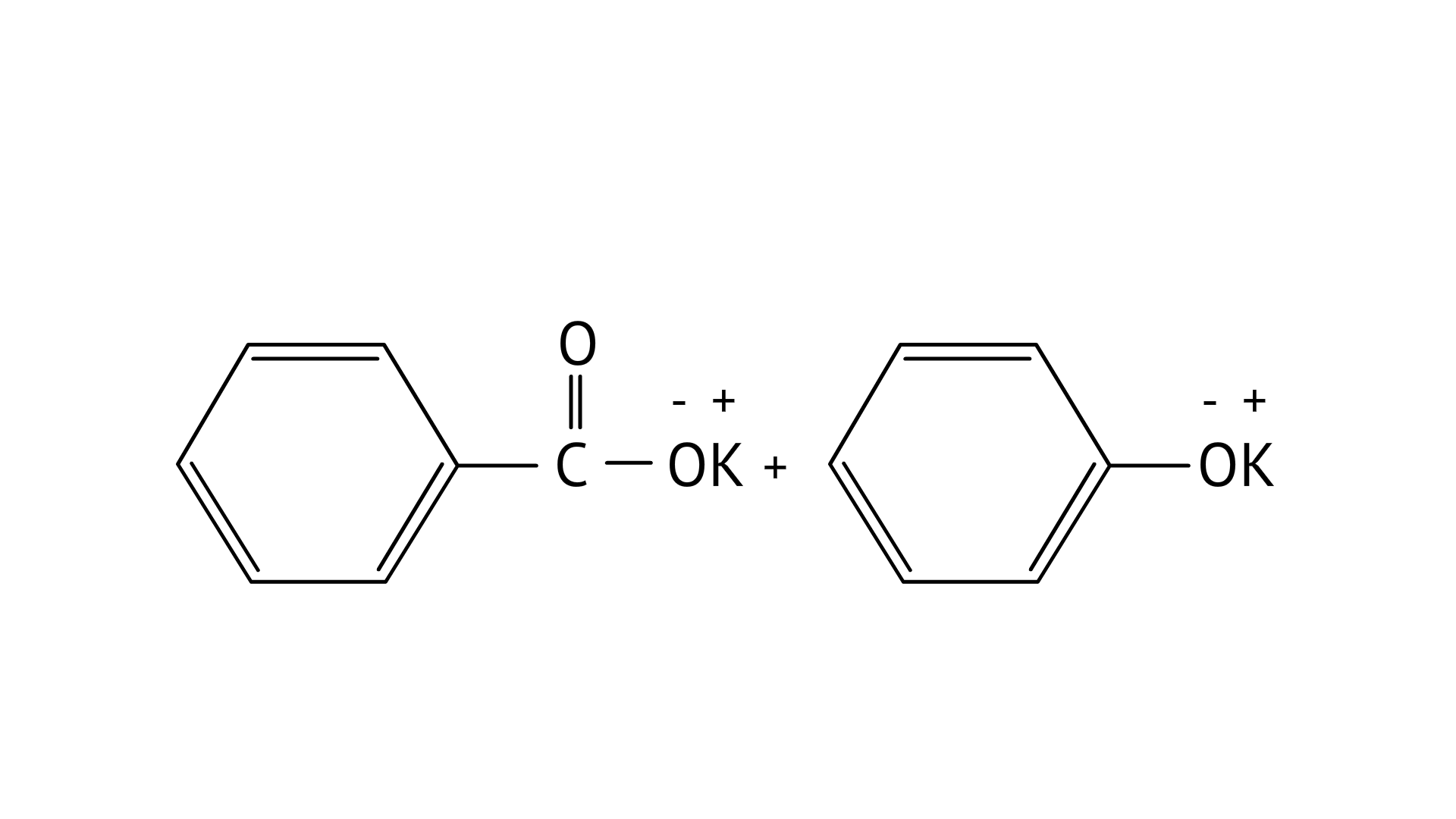
Ans: Correct option: B
In KOH adds to the compound

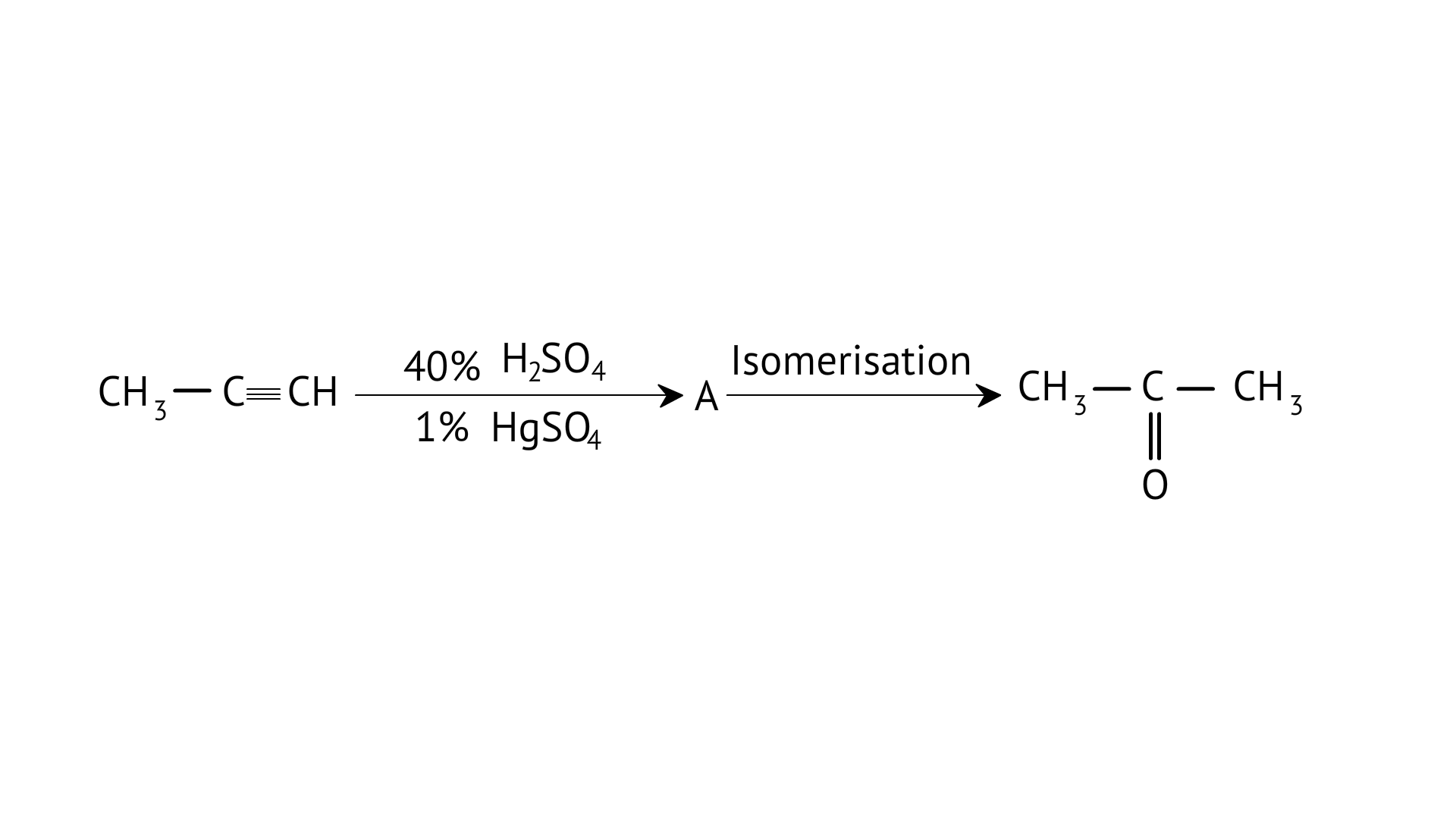
8.Structure of ‘A’ and type of isomerism in the above reaction are respectively
A: Prop–1–en–2–ol, metamerism
B: Prop-1-en-1-ol, tautomerism
C: Prop-2-en-2-ol, geometrical isomerism
D: Prop-1-en-2-ol, tautomerism
Ans: Correct option: D
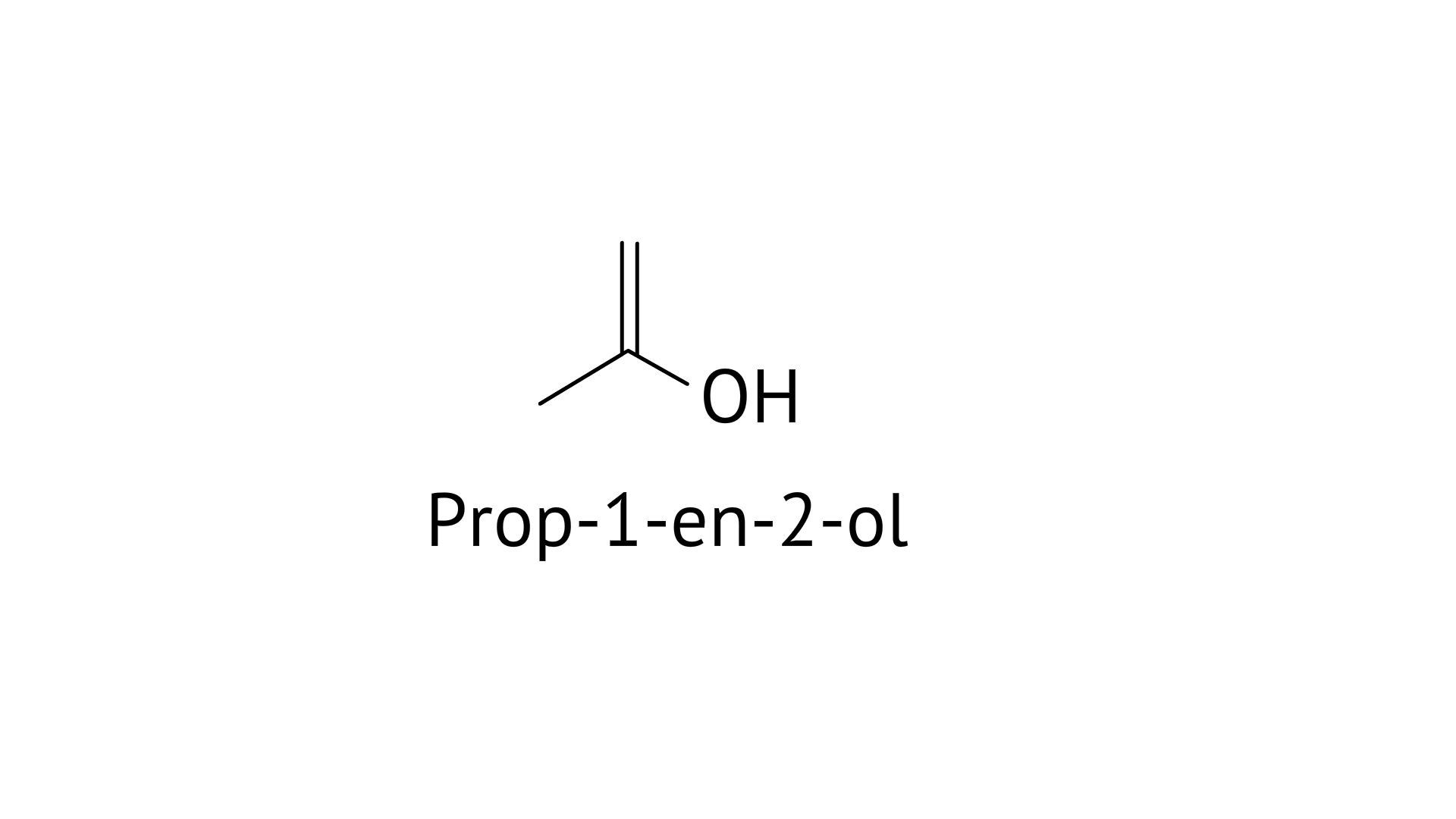
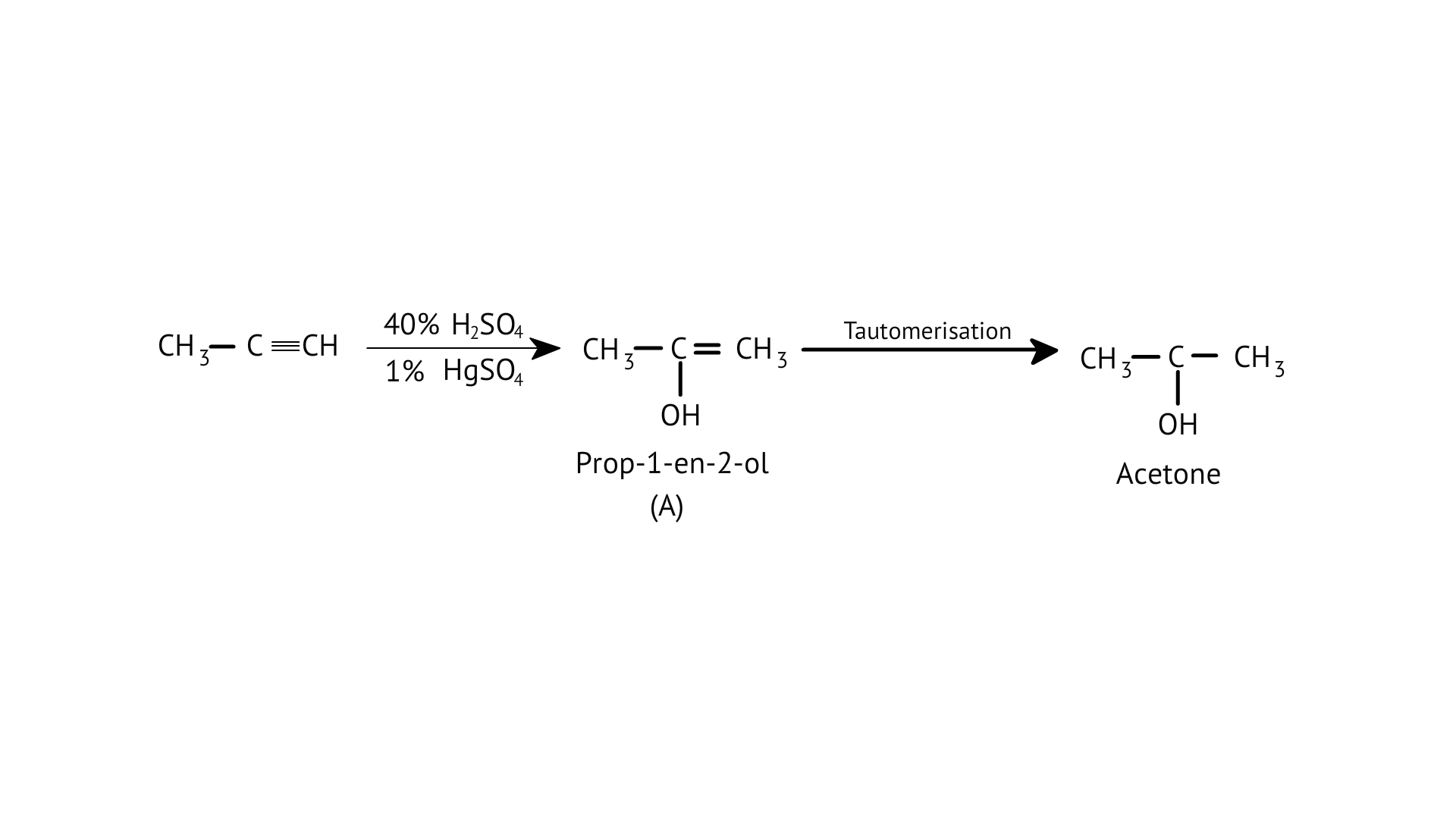

Tautomers are structural isomers that exist in two or more interconvertible structures of a single chemical molecule. Tautomerism transforms 'A' into acetone.
9. Compounds A and C in the following reaction are __________.
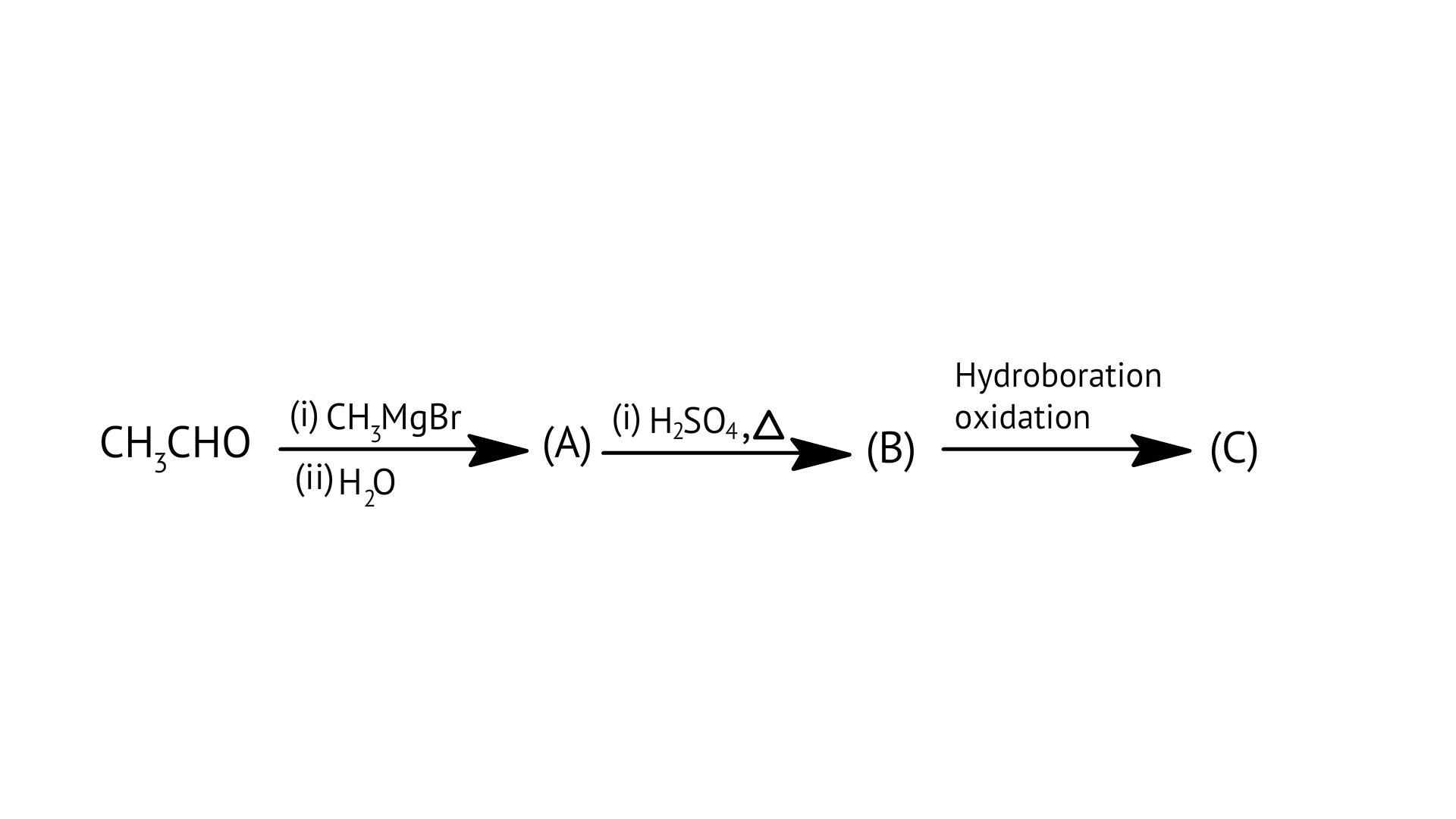
A: identical
B: positional isomers
C: functional isomers
D: optical isomers
Ans: Correct option: B
The position of a functional group in the same carbon chain differs in positional isomerism. The functional group in the chemical or the unsaturated double or triple bond in the compound can help us figure it out.
10. Which is the most suitable reagent for the following conversion?
A: Tollen’s reagent
B: Benzoyl peroxide
C: ${{\text{I}}_2}{\text{ and NaOH}}$solution
D: ${\text{Sn and NaOH}}$ solution
Ans: Correct option: C
${{\text{I}}_2}{\text{ and NaOH}}$ It is an iodoform reaction involving methyl ketones, the solution is the correct reagent. Because the reactants and product have double bonds, double bonds do not work throughout the reaction. There are also ketone and carboxylic groups present. The ketonic group is oxidised under the carboxylic group during the process.
11. Which of the following compounds will give butanone on oxidation with alkaline $KMn{O_4}$ solution?
A: Butan-1-ol
B: Butan-2-ol
C: Both
D: None of these
Ans: Correct option: B
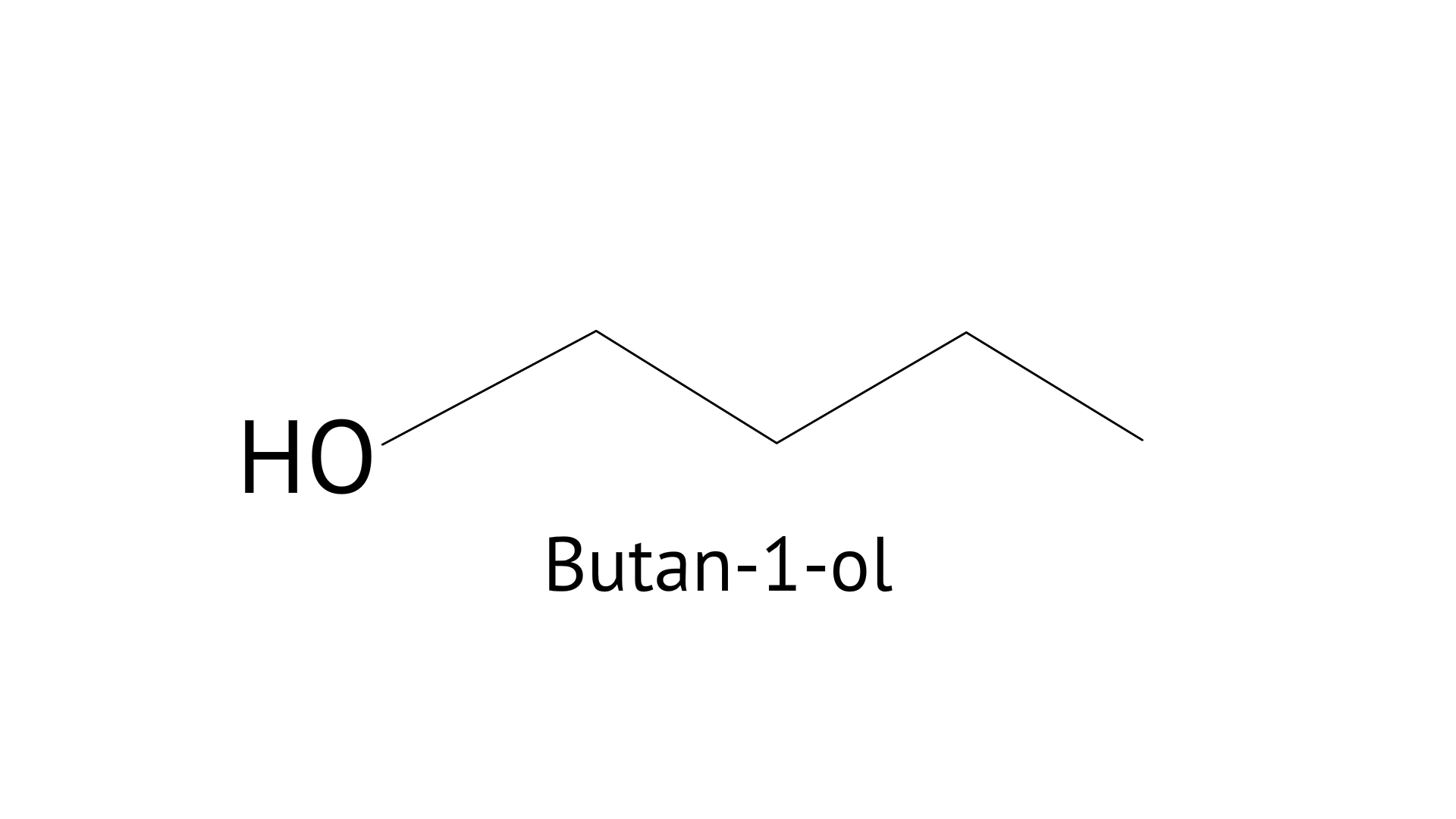
When a primary alcohol, such as Butan-1-ol, reacts with a powerful oxidising agent, such as ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$, it produces carboxylic acid, however when a secondary alcohol, such as Butan-2-ol, is oxidised under the pressure of ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$, it produces ketone. As a result, option B is right.
