Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Extra Questions and Answers Free PDF Download
Looking for a reliable way to prepare Chapter 3: Trigonometric Functions in CBSE Class 11 Maths? Our carefully prepared set of important questions is the perfect resource to help you prepare effectively. This chapter is a key part of the Class 11 Maths syllabus, covering essential topics like trigonometric identities, functions, equations, and inverse trigonometric concepts. These important questions focus on exam-relevant problems, ensuring you gain a thorough understanding of all key concepts.
Download the Important Questions for Class 11 Maths FREE PDF now to access a wide range of questions that are designed to strengthen your problem-solving skills and boost your confidence for exams. With step-by-step solutions and a focus on commonly tested topics, this resource is an excellent tool for students aiming for high marks. Start practising today.
Access Important Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 - Trigonometric Functions
1 Mark Questions
1. Find the radian measure corresponding to $ 5{}^\circ \text{ }37'\text{ }30'' $
Ans-
Converting the given value to a pure degree form
$ {{5}^{\circ }}37'30''={{5}^{\circ }}37'\left( \dfrac{30}{60} \right)' $
$ \Rightarrow {{5}^{\circ }}37'60''={{5}^{\circ }}\left( \dfrac{75}{2} \right)' $
$ \Rightarrow {{5}^{\circ }}37'60''={{5}^{\circ }}{{\left( \dfrac{75}{2\left( 60 \right)} \right)}^{\circ }} $
$ \Rightarrow {{5}^{\circ }}37'60''={{\left( \dfrac{45}{8} \right)}^{\circ }} $
Degree to Radian Conversion
$ \left( \dfrac{45}{8} \right)\left( \dfrac{\pi }{180} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{32}\text{rad} $
2. Find degree measure corresponding to $ {{\left( \dfrac{\pi }{16} \right)}^{c}} $
Ans-
Converting the given value from radian to degree form
$ \dfrac{\pi }{16}\times \dfrac{180}{\pi }={{\left( \dfrac{45}{4} \right)}^{\circ }} $
Simplify degree form
$ {{\left( \dfrac{45}{4} \right)}^{\circ }}={{11}^{\circ }}15' $
3. Find the length of an arc of a circle of radius $ 5cm $ subtending a central angle measuring $ 15{}^\circ $
Ans-
The arc of a circle with a radius of $ 5\,\text{cm} $ with a central angle of $ {{15}^{\circ }} $ should be of the length $ \dfrac{5\pi }{12}cm $ using the formula $ \text{Arc}\,\text{=}\,\pi \times \left( \theta \right) $ .
4. Find the value of $ \dfrac{19\pi }{3} $
Ans-
We have $ \tan \dfrac{19\pi }{3} $
$ \tan \dfrac{19\pi }{3}=\tan \left( 6\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right) $
$ =\tan \left( 6\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right) $
$ =\tan \left( 3\times 2\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right) $
$ =\tan \left( \dfrac{\pi }{3} \right) $
$ =\sqrt{3} $
5. Find the value of $ \sin \left( -1125{}^\circ \right) $
Ans-
We have $ \sin \left( -{{1125}^{\circ }} \right) $
$ \sin \left( -\dfrac{1125}{360}\times {{360}^{\circ }} \right) $
$ =-\sin \left( \left( 3+\dfrac{45}{360} \right)\times {{360}^{\circ }} \right) $
$ =-\sin \left( {{45}^{\circ }} \right) $
$ =-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} $
6. Find the value of $ \tan \left( {{15}^{\circ }} \right) $
Ans-
We have $ \tan {{15}^{\circ }} $
$ \tan {{15}^{\circ }}=\tan \left( {{60}^{\circ }}-{{45}^{\circ }} \right) $
$ =\dfrac{\tan {{60}^{\circ }}-\tan {{45}^{\circ }}}{1+\tan {{60}^{\circ }}\times \tan {{45}^{\circ }}} $
$ =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1}{\sqrt{3}+1} $
7. If $ \sin A=\dfrac{3}{5} $ and $ \dfrac{\pi }{2}<A< $ find $ \cos A $
Ans-
The condition $ \dfrac{\pi }{2}<A $ denotes that we need to take into account for the second quadrant, hence the cosine value will be negative.
Therefore,
$ \cos A=\dfrac{-4}{5} $
8. If $ \tan A=\dfrac{a}{a+1} $ and $ \tan B=\dfrac{1}{2a+1} $ then find the value of $ A+B $
Ans-
$ \tan \left( A+B \right)=\dfrac{\tan A+\tan B}{1-\tan A\tan B} $
$ =\dfrac{\dfrac{a}{a+1}+\dfrac{1}{2a+1}}{1-\dfrac{a}{a+1}\cdot \dfrac{1}{2a+1}} $
$ =\dfrac{\dfrac{2{{a}^{2}}+2a+1}{\left( a+1 \right)\left( 2a+1 \right)}}{\dfrac{\left( a+1 \right)\left( 2a+1 \right)-a}{\left( a+1 \right)\left( 2a+1 \right)}} $
$ =1 $
Which can only be possible if $ A+B={{45}^{\circ }} $ .
9. Express $ \sin 12\theta +\sin 4\theta $ as the product of sines and cosine
Ans-
Using the trigonometric difference formula, we get
$ \sin 12\theta +\sin 4\theta =\sin \left( 8\theta +4\theta \right)+\sin \left( 8\theta -4\theta \right) $
$ =2\sin 8\theta \cos 4\theta $
10. Express $ 2\cos 4x\sin 2x $ as an algebraic sum of sines or cosine.
Ans-
$ 2\cos 4x\sin 2x=\sin \left( 2x+4x \right)+\sin \left( 2x-4x \right) $
$ =\sin 6x+\sin \left( -2x \right) $
$ =\sin 6x-\sin 2x $
11. Write the range of $ \cos \theta $
Ans-
The cosine function is a periodic function with a domain of $ \mathbb{R} $ and a range of $ \left[ -1,1 \right] $ .
