NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry - Surface Chemistry - Free PDF Download
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Surface Chemistry solved by expert Chemistry teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 5 - Surface Chemistry Exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your Examinations.
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Surface Chemistry
Exercise
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following process does not occur at the interface of phases?
(i) Crystallisation
(ii) Heterogeneous catalysis
(iii) Homogeneous catalysis
(iv) Corrosion
Ans: Correct option is (iii)
In homogeneous catalysis, the reactant as well as the product both are in same phase and composition is uniform throughout hence the correct option is (iii).
2. At the equilibrium position in the process of adsorption ?
(i) ΔH > 0
(ii) ΔH = TΔS
(iii) ΔH > TΔS
(iv) ΔH < TΔS
Ans: Correct option is (iv)
In equilibrium ΔG=0 so ΔG=ΔH-TΔS which means ΔH=TΔS therefore the correct option is (ii).
3. Which of the following interface cannot be obtained?
(i) Liquid-liquid
(ii) Solid-liquid
(iii) Liquid-gas
(iv) Gas-gas.
Ans: Correct option is (iv)
As gas-gas forms up a homogeneous composition, so the correct option is (iv).
4. The term ‘sorption’ stands for .
(i) Absorption
(ii) Adsorption
(iii) Both absorption and adsorption
(iv) Desorption
Ans: Correct option is (iii)
When both adsorption and absorption occur simultaneously it is known as sorption; hence the correct option is (iii).
5. Extent of physisorption of a gas increases with
(i) Increase in temperature.
(ii) Decrease in temperature.
(iii) Decrease in surface area of adsorbent.
(iv) Decrease in strength of van der waals forces
Ans: Correct option is (ii)
As the process of adsorption is an exothermic one; physical adsorption occurs readily at low temperature and decreases with an increase in the temperature as equilibrium shifts in the backward direction. This is known as Le-Chatelier’s principle, hence the correct option is (ii).
6. Extent of adsorption of adsorbate from solution phase increases with
(i) Increase in amount of adsorbate in solution.
(ii) Decrease in surface area of adsorbent.
(iii) Increase in temperature of solution.
(iv) Decrease in amount of adsorbate in solution.
Ans: Correct option is (i)
Extent of adsorption depends on the concentration of the solute in a solution. The concentration of adsorbate increases the interaction between adsorbate and adsorbent thus the extent of adsorption also increases; hence the correct option is (i).
7. Which one of the following is not applicable to the phenomenon of adsorption?
(i) ΔH > 0
(ii) ΔG < 0
(iii) ΔS < 0
(iv) ΔH < 0
Ans: Correct option is (i)
As adsorption is an exothermic process so ΔH cannot be greater than zero, hence the correct option is (i).
8. Which of the following is not a favourable condition for physical adsorption?
(i) High pressure
(ii) Negative δh
(iii) Higher critical temperature of adsorbate
(iv) High temperature
Ans: Correct option is (i)
High temperature is not favourable for physical adsorption since it is an exothermic process, hence the correct option is (i).
9. Physical adsorption of a gaseous species may change to chemical adsorption with
(i) Decrease in temperature
(ii) Increase in temperature
(iii) Increase in surface area of adsorbent
(iv) Decrease in surface area of adsorbent.
Ans: Correct option is (ii)
On increasing the temperature activation energy of the adsorbate molecule increases which convert physical adsorption into chemisorptions hence the correct option is (ii).
10. In physisorption adsorbent does not show specificity for any particular gas because
(i) Involved van der Waals forces are universal.
(ii) Gases involved behave like ideal gases.
(iii) Enthalpy of adsorption is low.
(iv) It is a reversible process.
Ans: Correct option is (i)
Physisorption adsorbent does not show specificity for any particular gas because it is involved van der Waals forces are universal, hence the correct option is (i).
11. Which of the following is an example of absorption?
(i) Water on silica gel
(ii) Water on calcium chloride
(iii) Hydrogen on finely divided nickel
(iv) Oxygen on metal surface
Ans: Correct option is (iii)
In absorption, a substance is uniformly distributed, through the body of the solid or liquid, hence the correct option is (iii).
12. On the basis of data given below predict which of the following gases shows least adsorption on a definite amount of charcoal?
Gas | CO2 | SO2 | CH4 | H2 |
Critical temp./K | 304 | 630 | 190 | 33 |
(i) CO2
(ii) SO2
(iii) CH4
(iv) H2
Ans: Correct option is (iv)
Lesser the value of critical temperature of gases, the lesser will be the force of attraction among molecules and least will be the adsorption hence the answer is option (iv).
13. In which of the following reactions heterogenous catalysis is involved?
(a) $2 \mathrm{SO}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{NO}(\mathrm{g}) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{SO}_{3}(\mathrm{~g})$
(b) $2 \mathrm{SO}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{Pt}(\mathrm{s}) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{SO}_{3}(\mathrm{~g})$
(c) $\mathrm{N}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})+3 \mathrm{H}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{s}) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{NH}_{3}(\mathrm{~g})$
(d) $\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COOCH}_{3} (I) + \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} (I) + HCI(I)\rightarrow \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COOH} (aq) + \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{OH} (aq)$
(i) (b), (c)
(ii) (b), (c), (d)
(iii) (a), (b), (c)
(iv) (d)
Ans: Correct option is (i)
When the reactant and catalyst are in different phase it is known as heterogeneous catalysis hence the answer is (i).
14. At high concentration of soap in water, soap behaves as
(i) Molecular colloid
(ii) Associated colloid
(iii) Macromolecular colloid
(iv) Lyophilic colloid
Ans: Correct option is (ii)
There are few substances which at low concentrations behave as normal strong electrolytes, but at higher concentrations exhibit colloidal behavior due to the formation of aggregates. The aggregated particles formed are called micelles. These are also known as associated colloids hence the answer is (ii).
15. Which of the following will show Tyndall effect?
(i) Aqueous solution of soap below critical micelle concentration.
(ii) Aqueous solution of soap above critical micelle concentration.
(iii) Aqueous solution of sodium chloride.
(iv) Aqueous solution of sugar.
Ans: Correct option is (ii).
Tyndall effect is defined as the optical property shown by colloidal particle. Above the critical micelle concentration, a solution of soap behaves as an associated colloid so it shows Tyndall effect hence the answer is (ii).
16. Method by which lyophobic sol can be protected.
(i) By addition of oppositely charged sol.
(ii) By addition of an electrolyte.
(iii) By addition of lyophilic sol.
(iv) By boiling.
Ans: Correct option is (iii).
Lyophilic colloids have unique property of protecting lyophobic colloids. When a lyophilic sol is added to lyophobic solution, the lyophilic particles form a layer around the lyophobic particles and protect the latter from electrolytes. Lyophilic colloids used for this purpose are called protective colloids hence the answer is (iii).
17. Freshly prepared precipitate sometimes gets converted to colloidal solution by _________.
(i) Coagulation
(ii) Electrolysis
(iii) Diffusion
(iv) Peptisation
Ans: Correct option is (iv)
Peptisation is the process in which freshly prepared precipitate can be converted into colloidal solution so the answer is (iv).
18. Which of the following electrolytes will have maximum coagulating value for AgI/Ag+ sol?
(i) Na2S
(ii) Na3PO4
(iii) Na2SO4
(iv) NaCl
Ans: Correct option is (ii)
The rate of coagulation will be faster if the value of oppositely charge electrolyte is high hence the answer is (ii).
19. A colloidal system having a solid substance as a dispersed phase and a liquid as a dispersion medium is classified as .
(i) Solid sol
(ii) Gel
(iii) Emulsion
(iv) Sol
Ans: Correct option is (iv).
Solid and liquid together forms up sol. In this case, solid is dispersed phase and liquid is the dispersion medium hence the answer is (iv).
20. The values of colligative properties of colloidal solution are of small order in comparison to those shown by true solutions of same concentration because of colloidal particles .
(i) Exhibit enormous surface area.
(ii) Remain suspended in the dispersion medium.
(iii) Form lyophilic colloids.
(iv) Are comparatively less in number.
Ans: Correct option is (iv).
Colloidal particles are bigger aggregate than the number of particles in a colloidal solution hence, the values of colligative are of small order as compared to values shown by true solutions at same concentration so the answer is (iv).