12. In Clemmensen Reduction carbonyl compound is treated with _____________.
A: Zinc amalgam ${\text{ + HCl}}$
B: Sodium amalgam ${\text{ + HCl}}$
C: Zinc amalgam + nitric acid
D: Sodium amalgam ${\text{ + HN}}{{\text{O}}_3}$
Ans: Correct option: A
The Clemmensen Reduction method is used to reduce a carbonyl group to ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$. Amalgams are a type of reducing agent that has been around for a long time. In the Clemmensen reduction, hydrogen chloride acts as an acid, protonating the ketone and transferring the electrons from the zinc amalgam to the carbon atoms.
II. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-II)
Note: In the following questions two or more options may be correct
13. Which of the following compounds do not undergo aldol condensation?
A: $C{H_3} - CHO$
B:
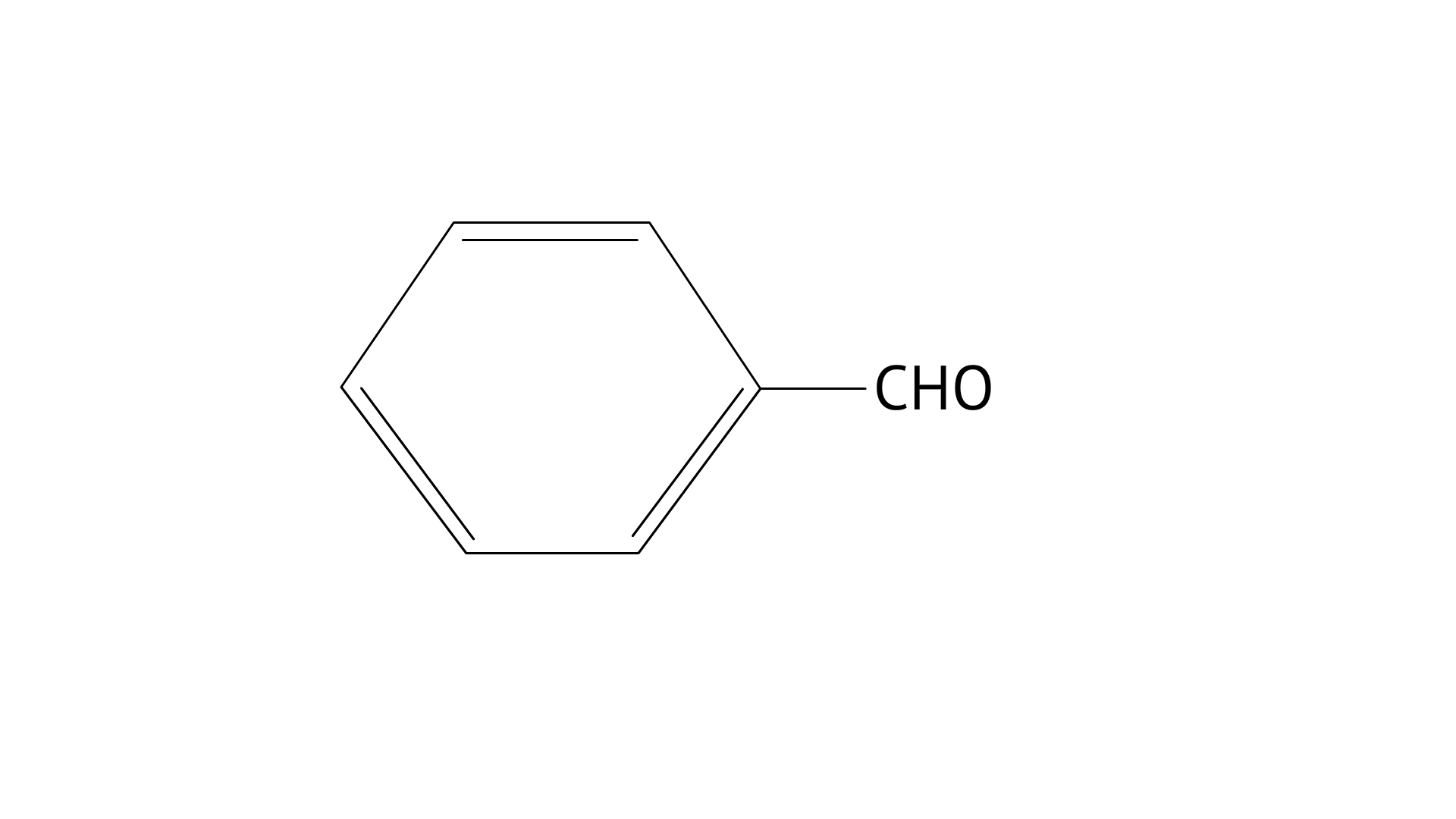
C:
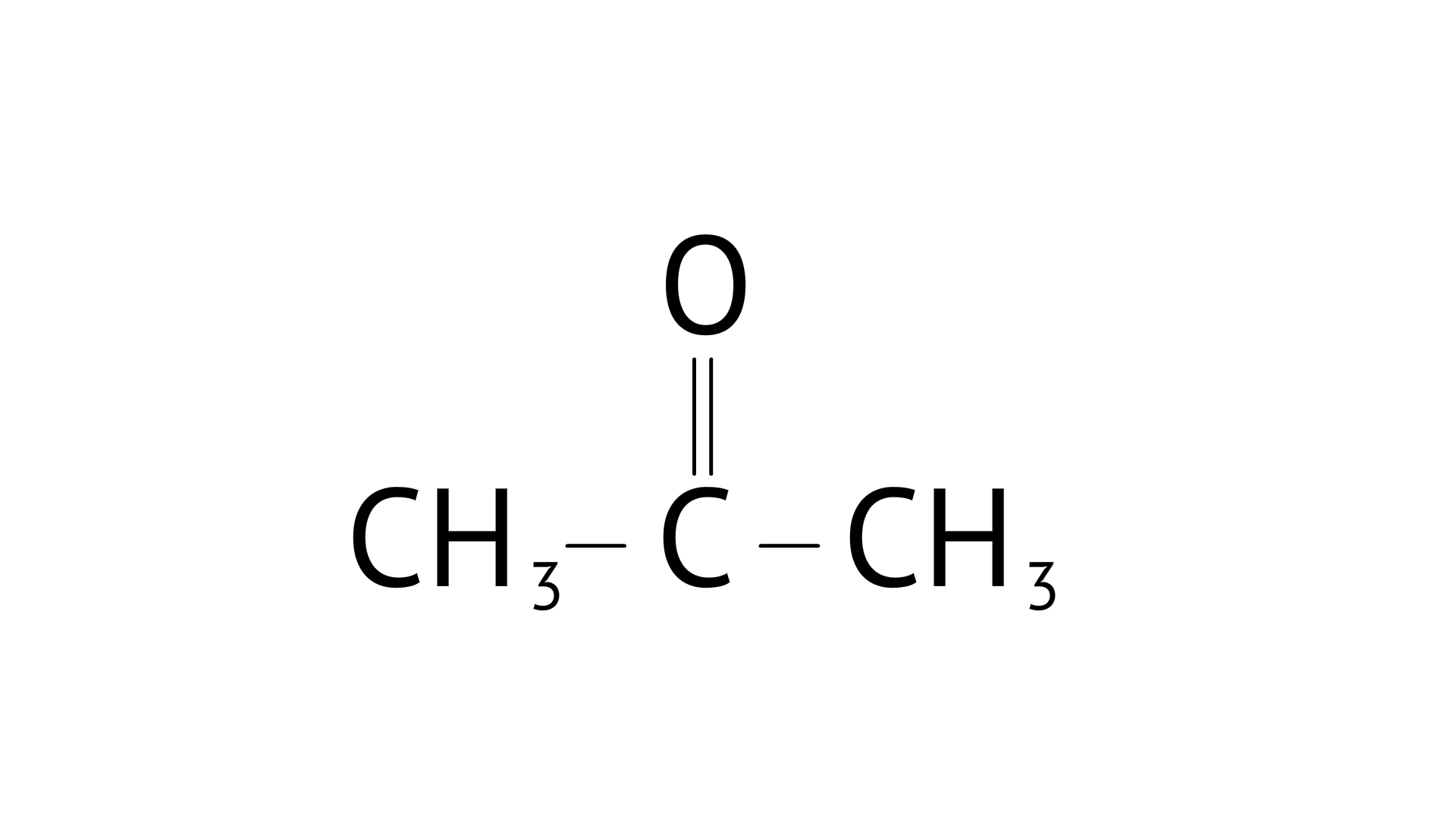
D:
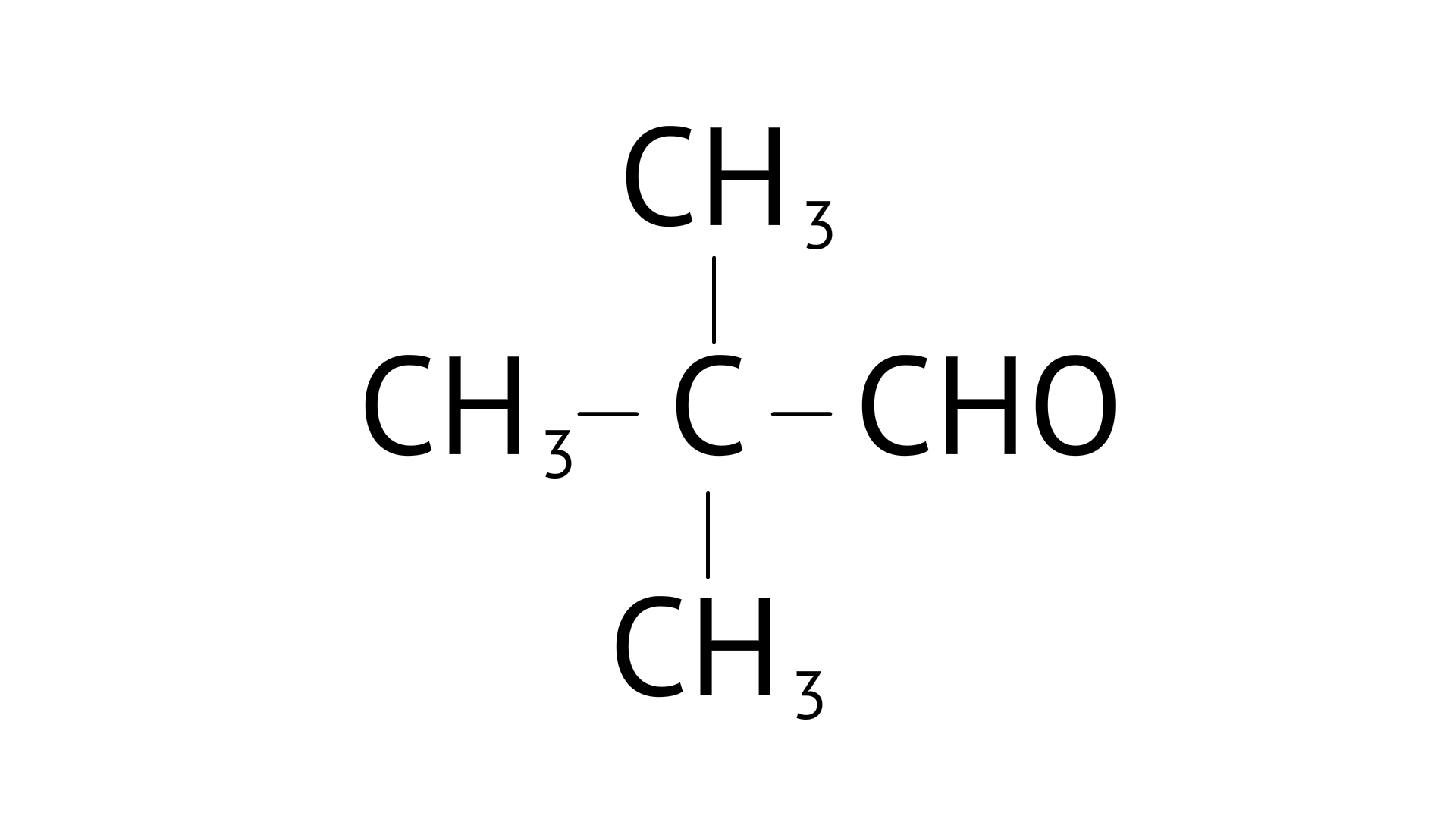
Ans: Correct options: B and D
Consider the following product ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ - CHO}}$ C and O are broken into positive and negative bonds. C should have one condition: hydrogen must be available; if it isn't, aldol condensation will not occur. When two products are mixed with the availability of - hydrogen, the positive and negative bonds between carbon and hydrogen are exchanged, and water (H20) is eliminated, resulting in aldol condensation.
14. Treatment of compound

A: Phenol
B: Sodium phenoxide
C: Sodium benzoate
D: Benzophenone
Ans: Correct options: B and D
The carbonyl group is replaced by a methyl group. Clemmensen Reduction is used for this conversion. It's utilised to make cyclohexanone and benzophenone into cyclohexane and diphenyl methane, respectively. The reagent is a zinc-hydrochloric acid amalgam.
15. Through which of the following reactions the number of carbon atoms can be increased in the chain?
A: Grignard reaction
B: Cannizaro’s reaction
C: Aldol condensation
D: HVZ reaction
Ans: Correct option: A and C
Grignard Reaction is the addition of an organomagnesium halide to form a tertiary or secondary alcohol.
Canizzaro’s Reaction involves the base induced disproportionation of two molecules. Aldol Condensation is an organic reaction when an enolate ion reacts with a carbonyl compound to form beta hydroxy ketone with dehydration to give a conjugated enone.
