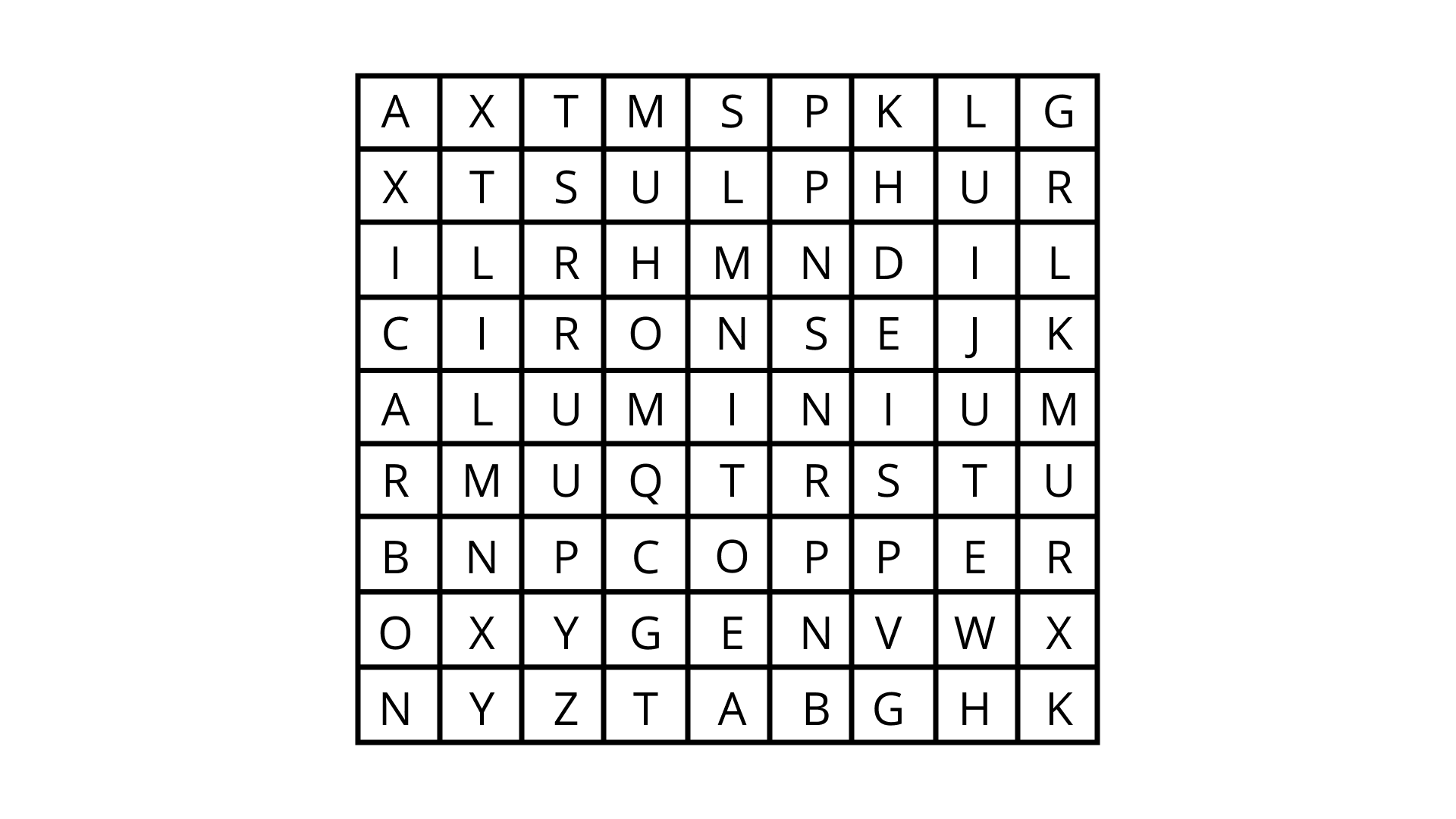
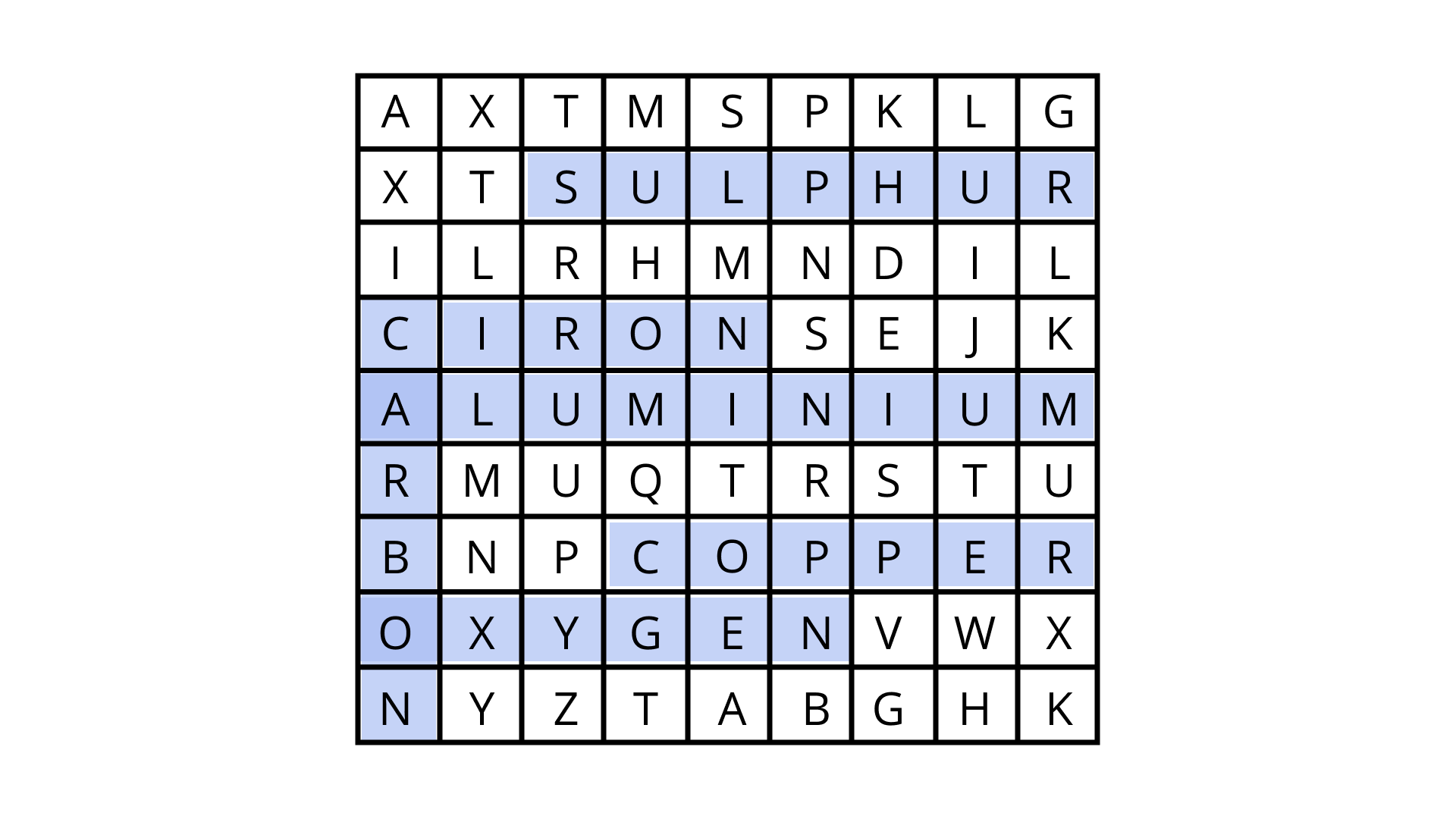
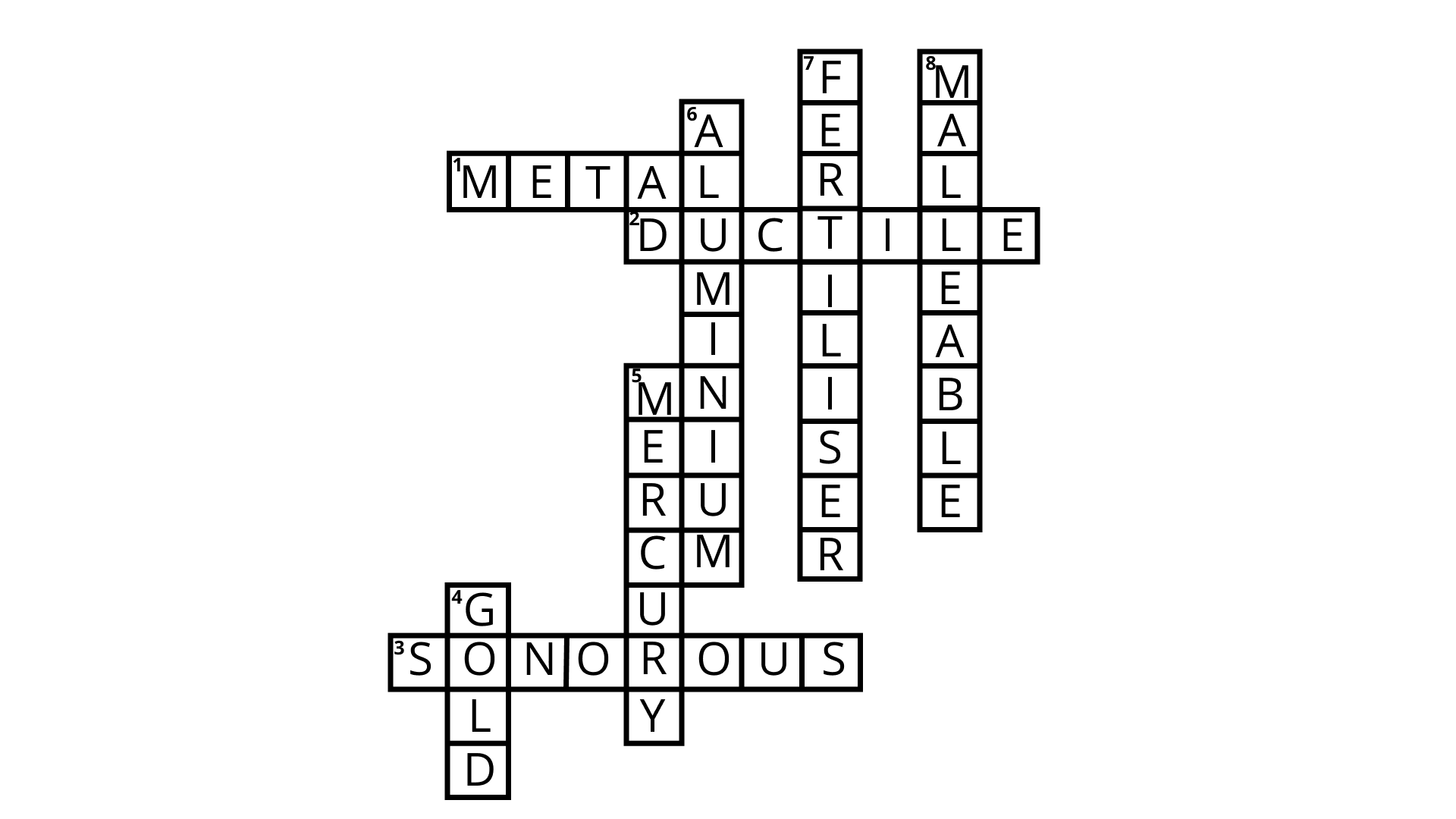
Class 8 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
1. How Do Metals and Non-metals React?
Metals lose one or more of their valence electrons and create cations.
Anions are formed when nonmetals acquire electrons in their valence shell.
Strong electrostatic forces draw the cation and anion together, resulting in the formation of an ionic bond. For example, oppositely charged calcium and chloride ions create an ionic connection in calcium chloride. The electron configuration of the calcium atom is changed to that of the closest noble gas(Ar) after it loses 2 electrons. It obtains a net charge of +2 as a result of this.
2. What is Ionic Compound?
Compounds whose atoms are held together by ionic bonds are called ionic compounds. Elements can gain or lose electrons to achieve their closest noble gas configuration. By forming ions for the completion of the octet, they are stabilized.
