Where Is the Pancreas and Why Is It Crucial for Your Body?
The pancreas is a glandular organ in the abdomen located behind the stomach. It plays a key role in both digestion and blood sugar regulation. The pancreas functions in the digestive system by releasing enzymes that help break down food, while its endocrine cells produce hormones to maintain normal blood glucose levels.
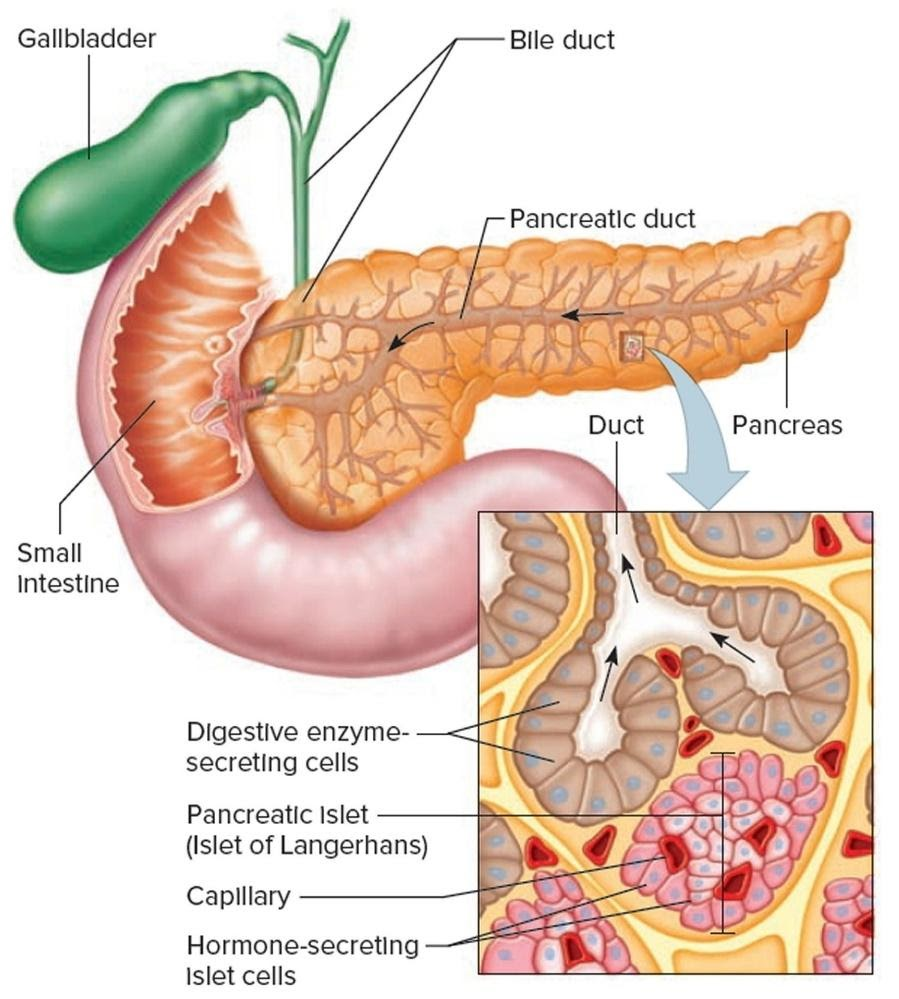
Pancreas Location
Understanding the pancreas location is essential. Part of it lies between the stomach and spine, and another portion rests within the curve of the duodenum (the first segment of the small intestine). The head of the pancreas is on the right side of the abdomen, connecting to the duodenum via a channel called the pancreatic duct. The narrow tail extends to the left side, often reaching near the spleen.
Pancreas Function
The pancreas function can be divided into two main categories:
Exocrine Function
The pancreas releases important enzymes such as amylase, proteases (like trypsin and chymotrypsin), and lipase.
These enzymes aid in the digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
When food enters the stomach, these enzymes are secreted into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct to support digestion.
Endocrine Function
The pancreas contains clusters of cells known as the Islets of Langerhans.
These islets produce pancreas hormones like insulin and glucagon, which are secreted directly into the bloodstream.
Pancreas function insulin is crucial in lowering high blood sugar, while glucagon helps increase it, keeping blood glucose at a normal level.
Symptoms of Pancreas Problems
Various issues can affect the pancreas. Symptoms of pancreas problems may include:
Persistent abdominal pain that may radiate to the back
Unintentional weight loss
Nausea and vomiting
Changes in stool (e.g., oily or foul-smelling stools)
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) in certain cases
If these symptoms appear or persist, it is important to seek medical advice.
Pancreatic Diseases and Conditions
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis occurs when pancreatic enzymes start digesting the organ from within, leading to inflammation and pain. It can be acute, causing sudden, painful attacks, or chronic, which lasts for a longer duration.