The HVZ reaction involves alpha bromination of carboxylic acids and this reacts with chlorine or bromine in presence of a small amount of red phosphorus to give alpha halo carboxylic acids.
16. Benzophenone can be obtained by ____________.
A: Benzoyl chloride + Benzene + $AlC{l_3}$
B: Benzoyl chloride + Diphenyl cadmium
C: Benzoyl chloride + Phenyl magnesium chloride
D: Benzene + Carbon monoxide + $ZnC{l_2}$
Ans: Correct options: A and B
A: Benzophenone can be obtained by Friedel-craft acylation reaction
B: Benzophenone can also be obtained by the reaction between benzoyl chloride and diphenyl cadmium.
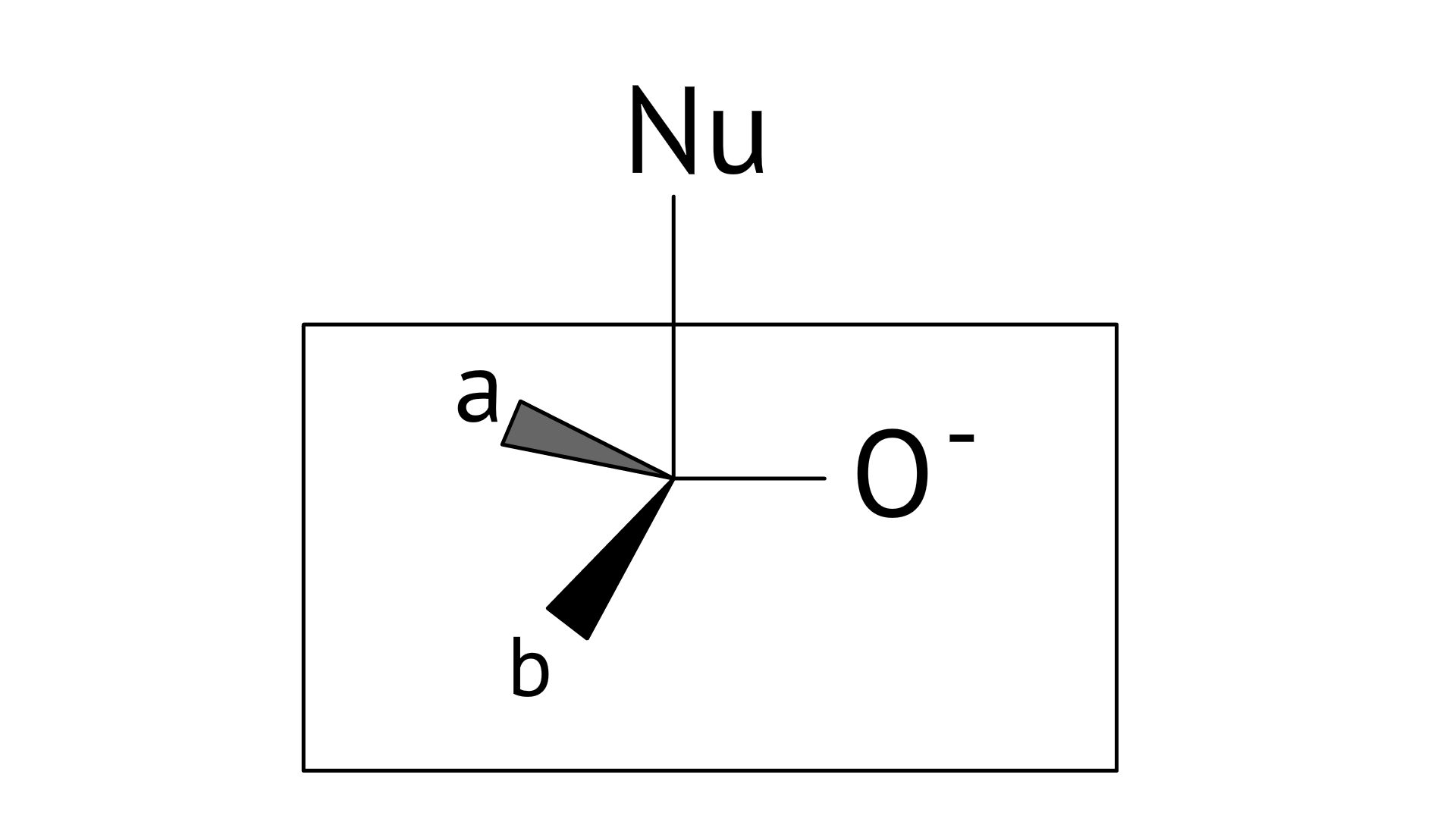
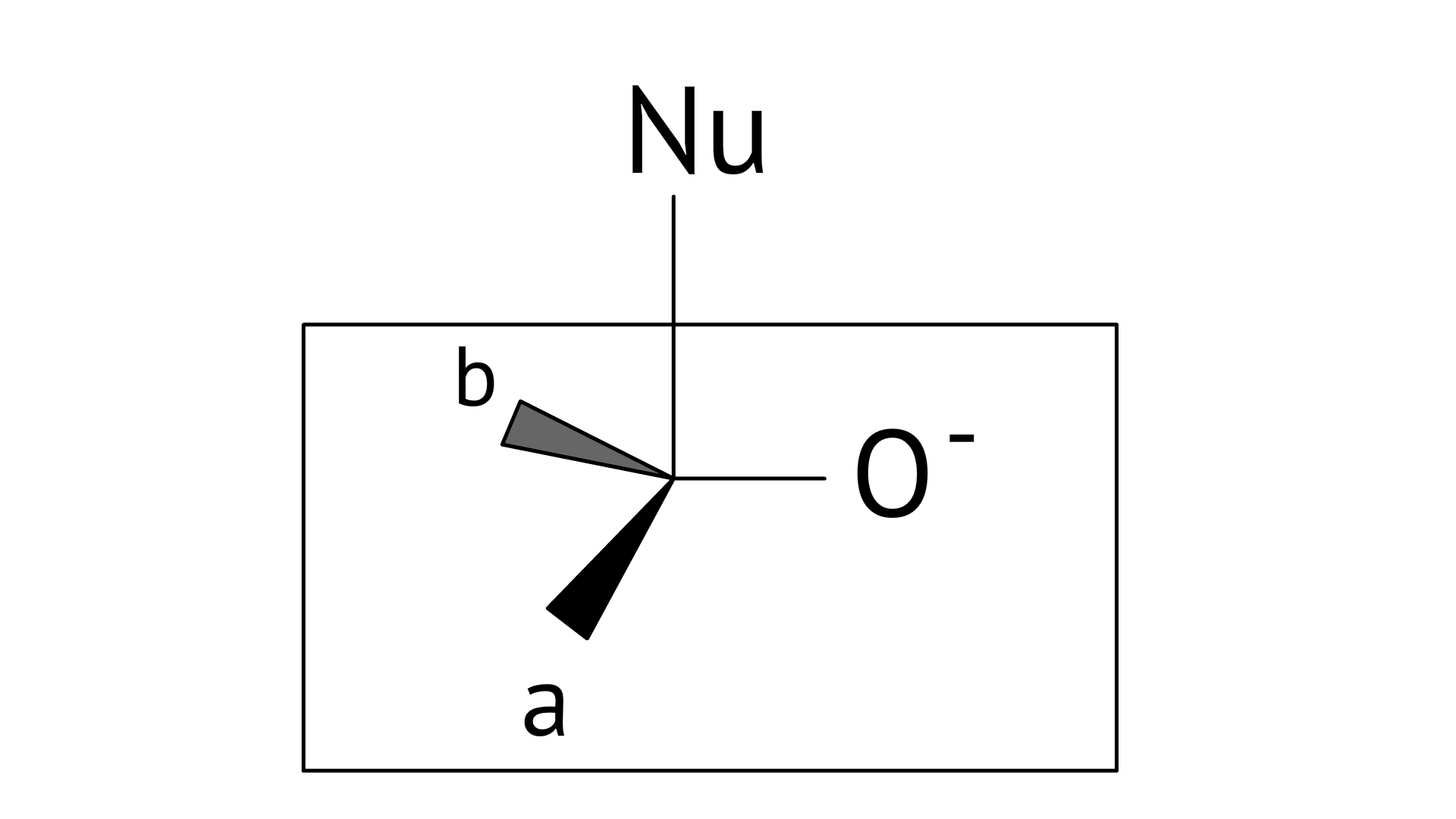
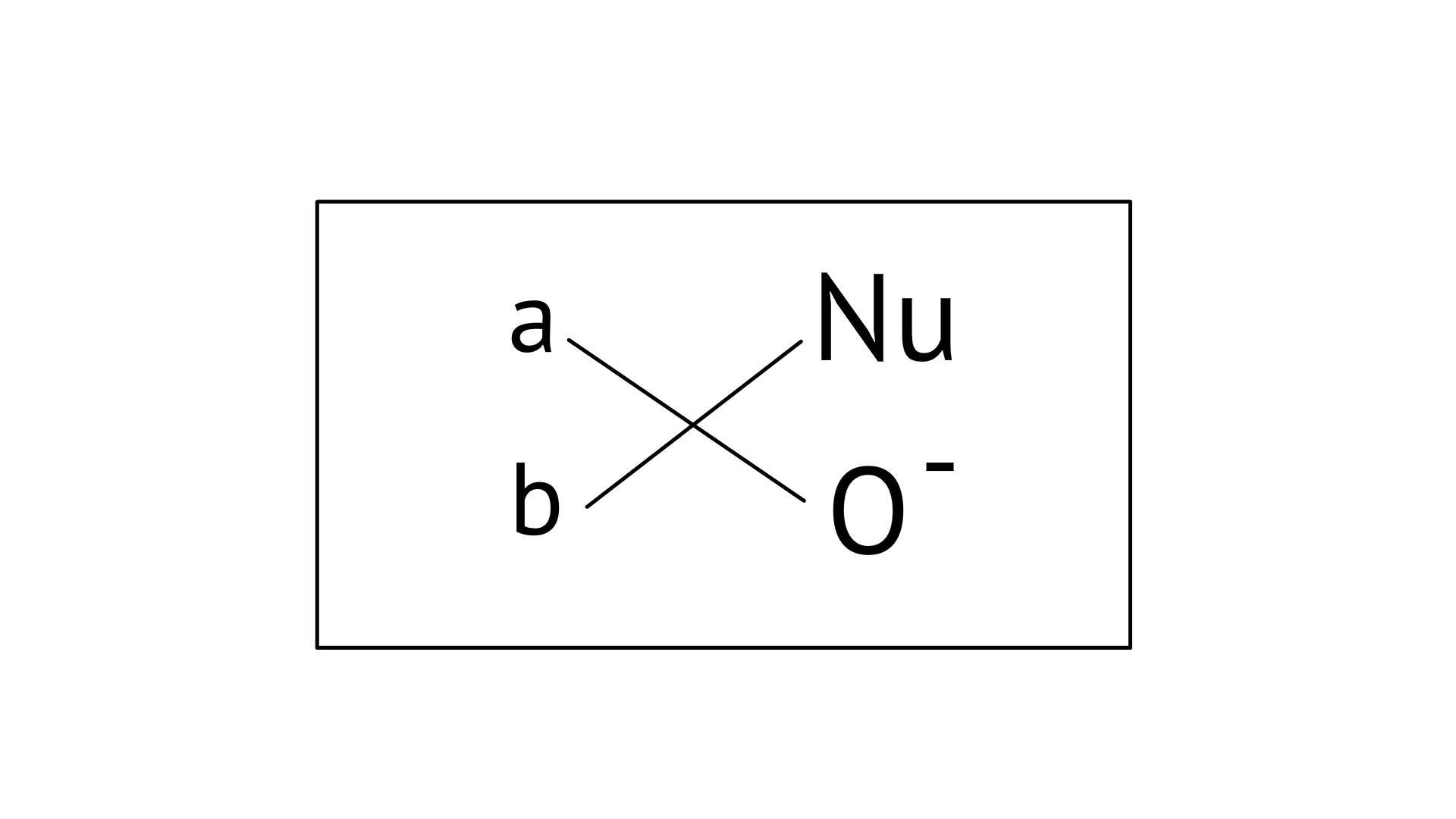
17. Which of the following is the correct representation for intermediate of nucleophilic addition reaction to the given carbonyl compound
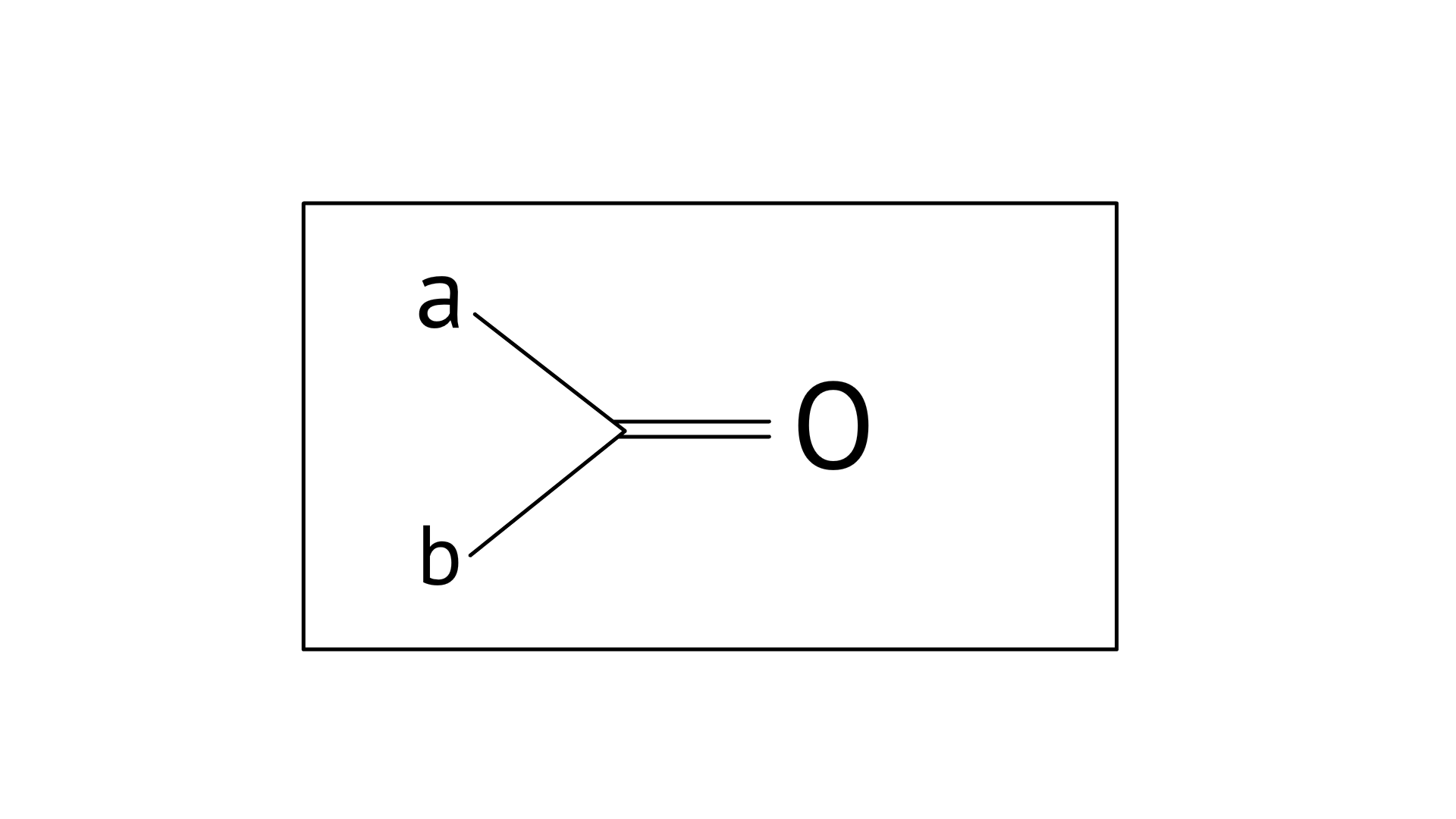
A:
B:
C:
D:
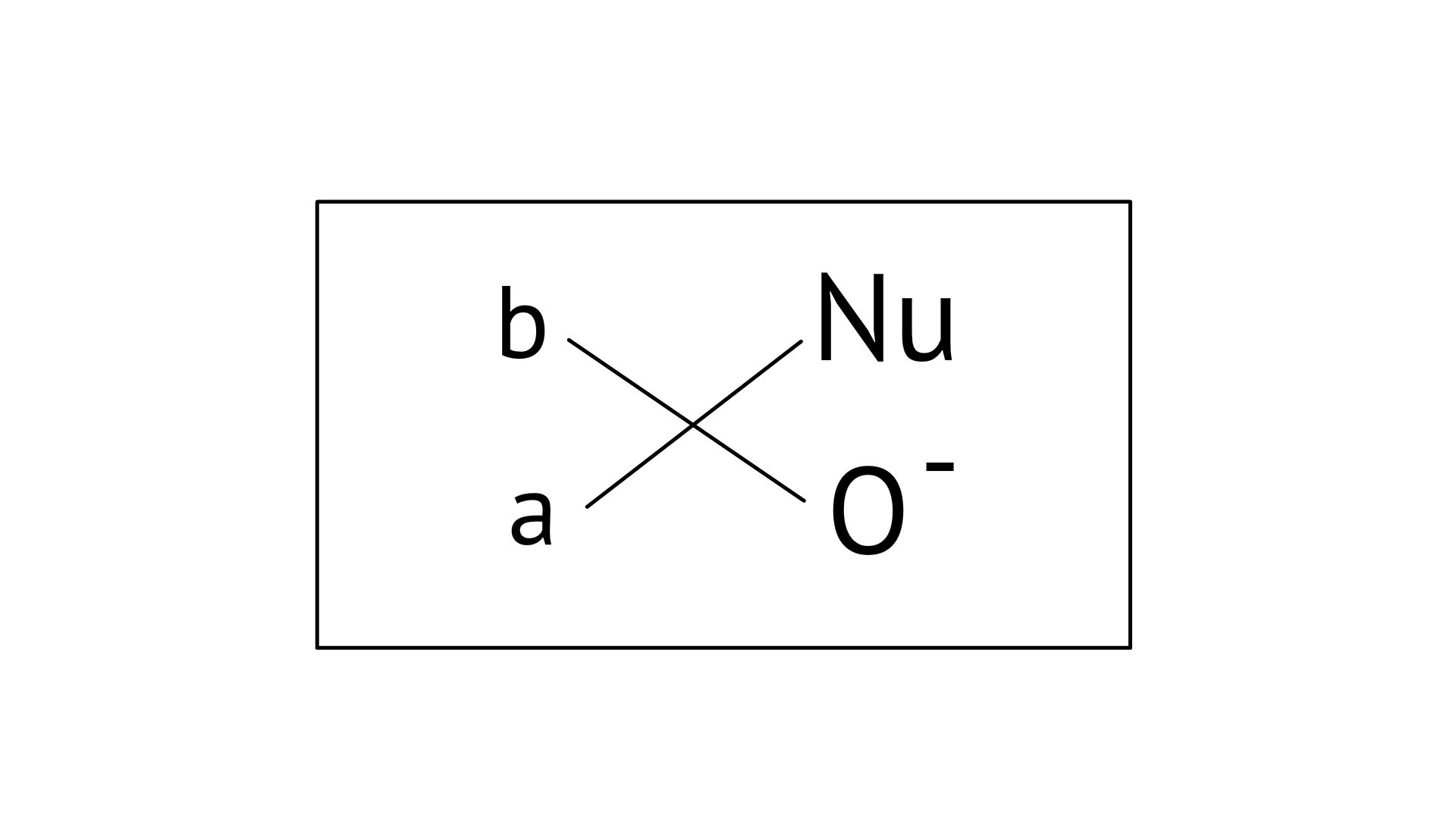
Ans: Correct options: A and B
The given compound is a planar molecule with ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridised carbon. Carbon atoms are attacked by nucleophiles. If the nucleophile approaches from the front, the A and B molecules shift to the front and back positions, respectively, and the carbon becomes tetrahedral. Another alternative is that A and B molecules will be located above and below the plane, respectively. As a result, the choices C and D aren't represented as planar molecules.
III. Short Ans: Type
18. Why is there a large difference in the boiling points of butanal and butan-1-ol?
Ans:
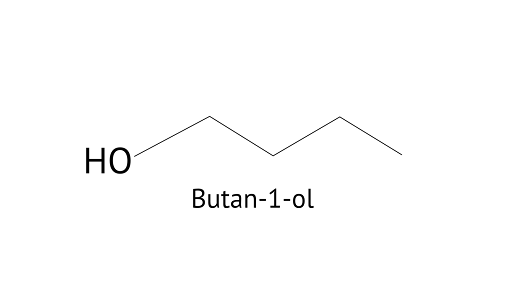
Butanol is a four-carbon aldehyde, with the aldehyde group on the fourth carbon. It has a functional group and a carbonyl group that interacts dipole-dipole. Because butanol possesses a polar O-H bond, it exhibits intermolecular H bonding, which is not feasible in butanal due to the lack of a polar bond. The boiling point of butanol is higher than that of butan-1-ol.
19. Write a test to differentiate between pentan-2-one and pentan-3-one
Ans:
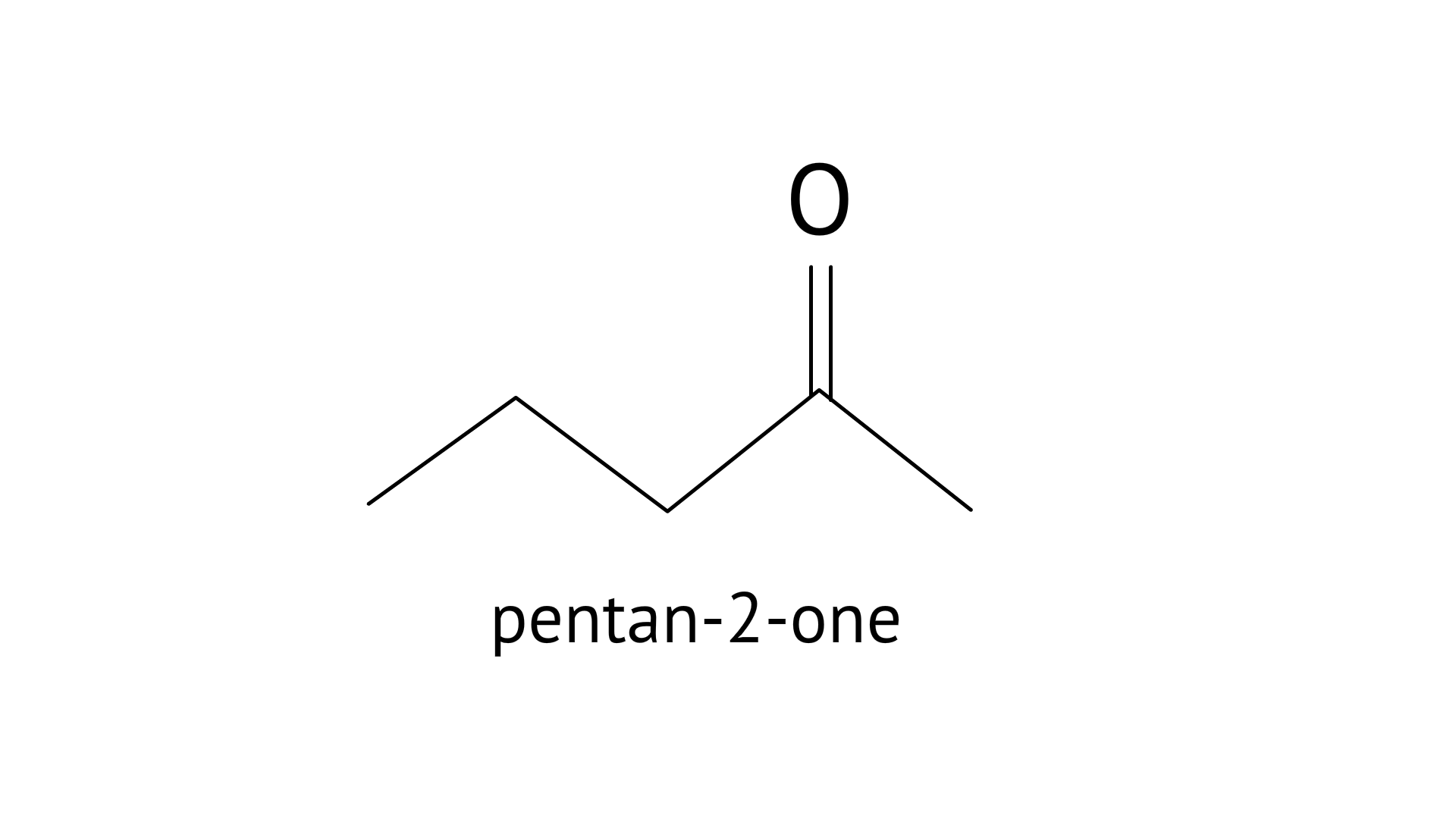
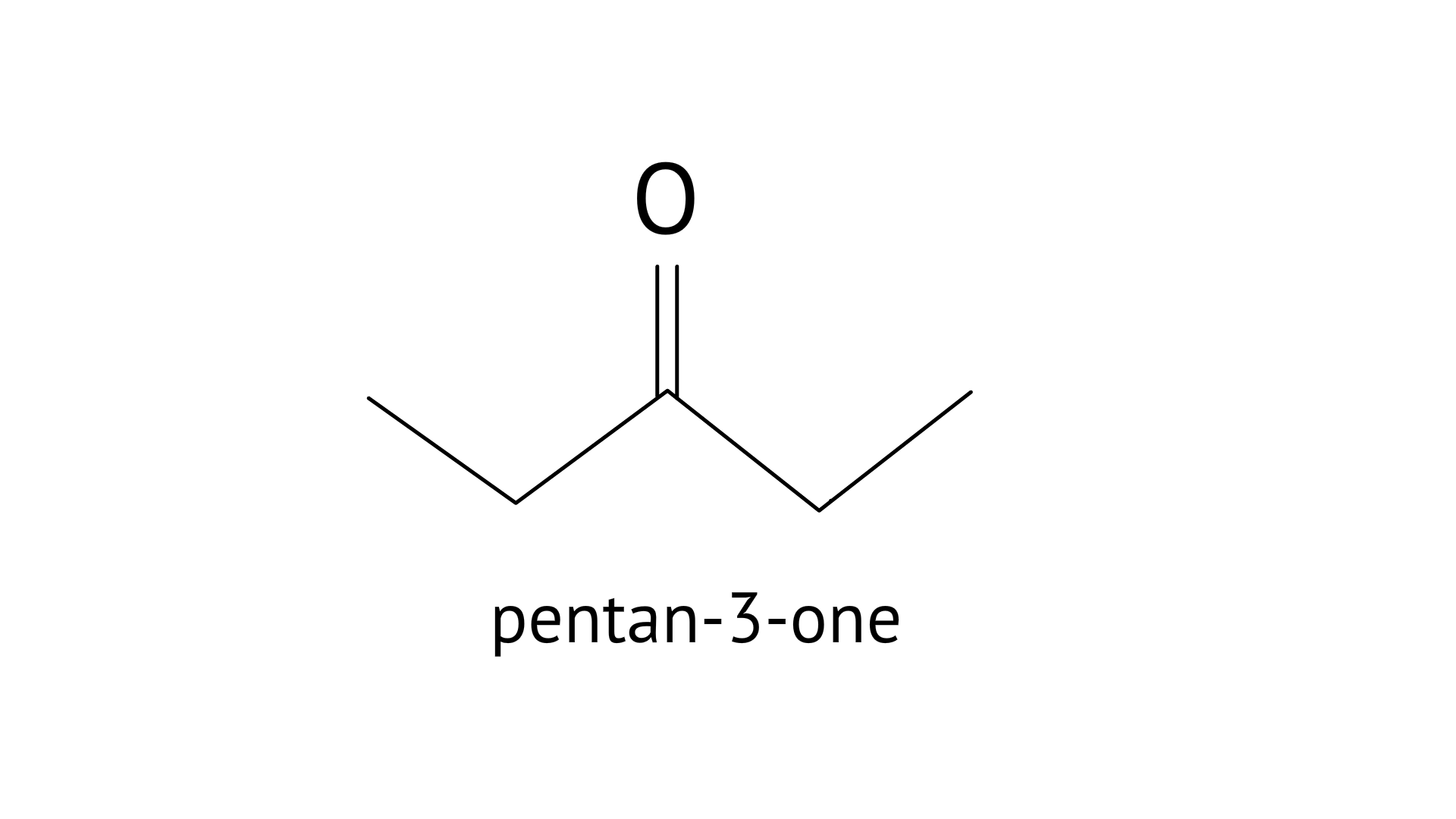
Ketone group should have methyl ketone in the iodoform test. Yellow ppt is formed when the ketone, base, and iodine react. If it's methyl ketone, the test will come back positive. Pentan-2-one and pentan-3-one are the methyl ketones.
