How Evolution Concept Maps Aid Exam Preparation
The term evolution has been derived from the Latin word ‘evolve’ which means to unroll. Evolution can be of two types:
Chemical Evolution - Chemical evolution states that life originated on earth as a result of several physicochemical changes.
Biological Evolution - Biological evolution is an appreciable and dramatic account of life on Earth and of human origins within. The change during biological evolution is gradual and orderly from simple to complex form.
Biological evolution is also referred to as organic evolution as organisms are made up of organic matter. A concept map can be the best way to focus on each important aspect of evolution to understand this in a better way.
What is Concept Map?
A concept map is a diagrammatic tool that visually represents relationships between concepts and ideas that can take the form of charts, graphic organisers, tables, flowcharts, Venn Diagrams, timelines, or T-charts.
Characteristics of Concept Map
The main characteristics of concept maps are based on the need to build up the strength of students' concepts in learning, understanding, creativity, critical thinking, and the ability to ask new questions and respond to them successfully. These characteristics are as follows:
They have four elements such as concepts, lines and arrows, linking words, and proposals.
They are a special scheme.
These focus on answering a ‘focus question’.
These help to build new knowledge.
These help to understand elaborate approaches.
Its elaboration depends completely on the student.
These results in processes of negotiation of meaning.
These help to boost self-esteem in the student.
Definition of Evolution
Evolution is an amazing topic of Biology that explains to us the change in the genetic features of biological populations in successive generations over a huge period of time. Evolution’s two special types are chemical and biological evolution.
Evolution Concept Map
The evolution concept map describes the key concepts of evolution by natural selection, including various theories of evolution. An evolution concept map template notes the physical (fossil), biochemical or molecular, anatomical, and various other evidence that justifies evolution on a broader scale.
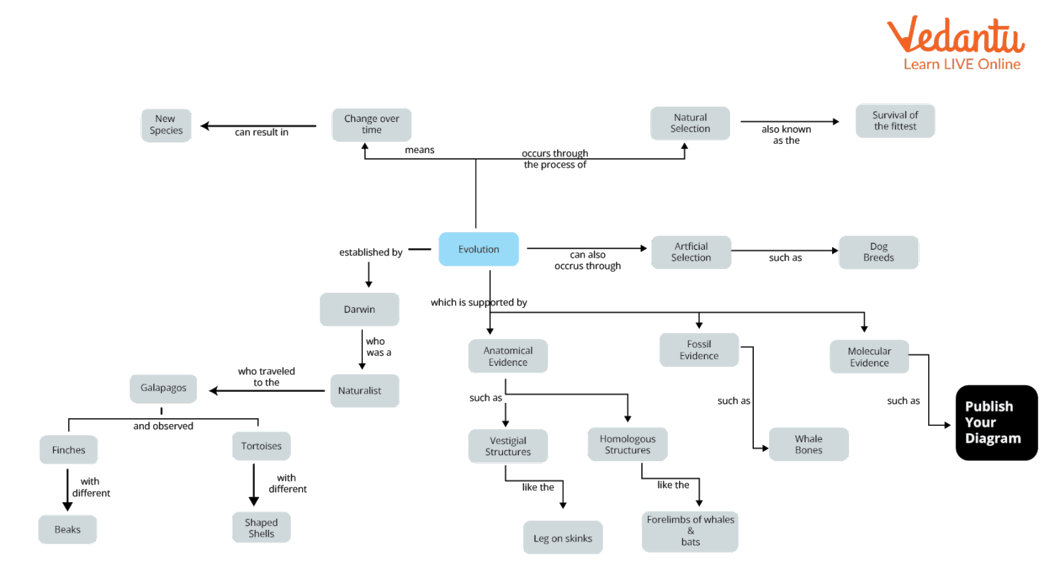
Evolution Content Map
Chemical Evolution Concept Map
The theory of chemical evolution, also known as the modern theory of evolution of life, is based on the belief that on a primitive earth, a mixture of simple chemicals congregated together into more complex molecular systems, from which, eventually came the first functioning cell.
Biological Evolution Concept Map
The cumulative changes which occur in a population over a huge period of time are called biological evolution. These changes occur at the genetic level because organisms' genes show mutation and may recombine in different ways during reproduction and are passed onto the next generations.