12. What is domain of $ \sec \theta $
Ans-
The secant function is the reciprocal of the cosine function, it has a domain of $ \mathbb{R}-\left\{ (2n+1)\dfrac{\pi }{2};n\in \mathbb{Z} \right\} $ because those are the points where the cosine function equates to $ 0 $ .
13. Find the principal solution of $ \cot x=3 $
Ans-
The principal solution of $ \cot x=3 $ is for the following input values $ x=\dfrac{5\pi }{6},\dfrac{11\pi }{6} $ .
14. Write the general solution of $ \cos \theta =0 $
Ans-
The general solution for the equation $ \cos \theta =0 $ is $ \theta =(2n+1)\dfrac{\pi }{2},n\in \mathbb{Z} $ .
15. If $ \sin x=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3} $ and $ 0\text{ }<\text{ }x\text{ }<\dfrac{\pi }{2} $ find the value of $ \cos 2x $
Ans-
We know that $ \cos 2x=1-{{\sin }^{2}}x $
$ \cos 2x=1-2{{\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3} \right)}^{2}} $
$ =1-2\times \dfrac{5}{9} $
$ =-\dfrac{1}{9} $
16. If $ \cos x=-\dfrac{1}{3} $ and $ x $ lies in quadrant $ \text{III} $ , find the value of $ \sin \dfrac{x}{2} $
Ans-
We know that $ \cos 2x=1-2{{\sin }^{2}}x $
$ \cos \left( 2\left( \dfrac{x}{2} \right) \right)=1-2{{\sin }^{2}}\left( \dfrac{x}{2} \right) $
$ \Rightarrow -\dfrac{1}{3}=1-2{{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{x}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow 2{{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{x}{2}=1+\dfrac{1}{3} $
$ \Rightarrow {{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{2}{3} $
$ \Rightarrow \sin \dfrac{x}{2}=\pm \sqrt{\dfrac{2}{3}} $
$ \Rightarrow \sin \dfrac{x}{2}=\sqrt{\dfrac{2}{3}}\,\,\,\,\,\left[ \text{2nd Quadrant} \right] $
17. Convert into radian measures $ -47{}^\circ 30' $
Ans-
Convert into pure degree form and then convert to radian
$ -47{}^\circ 30'=-{{\left( 47+\dfrac{30}{60} \right)}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ =-{{\left( 47+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ =-\left( \dfrac{95}{2}\times \dfrac{\pi }{180} \right)\text{rad} $
$ =-\dfrac{19\pi }{72}\text{rad} $
18. Evaluate $ \tan 75{}^\circ $
Ans-
Use the trigonometric addition formula for the tangent function
$ \tan {{75}^{\circ }}=\tan ({{45}^{\circ }}+{{30}^{\circ }}) $
$ =\dfrac{\tan {{45}^{\circ }}+\tan {{30}^{\circ }}}{1-\tan {{45}^{\circ }}\tan {{30}^{\circ }}} $
$ =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+1}{\sqrt{3}-1} $
19. Prove that $ \sin (40+\theta )\cdot \cos (10+\theta )-\cos (40+\theta )\cdot \sin (10+\theta )=\dfrac{1}{2} $
Ans-
Let us take the left-hand side of the equation and make some manipulations.
We know, $ \sin \left( a-b \right)=\sin a\cos b-\cos a\sin b $
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}=\sin (40+\theta )\cos (10+\theta )-\cos (40+\theta )\sin (10+\theta ) $
$ =\sin \left[ 40+\theta -10-\theta \right]=\sin 30 $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2} $
20. Find the principal solution of the eq. $ \sin x=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} $
Ans-
The principal solution of $ \sin x=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} $ is the input values of $ x=\dfrac{\pi }{3},\dfrac{2\pi }{3} $
21. Prove that $ \cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{4}+x \right)+\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{4}-x \right)=\sqrt{2}\cos x $
Ans-
Let us start with the left-hand side and use the trigonometric differences formula for the cosine function
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}=\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{4}+x \right)+\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{4}-x \right) $
$ =2\cos \dfrac{\pi }{4}\cos x $
$ =2\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\cos x $
$ =\sqrt{2}\cos x $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S} $
22. Convert into radian measures $ -37{}^\circ 30' $
Ans-
Convert into pure degree form and then convert from degree to radian
$ -37{}^\circ 30'={{\left( 37+\dfrac{30}{60} \right)}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ =-{{\left( \dfrac{75}{2} \right)}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ =-\dfrac{75}{2}\times \dfrac{\pi }{180}\text{rad} $
$ =-\dfrac{5\pi }{24}\text{rad} $
23. Prove
$ Sin\text{ }\left( n+1 \right)\text{ }x\text{ }Sin\text{ }\left( n+2 \right)\text{ }x\text{ }+\text{ }Cos\text{ }\left( n+1 \right)\text{ }x.\text{ }Cos\text{ }\left( n+2 \right)\text{ }x\text{ }=\text{ }Cos\text{ }x $
Ans-
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\,\text{. = sin}\left( n+1 \right)x\sin \left( n+2 \right)x+\cos \left( n+1 \right)x\cos \left( n+2 \right)x $
$ =\cos \left\{ \left( n+1 \right)x-\left( n+2 \right)x \right\} $
$ =\cos \left( nx+x-n-2x \right) $
$ =\cos \left( -x \right) $
$ =\cos \left( x \right) $
Find the value of $ \operatorname{Sin}\dfrac{31\pi }{3} $
Ans-
We have $ \sin \dfrac{31\pi }{3} $
$ \operatorname{Sin}\dfrac{31\pi }{3}=\operatorname{Sin}\left( 10\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right) $
$ =\operatorname{Sin}\left( 2\pi \times 5+\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)\,\,\,\,\,\,\left[ \text{Periodic Function} \right] $
$ =\operatorname{Sin}\dfrac{\pi }{3} $
$ =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} $
Find the principal solution of the eq. $ \tan x=-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} $ .