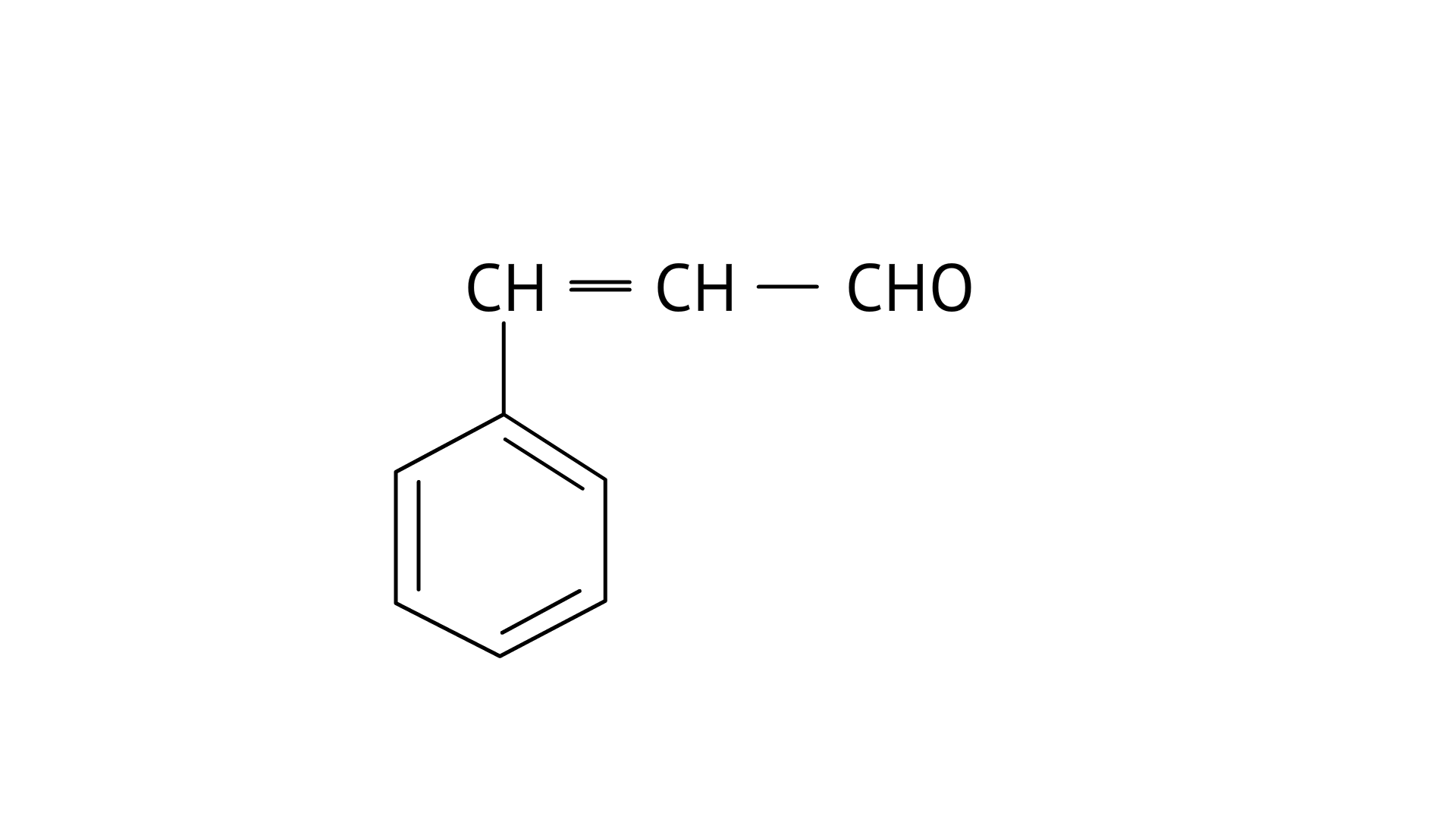
20. Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds
A:
B:
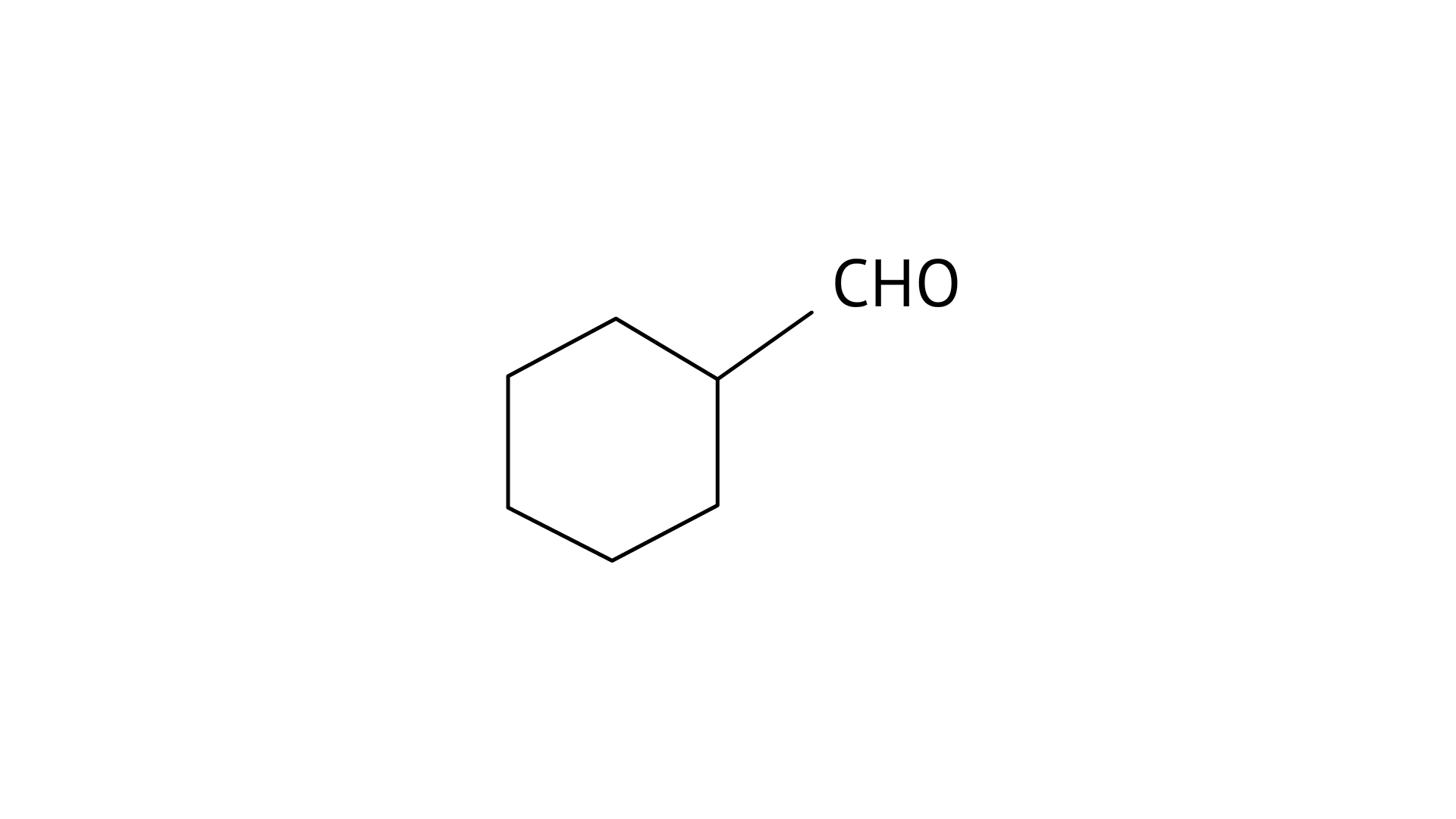
C:
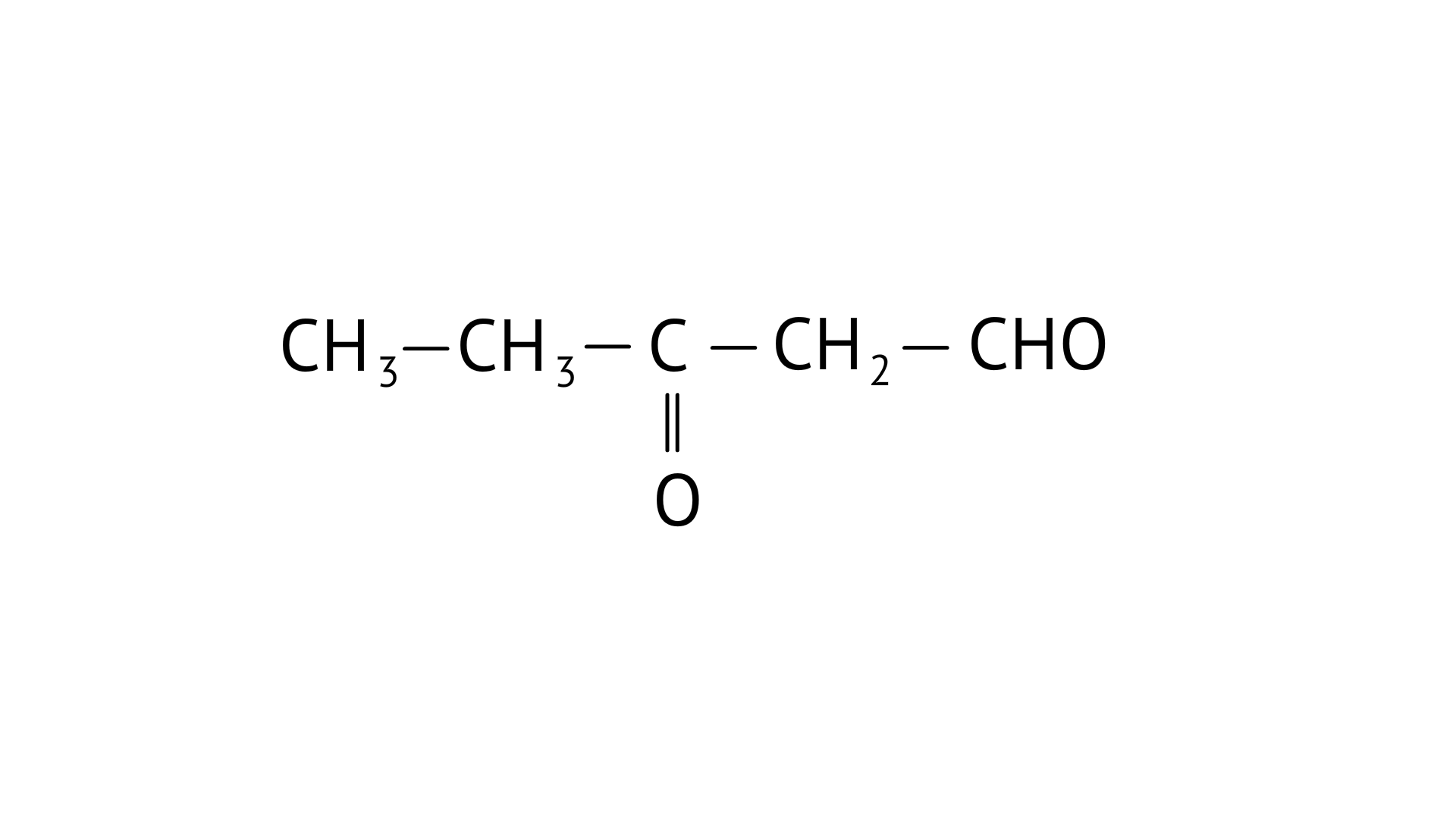
D: ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ - CH = CH - CHO}}$
Ans:
(i) 3-Phenylprop-2-enal
(ii) Cyclohexanecarbaldehyde
(iii) 3-oxopentanal
(iv) But -2-enal
21. Give the structure of the following compounds.
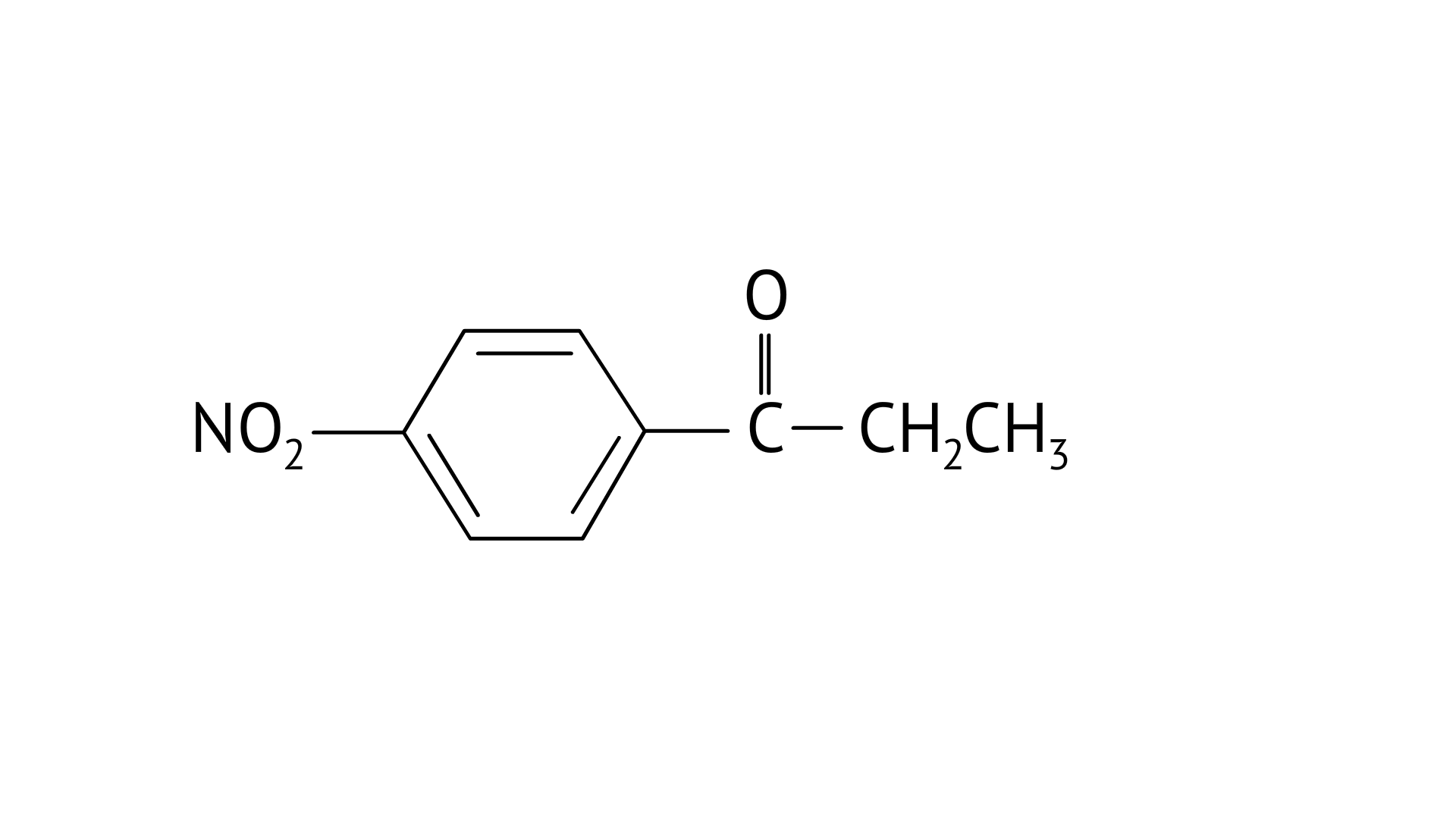
A: 4-Nitropropiophenone
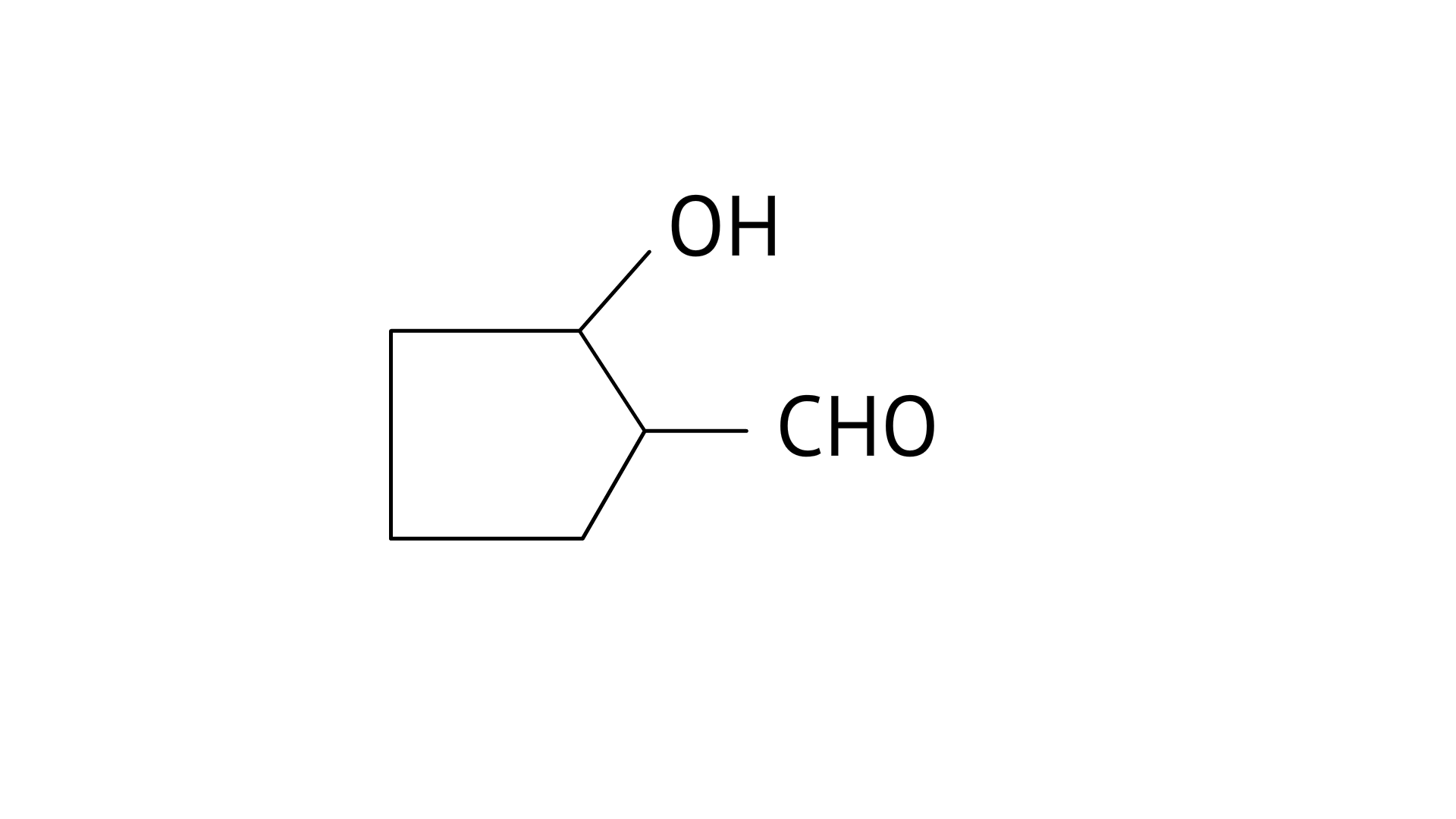
B: 2-Hydroxycyclopentanecarbaldehyde
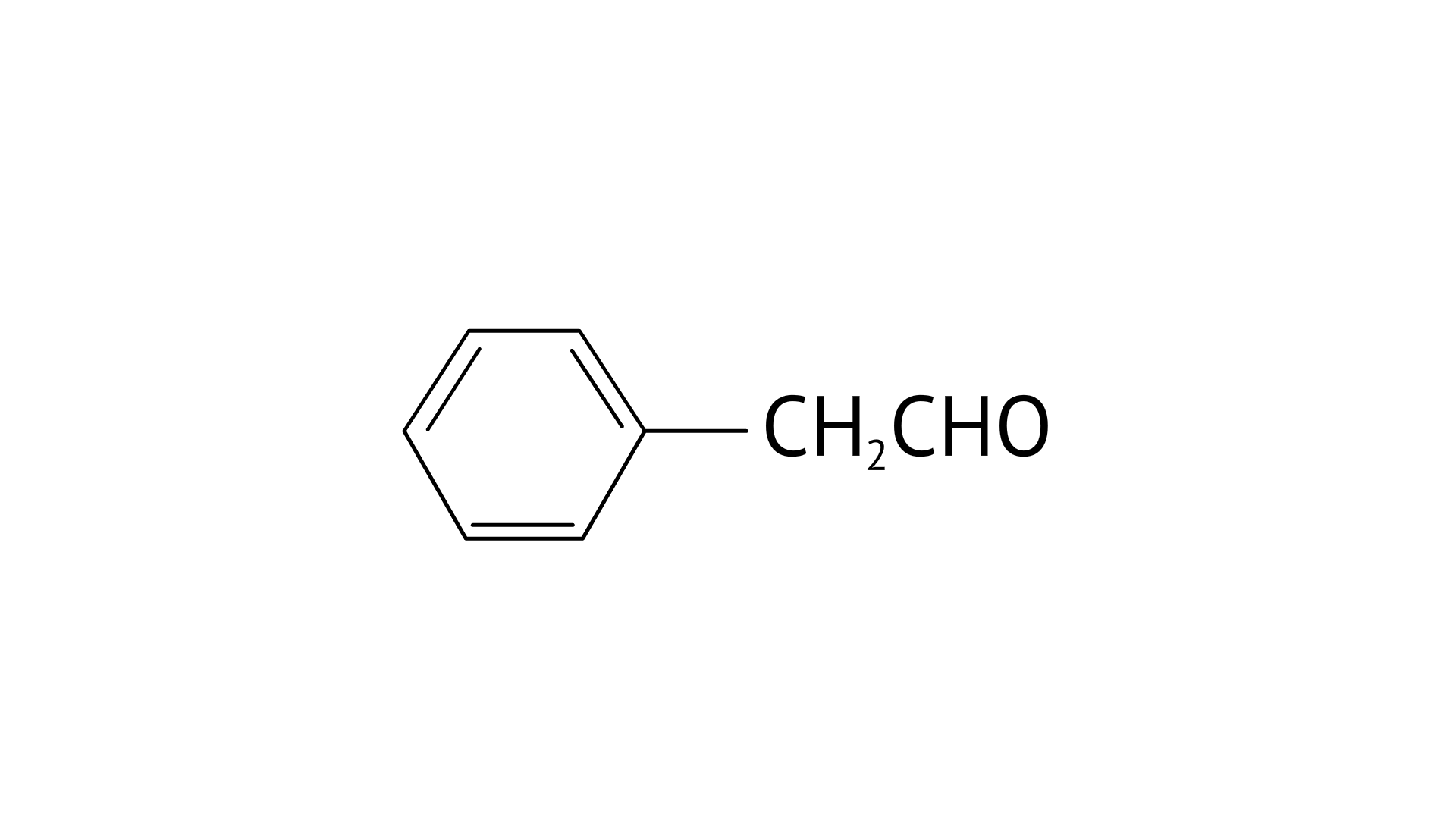
C: Phenyl acetaldehyde
Ans:
A:
B:
C:
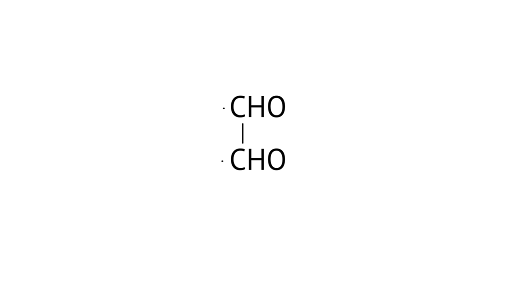
22. Write IUPAC names of the following structures.
A:
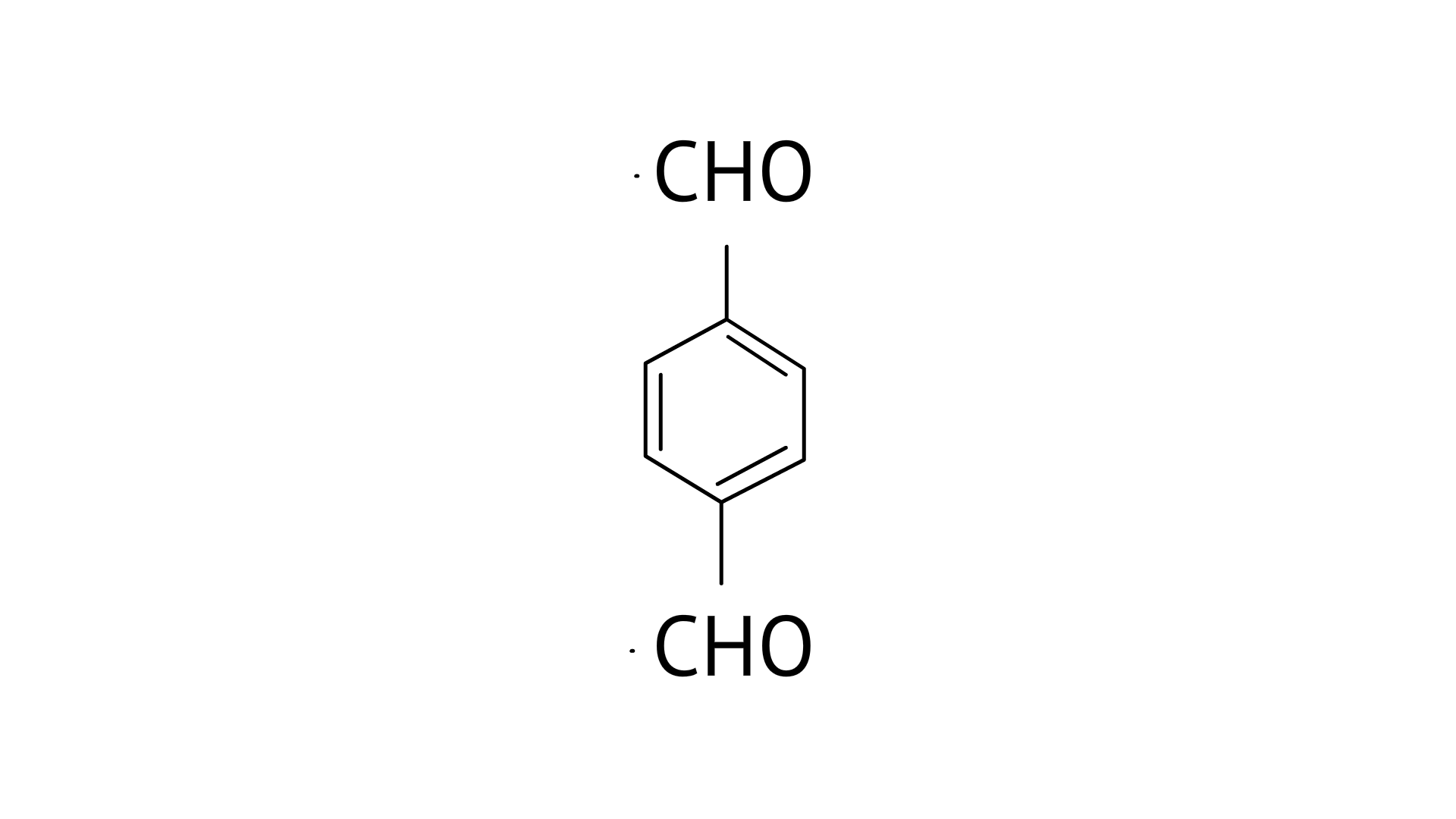
B:
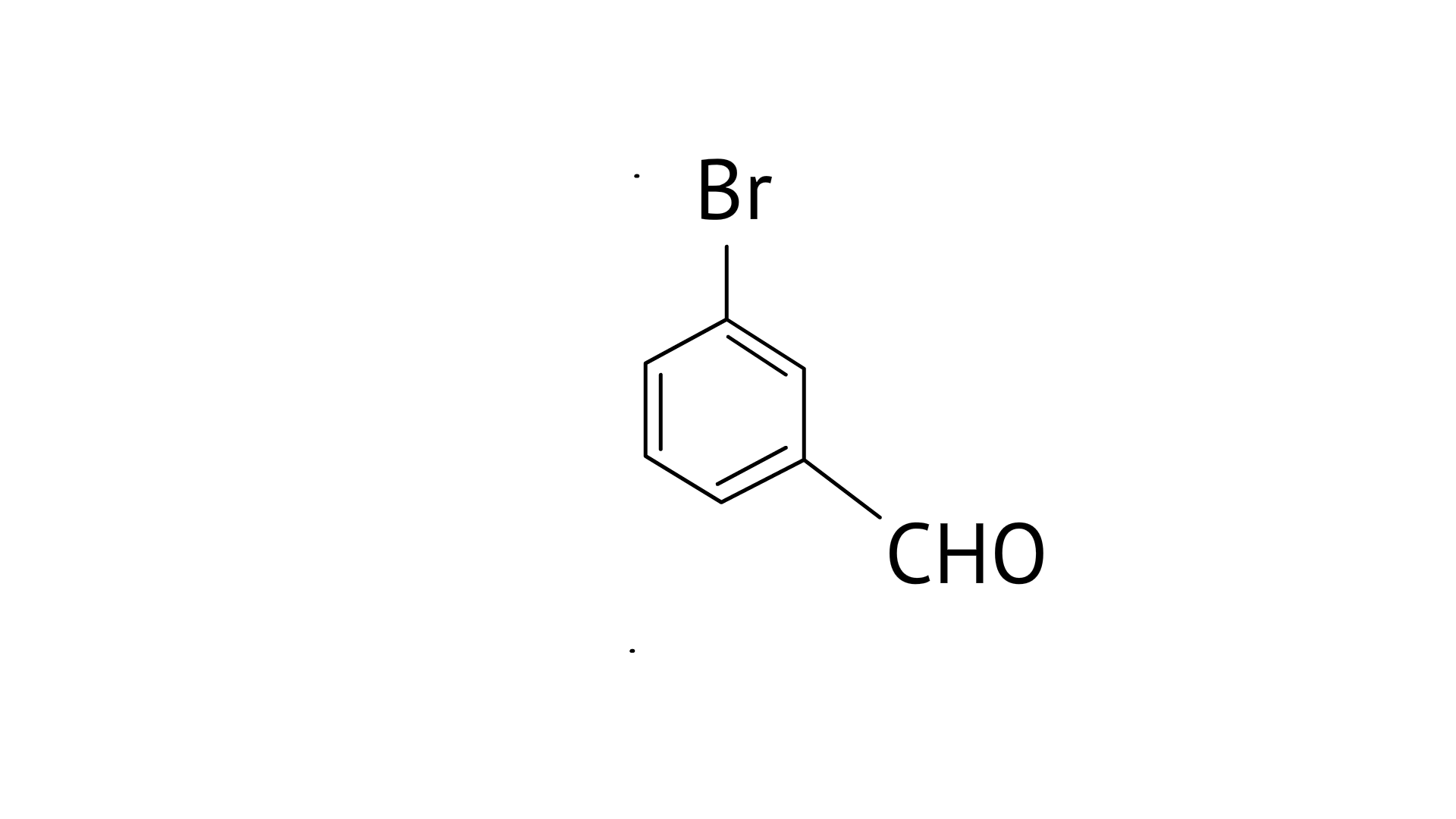
C:
Ans:
A: Ethane-1, 2-dial
B: Benzene-1, 4-carbaldehyde
C: 3-Bromobenzaldehyde
23. Benzaldehyde can be obtained from benzal chloride. Write reactions for obtaining benzalchloride and then benzaldehyde from it
Ans:
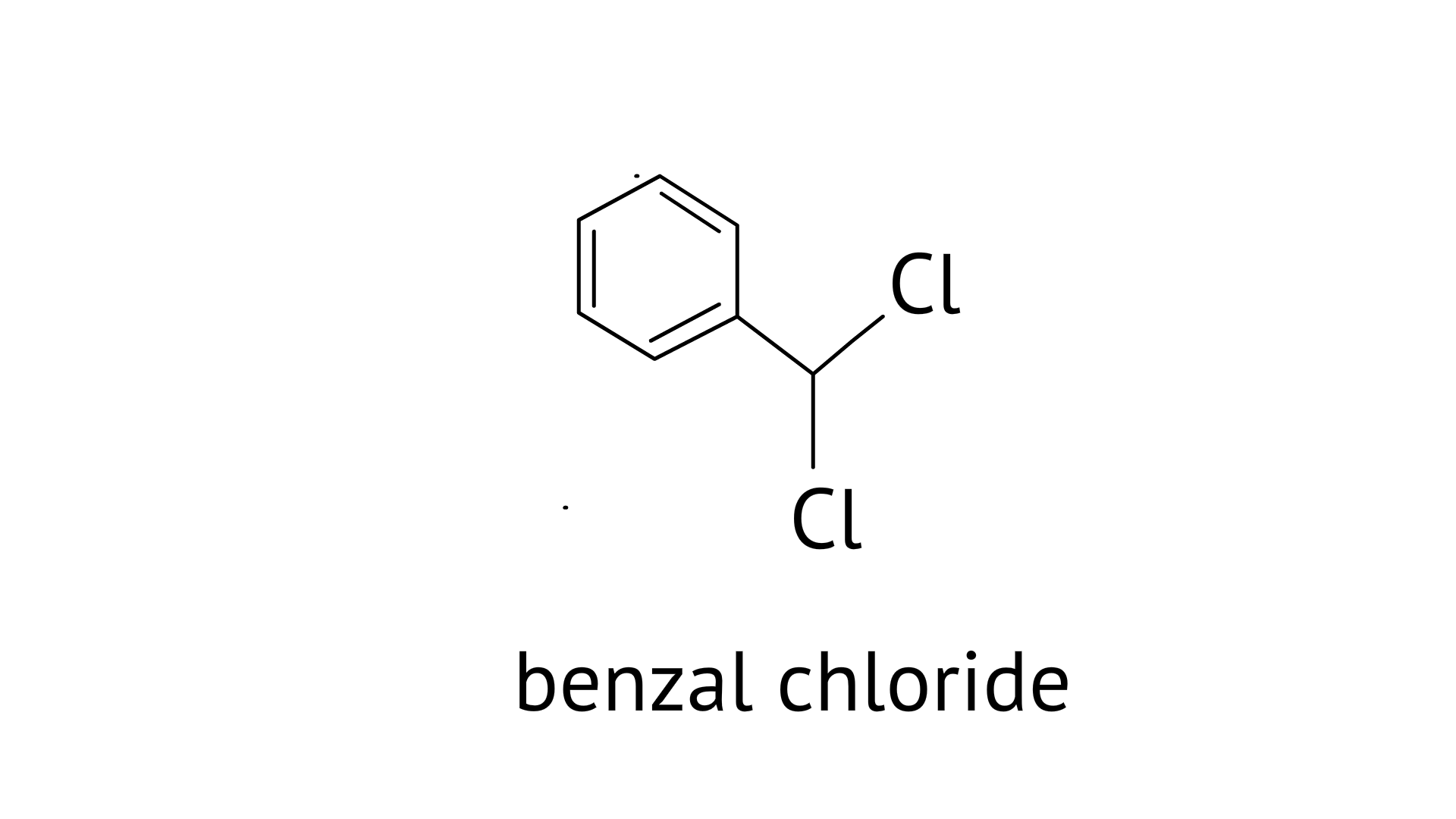
Benzal chloride can be made by chlorinating toluene in the presence of sunshine and then using the hydrolysis process to obtain benzaldehyde. This method can be used to make benzaldehyde in a commercial setting.
24. Name the electrophile produced in the reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous ${\text{AlC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$. Name the reaction also.
Ans: The electrophile formed when benzene reacts with benzoyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous ${\text{AlC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ is benzoylinium cation, and the resultant product is benzophenone. Friedel Crafts acylation reaction is the name for this reaction.
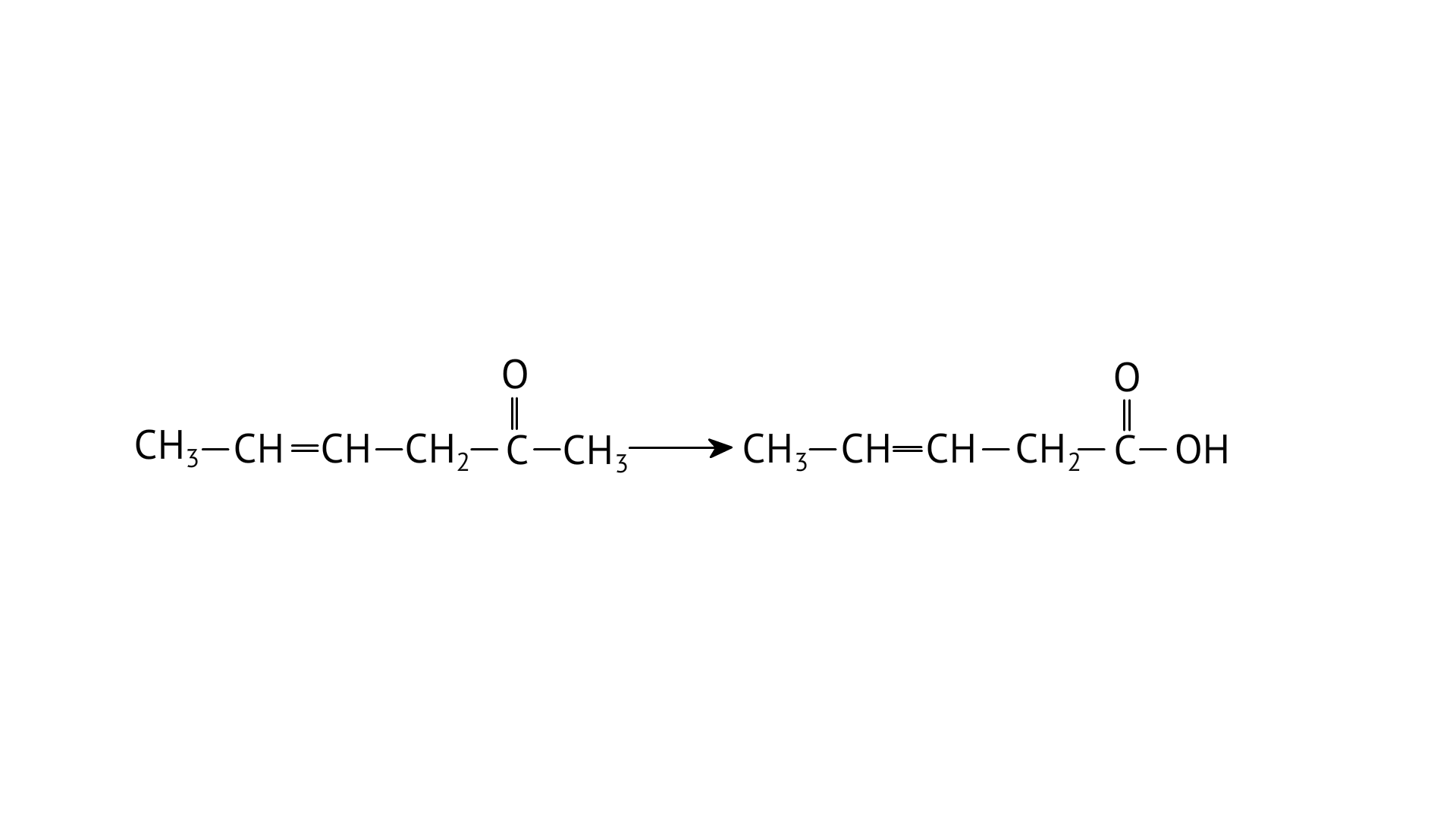
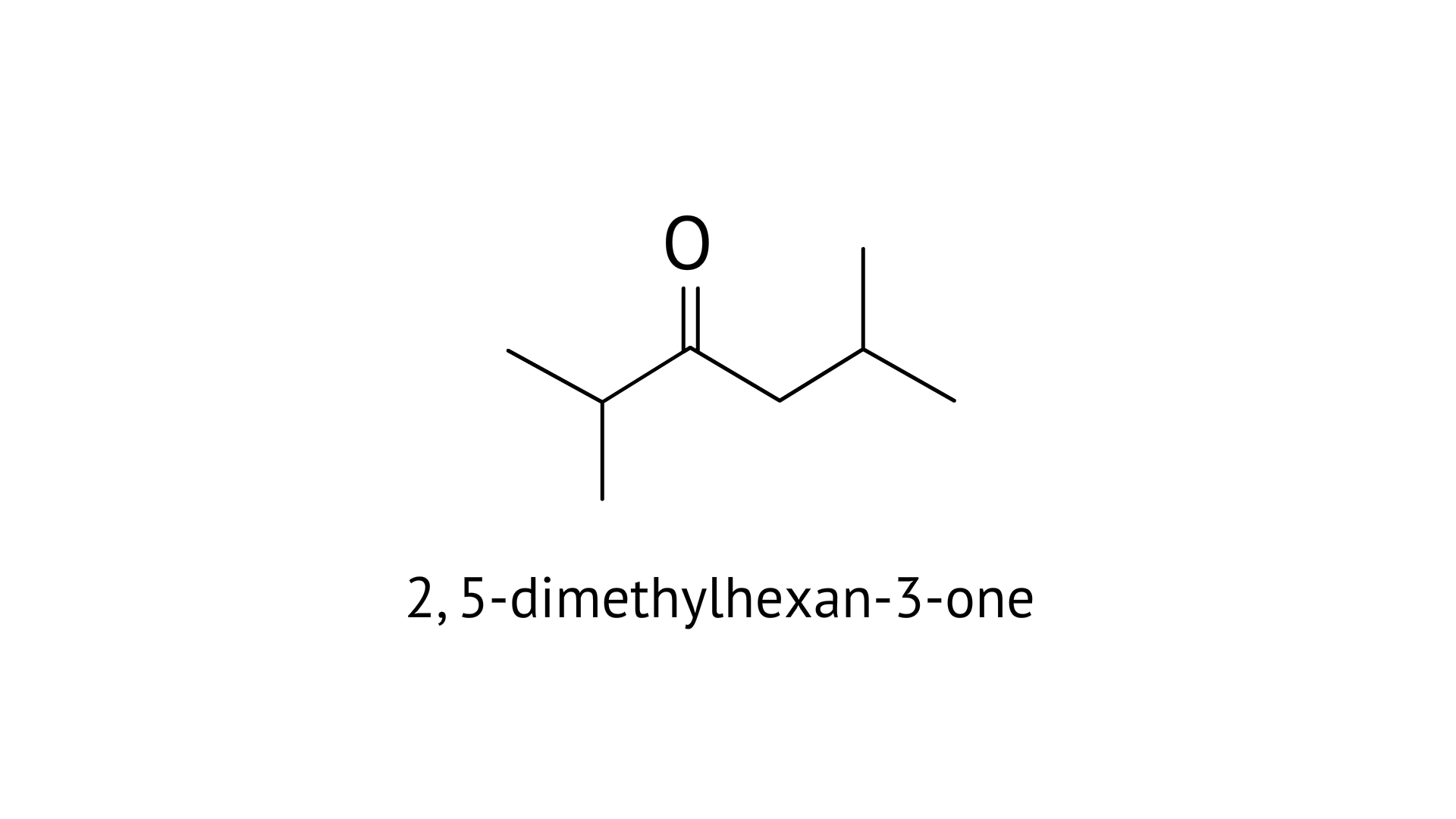
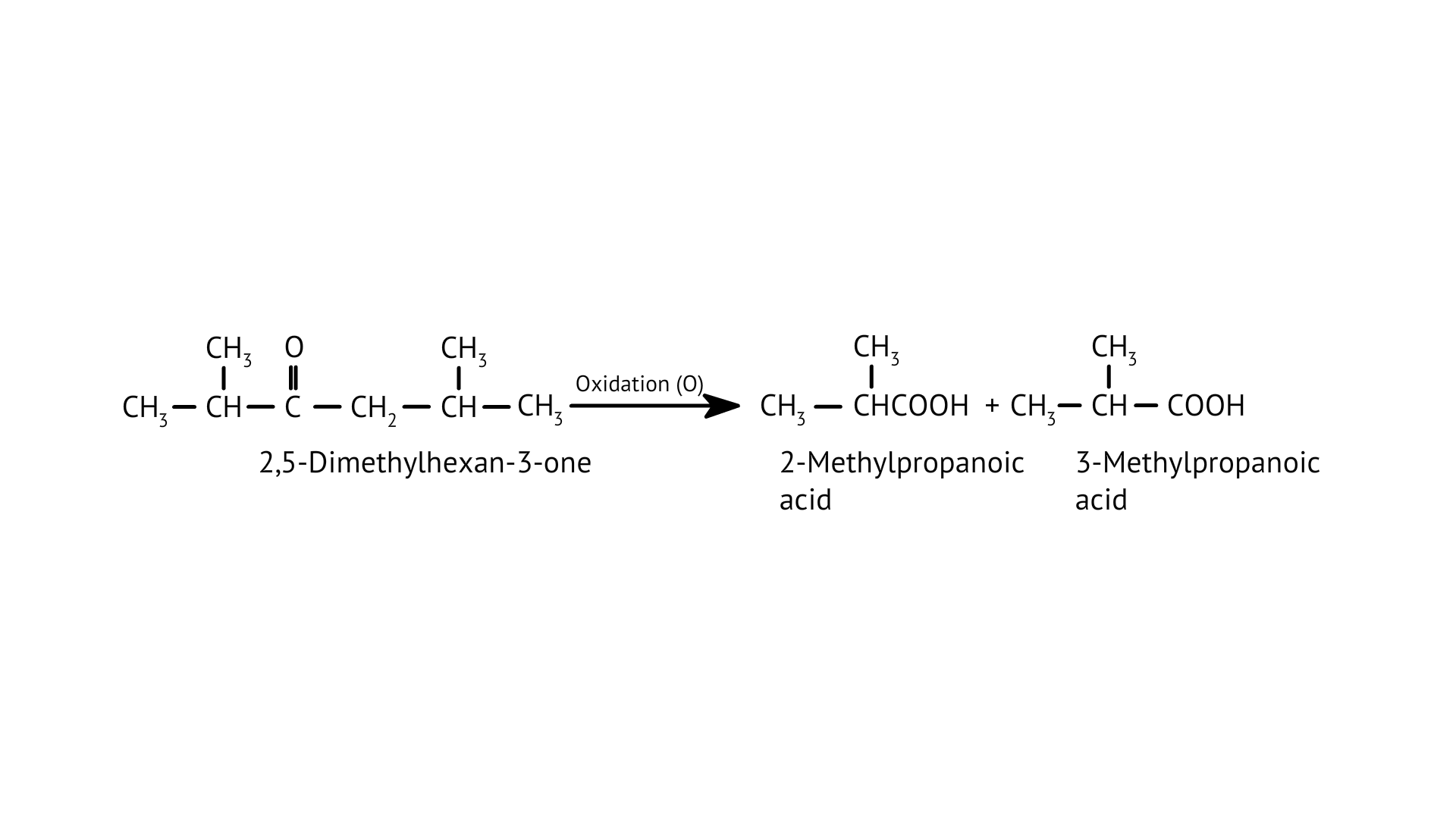
25. Oxidation of ketones involves carbon-carbon bond cleavage. Name the products formed on oxidation of 2, 5-dimethylhexan-3-one.
Ans:
26. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their acidic strength and give reason for your Ans:.
$C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH,C{{H}_{3}}COOH,\text{ }ClC{{H}_{2}}COOH,\text{ }FC{{H}_{2}}COOH,\text{ }{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH$.
Ans: $ClC{{H}_{2}}COOH~>~FC{{H}_{2}}COOH~>~{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH~>~C{{H}_{3}}COOH~>~C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$
When compared to other alcohols, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$ is the least acidic. Because of the halogen, ${\text{FC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}$ is quite acidic. It is either an electron donating group or an electron receiving group in acidic strength. Acidic strength increases as the number of electron withdrawing groups increases. The acidic strength of electron donating groups diminishes.