Precursors to Pancreatic Cancer
While the exact cause is not fully understood, certain factors can increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. These include a family history of cancer, genetic syndromes, smoking, and chronic pancreatitis.
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, an exocrine tumour, is one of the most common forms of pancreatic cancer. Endocrine tumours (also called neuroendocrine tumours or islet cell tumours) make up a smaller percentage of pancreatic cancers but still pose significant health concerns.
Quiz on Pancreas (with Answers)
Test your knowledge with this short quiz:
Which part of the small intestine receives the digestive enzymes from the pancreas?
Answer: The duodenum.
Which cells in the pancreas secrete insulin and glucagon?
Answer: Islets of Langerhans.
Name any two major enzymes involved in protein digestion secreted by the pancreas.
Answer: Trypsin and chymotrypsin.
Which hormone lowers blood sugar levels?
Answer: Insulin.
Mention one common symptom of pancreas problems.
Answer: Persistent abdominal pain.
Related Topics


FAQs on Pancreas: Structure, Functions, Diseases & Essential Insights
1. What is the pancreas and where is it located in the human body?
The pancreas is a soft, elongated organ located deep in the abdomen, positioned horizontally behind the stomach. It plays a crucial role in both the digestive and endocrine systems by producing essential enzymes and hormones.
2. Why is the pancreas called a mixed or heterocrine gland?
The pancreas is called a mixed gland because it performs both exocrine and endocrine functions. Its exocrine part produces digestive enzymes that travel through a duct to the small intestine, while its endocrine part secretes hormones like insulin and glucagon directly into the bloodstream.
3. What are the main exocrine functions of the pancreas in digestion?
The primary exocrine function of the pancreas is to produce and secrete pancreatic juice into the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). This juice contains key enzymes that break down different food components:
- Pancreatic amylase: Digests carbohydrates (starches).
- Trypsin and Chymotrypsin: Digest proteins.
- Lipase: Digests fats (lipids).
4. What is the endocrine function of the pancreas, and which cells are responsible?
The endocrine function of the pancreas is to regulate blood glucose levels. This is carried out by specialised cell clusters called the Islets of Langerhans. These islets contain different cells:
- Alpha cells which secrete the hormone glucagon to raise blood sugar.
- Beta cells which secrete the hormone insulin to lower blood sugar.
5. How do insulin and glucagon work together to maintain blood sugar balance?
Insulin and glucagon are antagonistic hormones that create a delicate balance. When blood sugar rises after a meal, the pancreas releases insulin, which helps cells absorb glucose for energy or storage. When blood sugar drops, the pancreas releases glucagon, which signals the liver to release stored glucose (glycogen) back into the blood, thus raising the levels.
6. What is the difference between the pancreatic duct and the Islets of Langerhans?
The main difference lies in their function and structure within the pancreas. The pancreatic duct is part of the exocrine system; it's a tube that collects and transports digestive enzymes out of the pancreas. In contrast, the Islets of Langerhans are part of the endocrine system; they are clusters of cells that release hormones directly into the bloodstream and are ductless.
7. What are some common diseases or disorders that affect the pancreas?
Several conditions can affect the pancreas, including:
- Pancreatitis: An inflammation of the pancreas where digestive enzymes become active inside the organ, causing damage.
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body's immune system destroys the insulin-producing beta cells.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A condition where the body either doesn't produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to it.
- Pancreatic Cancer: The uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the pancreas.
8. How can lifestyle choices like diet and alcohol consumption impact pancreatic health?
Lifestyle choices have a direct impact on the pancreas. A diet high in fats can force the pancreas to work harder, increasing the risk of pancreatitis. Excessive alcohol consumption is a leading cause of both acute and chronic pancreatitis. Maintaining a healthy weight and a balanced diet helps reduce strain on the pancreas, particularly in regulating blood sugar, which is crucial for preventing Type 2 diabetes.
9. What would happen if the pancreatic duct gets blocked?
If the pancreatic duct is blocked, the flow of digestive enzymes into the small intestine is obstructed. These enzymes can build up within the pancreas and get activated prematurely. This leads to the enzymes beginning to digest the pancreas itself, causing a severe and painful condition known as acute pancreatitis, which requires immediate medical attention.
10. Is it possible to live without a pancreas, and what are the medical consequences?
While it is surgically possible to live without a pancreas (a procedure called a pancreatectomy), it has life-altering consequences. A person would lose both pancreatic functions. They would immediately develop Type 1 diabetes and require lifelong insulin therapy to manage blood sugar. Additionally, they would need to take digestive enzyme replacement pills with every meal to absorb nutrients from food properly.