Ans-
The principal solution of the equation $ \tan x=-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} $ will be the input values of $ x=\dfrac{5\pi }{6},\dfrac{11\pi }{6} $
Convert into radian measures $ 5{}^\circ \text{ }37'\text{ }30'' $
Ans-
Converting the given value to a pure degree form
$ {{5}^{\circ }}37'30''={{5}^{\circ }}37'\left( \dfrac{30}{60} \right)' $
$ \Rightarrow {{5}^{\circ }}37'60''={{5}^{\circ }}\left( \dfrac{75}{2} \right)' $
$ \Rightarrow {{5}^{\circ }}37'60''={{5}^{\circ }}{{\left( \dfrac{75}{2\left( 60 \right)} \right)}^{\circ }} $
$ \Rightarrow {{5}^{\circ }}37'60''={{\left( \dfrac{45}{8} \right)}^{\circ }} $
Degree to Radian Conversion
$ \left( \dfrac{45}{8} \right)\left( \dfrac{\pi }{180} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{32}\text{rad} $
Prove $ Cos70{}^\circ .\text{ }Cos10{}^\circ +\text{ }Sin70{}^\circ .\text{ }Sin10{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{2} $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric differences formula for the cosine function.
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}=\text{cos}\left( {{70}^{\circ }}{{10}^{\circ }} \right) $
$ =\cos {{60}^{\circ }} $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2} $
Evaluate $ 2\operatorname{Sin}\dfrac{\pi }{12} $
Ans-
Use the trigonometric difference formula for the sine function and expand
$ 2\sin \dfrac{\pi }{12}=2\sin \left[ \dfrac{\pi }{4}-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right] $
$ =2\left[ \sin \dfrac{\pi }{4}\cos \dfrac{\pi }{6}-\cos \dfrac{\pi }{4}\sin \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right] $
$ =2\left[ \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\times \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\times \dfrac{1}{2} \right] $
$ =\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1}{\sqrt{2}} $
Find the solution of $ \operatorname{Sin}x=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} $
Ans-
We are required to find the general solution for the equation $ \sin x=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} $
$ \operatorname{Sin}x=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow \operatorname{Sin}x=\operatorname{Sin}\left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right) $
$ \Rightarrow \operatorname{Sin}x=\operatorname{Sin}\dfrac{4\pi }{3} $
When
$ \operatorname{Sin}\theta =\operatorname{Sin}\alpha $
$ \theta =n\pi +{{(-1)}^{n}}\cdot \alpha $
$ x=n\pi +{{(-1)}^{n}}\cdot \dfrac{4\pi }{3} $
Prove that $ \dfrac{\operatorname{Cos}9{}^\circ -\operatorname{Sin}9{}^\circ }{\operatorname{Cos}9{}^\circ +\operatorname{Sin}9{}^\circ }=\tan 36{}^\circ $
Ans-
Let us start with the right-hand side and use the trigonometric differences formula for the tangent function.
$ \text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}=\tan 36{}^\circ $
$ =\tan \left( {{45}^{\circ }}-{{9}^{\circ }} \right) $
$ =\dfrac{\tan {{45}^{\circ }}-\tan {{9}^{\circ }}}{1+\tan {{45}^{\circ }}\tan {{9}^{\circ }}} $
$ =\dfrac{1-\tan {{9}^{\circ }}}{1+\tan {{9}^{\circ }}} $
$ =\dfrac{\cos {{9}^{\circ }}-\sin {{9}^{\circ }}}{\cos {{9}^{\circ }}+\sin {{9}^{\circ }}} $
$ =\text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
Find the value of $ \tan \dfrac{19\pi }{3} $
Ans-
We have $ \tan \left( \dfrac{19\pi }{3} \right) $
$ \tan \dfrac{19\pi }{3}=\tan \left( 6\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right) $
$ =\tan \left[ 3\times 2\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right]\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left[ \text{Periodic Function} \right] $
$ =\tan \dfrac{\pi }{3} $
$ =\sqrt{3} $
Prove $ \operatorname{Cos}4x=1-8{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}x.{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}x $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric addition formula, $ \cos 2x=1-2{{\sin }^{2}}x $
We get,
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}=\operatorname{Cos}4x $
$ =1-2{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}2x $
$ =1-2{{(\operatorname{Sin}2x)}^{2}} $
$ =1-2{{(2\operatorname{Sin}x.\operatorname{Cos}x)}^{2}} $
$ =1-2(4{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}x.{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}x) $
$ =1-8{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}x.{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}x $
Prove $ \dfrac{\operatorname{Cos}(\pi +x).\operatorname{Cos}(-x)}{\operatorname{Sin}(\pi -x).\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\pi }{2}+x \right)}=Co{{t}^{2}}x $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric periodic identities, we obtain the following
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\dfrac{\cos \left( \pi +x \right)\cos \left( -x \right)}{\sin \left( \pi -x \right)\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2}+x \right)} $
$ =\dfrac{-\cos x\cos x}{-\sin x\sin x} $
$ ={{\cot }^{2}}x $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
Prove that $ \tan {{56}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{\operatorname{Cos}{{11}^{\circ }}+\operatorname{Sin}{{11}^{\circ }}}{\operatorname{Cos}{{11}^{\circ }}-\operatorname{Sin}{{11}^{\circ }}} $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric addition formula for the tangent function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\tan {{56}^{\circ }} $
$ =\tan ({{45}^{\circ }}+{{11}^{\circ }}) $
$ =\dfrac{\tan {{45}^{\circ }}+\tan {{11}^{\circ }}}{1-\tan {{45}^{\circ }}\cdot \tan {{11}^{\circ }}} $