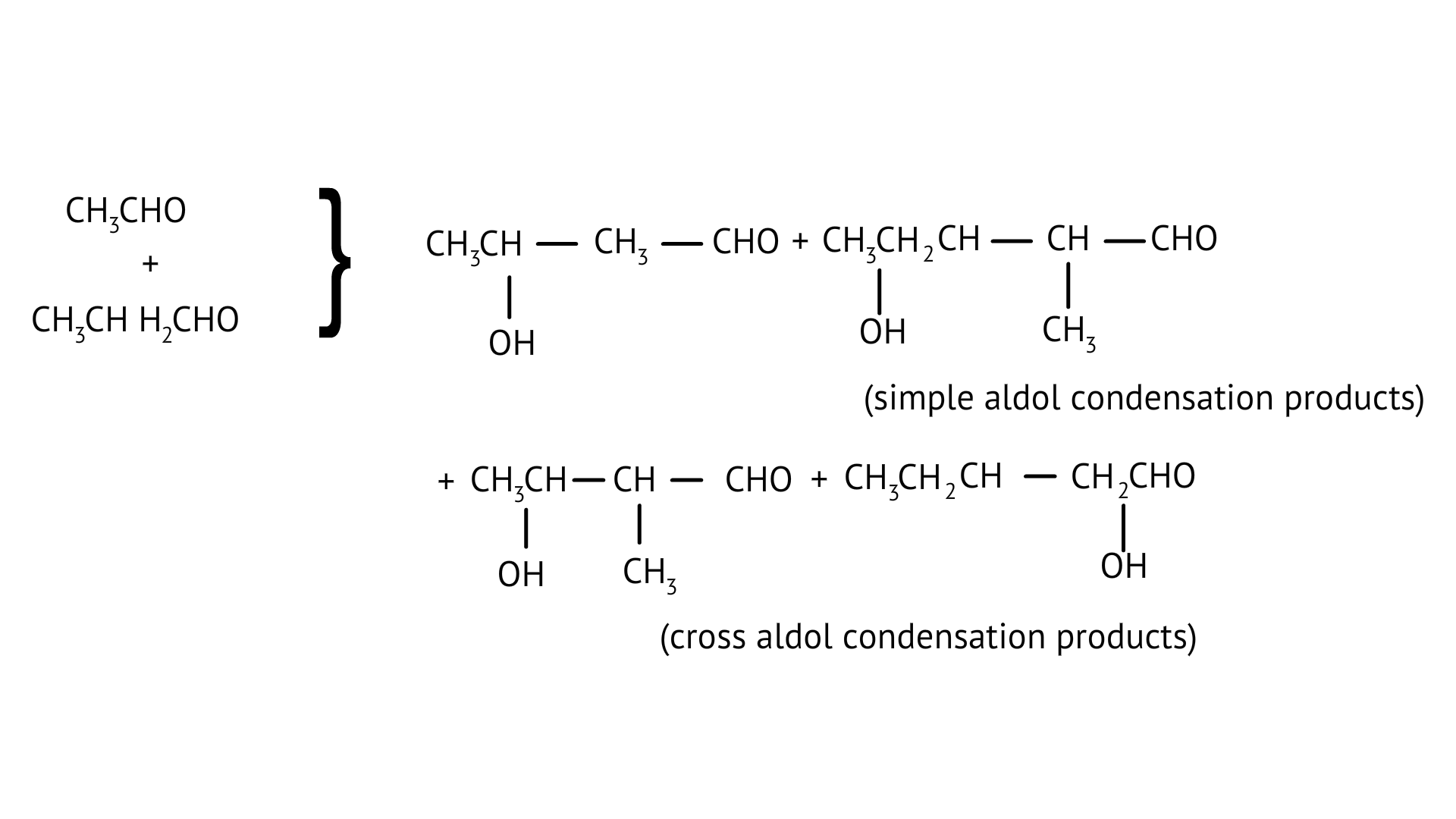
27. What product will be formed on reaction of propanal with 2-methylpropanal in the presence of ${\text{NaOH}}$? What products will be formed? Write the name of the reaction also?
Ans: It's referred to as cross Aldol Condensation.
Cross aldol condensation occurs when two separate aldehydes or ketones combine to form a single molecule.
30. Compound ‘A’ was prepared by oxidation of compound ‘B’ with alkaline ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$. Compound ‘A’ on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride gets converted back to compound ‘B’. When compound ‘A’ is heated with compound B in the presence of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ it produces a fruity smell of compound C to which family the compounds ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ belong to?
Ans: When alkaline ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ oxidises compound "B" with compound "A," acid is formed. $\text{B}\xrightarrow[\text{alkaline}\ KMn{{O}_{4}}]{\left[ O \right]}\text{A}\to \text{acid}$
When compound "A" is reduced with ${\text{LiAl}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$, it transforms into compound "B." The letter "B" stands for a type of alcoholic beverage.
${\text{A}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{LiAl}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}}}{\text{B}} \to {\text{Alcohol}}$
When compounds "A" and "B" are heated with conc. ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$, compound "C" is formed, which has a fruity odour.
$\text{A + B}\xrightarrow[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}]{\Delta }fruity smell\left( ester \right)$
31. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their acidic strength. Give for the arrangement.
${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{COOH, FC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH, N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}$
Ans:
${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH > FC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH > }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{COOH}}$
To begin, determine whether it has an acidic strength associated with it, and whether it is an electron donating or electron withdrawing group. Acidic strength increases as the number of electron withdrawing groups increases. The acidic strength reduces as the electron donating group increases. In decreasing order, the most influential acidic strength is $-N{{O}_{2}}>~-F>~-{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}$.
32. Alkenes
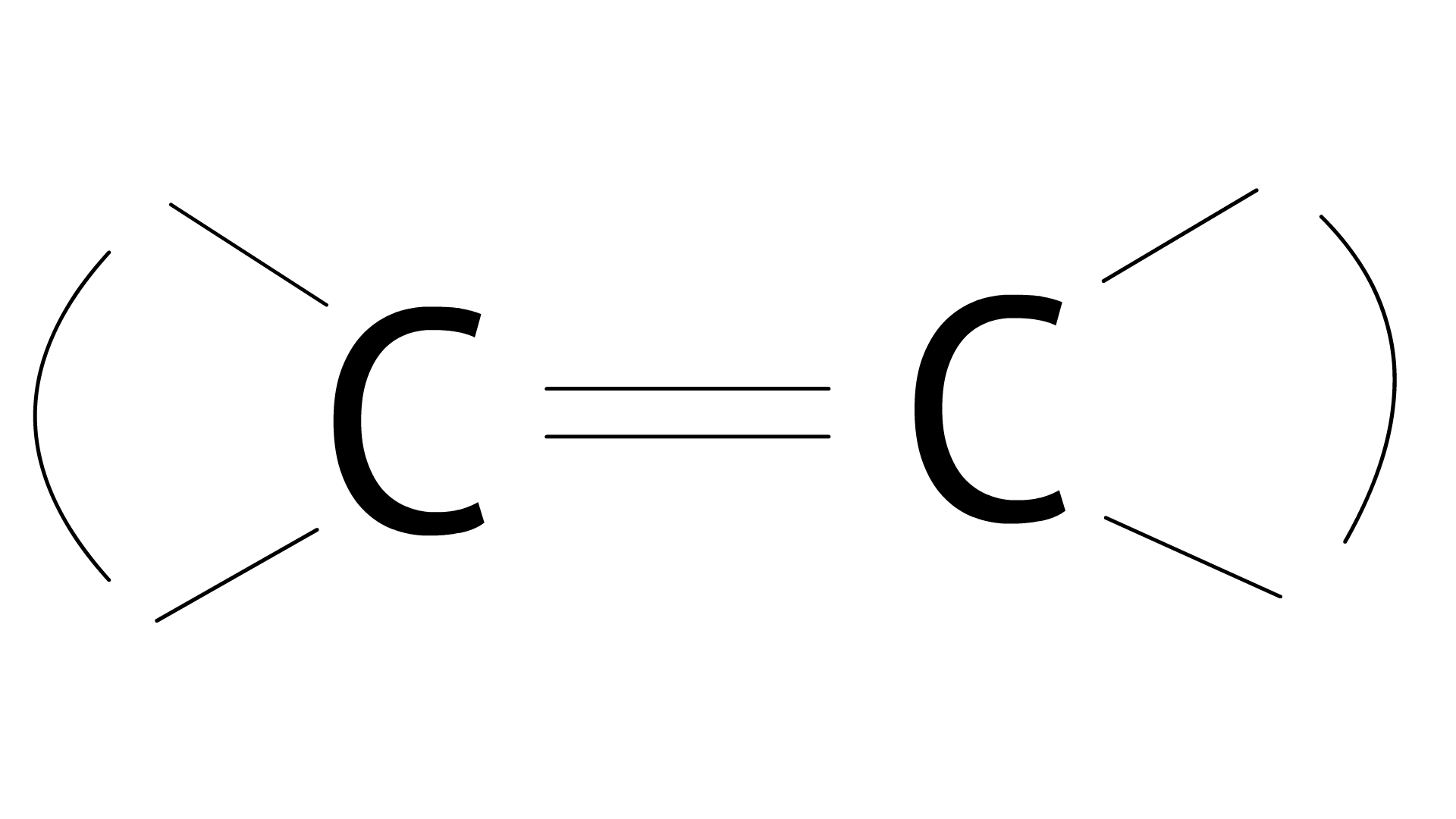
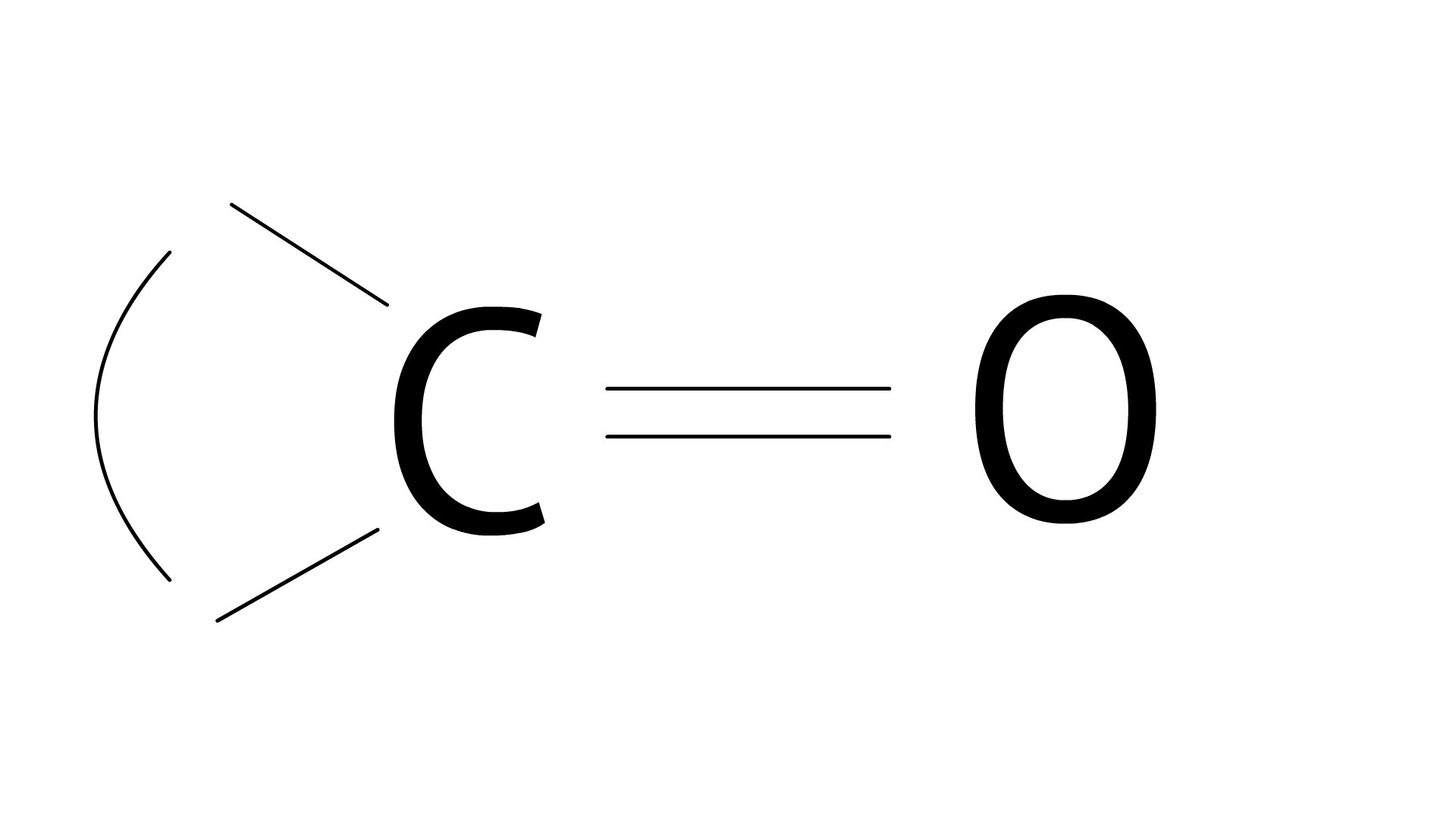
Ans:
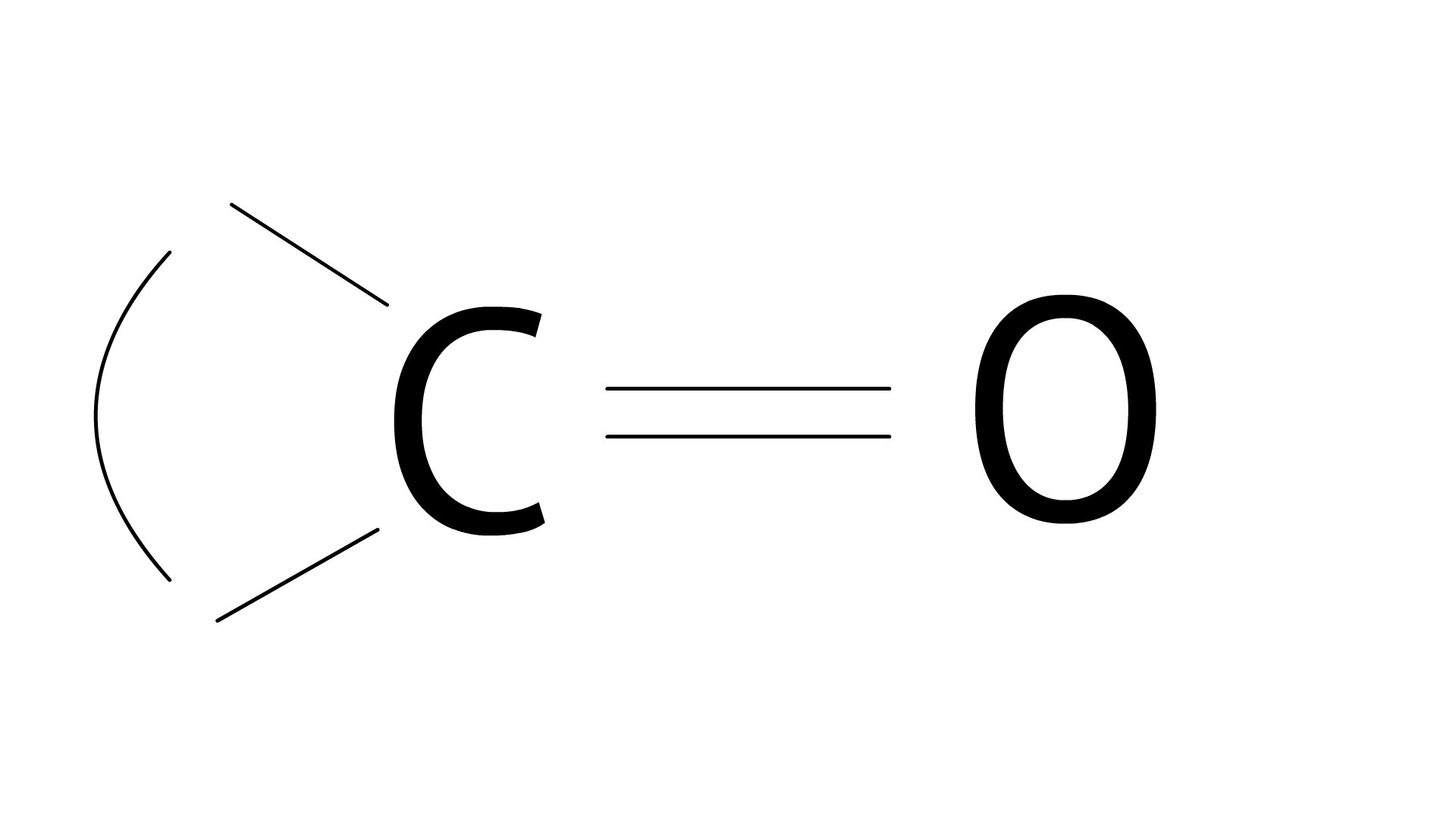
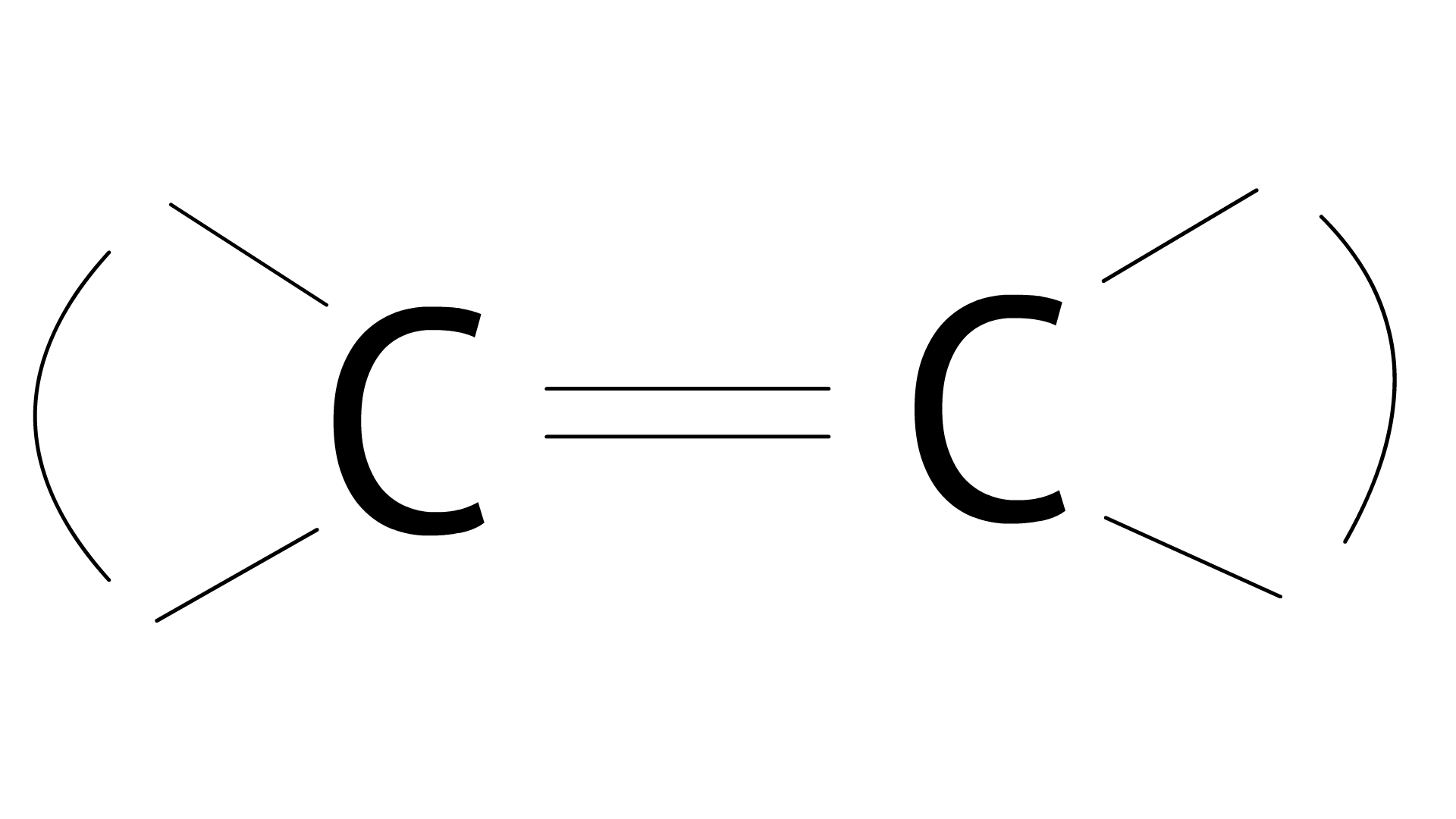
33. Carboxylic acids contain carbonyl group but do not show the nucleophilic addition reaction like aldehydes or ketones. Why?
Ans: The presence of a lone pair of electrons on an atom of the OH group diminishes the electrophilic character of C through resonance; carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl group. As a result, the carbonyl atom's partial positive charge is lowered.