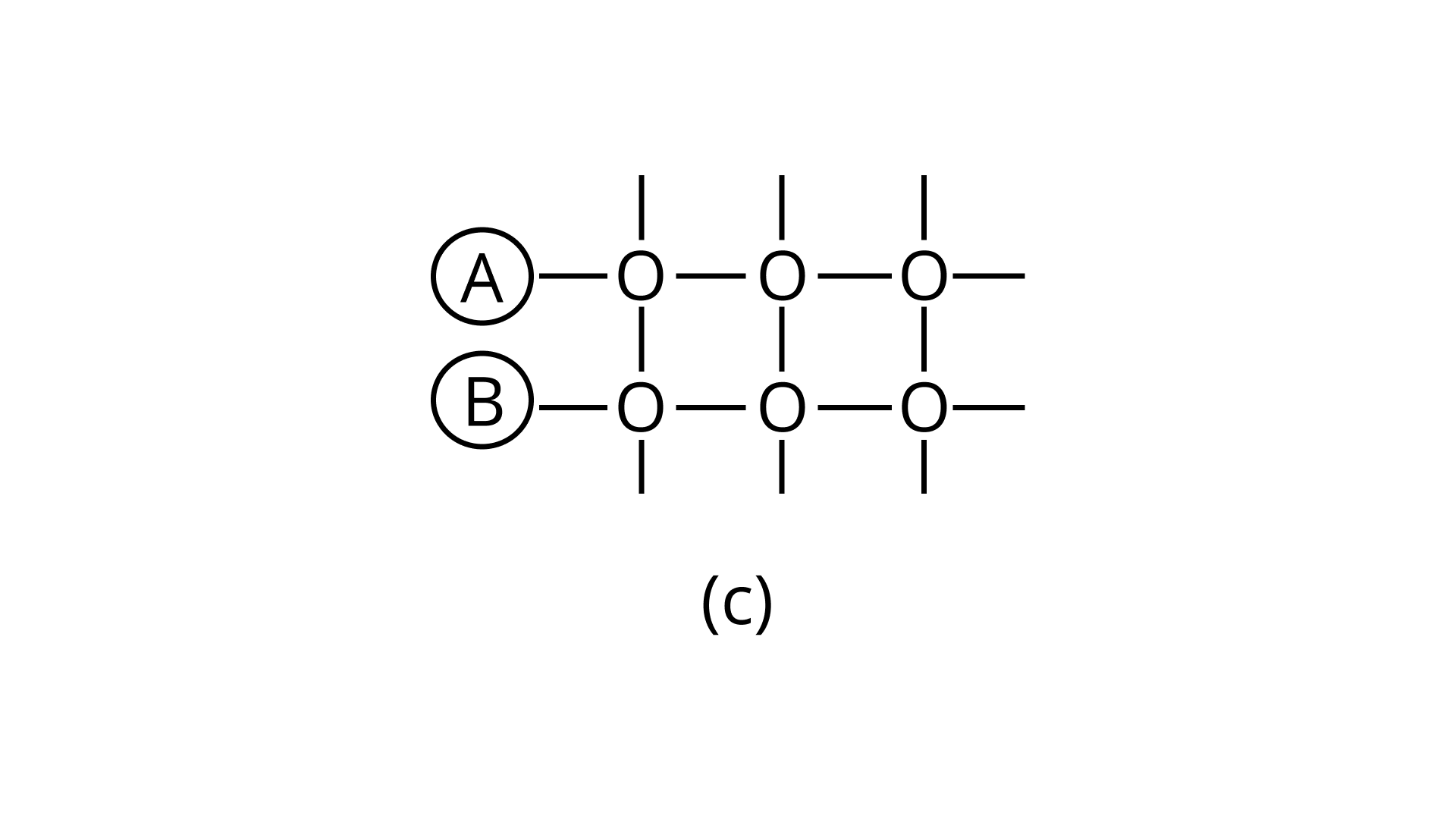
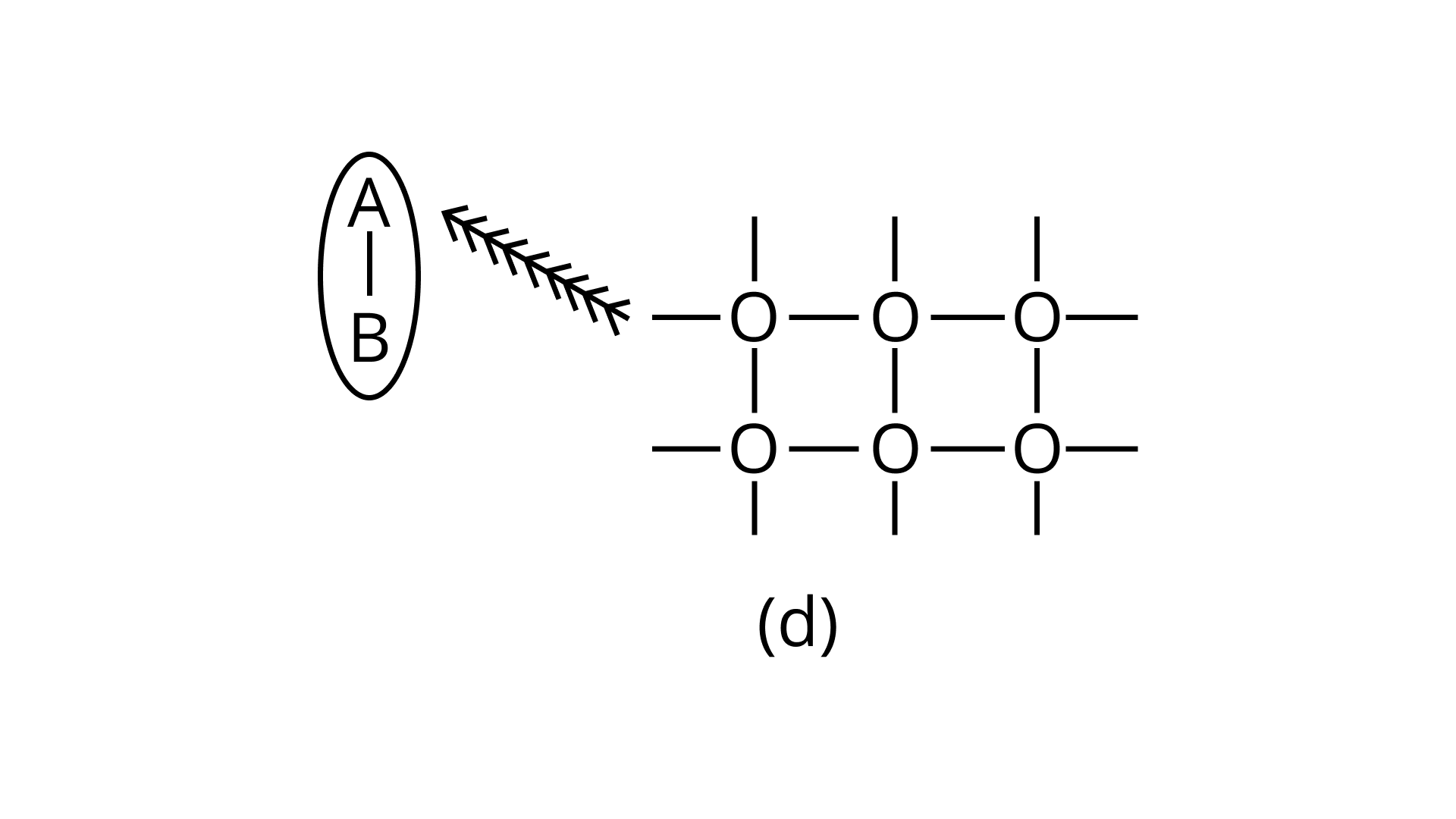
21. Arrange the following diagrams in correct sequence of steps involved in the mechanism of catalysis, in accordance with modern adsorption theory
a.
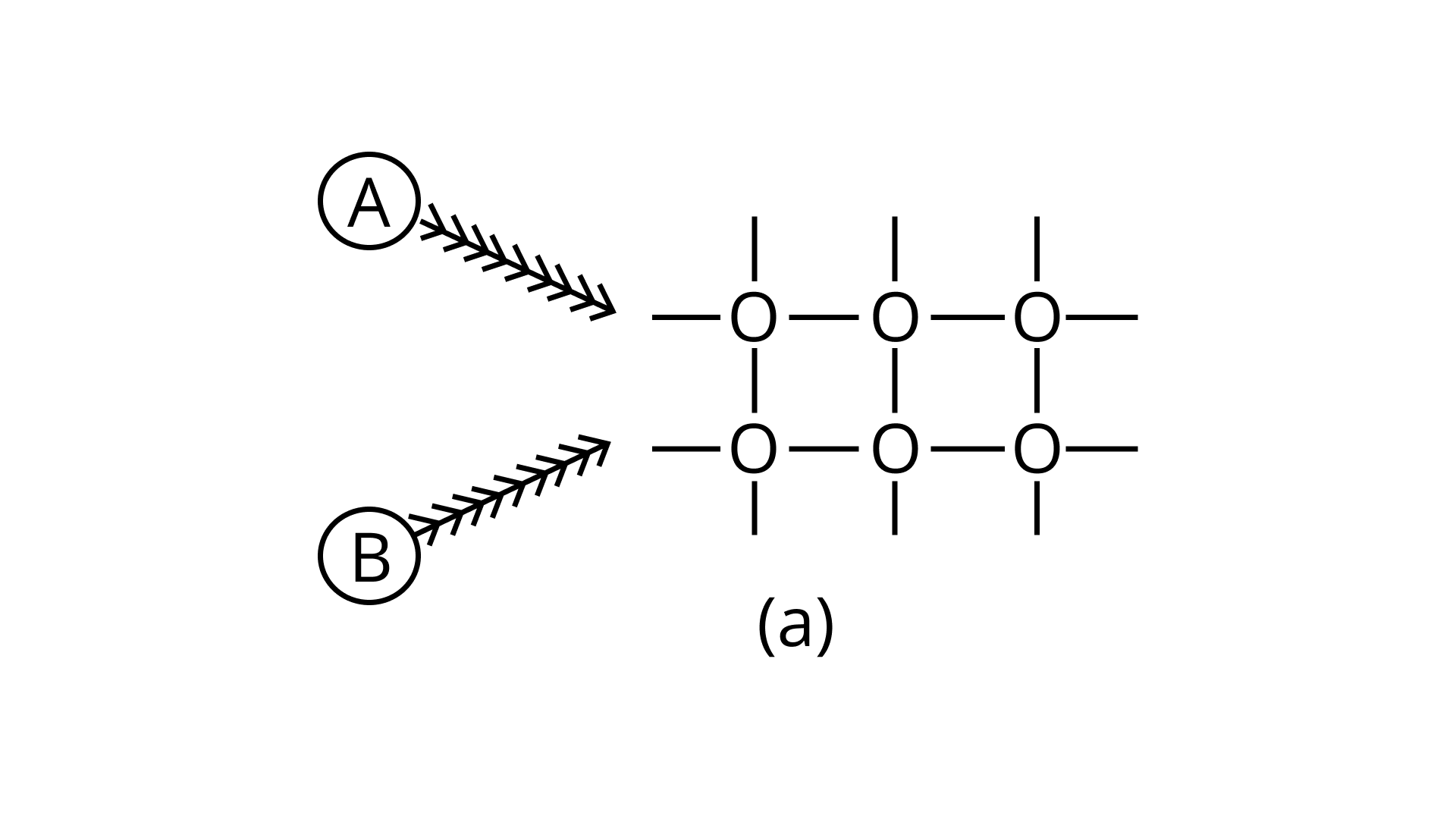
b.