$ =\dfrac{1+\tan {{11}^{\circ }}}{1-\tan {{11}^{\circ }}} $
$ =\dfrac{\cos {{11}^{\circ }}+\sin {{11}^{\circ }}}{\cos {{11}^{\circ }}-\sin {{11}^{\circ }}} $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
Prove that $ \operatorname{Cos}{{105}^{\circ }}+\operatorname{Cos}{{15}^{\circ }}=\operatorname{Sin}{{75}^{\circ }}-\operatorname{Sin}{{15}^{\circ }} $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric difference formula for the cosine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\operatorname{Cos}{{105}^{\circ }}+\operatorname{Cos}{{15}^{\circ }} $
$ =\operatorname{Cos}({{90}^{\circ }}+{{15}^{\circ }})+\operatorname{Cos}({{90}^{\circ }}-{{75}^{\circ }}) $
$ =-\operatorname{Sin}{{15}^{\circ }}+\operatorname{Sin}{{75}^{\circ }} $
$ =\operatorname{Sin}{{75}^{\circ }}-\operatorname{Sin}{{15}^{\circ }} $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
Find the value of $ \operatorname{Cos}(-{{1710}^{\circ }}) $
Ans-
We have $ \cos \left( -{{1710}^{\circ }} \right) $ . We also know $ \cos \left( -x \right)=\cos x $
$ \operatorname{Cos}(-{{1710}^{\circ }})=\operatorname{Cos}(1800-90) $
$ =\operatorname{Cos}\left[ 5\times 360+90 \right] $
$ =\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{\pi }{2} $
$ =0 $
A wheel makes $ 360 $ revolutions in $ 1 $ minute. Through how many radians does it turn in $ 1 $ second.
Ans-
Given,
$ \text{Number of revolutions made in 60s}=360 $
$ \text{Number of revolutions made in 1s}=\dfrac{360}{60} $
$ \text{Angle moved in 6 revolutions}=2\pi \times 6 $
$ =12\pi $
Prove that $ {{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}6x-{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}4x=\operatorname{Sin}2x.\operatorname{Sin}10x $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric addition formula for the sine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}={{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}6x-{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}4x $
$ =\sin \left( 6x+4x \right)\sin \left( 6x-4x \right) $
$ =\sin 10x\sin 2x $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
Prove that $ \dfrac{\tan 69+\tan 66}{1\tan 69.\tan 66}=-1 $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric difference identity for the tangent function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\dfrac{\tan {{69}^{\circ }}+\tan {{66}^{\circ }}}{1-\tan {{69}^{\circ }}\tan {{66}^{\circ }}} $
$ =\tan ({{69}^{\circ }}+{{66}^{\circ }}) $
$ =\tan \left( {{135}^{\circ }} \right) $
$ =\tan \left( {{90}^{\circ }}+{{45}^{\circ }} \right) $
$ =-1 $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
Prove that $\dfrac{\operatorname{Sin}x}{1+\operatorname{Cos}x}=\tan
\dfrac{x}{2} $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric addition identities for the sine and cosine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\dfrac{\sin x}{1+\cos x} $
$ =\dfrac{2\sin \dfrac{x}{2}\cos \dfrac{x}{2}}{2{{\cos }^{2}}\dfrac{x}{2}} $
$ =\dfrac{\sin \dfrac{x}{2}}{\cos \dfrac{x}{2}} $
$ =\tan \dfrac{x}{2} $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
4 Marks Questions
Prove the following identities
1. The minute hand of a watch is $ 1.5cm $ long. How far does its tip move in $ 40 $ minute?
Ans-
Analysing the given information, we have
$ r=1.5cm $
$ \text{Angle made in }60\min ={{360}^{\circ }} $
$ \text{Angle made in 1min}={{6}^{\circ }} $
$ \text{Angle made in 40min}={{6}^{\circ }}\times {{40}^{\circ }}={{240}^{\circ }} $
Calculating the arc distance
$ \theta =\dfrac{l}{r} $
$ 240\times \dfrac{\pi }{180}=\dfrac{l}{1.5} $
$ 2\times 3.14=l $
$ 6.28=l $
$ l=6.28cm $
2. Show that $ tan\text{ }3x.\text{ }tan\text{ }2x.\text{ }tan\text{ }x\text{ }=\text{ }tan\text{ }3x\text{ }\text{ }tan\text{ }2x\text{ }\text{ }tan\text{ }x $
Ans-
Let us start with $ \tan 3x $ and we know $ 3x=2x+x $
$ \tan 3x=\tan (2x+x) $
$ \dfrac{\tan 3x}{1}=\dfrac{\tan 2x+\tan x}{1-\tan 2x.\tan x} $
$ \tan 3x(1-\tan 2x.\tan x)=\tan 2x+\tan x $
$ \tan 3x-\tan 3x.\tan 2x.\tan x=\tan 2x+\tan x $
$ \tan 3x.\tan 2x.\tan x=\tan 3x-\tan 2x-\tan x $
3. Find the value of $ \tan \dfrac{\pi }{8} $
Ans-
We know that
$ \tan 2x=\dfrac{2\tan x}{1-{{\tan }^{2}}x} $
Therefore, we have
$ \tan \left( 2\dfrac{\pi }{8} \right)=\dfrac{2\tan \dfrac{\pi }{8}}{1-{{\tan }^{2}}\dfrac{\pi }{8}} $
$ \Rightarrow 1=\dfrac{2\tan \dfrac{\pi }{8}}{1-{{\tan }^{2}}\dfrac{\pi }{8}} $
Put $ \tan \dfrac{\pi }{8}=x $
$ 1=\dfrac{2x}{1-{{x}^{2}}} $
$ \Rightarrow 2x=1-{{x}^{2}} $
$ \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-1\pm \sqrt{2}}{1} $
Since, $ \dfrac{\pi }{8} $ lies in the first quadrant, the value must be positive, hence
$ \tan \dfrac{\pi }{8}=\sqrt{2}-1 $
4. Prove that $ \dfrac{\operatorname{Sin}(x+y)}{\operatorname{Sin}(x-y)}=\dfrac{\tan x+\tan y}{\tan x-\tan y} $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric difference formula for the sine function, we get
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\dfrac{\operatorname{Sin}(x+y)}{\operatorname{Sin}(x-y)} $
$ =\dfrac{\operatorname{Sin}x.\operatorname{Cos}y+\operatorname{Cos}x.\operatorname{Sin}y}{\operatorname{Sin}x.\operatorname{Cos}y-\operatorname{Cos}x.\operatorname{Sin}y} $
Dividing numerator and denominator by $ \operatorname{Cos}x.\operatorname{Cos}y $
$ =\dfrac{\tan x+\tan y}{\tan x-\tan y} $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
5. If in two circles, arcs of the same length subtend angles $ {{60}^{\circ }} $ and $ {{75}^{\circ }} $ at the center find the ratio of their radii.