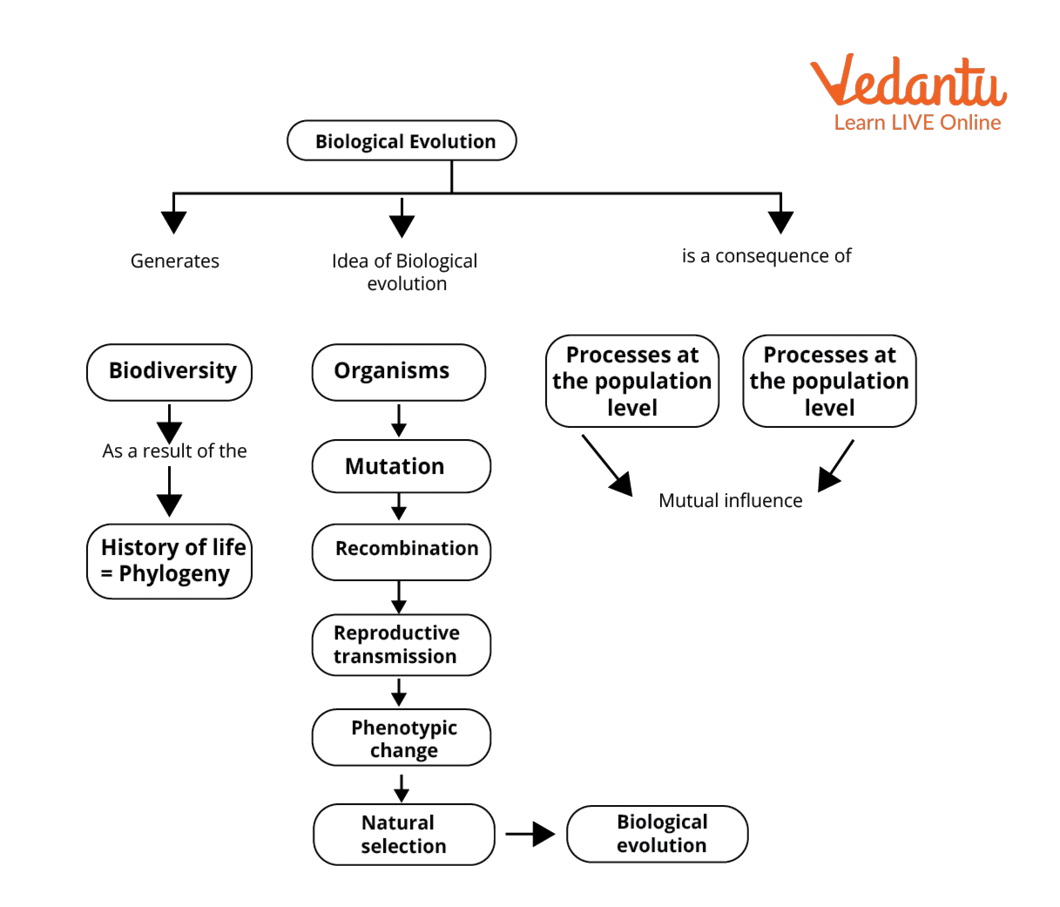
Biological Evolution Concept Map
Theory of Evolution Concept Map
The three main theories of evolution are as follows:
Theory of Inheritance of Acquired Characters by Lamarck: First theory of evolution was proposed by Jean Baptiste de Lamarck (1744-1829) in his book Philosophie Zoologique (1809). The term Biology was given by Lamarck & Treviranus. According to Lamarck,
Some internal forces are present in all organisms. In the presence of these forces, organisms have the tendency to increase the size of organs or the entire body.
Environment influences all types of organisms. Changing the environment gives rise to new needs.
New needs or desires produce new structures and change the habits of the organism.
If an organ is constantly used, it would be better developed whereas disuse of the organ results in its degeneration.
During the lifetime of an organism, new characteristics develop due to internal vital forces, effects of the environment, new needs, and use and disuse of organs. These acquired characteristics are inherited from one generation to the next generations.
By continuous inheritance, through many generations, these acquired characteristics tend to make the new generation quite different from its ancestors resulting in the formation of new species.
Theory of Natural Selection by Darwin: After the study of T.R.Malthus essay, Wallace got the idea of survival of the fittest and also wrote an essay using the title – “On the tendency of varieties to depart indefinitely, from their original type.” and send it to Darwin. Darwin, after reviewing this, postulated the theory of natural selection. According to Darwin,
Multiplication of individuals of a species occurs in a geometric proportion.
Due to the geometric multiplication and due to the availability of limited food and space for these individuals, the struggle for existence is seen.
They are the rule of nature and are provided to be beneficial for a better existence.
The operation of natural selection on the existing variability in order to select the best-fitted variations.
Natural selection is the principal element of Darwin’s theory. The principle by which the preservation of useful variations is brought about was called natural selection.
Mutation Theory by De Vries: According to De Vries, sudden, stable, inherited characteristics which are completely different from their parents are called a mutation.
Hugo De Vries believed that mutation causes the origin of new species and hence he used the term Saltation.