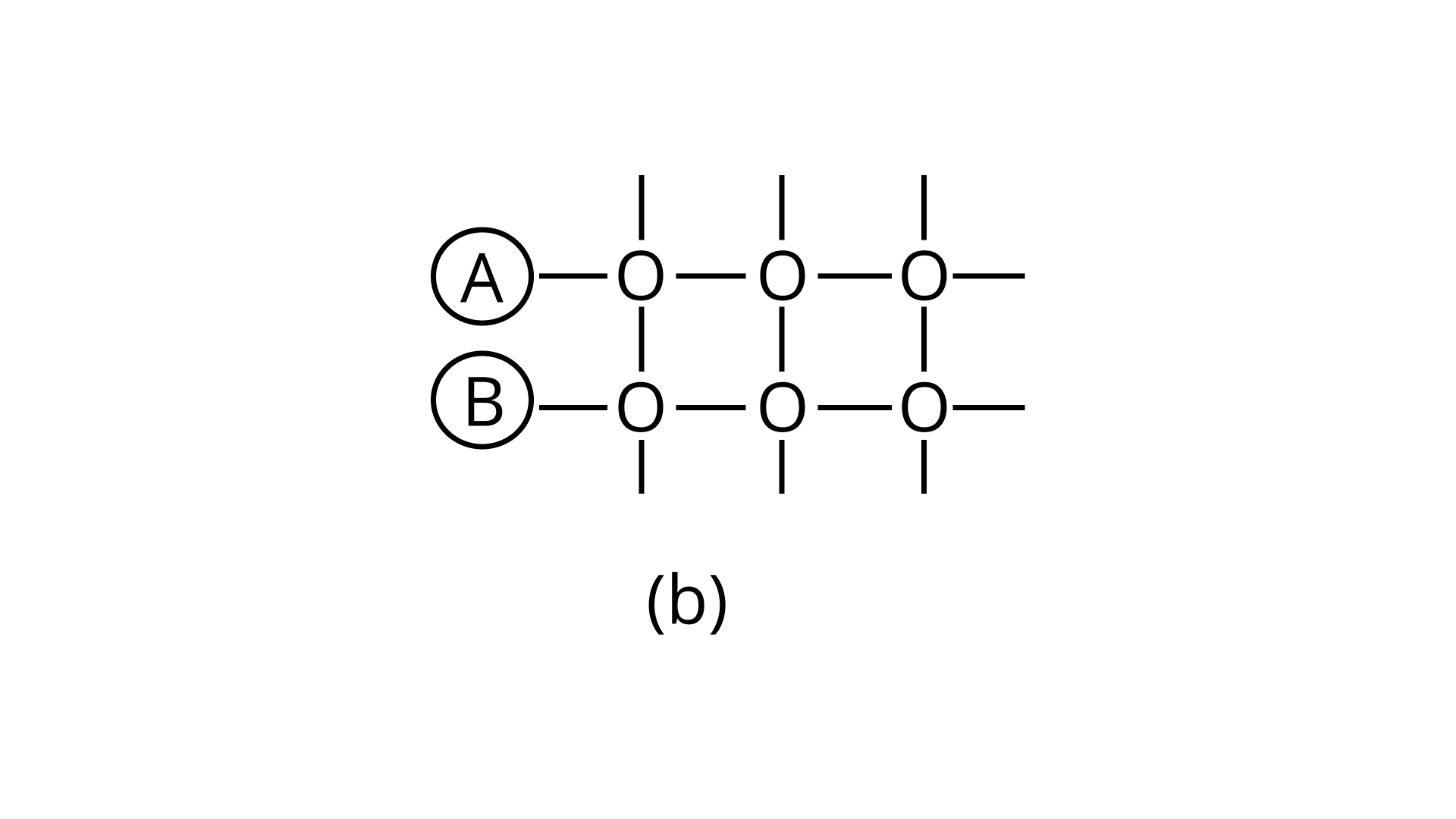
c.
d.
e.
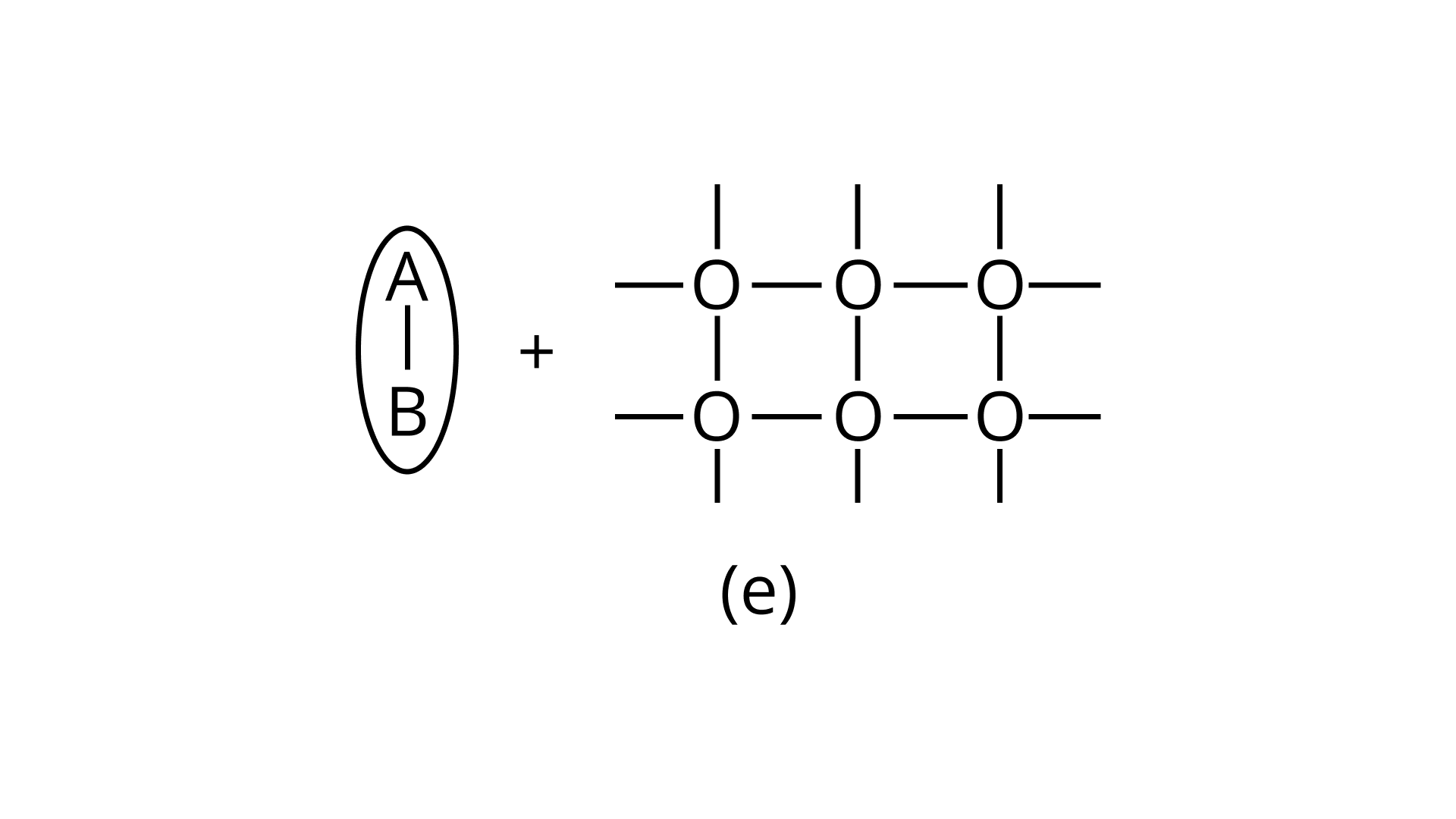
(i) a →b →c →d →e
(ii) a →c →b →d →e
(iii) a →c →b →e →d
(iv) a →b →c →e →d
Ans: Correct answer is (ii)
The correct sequence of steps involved in catalysis are:
(i) Adsorption of A and B on surface
(ii) Interaction between A and B to form intermediate
(iii) Starting of desorption from surface
(iv) Complete desorption from the surface
Therefore, the correct answer is (ii)
22. Which of the following process is responsible for the formation of delta at a place where rivers meet the sea?
(i) Emulsification
(ii) Colloid formation
(iii) Coagulation
(iv) Peptisation
Ans: Correct option is iii.