Ans-
We know that the length of the arc and its subtended angle is related using the following formula
$ \theta =\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{1}}} $
Therefore, we have
$ 60\times \dfrac{\pi }{18}=\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{1}}} $
$ {{r}_{1}}=\dfrac{3l}{\pi } $ ….. $ (1) $
$ \theta =\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{2}}} $
$ 75\times \dfrac{\pi }{18}=\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{2}}} $
$ {{r}_{2}}=\dfrac{12l}{5\pi } $ ….. $ (2) $
$ (1)\div (2) $
$ \dfrac{{{r}_{1}}}{{{r}_{2}}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{3l}{\pi }}{\dfrac{12l}{5\pi }} $
$ =\dfrac{31}{\pi }\times \dfrac{5\pi }{12l} $
$ =5:4 $
6. Prove that $ \operatorname{Cos}6x=32{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}x-48{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{4}}x+18{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}x-1 $
Ans.
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric identities for the cosine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\operatorname{Cos}6x $
$ =\operatorname{Cos}2(3x)=2{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}3x-1 $
$ =\operatorname{Cos}2(3x) $
$ =2{{(4co{{s}^{3}}x-3\cos x)}^{2}}-1 $
$ =2\left[ 16{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{6}}x+9{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}x-24{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{4}}x \right]-1 $
$ =32{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{6}}x+18{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}x-48{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{4}}x-1 $
$ =32{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{6}}x-48{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{4}}x+18{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}x1 $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
7. Solve $ \operatorname{Sin}2x-\operatorname{Sin}4x+\operatorname{Sin}6x=0 $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric addition identity for the sine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\operatorname{Sin}6x+\operatorname{Sin}2x-\operatorname{Sin}4x $
$ =2\sin \left( \dfrac{6x+2x}{2} \right)\cos \left( \dfrac{6x-2x}{2} \right)-\sin 4x $
$ =\sin 4x\left( 2\cos 2x-1 \right) $
$ =0 $
Now,
$ \sin 4x=0 $
$ 4x=n\pi $
$ x=\dfrac{n\pi }{4} $
Also,
$ 2\cos 2x-1=0 $
$ \cos 2x=\cos \dfrac{\pi }{3} $
$ 2x=2n\pi \pm \dfrac{\pi }{3} $
$ x=n\pi \pm \dfrac{\pi }{6} $
8. In a circle of diameter $ 40cm $ , the length of a chord is $ 20cm $ . Find the length of the minor area of the chord.
Ans-
Given,
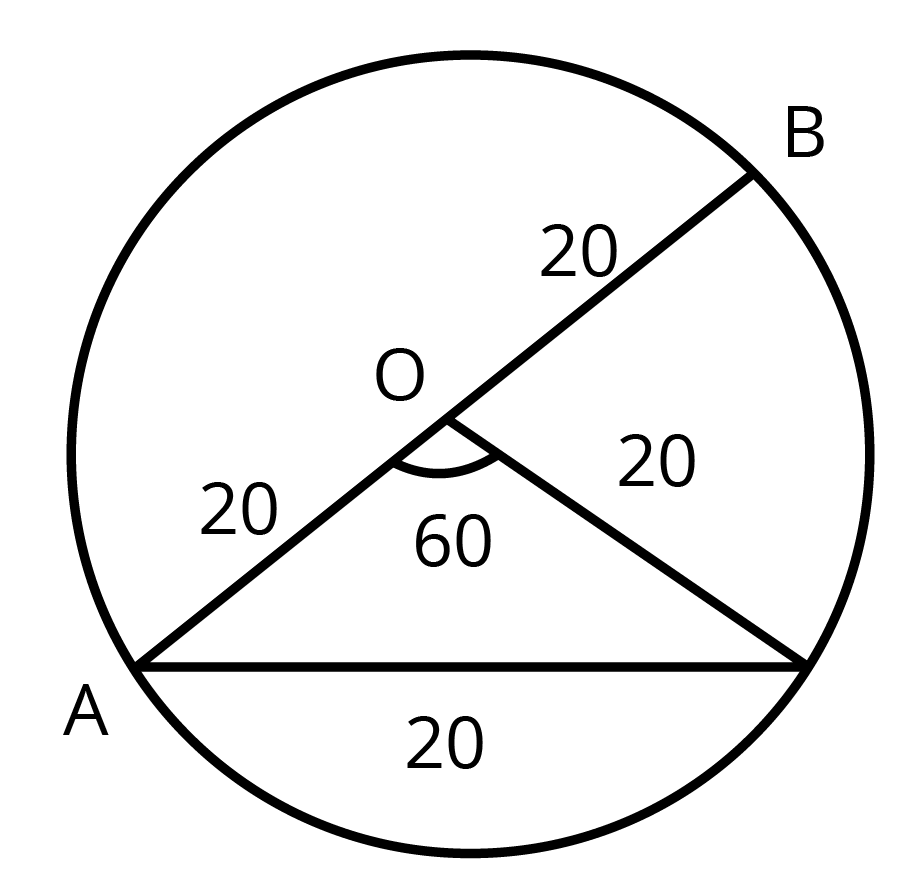
$ \theta =\dfrac{l}{r} $
$ \Rightarrow 60\times \dfrac{\pi }{180}=\dfrac{l}{20} $
$ \Rightarrow l=\dfrac{20\pi }{3}\text{cm/s} $
9. Prove that $ \tan 4x=\dfrac{4\tan x(1-{{\tan }^{2}}x)}{1-6{{\tan }^{2}}x+{{\tan }^{4}}x} $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric addition identities for the tangent function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\tan 4x $
$ =\dfrac{2\tan 2x}{1-{{\tan }^{2}}2x} $
$ =\dfrac{2.\dfrac{2\tan 2x}{1-{{\tan }^{2}}2x}}{1-{{\left( \dfrac{2\tan 2x}{1-{{\tan }^{2}}2x} \right)}^{2}}} $
$ =\dfrac{\dfrac{4\tan x}{1-{{\tan }^{2}}x}}{\dfrac{{{(1-{{\tan }^{2}}x)}^{2}}-4{{\tan }^{2}}x}{{{(1-{{\tan }^{2}}x)}^{2}}}} $
$ =\dfrac{4\tan x}{(1-{{\tan }^{2}}x)}\times \dfrac{(1-{{\tan }^{2}}x)}{1+{{\tan }^{4}}x-2{{\tan }^{2}}x-4{{\tan }^{2}}x} $