Saltation means single-step large mutation (variation originates in single steps and in full form) and is just opposite to the adaptation and natural selection of Darwin (variations are small and gradual, directional).
Useful mutations are selected by nature while lethal and harmful mutations are eliminated.
Evidence of Evolution Concept Map
There are different types of evidence including physical and molecular features and fossils which provide evidence for evolution and can allow us to rebuild macroevolutionary events.
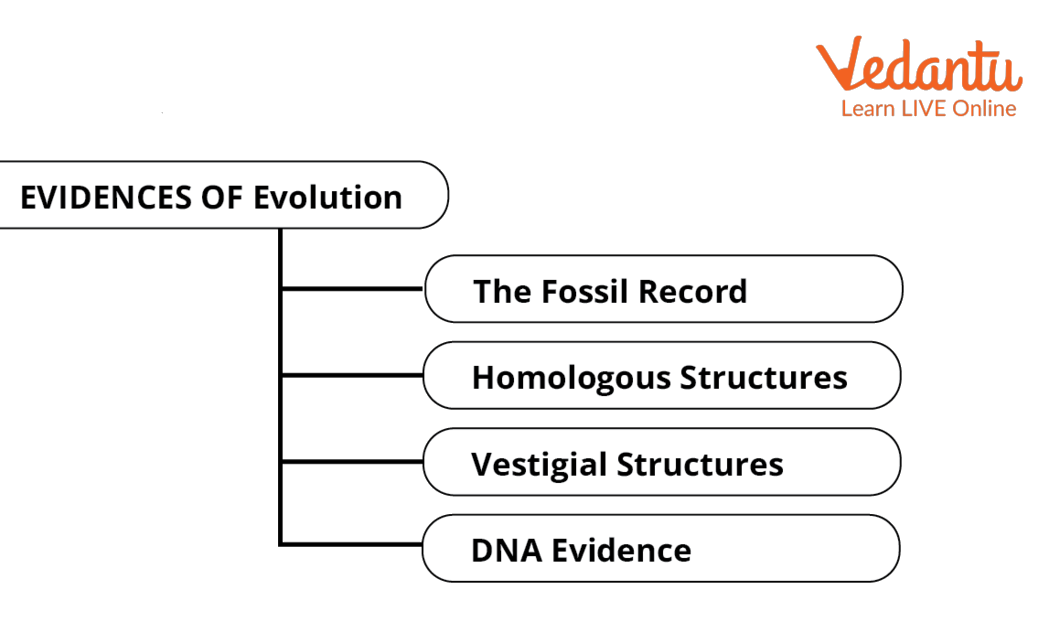
Evidence of Evolution
Interesting Facts
Humans evolved from apelike ancestors, not actual monkeys or apes.
Dinosaurs (reptiles) are birds' genetic ancestors.
Evolution is more like a tree with different branches instead of a straight line from one species to the next.
Important Questions
What is Neo Darwinism?
Ans: After Mendel’s laws were rediscovered and the concept of variations came into force, a new theory called synthetic theory of evolution or neo-Darwinisim came into existence. According to this theory, mutation and natural selection (dominant factor) play a major role in shaping the genetic makeup of populations.
What are convergent and divergent evolution?
Ans: Unrelated organisms when use the same form or structure due to adaptations, this is called convergent evolution. Divergent evolution is the process in which two or more related organisms become distinct. This evolution produces homologous structures.
Key Features of the Evolution Concept Map
A concept map is a diagrammatic tool that visually represents relationships between concepts and ideas.
Evolution is an amazing topic of Biology that explains to us the successive changes in organisms over a huge period of time.
Chemical evolution states that life originated on earth as a result of several physicochemical changes.
The cumulative changes which occur in a population over a huge period of time are called biological evolution.
There are various theories of evolution such as Lamarckism, Darwinism, Theory of Hugo de Vries.
There are different types of evidence including physical and molecular features and fossils which provide evidence for evolution and can allow us to rebuild macroevolutionary events.


FAQs on Evolution Concept Map: Terms, Examples & Applications
1. What do you understand about the term ‘Fossil’?
A fossil is any preserved remains or traces of any once-living thing from a past geological time period.
2. What was the Weismann theory?
August Weismann gave germplasm theory. It explains that heritable information is transmitted only by germ cells present in the gonads. This theory disapproved of Lamarcks’ theory of inheritance of acquired characters.
3. What are the 5 important stages of human evolution?
The process of human evolution is the one by which human beings developed on Earth from now-extinct primates. The five stages of human evolution are as follows:
Dryopithecus
Ramapithecus
Australopithecus
Homo erectus
Homo sapiens Neanderthalensis










