What is the structure and main function of the Golgi apparatus (Golgi body)?
The Golgi Apparatus is a vital organelle found in all eukaryotic cells. It functions as the cell's shipping and packaging center, modifying, sorting, and transporting proteins and lipids. This organelle plays a key role in cell growth, secretion, and communication. Understanding its structure and function is essential for students learning about cell biology, human physiology, and related subjects.
What is the Golgi Apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus, also called the Golgi body or Golgi complex, is a membrane-bound cell organelle. It was first discovered by Italian physician Camillo Golgi in 1898. The main role of the Golgi apparatus in the cell is to modify, package, and transport proteins and lipids made in the endoplasmic reticulum. It exists in both animal and plant cells and helps maintain cellular organization.
Golgi Apparatus Structure
The Golgi apparatus structure is unique and can be recognized under a microscope. It consists of a series of flattened, stacked membrane sacs called cisternae. There are usually 4 to 8 cisternae in animal and plant cells, but some unicellular organisms may have up to 60. The Golgi body is supported by cytoskeletal elements like microtubules, ensuring its position near the cell nucleus.
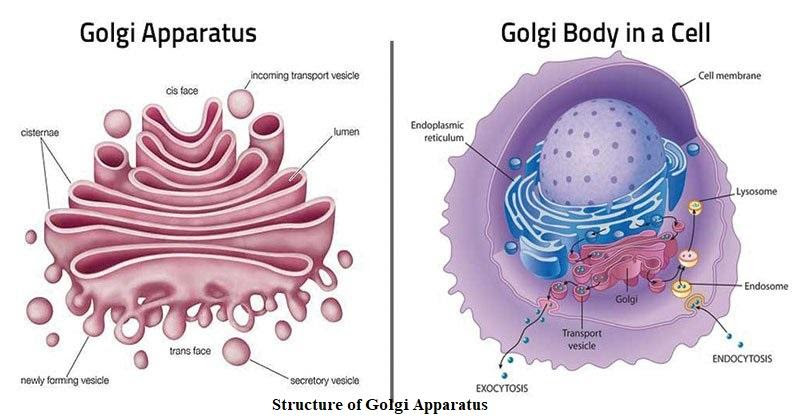
- Cis Face: The entry side, facing the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
- Medial Cisternae: The central region, where protein and lipid modification continues.
- Trans Face: The exit side, where processed materials are sorted and packed into vesicles.
The arrangement of these regions gives the Golgi complex its polarity. The cis Golgi network receives proteins and lipids from the ER, while the trans Golgi network releases them to their next destination. This structure is critical for directing materials efficiently within the cell.
Golgi Apparatus Function
The main functions of the Golgi body include the modification, sorting, and transportation of proteins and lipids to their specific destinations within or outside the cell. These processes are essential for processes like secretion, cell wall formation in plants, and production of certain hormones. This section will cover major functions, relevant to students from Class 9 onwards and in advanced biology courses.
- Protein Modification: Adds carbohydrates (glycosylation), phosphates (phosphorylation), and sulfates to proteins.
- Lipid Transformation: Modifies and sorts lipids for inclusion in cell membranes or secretion.
- Sorting and Packaging: Sorts proteins and lipids and packs them into vesicles (Golgi vesicles).
- Formation of Lysosomes: Creates enzymes required for lysosome formation—vital for digestion and waste removal in cells (see Lysosomes).
- Secretion: Directs secretory vesicles to the plasma membrane for exocytosis, such as releasing hormones and enzymes.
- Cell Wall Synthesis (Plants): Supplies polysaccharides and proteins for building the plant cell wall (see Plant Cell).
For example, insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, requires proper modification in the Golgi apparatus before it can act in regulating blood glucose. This demonstrates the organelle's real-world relevance in human health and medicine.
Golgi Apparatus in Animal and Plant Cells
The Golgi apparatus in animal cells and plant cells is structurally similar, but there are some differences. In animal cells, the Golgi apparatus is usually singular and located near the nucleus. In plant cells, multiple Golgi bodies, called dictyosomes, are scattered throughout the cytoplasm.
- Animal Cell Golgi: Central location, single complex, involved in secretion and lysosome formation (Animal Cell).
- Plant Cell Golgi: Multiple dictyosomes, play a key role in cell wall and membrane formation.
You can find more details about cell structure in our dedicated resource on cell structure and function.
Golgi Apparatus Process: Protein Trafficking and Modification
The Golgi apparatus in the cell handles protein trafficking via a complex but fascinating pathway. Here is a simplified process:
- Proteins and lipids are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
- Transport vesicles carry these molecules to the cis face of the Golgi apparatus.
- Proteins and lipids travel through the cisternae, undergoing modifications like glycosylation or cleavage of certain chains.
- In the trans face, modified products are tagged and sorted according to their final destinations.
- Packaged materials are sent to lysosomes, cell membrane, or released by exocytosis.
Misprocessed proteins can lead to cellular problems or diseases, highlighting the importance of the Golgi functions. In medicine, defects in Golgi function are linked to conditions such as congenital disorders of glycosylation.
Golgi Apparatus Diagram
A Golgi body diagram helps visualize its major components: stacks of cisternae, vesicles nearby, and close proximity to the ER. Understanding the labeled diagram is crucial for exams and practicals.