34. Identify the compounds A, B and C in the following reaction
$C{{H}_{3}}-Br\xrightarrow{\frac{Mg}{Ether}}\left( A \right)\xrightarrow[(ii)water]{\left( i \right)C{{O}_{2}}}(B)\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{\frac{C{{H}_{3}}OH}{{{H}^{\text{ }+\text{ }}}}}(C)$
Ans:
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{MgBr}}$
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH}}$
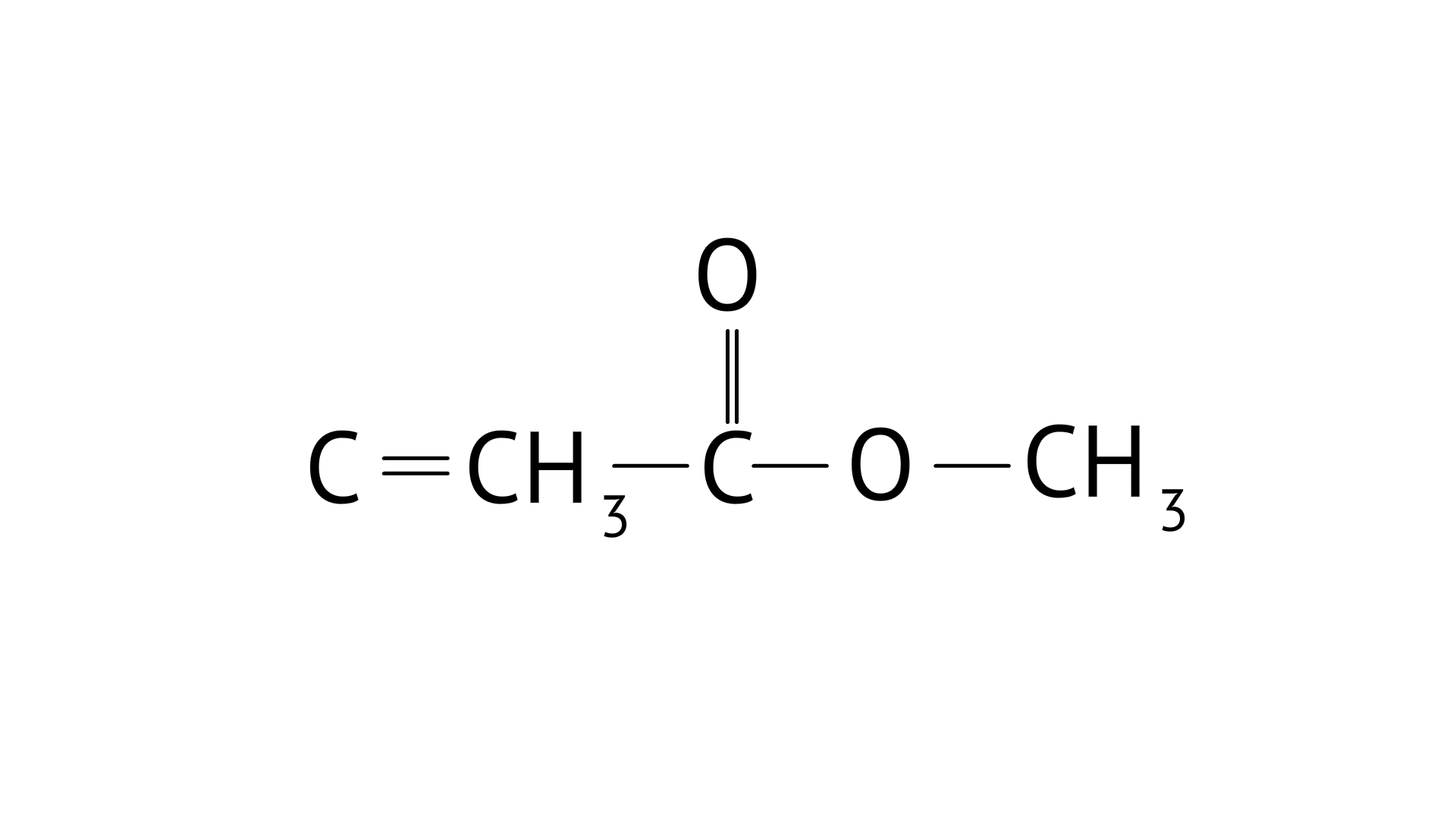
35. Why are carboxylic acids more acidic than alcohols or phenols although all of them have hydrogen atom attached to an oxygen atom (—O—H)?
Ans: Although all of them have a hydrogen atom connected to an oxygen atom (—O—H), carboxylic acids are more acidic than alcohols or phenols. This can be explained by the conjugate base's stability after ${{H}^{+}}$ ions have been removed from the acid and phenol.
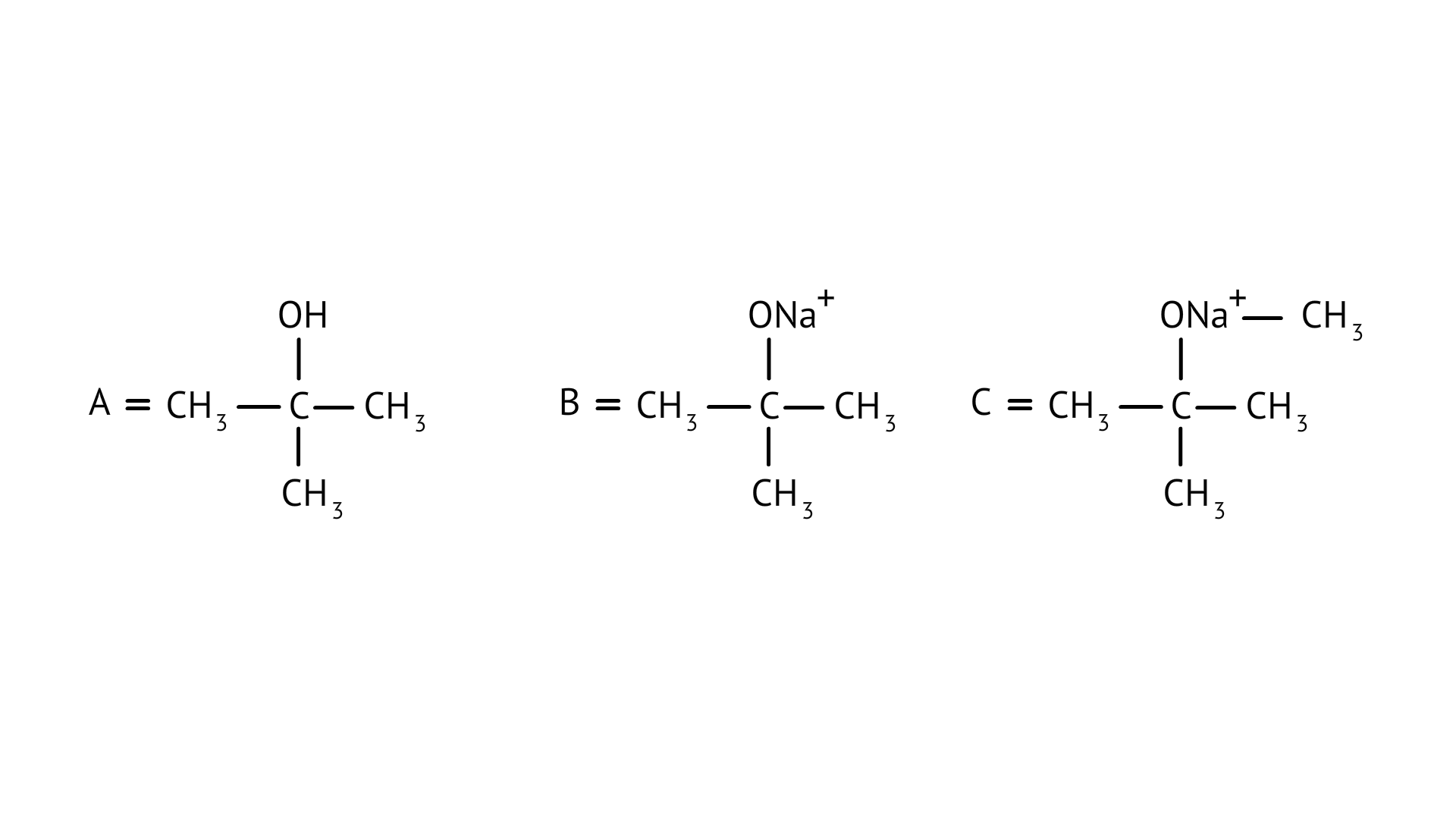
36. Complete the following reaction sequence.
\[C{{H}_{3}}\text{ }-\text{ }Br\xrightarrow{\frac{Mg}{Ether}}\left( A \right)\xrightarrow[(ii)water]{\left( i \right)C{{O}_{2}}}(B)\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{C{{H}_{3}}OH/{{H}^{\text{ }+\text{ }}}}(C)\]
Ans:
37. Ethylbenzene is generally prepared by acetylation of benzene followed by reduction and not by direct alkylation. Think of a possible reason.
Ans:
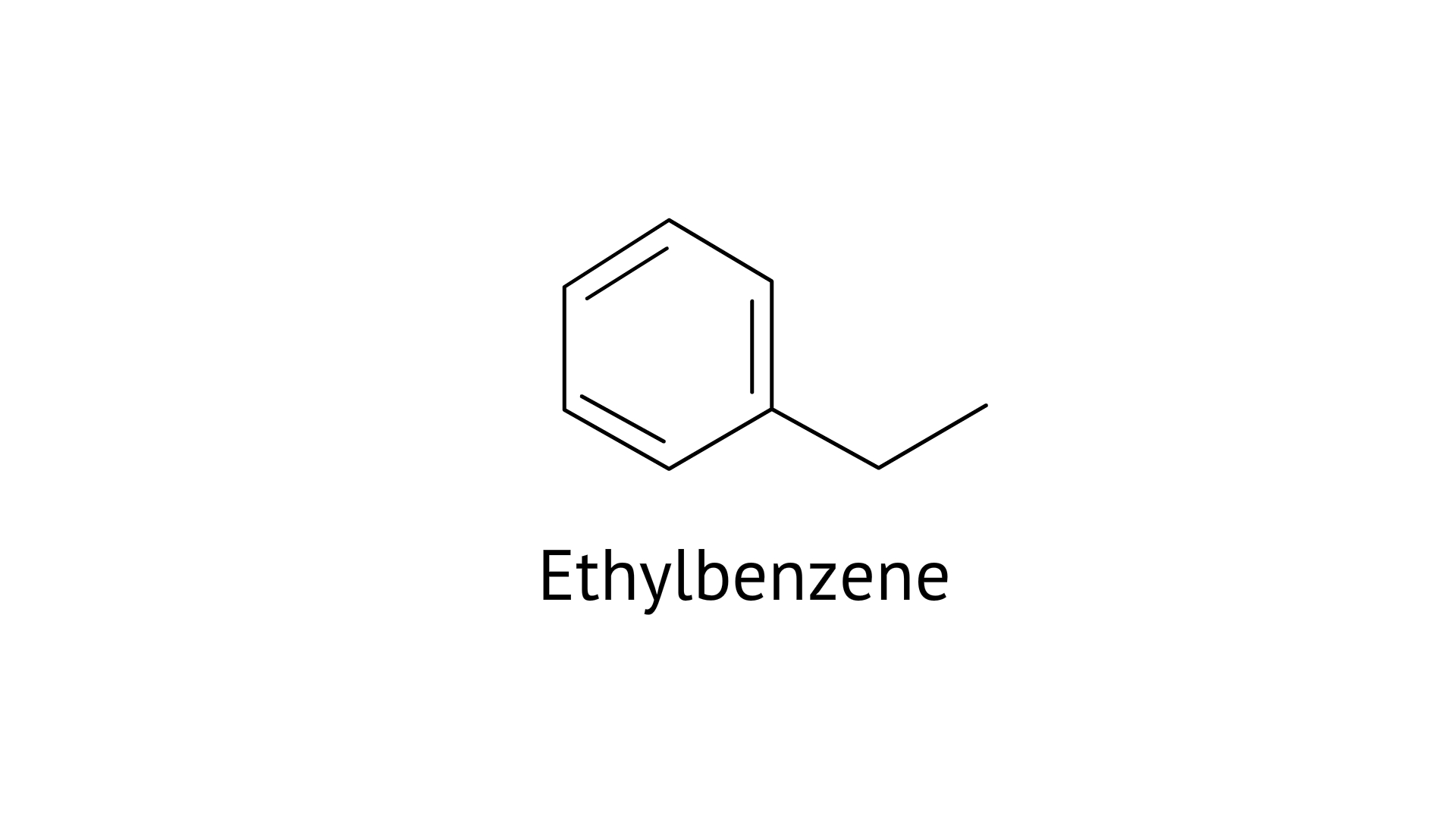
Due to the development of polysubstitution products, ethylbenzene is usually made through acetylation of benzene followed by reduction and direct alkylation.
Due to resonance, the benzene ring must be deactivated. The electrophilic attacking agent is rarely produced by the benzene ring.
38. Can Gatterman-Koch reaction be considered like Friedel Craft’s acylation? Discuss.
Ans: Yes, both reactions look to be the same, but they are not. To convert benzene to benzaldehyde, the Gatterman-Koch reaction is performed. Benzene is treated with an acid chloride in the presence of anhydrous ${\text{AlC}}{{\text{l}}_3}$ in acylation processes. The Gatterman-Koch reaction is used to make ${\text{HCOCl}}$ in situ by reacting ${\text{CO}}$ with ${\text{HCl}}$ gas in the presence of anhydrous ${\text{AlC}}{{\text{l}}_3}$.
IV. Matching Type
Note: Match the items of Column I and Column II in the following questions.
39. Match the common names given in Column I with the IUPAC names given in Column II.
Match the common names given in Column I with the IUPAC names given in Column II.
Column I | Column II |
Common names | (IUPAC names) |
A: Cinnamaldehyde | (a) Pentanal |
B: Acetophenone | (b) Prop-2-enal |
C: Valeraldehyde | (c) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one |
D: Acrolein | (d) 3-Phenylprop-2-enal |
E: Mesityl oxide | (e) 1-Phenylethanone |
Ans:
Column I | Column II |
Common names | (IUPAC names) |
A: Cinnamaldehyde | (d) 3-Phenylprop-2-enal |
B: Acetophenone | (e) 1-Phenylethanone |
C: Valeraldehyde | (a) Pentanal |
D: Acrolein | (b) Prop-2-enal |
E: Mesityl oxide | (c) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one |
40. Match the acids given in Column I with their correct IUPAC names given in Column II
Column I | Column II |
Acids | (IUPAC names) |
A: Phthalic acid | (a) Hexane-1,6-dioic acid |
B: Oxalic acid | (b) Benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid |
C: Succinic acid | (c) Pentane-1,5-dioic acid |
D: Adipic acid | (d) Butane-1,4-dioic acid |
E: Glutaric acid | (e) Ethane-1,2-dioic acid |
Ans:
Column I | Column II |
Acids | (IUPAC names) |
A: Phthalic acid | (b) Benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid |
B: Oxalic acid | (e) Ethane-1,2-dioic acid |
C: Succinic acid | (d) Butane-1,4-dioic acid |
D: Adipic acid | (a) Hexane-1,6-dioic acid |
E: Glutaric acid | (c) Pentane-1,5-dioic acid |
41. Match the reactions given in Column I with the suitable reagents given in Column II
Column I | Column II |
(Reactions) | (Reagents) |
(i) Benzophenone to Diphenylmethane | (a) ${\text{LiAl}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$ |
(ii) Benzaldehyde to 1-Phenylethanol | (b) ${\text{DIBAL - H}}$ |
(iii) Cyclohexanone to Cyclohexanol | (c) $\frac{{{\text{Zn(Hg)}}}}{{{\text{Conc}}{\text{.HCl}}}}$ |
(iv) Phenyl benzoate to Benzaldehyde | (d) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{MgBr}}$ |
Ans:
Column I | Column II |
(Reactions) | (Reagents) |
(i) Benzophenone to Diphenylmethane | (c) $\frac{{{\text{Zn(Hg)}}}}{{{\text{Conc}}{\text{.HCl}}}}$ |
(ii) Benzaldehyde to 1-Phenylethanol | (d) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{MgBr}}$ |
(iii) Cyclohexanone to Cyclohexanol | (a) ${\text{LiAl}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$ |
(iv) Phenyl benzoate to Benzaldehyde | (b) ${\text{DIBAL - H}}$ |
42. Match the example given in Column I with the name of the reaction in Column II
Column I | Column II |
Example | (Reaction) |
A: 
| (a) Friedel Crafts acylation |
B: 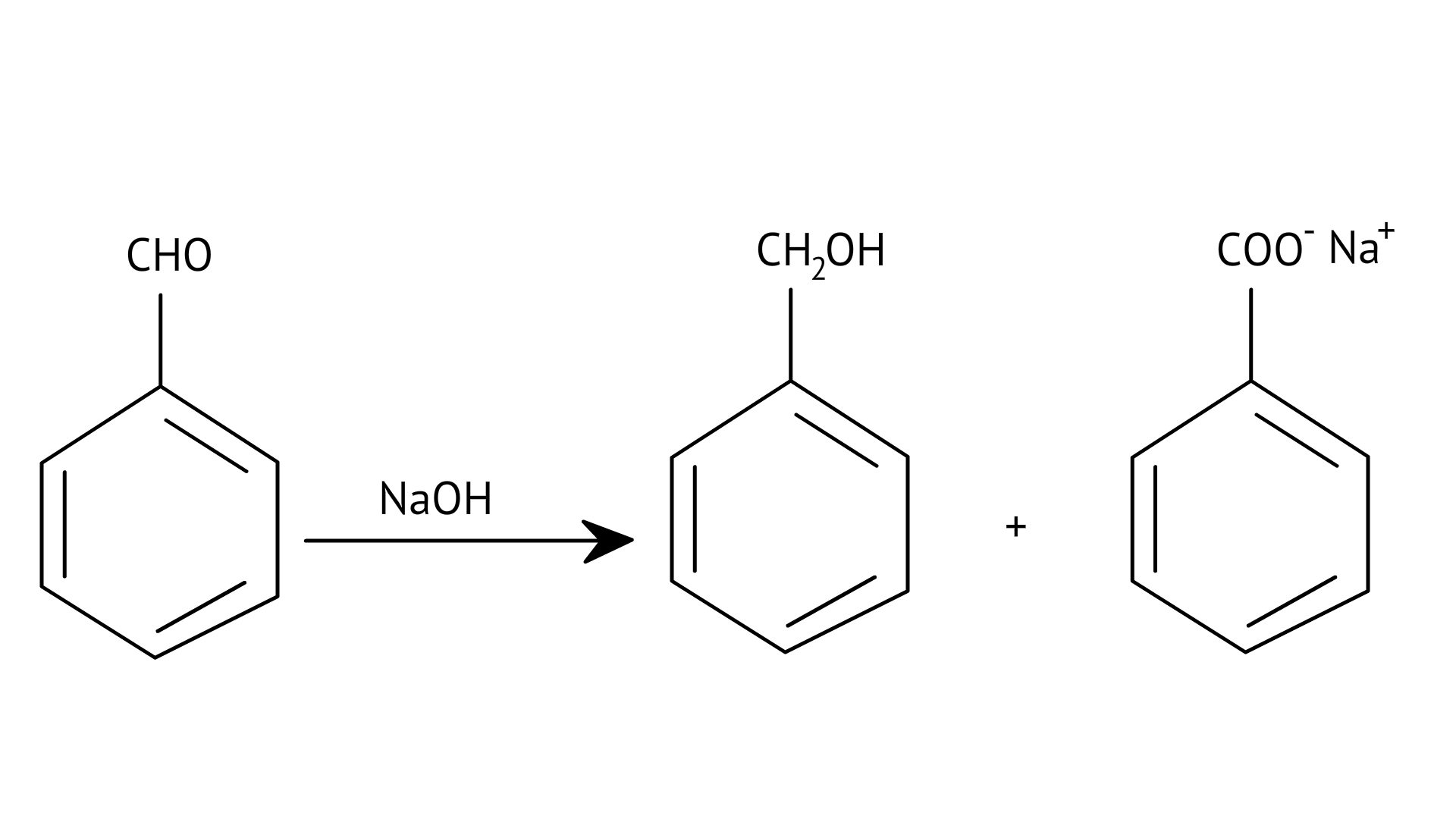
| (b) HVZ reaction |
C: 
| (c) Aldol condensation |
D: 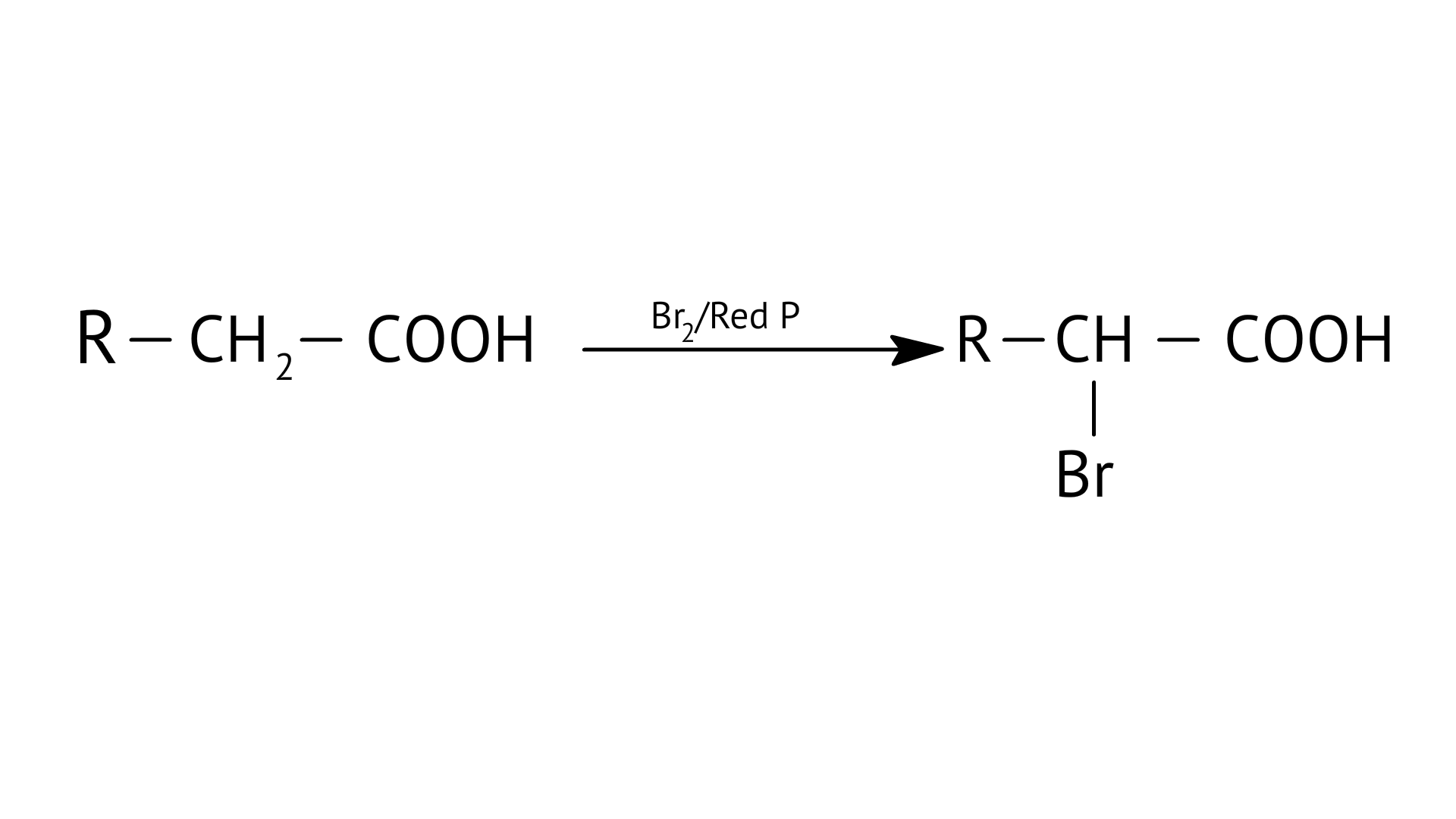
| (d) Cannizaro’s reaction |
E: 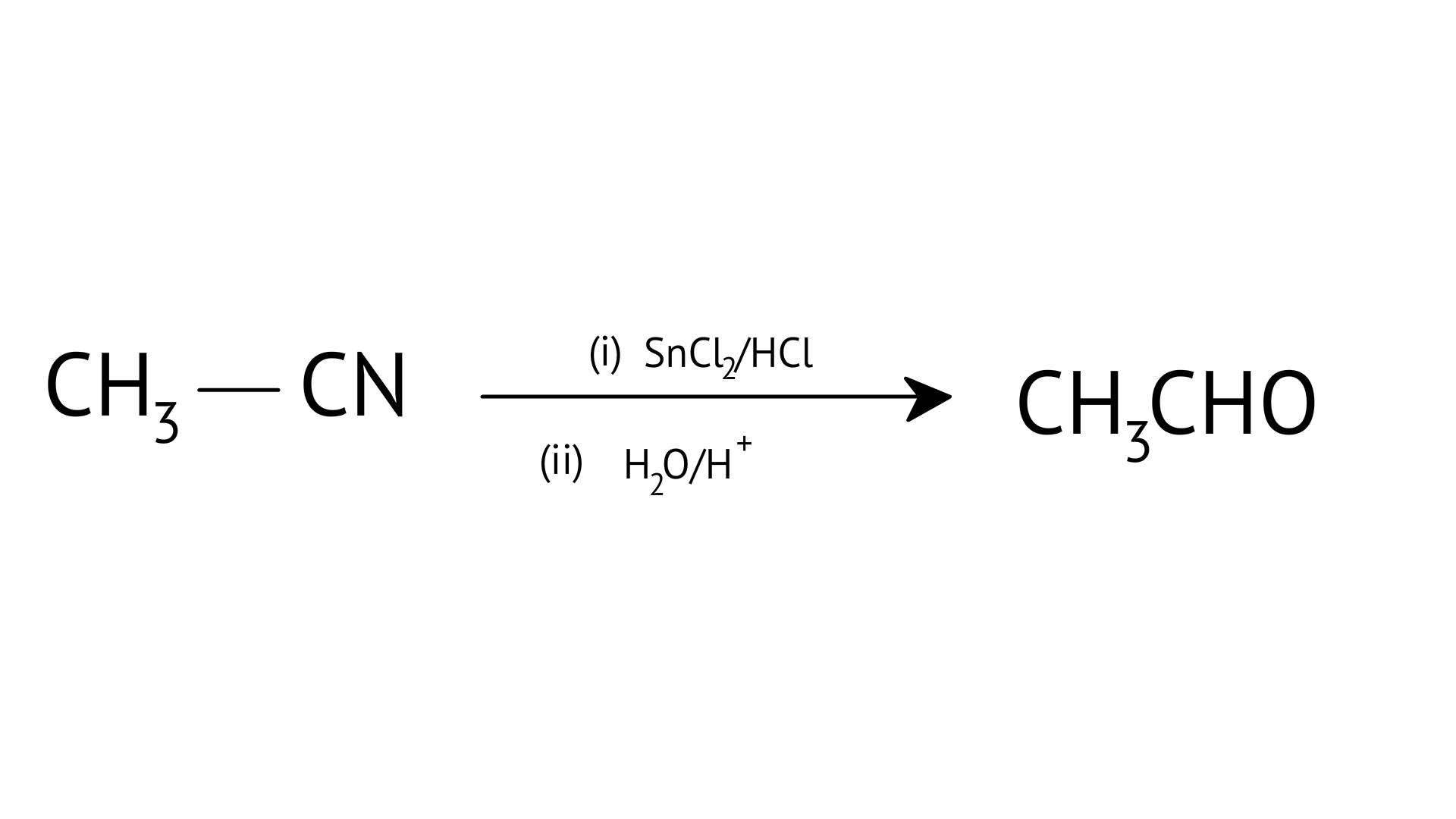
| (e) Rosenmund’s reduction |
F: $\mathrm{Z} \mathrm{C} \mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{C} \mathrm{H} \mathrm{O} \stackrel{\mathrm{Na} \mathrm{O} \mathrm{H}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{CH}_{3}-\mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CHCHO}$ | (f) Stephen’s reaction |
Ans:
Column I | Column II |
Example | (Reaction) |
A: 
| (c) Aldol condensation |
B: 
| (d) Cannizaro’s reaction |
C: 
| (a) Friedel Crafts acylation |
D: 
| (b) HVZ reaction |
E: 
| (f) Stephen’s reaction |
F: $\mathrm{Z} \mathrm{C} \mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{C} \mathrm{H} \mathrm{O} \stackrel{\mathrm{Na} \mathrm{O} \mathrm{H}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{CH}_{3}-\mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CHCHO}$ | (e) Rosenmund’s reduction |
V. Assertion and Reason Type
Note: In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct Ans: out of the following choices
A: Assertion and reason both are correct, and reason is the correct of assertion.