$ =\dfrac{4\tan x(1-{{\tan }^{2}}x)}{1-6{{\tan }^{2}}x+{{\tan }^{4}}x} $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
10. Prove that $ {{\left( Cosx+Cosy \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( SinxSiny \right)}^{2}}=4Co{{s}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{x+y}{2} \right) $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric addition identities for the cosine and sine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}={{\left( Cosx+Cosy \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( SinxSiny \right)}^{2}} $
$ ={{\left( 2\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{x+y}{2}.\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{x-y}{2} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{x+y}{2} \right).\operatorname{Sin}\left( \dfrac{x-y}{2} \right) \right)}^{2}} $
$ =4{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}\dfrac{x+y}{2}.{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{x-y}{2} \right)+4{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}\dfrac{x+y}{2}.{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}\dfrac{x-y}{2} $
$ =4{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{x+y}{2} \right)\left[ {{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}\dfrac{x-y}{2}+{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}\dfrac{x-y}{2} \right] $
$ =4{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{x+y}{2} \right) $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
11. If $ Cotx=-\dfrac{5}{12},x $ lies in second quadrant find the values of other five trigonometric functions
Ans-
Given
$ Cotx=-\dfrac{5}{12} $
Using some trigonometric identities, we obtain
$ \tan x=-\dfrac{12}{5} $
$ {{\operatorname{Sec}}^{2}}x=1+{{\tan }^{2}}x $
$ \operatorname{Sec}x=\pm \dfrac{13}{5} $
Since $ x $ lies in the second quadrant, the cosine value will be negative
$ \operatorname{Sec}x=-\dfrac{13}{5} $
$ \operatorname{Cos}x=-\dfrac{5}{13} $
$ \operatorname{Sin}x=\tan x.\operatorname{Cos}x $
$ =\dfrac{-12}{5}\times \left( \dfrac{-5}{13} \right) $
$ =\dfrac{12}{13} $
$ \operatorname{Csc}x=\dfrac{13}{12} $
12. Prove that $ \dfrac{\operatorname{Sin}5x-2\operatorname{Sin}3x+\operatorname{Sin}x}{\operatorname{Cos}5x-\operatorname{Cos}x}=\tan x $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric difference identities for the sine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\dfrac{\operatorname{Sin}5x+\operatorname{Sin}x-2\operatorname{Sin}3x}{\operatorname{Cos}5x-\operatorname{Cos}x} $
$ =\dfrac{2\operatorname{Sin}3x.\operatorname{Cos}2x-2\operatorname{Sin}3x}{-2\operatorname{Sin}3x.\operatorname{Sin}2x} $
$ =\dfrac{2\operatorname{Sin}3x(\operatorname{Cos}2x-1)}{-2\operatorname{Sin}3x.\operatorname{Sin}2x} $
$ =\dfrac{-(1-\operatorname{Cos}2x)}{-\operatorname{Sin}2x} $
$ =\dfrac{2{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}x}{2\operatorname{Sin}x.\operatorname{Cos}x} $
$ =\dfrac{\operatorname{Sin}x}{\operatorname{Cos}x} $
$ =\tan x $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
13. Prove that $ Sinx+Sin3x+Sin5x+Sin7x=4Cosx.Cos2x.Sin4x $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric addition identities for the sine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=Sinx+Sin3x+Sin5x+Sin7x $
$ =\operatorname{Sin}x+\operatorname{Sin}7x+\operatorname{Sin}3x+\operatorname{Sin}5x $
$ =2\operatorname{Sin}\left( \dfrac{x+7x}{2} \right).\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{x-7x}{2} \right)+2\operatorname{Sin}\left( \dfrac{3x+5x}{2} \right)\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{3x-5x}{2} \right) $