River water is a colloidal solution of clay. Sea water contains a number of electrolytes. When river water meets the sea water, the electrolytes present in sea water coagulate the colloidal solution of clay resulting in its deposition with the formation of delta hence the answeris (iii).
23. Which of the following curves is in accordance with Freundlich adsorption isotherm?
(i)
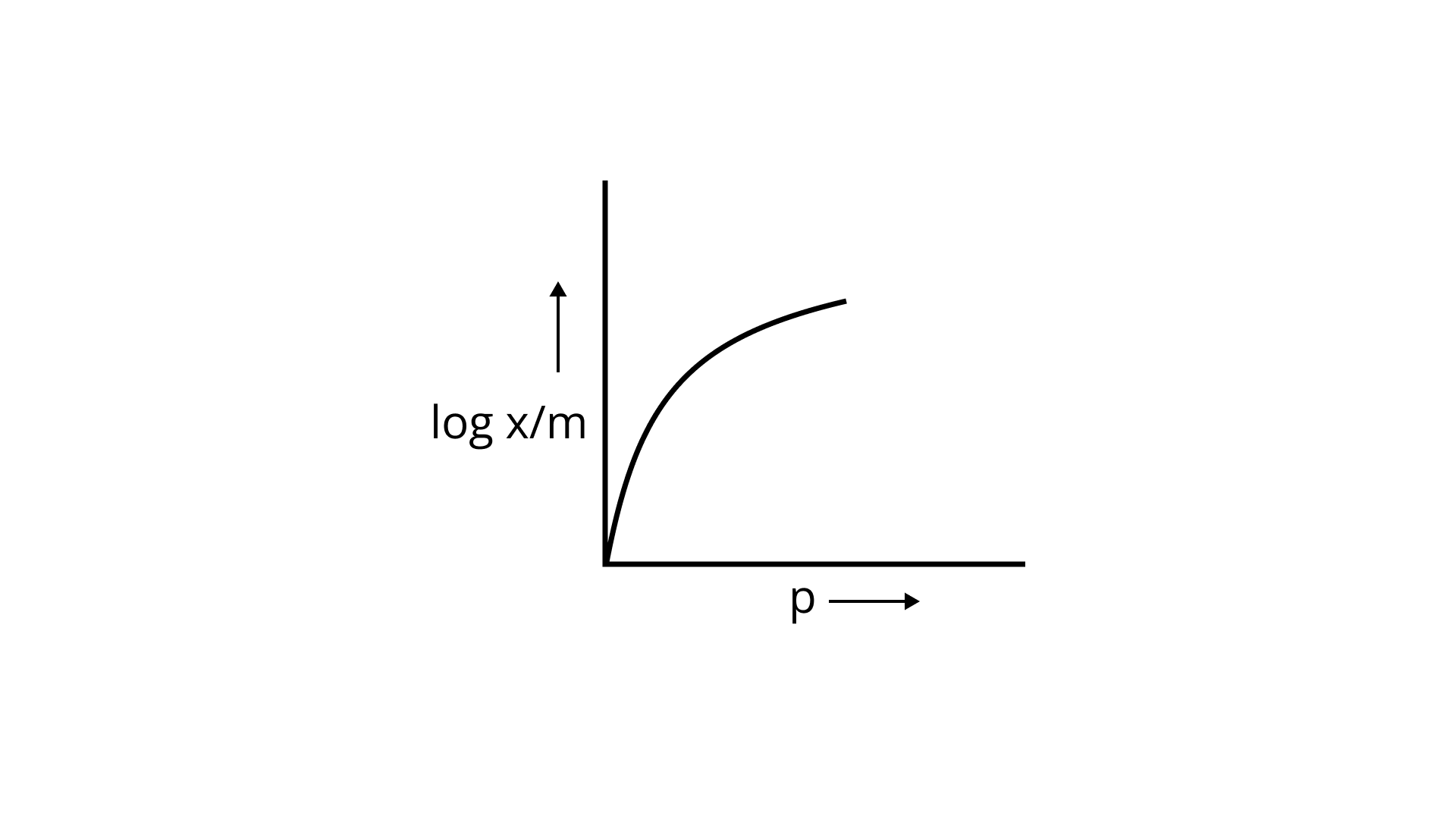
(ii)
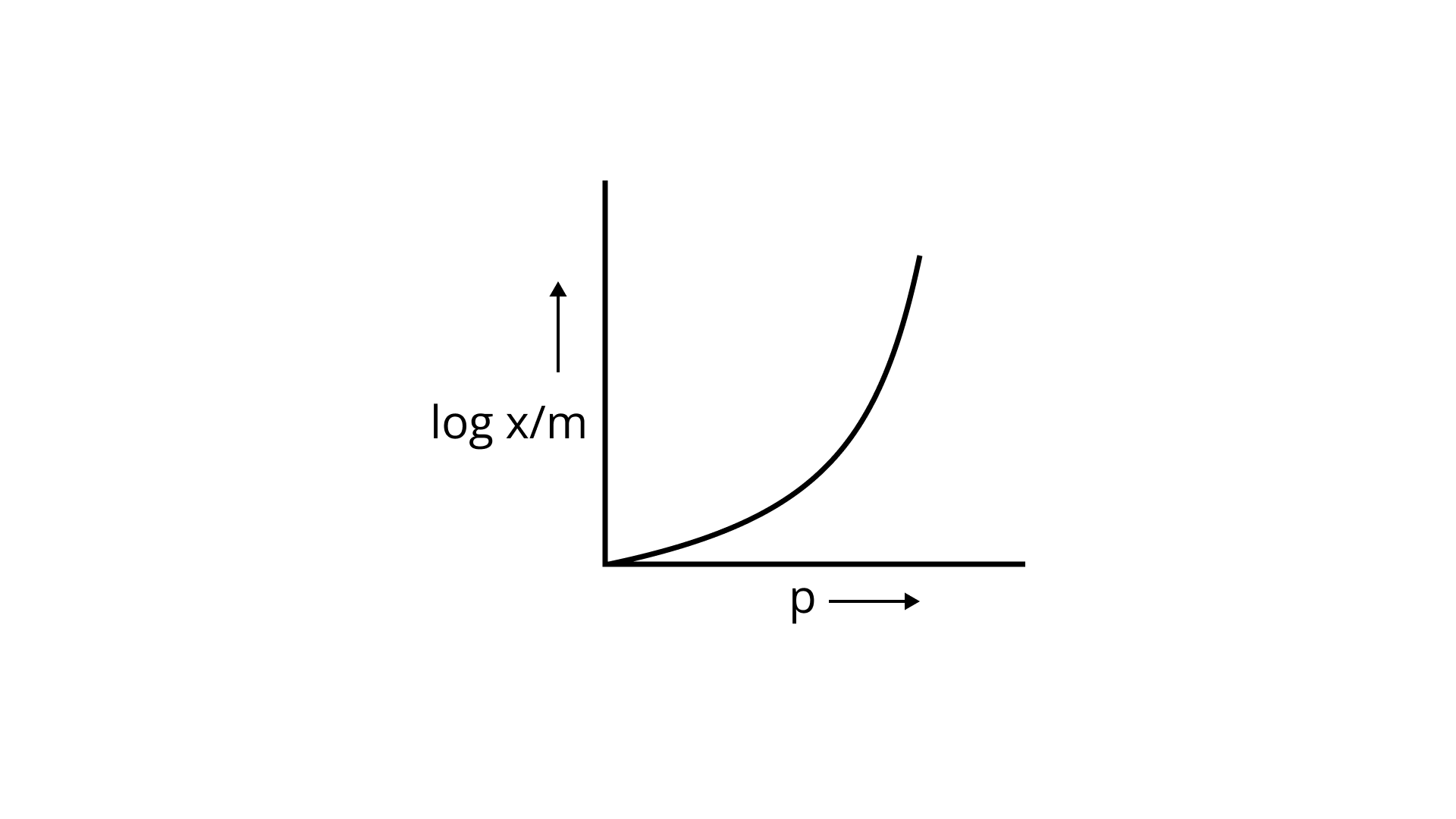
(iii)
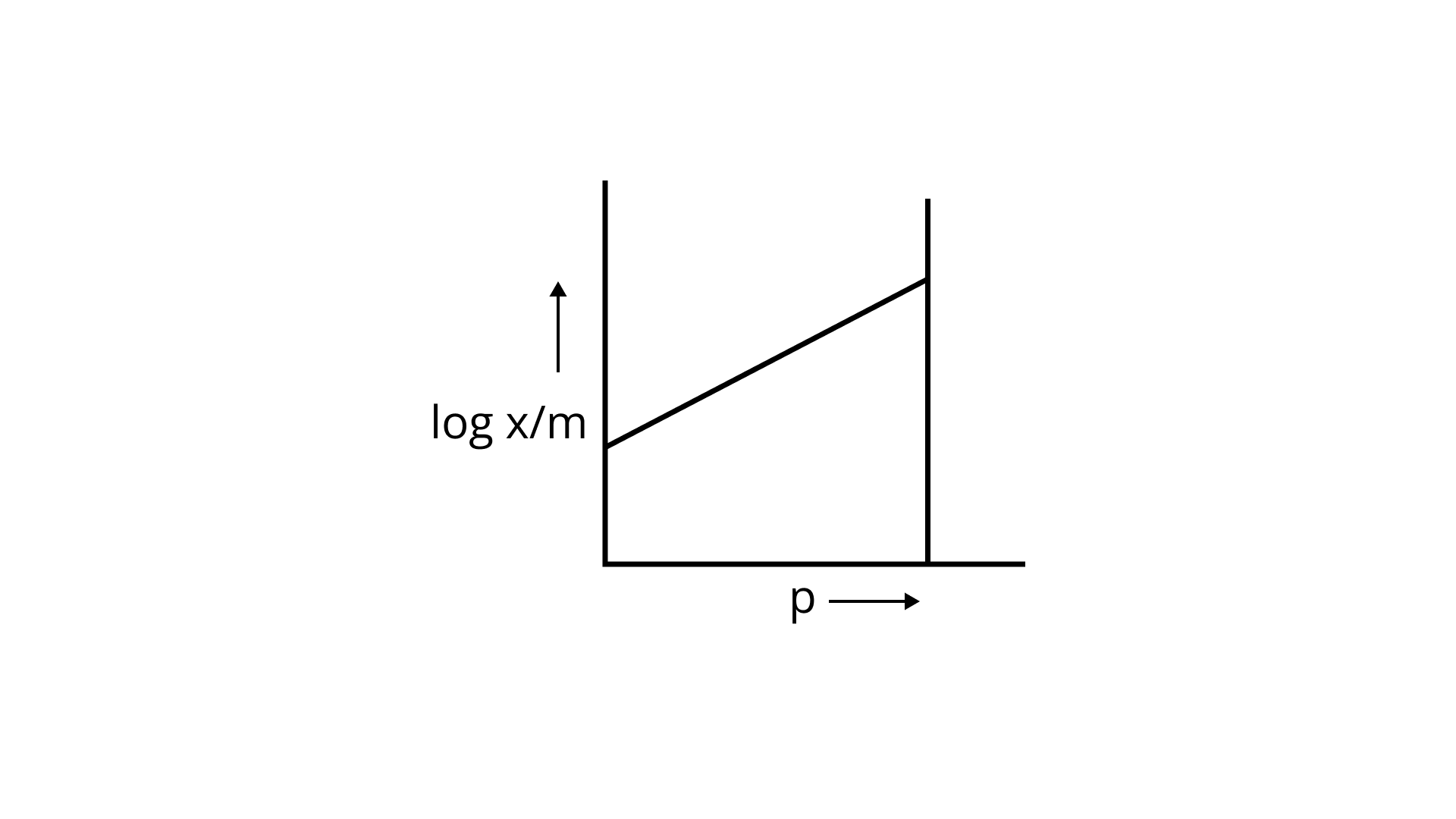
(iv)
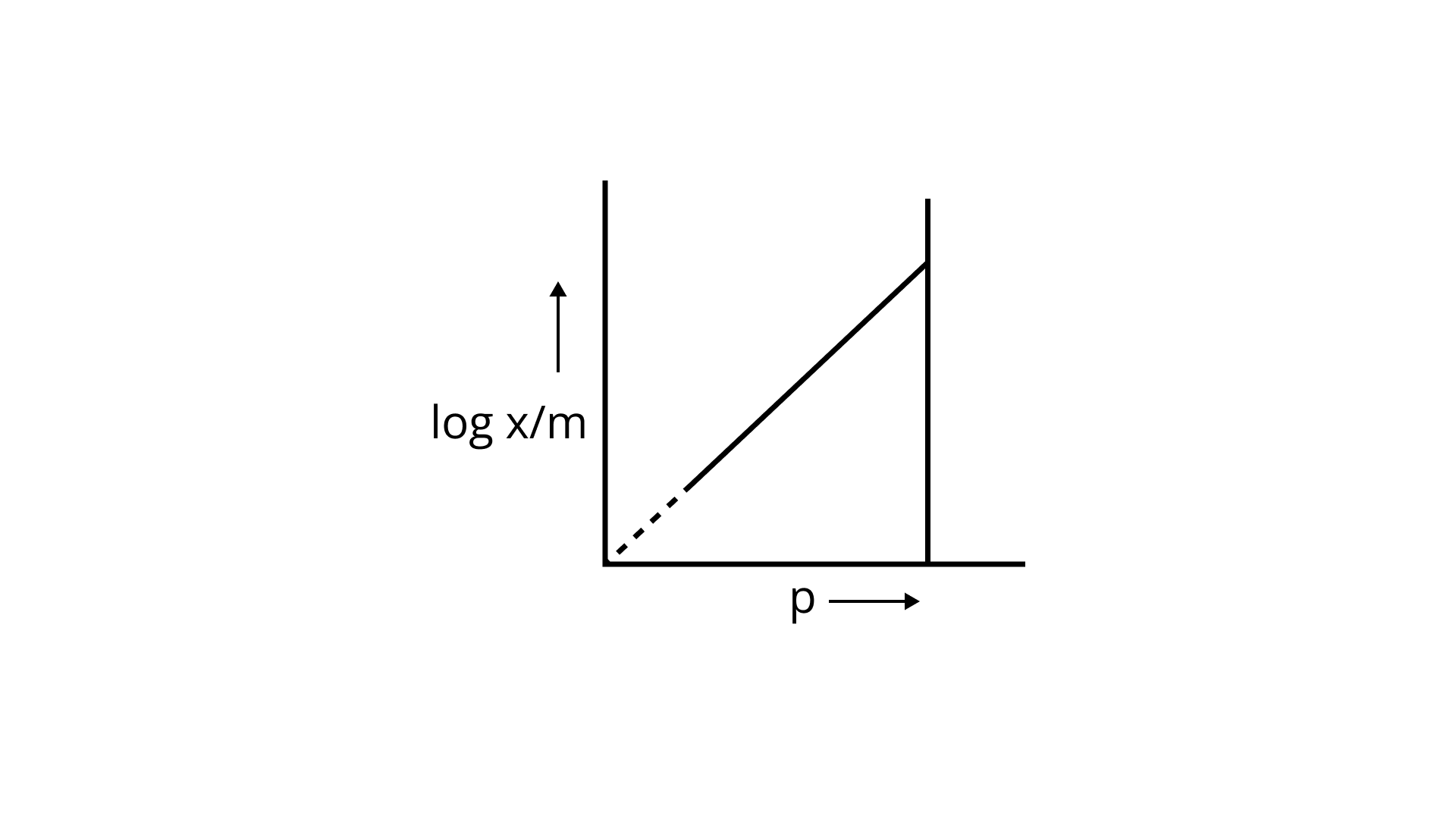
Ans: Correct option is i.
Freundlich, in 1909, gave an empirical relationship between the quantity of gas adsorbed by unit mass of solid adsorbent and pressure at a particular temperature.
x/m= kp1/n (n>1)
The adsorption varies directly. Where x/m=mass of gas adsorbed per unit mass of adsorbent particle p= Pressure of gas at particular temperature.
24. Which of the following process is not responsible for the presence of electric charge on the sol particles?
(i) Electron capture by sol particles.
(ii) Adsorption of ionic species from solution.
(iii) Formation of Helmholtz electrical double layer.
(iv) Absorption of ionic species from solution.
Ans: Correct answer is (iv)
Charge on the sol particles can be a result of the following:
Due to electron capture by sol particles during electrodispersion of metals,
Due to preferential adsorption of ions from solution and/or
Due to formulation of electrical double layer.
Hence the correct answer is (iv)
25. Which of the following phenomenon is applicable to the process shown in the Fig. 5.1?

(i) Absorption
(ii) Adsorption
(iii) Coagulation
(iv) Emulsification
Ans: Correct option is (ii)
In the figure adsorption of coloured particle from charcoal is shown. Solution of raw sugar is filtered by animal charcoal and yellowish brown colour of raw sugar is adsorbed and filterate is colourless which gives white colour on crystallization hence the answer is (ii).