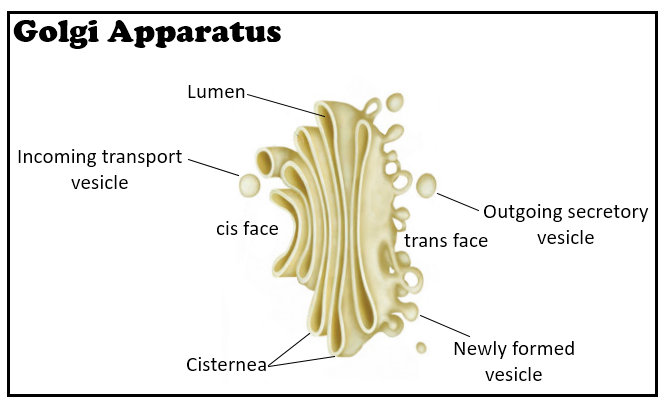
Students are often asked to draw and label the Golgi complex, marking the cis face, trans face, cisternae, and vesicles. For more diagram practice, visit our important biology diagrams section.
Importance in Biology and Everyday Life
The functions of the Golgi body are crucial in many real-world areas:
- Medicine: Understanding Golgi functions aids in diagnosing and treating cell-related diseases.
- Agriculture: Golgi bodies in plant cells are vital for cell wall construction and crop yield (Plants).
- Biotechnology: Genetic engineering often requires Golgi-mediated secretion of recombinant proteins (Genetic Engineering).
- Education: Studying the Golgi apparatus is foundational in life science and cell biology.
For further exploration, Vedantu offers resources on related topics such as endocrinology, biomolecules, and genetic traits.
Key Facts About the Golgi Apparatus
- Discovered by Camillo Golgi in 1898.
- Present in all eukaryotic cells.
- Consists of stacked cisternae (usually 4-8 in most cells).
- Directs protein and lipid traffic within the cell.
- Essential for secretion, cell wall synthesis in plants, and lysosome formation.
- Plays a crucial role in human physiology (e.g., hormone processing).
These facts are especially useful for functions of Golgi body class 9 notes and quick revision before exams.
Page Summary
The Golgi apparatus is an essential component of eukaryotic cells, acting as the central hub for modifying and routing proteins and lipids. Its structure and function underpin key biological processes and modern Biotech applications. By grasping the role of the Golgi complex, students gain deeper insight into cell biology, health, and technology advances supported by its functions.


FAQs on Golgi apparatus in the cell: structure, function, and easy diagram
1. What is the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi complex or Golgi body, is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles. Key functions of the Golgi apparatus include:
- Processing and modification of proteins and lipids received from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
- Packaging molecules into vesicles for transport.
- Producing lysosomes and other related vesicles.
2. What are the main functions of the Golgi apparatus?
The main functions of the Golgi apparatus include processing, packaging, and transporting cell products. Its key roles are:
- Modification of proteins and lipids (e.g., glycosylation).
- Sorting and packaging of molecules into vesicles.
- Formation of lysosomes.
- Secretion of cellular products.
3. Where is the Golgi apparatus located in a cell?
The Golgi apparatus is usually located near the cell nucleus and endoplasmic reticulum. It often appears as a stack of flattened, membrane-bound sacs known as cisternae. Its strategic position allows efficient transport and modification of substances between the nucleus, ER, and other cellular compartments.
4. What is the structure of the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus consists of a series of flattened, stacked pouches called cisternae. Its structure includes:
- Cis face (receiving side) facing the ER.
- Trans face (shipping side) facing the cell membrane.
- Intermediate cisternae between the cis and trans faces.
5. How does the Golgi apparatus modify proteins?
The Golgi apparatus modifies proteins through processes such as glycosylation and phosphorylation as they pass through its cisternae. Key modifications include:
- Adding carbohydrate groups (glycosylation).
- Phosphorylation of proteins and lipids.
- Proteolytic processing (cutting proteins at specific sites).
6. What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in secretion?
The Golgi apparatus plays a central role in packaging and secreting cellular products. It:
- Sorts proteins and lipids into vesicles.
- Directs vesicles to their target locations (such as the cell membrane or lysosomes).
- Facilitates exocytosis (release of substances outside the cell).
7. Who discovered the Golgi apparatus and when?
Camillo Golgi, an Italian physician and scientist, discovered the Golgi apparatus in 1898. He observed this organelle in nerve cells using a special staining technique, and it was named in his honour. The discovery greatly advanced our understanding of eukaryotic cell structure and function.
8. What would happen if the Golgi apparatus stopped working?
If the Golgi apparatus stopped functioning, cells would be unable to properly process, package, or transport proteins and lipids. This could lead to:
- Accumulation of unprocessed proteins in the ER.
- Failure to form lysosomes, affecting waste breakdown.
- Disruption of secretion, impacting cell signalling and function.
9. Is the Golgi apparatus present in both plant and animal cells?
Yes, the Golgi apparatus is present in both plant and animal cells. In plant cells, it is often called the dictyosome. Its functions—processing, packaging, and transporting cellular products—are essential in all eukaryotic cells, regardless of organism type.
10. How is the endoplasmic reticulum related to the Golgi apparatus?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi apparatus work closely in the cell's protein synthesis and transport pathway. The relationship involves:
- Proteins and lipids produced by the ER are transported to the Golgi apparatus via vesicles.
- The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages these molecules for delivery.
- This cooperation ensures proper distribution and function of biomolecules within the cell.
11. What is cis face and trans face of the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus has two distinct surfaces: the cis face and the trans face.
- Cis face: The receiving side facing the endoplasmic reticulum, where vesicles deliver newly synthesized proteins and lipids.
- Trans face: The shipping side where processed molecules exit the Golgi, packaged in vesicles for their final destinations.