Metals lose electrons to complete their octet in a reaction between metals and nonmetals, whereas non-metals acquire electrons to complete their octet. Metals and nonmetals react to generate ionic compounds. The relative sizes of the cations and anions determine the structure of an ionic molecule. Salts, oxides, hydroxides, sulfides, and the bulk of inorganic compounds are ionic compounds. Ionic solids are held together by the electrostatic contact between positive and negative ions.
3. What is Calcination?
Calcination is described as the process of turning ore into an oxide by heating it to a high temperature. The ore is heated below its melting point in the absence of air or with a limited supply of air. This method is commonly used to convert carbonates and hydroxides to corresponding oxides. During calcination, moisture and volatile impurities are also removed. Calcination is a thermal process that causes thermal breakdown to change ores and other solid materials into liquids. In calcination, the reaction occurs most of the time at or near the thermal breakdown temperature.
4. What is Roasting?
Roasting is a process for transforming sulfide ores, while calcination is primarily employed for the oxidation of carbonates. The roasting process emits volatile gasses that contain moisture and nonmetallic contaminants. The roasting process is made up of solid-gas thermal reactions including oxidation, reduction, sulfation, chlorination, and pyro hydrolysis. Roasting with sulfides, on the other hand, is a major source of air pollution, and the main disadvantage of this process is that it releases a considerable quantity of metallic, poisonous, and acidic chemicals, all of which are harmful to the environment.
5. From where do I get free material for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals?
Vedantu is a website that offers students free NCERT solutions and other study tools. NCERT answers PDF from Vedantu is a free PDF available online to aid students in their final exam preparations from classes 1 to 12. The PDF follows CBSE criteria to assist you to succeed in these exams. To foster concept-based learning, more attention is placed on subject comprehension, with a particular focus on each topic and idea. Students would feel well prepared to take the exams after reading the PDF. Students may use the NCERT answer PDF as a full study material guide.