Multiple Choice Questions (Type-II)
Note: In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
26. Which of the following options are correct?
(i) Micelle formation by soap in aqueous solution is possible at all temperatures.
(ii) Micelle formation by soap in aqueous solution occurs above a particular concentration.
(iii) On dilution of soap solution micelles may revert to individual ions.
(iv) Soap solution behaves as a normal strong electrolyte at all concentrations.
Ans: (ii) and (iii)
The formation of micelles takes place only above a particular temperature which is the Kraft temperature (Tk ) and above a particular concentration i.e., the critical micelle concentration (CMC). Upon dilution, these colloids revert back to the individual ions hence the answer is (ii) and (iii).
27. Which of the following statements are correct about solid catalyst?
(i) Same reactants may give different product by using different catalysts.
(ii) Catalyst does not change ΔH of reaction.
(iii) Catalyst is required in large quantities to catalyse reactions.
(iv) Catalytic activity of a solid catalyst does not depend upon the strength of chemisorption.
Ans: (i) and (ii)
The action of a catalyst is selective in nature and so a substance which acts as a catalyst in one reaction may fail to catalyse another reaction. They also do not change the enthalpy of reaction hence the answer is (i) and (ii).
28. Freundlich adsorption isotherm is given by the expression x/m= kp1/x which of the following conclusion can be drawn from this expression.
When 1/n= 0, the adsorption is independent of pressure.
(ii) When 1/n= 0, the adsorption is directly proportional to pressure.
(iii) When n= 0, x/m vs p graph is a line parallel to x-axis.
(iv) When n= 0, plot of x/m vs p is a curve.
Ans: (i) and (iii)
Freundlich gave an empirical relationship between the quantity of gas adsorbed by unit mass of solid adsorbed and pressure at a particular temperature.
$\dfrac{x}{m}=k{{p}^{{}^{1}/{}_{n}}}$
If \[\dfrac{1}{n}=0;\text{ }\dfrac{x}{m}=k\] extent of adsorption is independent of pressure
When \[n=0;\text{}\dfrac{x}{m}=kp\]
\[\dfrac{x}{m}\] vs p is a line
parallel to x-axis
29. H2 gas is adsorbed on activated charcoal to a very little extent in comparison to easily liquefiable gases due to ____________.
(i) very strong van der Waal’s interaction.
(ii) very weak van der Waals forces.
(iii) very low critical temperature.
(iv) very high critical temperature.
Ans: (ii) and (iii)
H2 molecule on an activated charcoal is adsorbed to a very little extent in comparison to easily liquefiable gases because it has (a) Very weak van der Waals force of attraction (b) Very low critical temperature hence the answer is (ii) and (iii).
30. Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Mixing two oppositely charged sols neutralises their charges and stabilises the colloid.
(ii) Presence of equal and similar charges on colloidal particles provides stability to the colloids.
(iii) Any amount of dispersed liquid can be added to emulsion without destabilising it.
(iv) Brownian movement stabilises sols.
Ans: (ii) and (iv)
The presence of equal and similar charges on colloidal particles is largely responsible in providing stability to the colloidal solution, because the repulsive forces between charged particles having same charge prevent them from coalescing or aggregating when they come closer to one another. The Brownian movement has stirring effect which does not permit the particles to settle and thus, is responsible for the stability of sols hence the answer is (ii) and (iv).
31. An emulsion cannot be broken by __________ and ___________.
(i) heating
(ii) adding more amount of dispersion medium
(iii) freezing
(iv) adding emulsifying agent
Ans: (ii) and (iv)
Emulsions can be broken into constituent liquids by heating, freezing and centrifuging hence the answer is (ii) and (iv).
32. Which of the following substances will precipitate the negatively charged
emulsions?
(i) KCl
(ii) glucose
(iii) urea
(iv) NaCl
Ans: (i) and (iv)
Negatively charged emulsion can be precipitated by oppositely charged electrolyte. Na+ and K+ from the electrolyte can neutralize the negatively charge emulsion and precipitate the colloid so the answers are (i) and (iv).
33. Which of the following colloids cannot be coagulated easily?
(i) Lyophobic colloids.
(ii) Irreversible colloids.
(iii) Reversible colloids.
(iv) Lyophilic colloids.
Ans: (iii) and (iv)
Sols directly formed by mixing substances like gum, gelatin, starch, rubber, etc., with a suitable liquid (the dispersion medium) are called lyophilic sols. They are also known as reversible colloid. These sols are very stable and cannot coagulate easily hence the answers are (iii) and (iv).
34. What happens when a lyophilic sol is added to a lyophobic sol?
(i) Lyophobic sol is protected.
(ii) Lyophilic sol is protected.
(iii) Film of lyophilic sol is formed over lyophobic sol.
(iv) Film of lyophobic sol is formed over lyophilic
Ans: (i) and (iii)
Lyophilic colloids have a unique property of protecting lyophobic colloids. When a lyophilic sol is added to the lyophobic sol, the lyophilic particles form a layer around lyophobic particles and thus protect the latter from electrolytes. Lyophilic colloids used for this purpose are called protective colloid so the answers are (i) and (iii).
35. Which phenomenon occurs when an electric field is applied to a colloidal solution and electrophoresis is prevented?
(i) Reverse osmosis takes place.
(ii) Electroosmosis takes place.
(iii) Dispersion medium begins to move.
(iv) Dispersion medium becomes stationary.
Ans: (ii) and (iii).
When electrophoresis, i.e, movement of particles is prevented by some suitable means, it is observed that the dispersion medium begins to move in an electric field. This phenomenon is termed electroosmosis so the answers are (ii) and (iii).
36. In a reaction, catalyst changes ____________.
(i) Physically
(ii) Qualitatively
(iii) Chemically
(iv) Quantitatively
Ans: (i) and (ii)
Substances which accelerate the rate of a chemical reaction and themselves remain chemically and quantitatively unchanged after the reaction, are known as catalysts they can undergo physical change so the answers are (i) and (ii).
37. Which of the following phenomenon occurs when a chalk stick is dipped in ink?
(i) Adsorption of coloured substance
(ii) Adsorption of solvent
(iii) Absorption and adsorption both of solvent
(iv) Absorption of solvent
Ans: (i) and (iv)
When a chalk stick is dipped in ink, the surface retains the colour of the ink due to adsorption of coloured molecules while the solvent of the ink goes deeper into the stick due to absorption so the answers are (i) and (iv).
Short Answer Type
38. Why is it important to have clean surface in surface studies?
Ans: It is important to have clean surface as it facilitates the adsorption of desired species.
39. Why is chemisorption referred to as activated adsorption?
Ans: Chemisorption involves formation of bond between gaseous molecules/atoms and the solid surface for which high activation energy is required. Thus it is referred to as activated adsorption.
40. What type of solutions are formed on dissolving different concentrations of soap in water?
Ans: At lower concentration soap forms a normal electrolytic solution with water. After a certain concentration called critical micelle concentration, colloidal solution is formed.
41. What happens when gelatin is mixed with gold sol?
Ans: Gold sol is a lyophobic sol. Addition of gelatin stabilises the gold sol.
42. How does it become possible to cause artificial rain by spraying silver iodide on the clouds?
Ans: Clouds are colloidal in nature and carry charge. Spray of silver iodide, an electrolyte, results in coagulation leading to rain.
43. Gelatin which is a peptide is added in ice creams. What can be its role?
Ans: Ice creams are emulsions which get stabilised by emulsifying agents like gelatin.
44. What is collodion?
Ans: It is a 4% solution of nitrocellulose in a mixture of alcohol and ether.
45. Why do we add alum to purify water?
Ans: The colloidal impurities present in water get coagulated by added alum, thus making water potable.
46. What happens when electric field is applied to colloidal solution?
Ans: The charged colloidal particles start moving towards oppositely charged electrodes.
47. What causes brownian motion in colloidal dispersion?
Ans: Unbalanced bombardment of the particles of dispersed phase by molecules of dispersion medium causes brownian motion. This stabilises the sol.
48. A colloid is formed by adding FeCl3 in excess of hot water. What will happen if excess sodium chloride is added to this colloid?
Ans: Positively charged sol of hydrated ferric oxide is formed and on adding excess of NaCl, negatively charged chloride ions coagulate the positively charged sol of hydrated ferric oxide.
49. How do emulsifying agents stabilise the emulsion?
Ans: The emulsifying agent forms an interfacial layer between suspended particles and the dispersion medium thereby stabilising the emulsion.
50. Why are some medicines more effective in the colloidal form?
Ans: Medicines are more effective in the colloidal form because of large surface area and are easily assimilated in this form.
51. Why does leather get hardened after tanning?
Ans: Animal hide is colloidal in nature and has positively charged particles. When it is soaked in tannin which has negatively charged colloidal particles, it results in mutual coagulation taking place.
52. How does the precipitation of colloidal smoke take place in Cottrell precipitator?
Ans: In Cottrell precipitator, charged smoke particles are passed through a chamber containing plates with charge opposite to the smoke particles. Smoke particles lose their charge on the plates and get precipitated.
