




Step-by-Step Guide to pH Testing in Fruits and Vegetables for Class 11 Chemistry Students
Soren Peder Lauritz Sorensen, a Danish chemist, was first introduced to pH. Based on the concentration of hydrogen ions, the pH value varies. Acids in water dissolve and donate H+ ions, whereas bases in water dissolve and give rise to OH- ions. Acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors. The acidity or basicity of a solution can be determined by knowing its pH. The pH of a solution is defined as the amount of hydrogen present in a given solution. The pH of a solution can be found out by the following formula: pH= -log[H+].
Table of Content
Aim
Apparatus Required
Theory
Procedure
Observation
Result
Precautions
Lab Manual Questions
Viva Questions
Practical Based Questions
Aim
To determine the pH of vegetable and fruit juices using pH paper and a universal indicator.
Apparatus Required
Test Tubes
Measuring Cylinder
Glass Rod
Watch Glass
Vegetable and Fruit Juice
Universal Indicator Solution
pH Paper
Theory
There are many methods to determine the pH of a solution. The most common method is pH paper, a universal indicator and a pH metre. The pH paper and universal solution when in contact with a solution show a change in colouration depending upon pH. A universal indicator is made up of several compounds. Thymol blue, methyl red, bromothymol blue, phenolphthalein etc. are the indicators which help in detecting pH over a wide range.
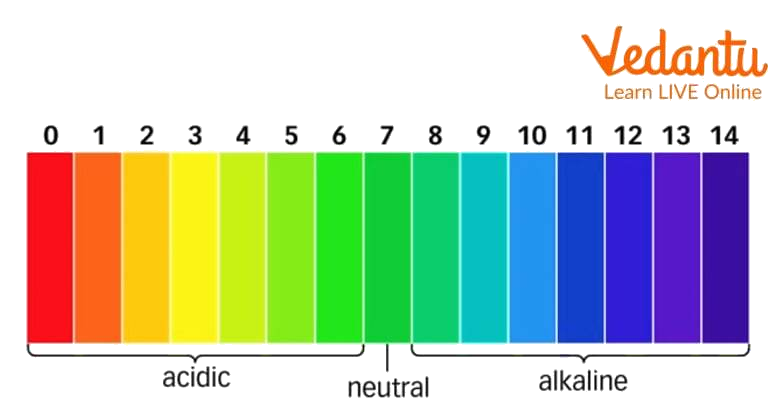
pH scale
Procedure
Using pH Paper
Take some clean and dry test tubes.
Next, put various vegetable and fruit juices into the test tubes.
Place the pH paper strip on a clean surface.
Using a clean dropper, put the sample of fruits and vegetables into the pH paper strips.
Now compare the colour of the pH paper strip to the standard pH chart.
Note down the value of the pH of the tested samples.
Using Universal Indicator
Take a given sample of juices like lemon juice, orange juice, tomato juice, pineapple juice, amla juice and mango juice in a separate test tube.
Make sure that 10 ml of juices should be transferred to the clean test tubes with the help of a measuring cylinder.
Add a universal indicator in each of the solutions and mix it thoroughly.
Observe the colour of each solution and compare it with the chart that presents in the bottle.
Note down the value of the pH of the tested samples.
Observation
Results
From this above experiment, we can reveal that:
The pH value of lemon juice is 2.
The pH value of tomato juice is 4.30-4.90.
The pH value of orange juice is 3.
The pH value of pineapple juice is 3.20-4.00.
The pH value of amla juice is 5.70-6.00.
The pH value of mango juice is 6.
Precautions
Test tubes should be properly cleaned and dry.
Avoid using the same dropper for the transfer of juice samples.
The universal indicator should be equal in quantity for all the samples.
pH paper should be clean and away from fumes.
Observe the colour of the solution that appears with the standard pH chart.
Lab Manual Questions
1. What do you mean by pH?
Ans: It is defined as the negative logarithm of hydrogen ions in a solution. It is used to determine the strength of an acid or base. The term pH refers to the “potential of hydrogen ions”.
2. What do you understand about the pH scale?
Ans: It is a scale containing various colours which indicate the strength of the acid or the base. pH is normally measured in a range of 0-14. 0 is a strong acid and 14 is a strong base.
3. How to analyse the pH of vegetables and fruit juices.
Ans: The pH of a solution can be determined using pH paper or a universal indicator. To analyse the pH of fruits or vegetable juices, either the pH paper is dipped into the solution or a universal indicator is put into the juices. Depending upon the pH, different coloured solutions are formed and this colour change can determine the pH of the solution which can be understood from the pH scale indicator.