$ =2\operatorname{Sin}4x.\operatorname{Cos}3x+2\operatorname{Sin}4x.\operatorname{Cos}x $
$ =2\operatorname{Sin}4x[\operatorname{Cos}3x+\operatorname{Cos}x] $
$ =2\operatorname{Sin}4x\left[ 2\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{3x+x}{2} \right).\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{3x-x}{2} \right) \right] $
$ =2\operatorname{Sin}4x[2\operatorname{Cos}2x.\operatorname{Cos}x] $
$ =4\operatorname{Cos}x.\operatorname{Cos}2x.\operatorname{Sin}4x $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
14. Find the angle between the minute hand and hour hand of a clock when the time is $ 7.20 $
Ans-
We know that the angle made by minute hand in $ 15\min =15\times 6={{90}^{\circ }} $
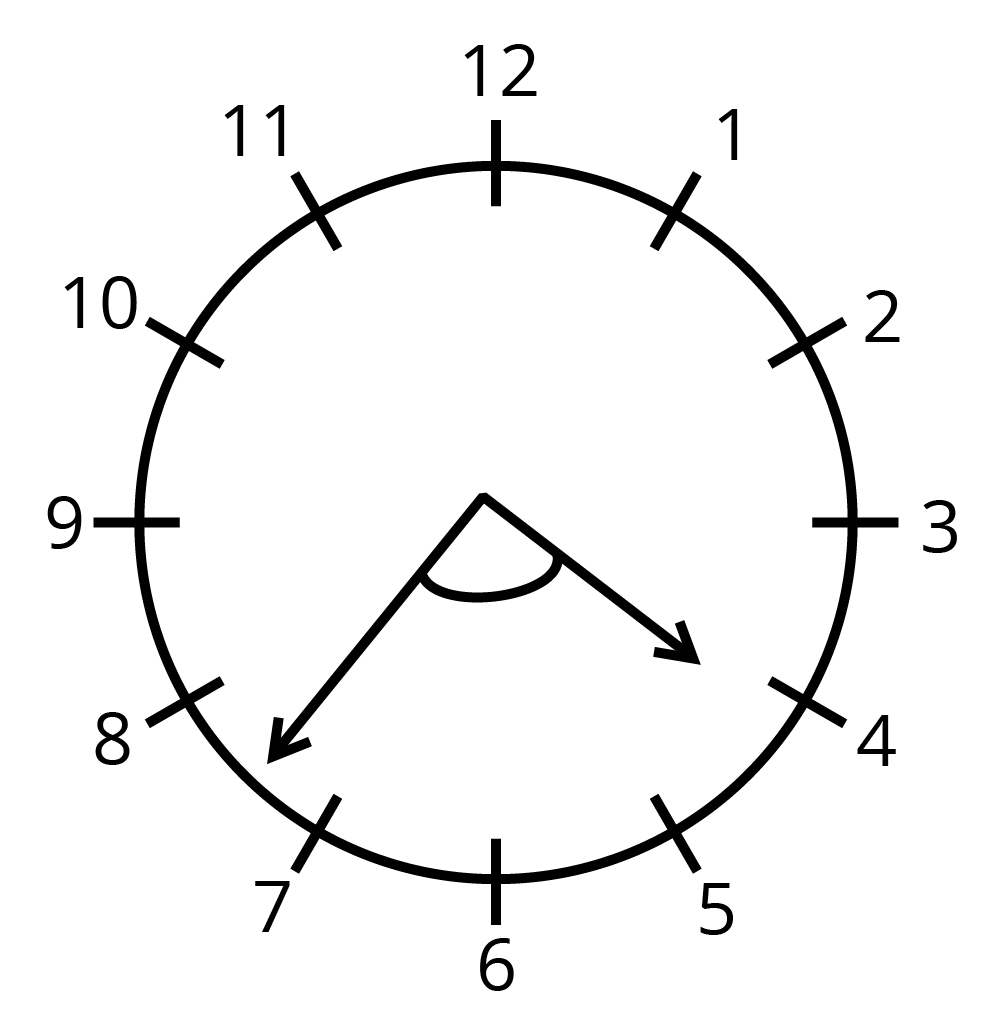
We also know that the angle made by the hour hand in $ 1hr={{30}^{\circ }} $
In $ 60 $ minute $ =\dfrac{30}{60} $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2} $
$ [\because $ Angle Travelled by $ hr $ hand in $ 12hr={{360}^{\circ }}] $
In $ 20 $ minutes $ =\dfrac{1}{2}\times 20 $
$ ={{10}^{\circ }} $
Angle made $ =90+10 $
$ ={{100}^{\circ }} $
15. Show that $ \sqrt{2+\sqrt{2+2\operatorname{Cos}4\theta }}=2\operatorname{Cos}\theta $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric addition identity for the cosine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\sqrt{2+\sqrt{2+2\operatorname{Cos}4\theta }} $
$ =\sqrt{2+\sqrt{2(1+\operatorname{Cos}4\theta )}} $
$ =\sqrt{2+\sqrt{2.2{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}2\theta }} $
$ =\sqrt{2+2\operatorname{Cos}2\theta } $
$ =\sqrt{2(1+\operatorname{Cos}2\theta )} $
$ =\sqrt{2.2{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}\theta } $
$ =2\operatorname{Cos}\theta $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
16. Prove that $ Cot4x\left( Sin5x+Sin3x \right)=Cotx\left( Sin5xSin3x \right) $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric addition identity for the sine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=Cot4x\left( Sin5x+Sin3x \right) $
$ =\dfrac{\operatorname{Cos}4x}{\operatorname{Sin}4x}\left[ 2\operatorname{Sin}\dfrac{5x+3x}{2}.\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{5x-3x}{2} \right] $
$ =\dfrac{\operatorname{Cos}4x}{\operatorname{Sin}4x}2\operatorname{Sin}4x.\operatorname{Cos}x $
$ =2\operatorname{Cos}4x.\operatorname{Cos}x $
Then, we move on to the right-hand side and using the trigonometric addition identity for the sine function, we obtain
$ \text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=Cotx\left( Sin5xSin3x \right) $
$ =\dfrac{\operatorname{Cos}x}{\operatorname{Sin}x}\left[ 2\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{5x+3x}{2}.\operatorname{Sin}\dfrac{5x-3x}{2} \right] $
$ =\dfrac{\operatorname{Cos}x}{\operatorname{Sin}x}[2\operatorname{Cos}4x.\operatorname{Sin}x] $
$ =2\operatorname{Cos}4x.\operatorname{Cos}x $
Therefore,
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}=\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S} $
6 Marks Questions
1. Find the general solution of $ sin2x+sin4x+sin6x=0 $
Ans-
We have that $ \sin 2x+\sin 4x+\sin 6x=0 $
$ \Rightarrow \left( \sin 2x+\sin 6x \right)+\sin 4x=0 $
$ \Rightarrow \left( 2\sin \left( \dfrac{2x+6x}{2} \right)\cos \left( \dfrac{2x-6x}{2} \right) \right)+\sin 4x=0 $
$ \Rightarrow 2\sin 4x\cos 2x+\sin 4x=0 $
$ \Rightarrow \sin 4x\left( 2\cos 2x+1 \right)=0 $
Now
$ \sin 4x=0 $
$ \Rightarrow x=n\pi $
$ 2\cos 2x+1=0 $