53. How will you distinguish between dispersed phase and dispersion medium in an emulsion?
Ans: On adding dispersion medium, emulsions can be diluted to any extent. The dispersed phase forms a separate layer if added in excess.
54. On the basis of Hardy-Schulze rule explain why the coagulating power of phosphate is higher than chloride.
Ans: Minimum quantity of an electrolyte required to cause precipitation of a sol is called its coagulating value. Greater the charge on flocculating ion and smaller is the amount of electrolyte required for precipitation, higher is the coagulating power of coagulating ion (Hardy-Schulze rule).
55. Why does bleeding stop by rubbing moist alum?
Ans: Moist alum coagulates the blood and so formed blood clot stops bleeding.
56. Why is Fe(OH)3 colloid positively charged, when prepared by adding FeCl3 to hot water?
Ans: The adsorption of positively charged Fe3+ ions by the sol of hydrated ferric oxide results in positively charged colloid.
57. Why dophysisorption and chemisorption behave differently with rise in temperature?
Ans: Physisorption involves weak van der Waals forces which weaken with rise in temperature. The chemisorption involves formation of chemical bond involving activation energy and like any other chemical reaction is favoured by rise in temperature.
58. What happens when dialysis is prolonged?
Ans: Due to excessive dialysis, traces of electrolyte which stabilises the colloids is removed completely, making the colloid unstable. As a result, coagulation takes place.
59. Why does the white precipitate of silver halide become coloured in the presence of dye eosin.
Ans: Eosin is adsorbed on the surface of silver halide precipitate making it coloured.
60. What is the role of activated charcoal in gas mask used in coal mines?
Ans: Activated charcoal acts as an adsorbent for various poisonous gases present in the coal mines.
61. How does a delta form at the meeting place of sea and river?
Ans: River water is a colloidal solution of clay and sea water contains lot of electrolytes. The point at which river and sea meet is the site for coagulation. Deposition of coagulated clay results in delta formation.
62. Give an example where physisorption changes to chemisorption with rise in temperature. Explain the reason for change.
Ans: The process of physisorption for example that of H2 on finely divided nickel, involves weak van der Waals’ forces. With increase in temperature, hydrogen molecules dissociate into hydrogen atoms which are held on the surface by chemisorption.
63. Why is desorption important for a substance to act as good catalyst?
Ans: After the reaction is over between adsorbed reactants, the process of desorption is important to remove products and further create space for the other reactant molecules to approach the surface and react.
64. What is the role of diffusion in heterogenous catalysis?
Ans: The gaseous molecules diffuse on to the surface of the solid catalyst and get adsorbed. After the required chemical changes the products diffuse away from the surface of the catalyst leaving the surface free for more reactant molecules to get adsorbed and undergo reaction.
65. How does a solid catalyst enhance the rate of combination of gaseous molecules?
Ans: When gaseous molecules come in contact with the surface of a solid catalyst, a weak chemical combination takes place between the surface of the catalyst and the gaseous molecules, which increases the concentration of reactants on the surface. Different molecules adsorbed side by side have better chance to react and form new molecules. This enhances the rate of reaction. Also, adsorption is an exothermic process. The heat released in the process of adsorption is utilised in enhancing the reaction rate.
66. Do the vital functions of the body such as digestion get affected during fever? Explain your answer.
Ans: The rate of an enzyme reaction is maximum at a definite temperature, called the optimum temperature. On either side of the optimum temperature, the enzyme activity decreases. The optimum temperature range for enzymatic activity is 298-310 K. Human body temperature being 310 K is suited for enzyme-catalysed reactions. Therefore, during fever, catalytic activity of the enzyme may get affected.
Matching Type
Note: Match the items of Column I and Column II in the following questions.
67. Method of information of solution is given in Column I. Match it with the type of solution given in Column II
Column I | Column II |
(i) Sulphur vapours passed through cold water | (a) Normal electrolyte solution |
(ii) Soap mixed with water above critical micelle concentration | (b) Molecular colloids |
(iii) White of egg whipped with water | (c) Associated colloid |
(iv) Soap mixed with water below critical micelle concentration | (d) Macro molecular colloids |
Ans: (i) By passing the vapours of Sulphur through cold water sulphur sol can be prepared which is a molecular colloid.
(ii) When soap is mixed with water above critical micelle concentration forms associated colloid.
(iii) White of egg whipped with water forms macromolecular colloid.
(iv) Soap mixed with water below critical micelle concentration behave as normal electrolyte so the answers are: (i)- (b) (ii)- (c) (iii)- (d) (iv)- (a)
Column I | Column II |
(i) Sulphur vapours passed through cold water | (b) Molecular colloids |
(ii) Soap mixed with water above critical micelle concentration | (c) Associated colloid |
(iii) White of egg whipped with water | (d) Macro molecular colloids |
(iv) Soap mixed with water below critical micelle concentration | (a) Normal electrolyte solution |
68. Match the statement given in Column I with the phenomenon given in Column II.
Column I | Column II |
(i) Dispersion medium moves in an electric field | (a) Osmosis |
(ii) Solvent molecules pass through semi permeable membrane towards solvent side | (b) Electrophoresis |
(iii) Movement of charged colloidal particles under the influence of applied electric potential towards oppositely charged electrodes | (c) Electroosmosis |
(iv) Solvent molecules pass through semi permeable membranes towards solution side | (d) Reverse osmosis |
Ans: (i) When electrophoresis i.e., movement of particles is prevented by some suitable means, it is observed that the dispersion medium begins to move in an electric field. This phenomenon is termed Electroosmosis.
(ii) Solvent molecules pass through semi-permeable membrane towards solvent side is termed as reverse osmosis.
(iii) When electric potential is applied across two platinum electrodes dipping in a colloidal solution, the colloidal particles move towards one or the other electrode. The movement of colloidal particles under an applied electric potential is called electrophoresis.
(iv) Solvent molecules pass through semipermeable membrane towards solution side is termed as osmosis.
So the answers are: . (i)- (c) (ii)- (d) (iii)- (b) (iv)- (a)
Column I | Column II |
(i) Dispersion medium moves in an electric field | (c) Electroosmosis |
(ii) Solvent molecules pass through semi permeable membrane towards solvent side | (d) Reverse osmosis |
(iii) Movement of charged colloidal particles under the influence of applied electric potential towards oppositely charged electrodes | (b) Electrophoresis |
(iv) Solvent molecules pass through semi permeable membranes towards solution side | (a) Osmosis |
69. Match the items given in Column I and Column II.
Column I | Column II |
(i) Protective colloid | (a) FeCl3 + NaOH |
(ii) Liquid - liquid colloid | (b) Lyophilic colloids |
(iii) Positively charged colloid | (c) Emulsion |
(iv) Negatively charged colloid | (d) FeCl3 + hot water |
Ans:
Column I | Column II |
(i) Protective colloid | (b) Lyophilic colloids |
(ii) Liquid - liquid colloid | (c) Emulsion |
(iii) Positively charged colloid | (d) FeCl3 + hot water |
(iv) Negatively charged colloid | (a) FeCl3 + NaOH |
(i) Lyophilic colloids have a unique property of protecting lyophobic colloids. When a lyophilic sol is added to the lyophobic sol, the lyophilic particles form a layer around lyophobic particles and thus protect colloid.
(ii) If a mixture of two immiscible or partially miscible liquids is shaken, a coarse dispersion of one liquid in the other is obtained which is called emulsion.
(iii) If FeCl3 is added to excess of hot water, a positively charged sol of hydrated ferric oxide is formed due to adsorption of Fe3+ ions.
(iv) When ferric chloride is added to NaOH a negatively charged sol is obtained with adsorption of OH- ions.
70. Match the types of colloidal systems given in Column I with the name given in Column II.
Column I | Column II |
(i) Solid in liquid | (a) Foam |
(ii) Liquid in solid | (b) Sol |
(iii) Liquid in liquid | (c) Gel |
(iv) Gas in liquid | (d) Emulsion |
Ans:
S.No. | Dispersed Phase | Dispersion medium | Colloid |
(i) | Solid | Liquid | (b) Sol |
(ii) | Liquid | Solid | (c) Gel |
(iii) | Liquid | Liquid | (d) Emulsion |
(iv) | Gas | Liquid | (a) Foam |
71. Match the items of Column I and Column II.
Column I | Column II |
(i) Dialysis | (a) Cleansing action of soap |
(ii) Peptisation | (b) Coagulation |
(iii) Emulsification | (c) Colloidal sol formation |
(iv) Electrophoresis | (d) Purification |
Ans: (i)- (d) (ii)- (c) (iii)- (a) (iv)- (b)
Column I | Column II |
(i) Dialysis | (d) Purification |
(ii) Peptisation | (c) Colloidal sol formation |
(iii) Emulsification | (a) Cleansing action of soap |
(iv) Electrophoresis | (b) Coagulation |
72. Match the items of Column I and Column II.
Column I | Column II |
(i) Butter | (a) dispersion of liquid in liquid |
(ii) Pumice stone | (b) dispersion of solid in liquid |
(iii) Milk | (c) dispersion of gas in solid |
(iv) Paints | (d) dispersion of liquid in solid |
Ans: The correct answers are:
Column I | Column II |
(i) Butter | (d) dispersion of liquid in solid |
(ii) Pumice stone | (c) dispersion of gas in solid |
(iii) Milk | (a) dispersion of liquid in liquid |
(iv) Paints | (b) dispersion of solid in liquid |
Ans: The answers are: (i)- (d) (ii)- (c) (iii)- (a) (iv)- (b)
Dispersed Phase | Dispersion medium | Example colloid solution |
Solid | Liquid | Butter |
Gas | Solid | Pumice stone |
Liquid | Liquid | Milk |
Solid | Liquid | Paint |
Assertion and Reason Type
Note: In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct and the reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(ii) Assertion and reason both are correct but reason does not explain assertion.