4. What is a universal indicator?
Ans: A universal indicator is a mixed indicator (it contains several colour-changing substances) and shows a range of colours depending on the pH of the solution. Universal indicator is a liquid solution.
Viva Questions
1. What is the formula to find the pH of a solution?
Ans: Formula of pH is pH= -log[H+].
2. What does the pH of a solution mean?
Ans: pH is a scale used to determine a liquid solution's acidity and basicity.
3. Name some weak acids and strong acids.
Ans: Sulphuric acid, Hydrochloric acid and nitric acid are strong acids. Acetic acid, Carbonic acid etc. are weak acids.
4. What are weak acids?
Ans: Weak acids are acids that when dissolved in solutions do not completely dissociate into their respective ions, i.e., upon dissociation do not release all the hydrogen ions present in them.
5. What are the components of universal indicators?
Ans: The components of the universal indicator are thymol blue, methyl red, bromothymol blue, phenolphthalein etc.
6. Give another name for NaOH.
Ans: NaOH is also known as caustic soda.
7. What will be the colour of pH paper when lemon juice is added to it?
Ans: The colour of the pH paper becomes orange when lemon juice is added to it.
8. In a pH metre, which part of it is sensitive to hydrogen ions?
Ans: A particular electronic bulb in a pH metre is sensitive to hydrogen ions.
9. Give examples of weak bases.
Ans: Ammonium hydroxide, Lead hydroxide, zinc hydroxide etc. are examples of weak bases.
10. What are strong bases?
Ans: Strong bases are bases which when in a solution completely dissociate into respective components, giving rise to OH- ions.
Practical Based Questions (MCQs)
Finding the pH of a solution, which of the following is not essential?
pH paper
HCl
Universal indicator
Standard pH value Chart
Ans: HCl
Which of the following is not a component of a universal indicator?
Methyl red
Thymol blue
Safranin
Phenolphthalein
Ans: Safranin
Find the odd one out.
Litmus paper
pH paper
pH metre
Universal indicator
Ans: Litmus paper
If a pH paper is dipped in an orange juice solution, what will be the possible colour of the pH paper?
Red
Blue
Orange
Violet
Ans: Orange
pH on the pH scale becomes ______as we move from left to right.
Basic
Acidic
Neutral
Remains unchanged
Ans: Basic
Find the odd man out.
Sodium hydroxide
Ammonium hydroxide
Aluminium hydroxide
Copper hydroxide
Ans: Sodium hydroxide
State which of the following is true.
pH helps in the digestion of food
pH helps in not important in soil.
HCl is the strongest acid
pH is not significant for various life processes.
Ans: pH helps in the digestion of food.
Fruit juice is tested for its pH value. What could be the possible pH if the colour is changed to yellow?
Less than 3.5
More than 7
7
Between 5.5 and 6.5
Ans: Between 5.5 and 6.5
What are the end products of the neutralisation reaction?
Acid and base
Salt and water
H+ ions and OH- ions
Water and OH- ions
Ans: Salt and water
Which of the following is not a property of acid?
Converts blue litmus paper red
pH value lower than 7
Are highly corrosive
pH value higher than 7
Ans: pH value higher than 7
Conclusion
From this experiment, we can conclude that the given solutions of vegetable juice are acidic and basic. That helps us determine which liquid samples are safe to consume. The pH can be measured with the help of a pH metre, pH paper and universal indicator.
FAQs on Experiment: Measuring pH of Vegetable and Fruit Juices in Class 11 Chemistry (2025-26)
1. Write the nature of the solution based on pH value.
The solutions having a pH value below 7 are acidic. These solutions turn blue litmus red. The solutions having a pH equal to 7 are neutral. These solutions do not show any colour change of litmus. The solutions having a pH of more than 7 are basic. These solutions turn red litmus blue.
2. Give examples of indicators.
It is a substance that can be used to identify the nature of chemicals due to their colour change. The indicator changes its colour when the pH of the solution slightly changes. When using indicators, the solution to be tested should be colourless. If the solution has a colour, it could interfere with the indicator's colour. Universal indicator or pH paper gives an approximate value of the pH.
3. What is thymol blue?
It is used to determine the acidity and basicity of a solution. It is a reddish-brown and brownish-green crystalline powder used as a pH indicator.
