B: Assertion and reason both are wrong statements
C: Assertion is correct statement, but reason is wrong statement.
D: Assertion is wrong statement, but reason is correct statement
E: Assertion and reason both are correct statements, but reason is not correct of assertion
43. Assertion: Formaldehyde is a planar molecule.
Reason: It contains ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridised carbon atom
Ans: A
The smallest aldehyde is formaldehyde. It features a triangular planar shape with two bond pairs and no lone pairings. C and O share one pair of electrons in their double bond. As a result, the C atom is ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridised. As a result, both Assertion and Reason are true.
44: Assertion: Compounds containing ${\text{ - CHO}}$ The group is easily oxidised to corresponding carboxylic acids.
Reason: Carboxylic acids can be reduced to alcohols by treatment with ${\text{LiAl}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$
Ans: E
The two reactions produce different products for different reasons. One involves the oxidation of aldehydes, while the other involves the reduction of carboxylic acids. Aldehydes are easily oxidised by mild oxidising agents, hence compounds containing ${\text{ - CHO}}$ are rapidly oxidised.
45. Assertion: The α-hydrogen atom in carbonyl compounds is less acidic.
Reason: The anion formed after the loss of α-hydrogen atom is resonance stabilised.
Ans: D
Because of the presence of electron withdrawing carbonyl groups, the alpha hydrogen atom in carbonyl compounds is acidic. In nature, hydrogen is very acidic.
Because the cation is released in the form of ${{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}$, the anion created after the loss of the -hydrogen atom is resonance stabilised.
46. Assertion: Aromatic aldehydes and formaldehyde undergo Cannizaro reaction.
Reason: Aromatic aldehydes are almost as reactive as formaldehyde
Ans: C
There is no alpha hydrogen atom in the Cannizaro process. Formaldehyde and aromatic aldehydes do not contain alpha hydrogen. It proceeds through the Cannizaro reaction. Formaldehyde is the most reactive of all aldehydes.
47: Assertion: Aldehydes and ketones, both react with Tollen’s reagent to form a silver mirror.
Reason: Both, aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group.
Ans: D
The silver mirror test can be used to determine Tollen's. ${\left[ {{\text{Ag(N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}} \right]^{\text{ + }}}{\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^{\text{ - }}}$. Only aldehydes, not ketones, react with Tollen's reagent to create silver.
A silver mirror test is not given with this affirmative test.
The carbonyl group is present in both aldehyde and ketone.
VI. Long Ans: Type
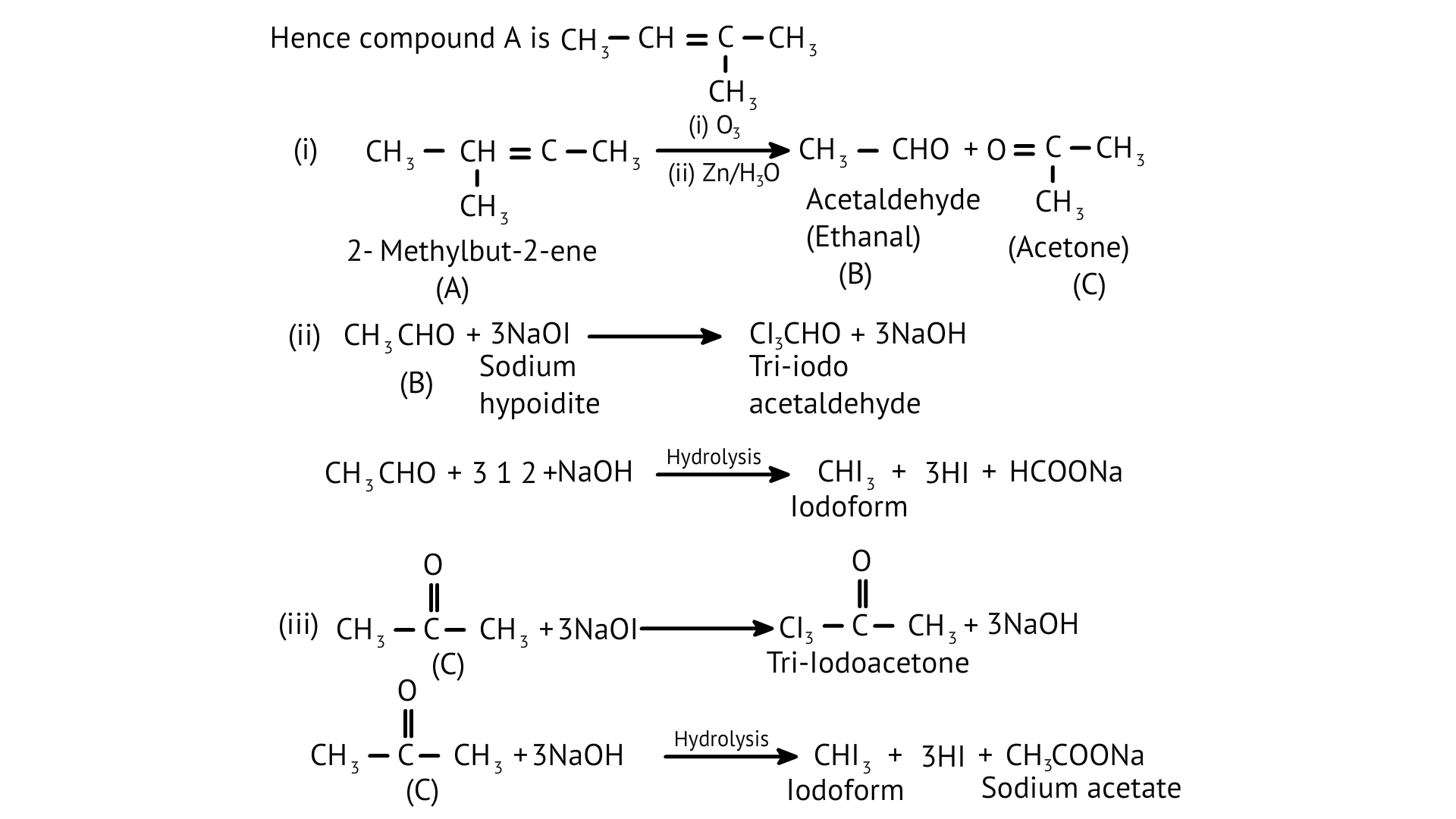
48: An alkene ‘A’ (Mol. formula \[{{C}_{5}}{{H}_{10}}\] on ozonolysis gives a mixture of two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ gives positive Fehling’s test and forms an iodoform on treatment with ${{\text{I}}_2}$ and ${\text{NaOH}}$. Compound ‘C’ does not give Fehling’s test but forms an iodoform. Identify the compounds A, B and C. Write the reaction for ozonolysis and formation of iodoform from B and C.
Ans:
Fehling's test is positive when compound 'B' is used. It gives an iodoform test and proves that it is an aldehyde. Because it fails Fehling's test, compound 'C' is a ketone.
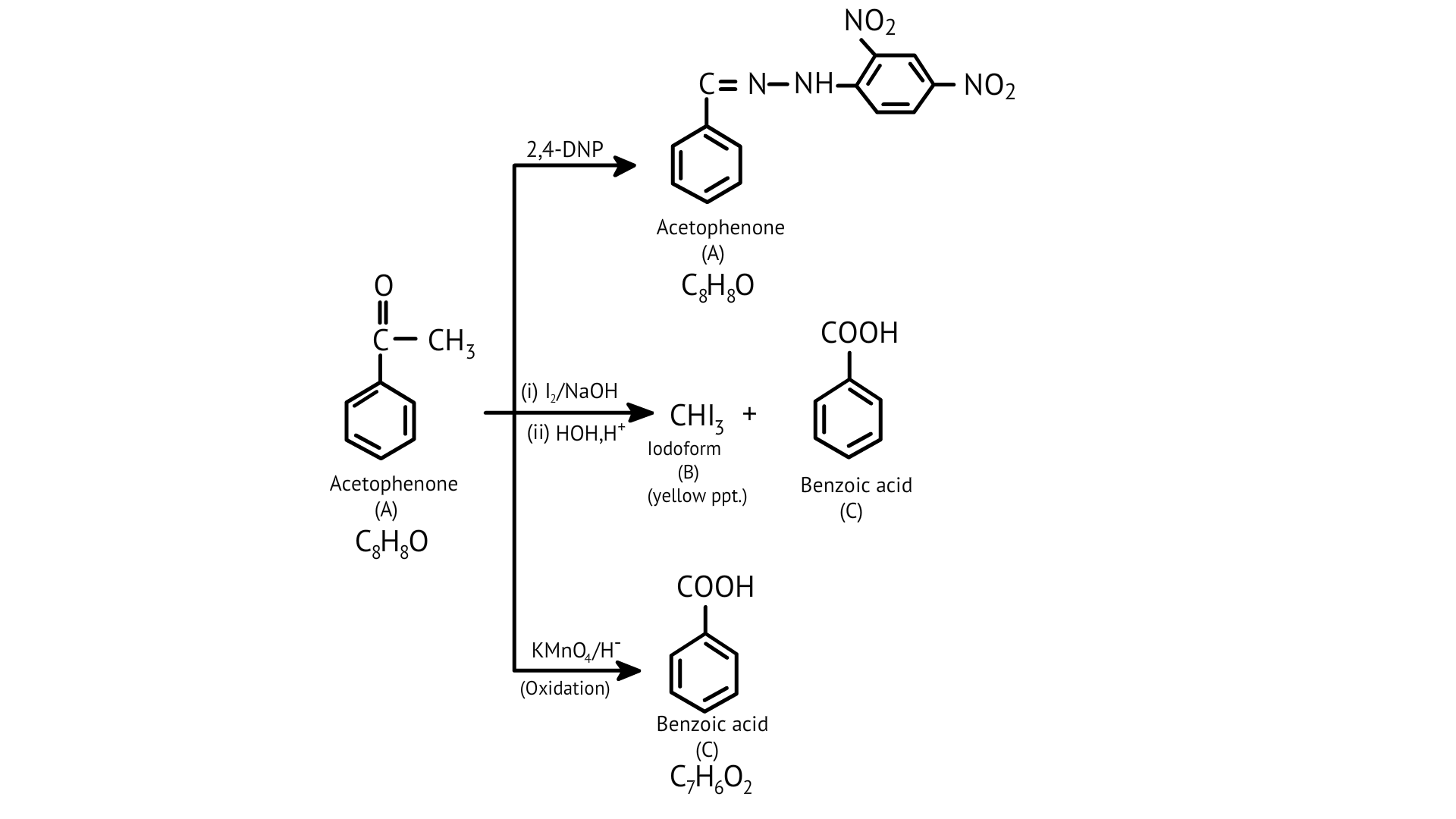
49. An aromatic compound ‘A’ (Molecular formula ${C_8}{H_8}O\])$ gives a positive 2, 4-DNP test. It gives a yellow precipitate of compound ‘B’ on treatment with iodine and sodium hydroxide solution. Compound ‘A’ does not give Tollen’s or Fehling’s test. On drastic oxidation with potassium permanganate it forms a carboxylic acid ‘C’ (Molecular formula ${C_7}{H_6}{O_2}$), which is also formed along with the yellow compound in the above reaction. Identify A, B and C and write all the reactions involved.
Ans: The aromatic compound ‘A’ does not give Tollen’s reagent test, it is not an aromatic aldehyde. As it responds to an iodoform test called methyl ketone.
50. Write down functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula ${C_3}{H_6}O$. Which isomer will react faster with $HCN$ and why? Explain the mechanism of the reaction also. Will the reaction lead to the completion with the conversion of whole reactant into product at reaction conditions? If a strong acid is added to the reaction mixture what will be the effect on concentration of the product and why?
Ans: Functional isomers of ${C_3}{H_6}O{C_3}{H_6}O$ containing carbonyl group are $C{H_3}C{H_2}CHO$ and $C{H_3}COC{H_3}$.
Propanol reacts faster with HCN because there is less steric hindrance and electronic factors which increases its electrophilicity. It is a reversible reaction. Addition of acid inhibits the reaction because of the formation of the $- CN$ ions. Next come the reaction mechanism
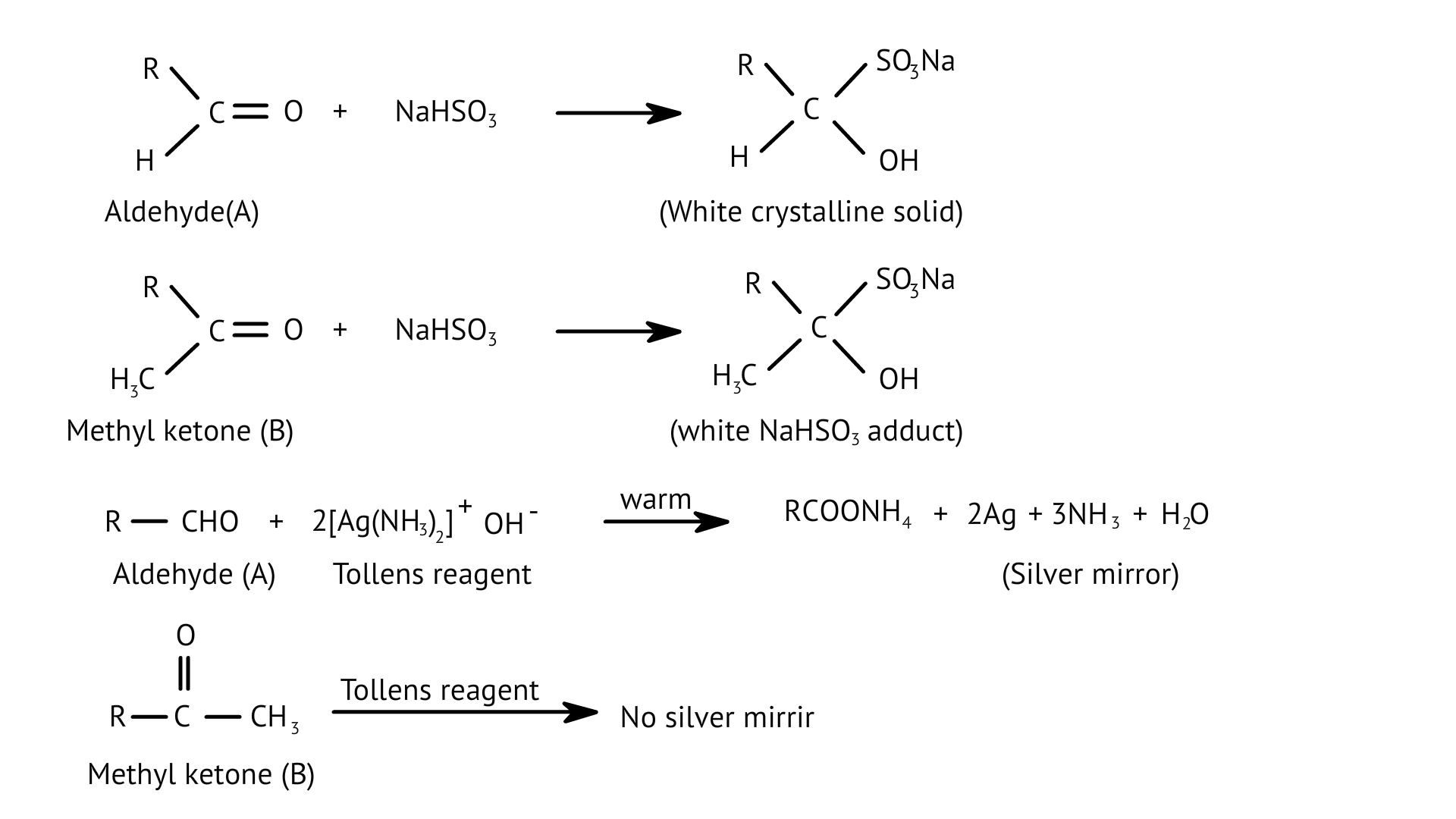
51. When liquid ‘A’ is treated with a freshly prepared ammoniacal silver nitrate solution, it gives bright silver mirror. The liquid forms a white crystalline solid on treatment with sodium hydrogensulphite. Liquid ‘B’ also forms a white crystalline solid with sodium hydrogensulphite but it does not give test with ammoniacal silver nitrate. Which of the two liquids is aldehyde? Write the chemical equations of these reactions also.
Ans: Liquid ‘A’ reduces ammoniacal silver nitrate and ‘B’ is a ketone which forms white crystalline solid on treatment with hydrogen sulphite
Perks of Studying With NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 – Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids:
You get a comprehensive explanation of everything that’s in the textbook chapter
You will be quite familiar with the kinds of questions that you may have to deal with in the examinations
Your brain’s thinking and absorption capacity will get enhanced
These solutions are quite useful before sitting for competitive examinations as well as the usual examinations
Making notes in your language will get simpler after having gone through these solved exercises.
Your Chemistry will improve by leaps and bounds and you will not have to devote any extra time to the subject
Time management will become smoother as you will be able to finish a certain number of questions within a stipulated time.
After analysing these benefits of the NCERT Exemplar, your next step should be to download the Vedantu PDF of solutions to assist you in making the most of this study guide. The book along with the solutions will truly give you an edge and help you understand the concepts, how to approach them in answers and also tackle any problems that may come your way in this topic!
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Free PDF Download
1. How do I secure high marks for my Class 12 Chemistry test on the chapter- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids?
You can solve the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. The book has been made in consultation with the science teachers, especially Chemistry teachers who are well aware of the NCERT guidelines.
Solving the exercises in the book and paying extra heed to how the approach has been tactfully used for solving those questions will help. Students must practice from the book regularly to get higher marks in their forthcoming examinations. The book is truly a boon for Chemistry lovers as well as for those who are struggling with the concepts.
2. What is Formaldehyde?
Also known as the formalin solution, it is used to preserve biological specimens. It is also utilized in the formation of certain vital polymers such as Bakelite.
Pertinent information about Formaldehyde has been provided in the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. The book has pertinent matters on Formaldehyde and has all the solved questions related to it which might come for the tests. It is available on Vedantu and can be downloaded too.
3. Do Revision notes and solving questions help before examinations on Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids?
Indeed. Making your notes after referring to NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids on Vedantu will prove to be quite advantageous for the students. Solving these exercises will provide the pupils with an idea of what they might have to encounter at the time of tests. Making notes while studying is an effective way of absorbing study material and helps one score well. Both prove to be equally important for the students.
4. What is the Cannizaro Reaction from Chapter 12?
The Cannizaro Reaction involves the base-induced disproportionation of two molecules of a non-enolizable aldehyde to give primary alcohol and a carboxylic acid. Such reactions have been thoroughly described in the NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. The book of solved questions and answers has too many exercises to choose from and learn from at the same time. You can understand these topics in their entirety and then make your notes to simplify down these concepts and understand them in your language.
5. Where can I find NCERT Exemplar for Class 12’s Chemistry Chapter 12?
Students can check out Vedantu and then find NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. Vedantu is India’s leading educational platform for e-learning and is one of the most reliable sites for subject material. It has all the revision notes and solved exercises for the students to practice from. You can go through the study material in the online mode or you can download it in a PDF format and go through them at a later point in time. Vedantu provides free access to chapter wise solutions for download in PDF format.




