(iii) Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
(iv) Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
(v) Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
73. Assertion: An ordinary filter paper impregnated with collodion solution stops the flow of colloidal particles.
Reason: Pore size of the filter paper becomes more than the size of colloidal particle.
Ans: Colloidal particles can pass through ordinary filter paper because the pores are too large. However, the pores of filter paper can be reduced in size by impregnating with collodion solution to stop the flow of colloidal particles hence the answer is (iii).
74. Assertion: Colloidal solutions show colligative properties.
Reason: Colloidal particles are large in size.
Ans: Colloidal particles being bigger aggregates, the number of particles in a colloidal solution is comparatively small as compared to a true solution. Hence, the values of colligative properties (osmotic pressure, lowering in vapour pressure, depression in freezing point and elevation in boiling point) are of small order as compared to values shown by true solutions at same concentration hence the answer is (i).
75. Assertion: Colloidal solutions do not show brownian motion.
Reason: Brownian motion is responsible for stability of sols.
Ans: Colloidal particle shows Brownian movement. The Brownian movement has a stirring effect which does not permit the particles to settle and thus, is responsible for the stability of sols so the answer is (v).
76. Assertion: Coagulation power of Al3+ is more than Na+.
Reason: Greater the valency of the flocculating ion added, greater is its power to cause precipitation (Hardy Schulze rule).
Ans: Greater the valence of the flocculating ion added, the greater is its power to cause precipitation. This is known as Hardy schulze rule. In the coagulation of a negative sol, the flocculating
77. Assertion: Detergents with low CMC are more economical to use.
Reason: Cleansing action of detergents involves the formation of micelles. These are formed when the concentration of detergents becomes equal to CMC.
Ans: Detergents with low CMC are more economical to use as they involve formation of micelle which is used for cleaning of oil and dirt from our cloth. Micelle formation takes place when the concentration of the detergent becomes equal to the CMC so the answer is (i).
Long Answer Type
78. What is the role of adsorption in heterogenous catalysis?
Ans: In heterogeneous catalysis reactants are generally in gas phase and catalyst are in solid phase. The activity of a catalyst depends upon the strength of chemisorption to a large extent. The reactants must get adsorbed reasonably strongly on to the catalyst to become active. However, they must not get adsorbed so strongly that they are immobilized and other reactants are left with no space on the catalyst’s surface for adsorption. It has been found that for hydrogenation reaction, the catalytic activity increases from Group 5 to Group 11 metals with maximum activity being shown by groups 7-9 elements of the periodic table. Catalyst also directs a reaction to yield a particular product. For example, starting with H2 and CO, and using different catalysts, we get different products.
79. What are the applications of adsorption in chemical analysis?
Ans: (i) Separation of inert gases: Due to a difference in the degree of adsorption of gases by charcoal, a mixture of noble gases can be separated by adsorption on coconut, a charcoal at different temperatures.
(ii) Adsorption indicators: Surfaces of certain precipitates such as silver halides have the property of adsorbing some dyes like eosin, fluorescein, and so produce a characteristic colour at end point.
(iii) Chromatographic analysis: It is based on the phenomenon of adsorption and has a number of applications in analytical and industrial fields.
80. What is the role of adsorption in froth floatation process used especially for concentration of sulphide ores?
Ans: This method is used for removing gangue from sulphide ores. In this, a suspension of powdered ore is made with water. To which both the collectors and froth stabilisers are added. Collectors for example pine oils, fatty acids, xanthates enhance non-wettability of the mineral particles and froth stabilisers such as cresols, aniline stabilise the froth.
81. What do you understand by shape selective catalysis? Why are zeolites good shape selective catalysts?
Ans: Catalytic reaction which depends on the pore structure of catalyst and size of the reactant, product molecules is known as shape-selective catalysis. Zeolites are considered as good shape-selective catalysts due to their honeycomb-like structures. They are aluminosilicates with three-dimensional network of silicates wherein some of the silicon atoms are replaced by aluminium atoms giving Al-O-Si frame work. The reactions taking place in zeolites depends upon size and shape of reactant and product molecules, the pores and cavities of the zeolites also. They are found in nature and synthesised for catalysts selectivity. Zeolites are widely used as catalysts in petrochemical industries for cracking of hydrocarbons and isomerisation.
Class 12 Chemistry Surface Chemistry Vedantu’s NCERT Exemplar Solutions
In Chemistry Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry, students learn about the interfacial phenomenon and its significance, adsorption and Classify physical and chemical adsorption, mechanism of adsorption, factors controlling adsorption from gases and solutions on solids, adsorption results on the basis of Freundlich adsorption isotherms, the role of catalysts in industry, nature of the colloidal state, the preparation, properties, and purification of colloids, emulsions, and their preparation and properties, the phenomenon of gel formation and the uses of colloids.
A Peek Into the Chapter and its Solutions
The study of Surface Chemistry is important for both theoretical and practical considerations. It finds many applications in industry, analytical work, and daily life situations. The NCERT solutions provided by Vedantu’s subject experts help Class 12 students to understand all the concepts covered in Chemistry Chapter 5. The solutions are easy to grasp. This Chapter includes various crucial topics for students that are important for their board Examinations and competitive Exams like JEE Mains and NEET. Students are advised to solve the NCERT exemplar problems for Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry to score great marks in all Chemistry Exams. NCERT exemplar problems should be solved thoroughly along with the previous year’s Chemistry question papers and sample papers.
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter-5 (Book Solutions)
1. Do I need to practice all the questions provided in NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5?
Solving NCERT exemplar problems for Class 12 is imperative to score good marks in the final board Examinations. Students can get their doubts cleared by solving all the NCERT exemplar problems. Exemplar problems help them in understanding all the important concepts covered in the Chapter. It is beneficial to refer to the solutions provided by Vedantu experts (as per CBSE guidelines). The solutions can be understood by the Class 12 students easily. Vedantu’s NCERT solutions comprise accurate answers and are curated by leading subject experts.
2. What are the important topics of Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry?
Let's take a closer look at the important topics covered in NCERT Chapter 5 Chemistry:
Adsorption
The distinction between Adsorption and Absorption
Mechanism of Adsorption
Types of Adsorption
Adsorption Isotherms
Adsorption from solution phase
Applications of Adsorption
Catalysis
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis
Adsorption Theory of Heterogeneous Catalysis
Shape- Selective Catalysis by Zeolites
Enzyme Catalysis
Catalysts in Industry
Colloids
Classification of Colloids
Dispersed Phase and Dispersion Medium
Interaction between Dispersed Phase and Dispersion Medium
The Dispersed Phase, Multimolecular, Macromolecular, and Associated Colloids
Preparation of Colloids
Purification of Colloidal Solutions
Properties of Colloidal Solutions
Emulsions
3. Where can I get the free PDF of NCERT Solutions of Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Surface Chemistry?
Students can download the free PDF of NCERT Exemplar Solutions of Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5 on Vedantu’s website which provides free PDF on all the topics of Chemistry. The free PDF by Vedantu contains all the NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry Chapter 5 - Surface Chemistry. The detailed explanations help students in revising all the crucial concepts in order to ace their Chemistry board Exams. The solutions are designed by Chemistry experts at Vedantu and follow the latest CBSE guidelines.
4. How is Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry important for board Exams?
Chapter 5 plays a vital role in CBSE Class 12 Board Exams and carries various important questions needed to score good marks in the final Chemistry board Examination as well as competitive Exams like JEE and NEET. Students are encouraged to solve the NCERT exemplar problems as they help them in understanding all concepts covered in Chapter 5 properly. In this Chapter, students learn about important topics such as micelles, emulsification, coagulation, dialysis, absorption, and adsorption. Vedantu provides a comprehensive free PDF of NCERT solutions designed by the best subject experts.
5. How should I practice the NCERT problems for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter - 5 Surface Chemistry?
Vedantu’s NCERT exemplar solutions have been crafted by Chemistry experts to benefit Class 12 students and provide them greater insights into the important topics. Solutions are explained in an elaborative way. The explanations provided for each answer boosts confidence in students. The NCERT solutions are provided by Vedantu’s expert faculty, helping students to understand the method of answering each type of question. The solutions by Vedantu are designed from an Exam point of view so that students are able to improve their time management skills.







