$ \Rightarrow x=n\pi \pm \dfrac{\pi }{3} $
2. Find the general solution of $ \cos \theta \cos 2\theta \cos 3\theta =\dfrac{1}{4} $
Ans-
We have that $ \cos \theta \cos 2\theta \cos 3\theta =\dfrac{1}{4} $
$ \Rightarrow 4\cos \theta \cos 2\theta \cos 3\theta =1 $
Using the trigonometric addition identity for the cosine function, we obtain
$ \Rightarrow 2\left( 2\cos \theta \cos 3\theta \right)\cos 2\theta -1=0 $
$ \Rightarrow 2\left( \cos 4\theta +\cos 2\theta \right)\cos 2\theta -1=0 $
$ \Rightarrow 2\left( 2{{\cos }^{2}}2\theta -1+\cos 2\theta \right)\cos 2\theta -1=0 $
$ \Rightarrow \left( 2{{\cos }^{2}}2\theta -1 \right)\left( 2\cos 2\theta +1 \right)=0 $
Now,
$ 2{{\cos }^{2}}2\theta -1=0 $
$ \Rightarrow \cos 4\theta =0 $
$ \Rightarrow 4\theta =\left( 2n+1 \right)\dfrac{\pi }{2} $
$ \Rightarrow \theta =\left( 2n+1 \right)\dfrac{\pi }{8} $
Also,
$ 2\cos 2\theta +1=0 $
$ \Rightarrow \cos 2\theta =-\dfrac{1}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow \theta =n\pi \pm \dfrac{\pi }{3} $
3. If $ \operatorname{Sin}\alpha +\operatorname{Sin}\beta =a $ and $ \operatorname{Cos}\alpha +\operatorname{Cos}\beta =b $
Show that $ \operatorname{Cos}(\alpha +\beta )=\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}} $
Ans-
Squaring both the equations and adding them together,
$ {{b}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}={{(\operatorname{Cos}\alpha +\operatorname{Cos}\beta )}^{2}}+{{(\operatorname{Sin}\alpha +\operatorname{Sin}\beta )}^{2}} $
$ ={{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}\alpha +{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}\beta +2\operatorname{Cos}\alpha .\operatorname{Cos}\beta +{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}\alpha +{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}\beta +2\operatorname{Sin}\alpha .\operatorname{Sin}\beta $
$ =1+1+2(\operatorname{Cos}\alpha .\operatorname{Cos}\beta +\operatorname{Sin}\alpha .\operatorname{Sin}\beta ) $
$ =2+2\operatorname{Cos}(\alpha -\beta ) $ $ (1) $
$ {{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}={{(\operatorname{Cos}\alpha +\operatorname{Cos}\beta )}^{2}}-{{(\operatorname{Sin}\alpha +\operatorname{Sin}\beta )}^{2}} $
$ =({{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}\alpha -{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}\beta )+({{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}\beta -{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}\alpha )+2\operatorname{Cos}(\alpha +\beta ) $
$ =\operatorname{Cos}(\alpha +\beta )\operatorname{Cos}(\alpha -\beta )+\operatorname{Cos}(\beta +\alpha )\operatorname{Cos}(\alpha -\beta )+2\operatorname{Cos}(\alpha +\beta ) $
$ =2\operatorname{Cos}(\alpha +\beta ).\operatorname{Cos}(\alpha -\beta )+2\operatorname{Cos}(\alpha +\beta ) $
$ =\operatorname{Cos}(\alpha +\beta )[2\operatorname{Cos}(\alpha -\beta )+2] $
$ =\operatorname{Cos}(\alpha +\beta ).({{b}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}) $ from $ (1) $
Dividing equation $ \left( 1 \right) $ with $ {{b}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}} $ , we get
$ \dfrac{{{b}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}=\operatorname{Cos}(\alpha +\beta ) $
4. Prove $ Cos\alpha +Cos\beta +Cos\gamma +Cos\left( \alpha +\beta +\gamma \right)=4\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2} \right).\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\beta +\gamma }{2} \right).\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\gamma +\alpha }{2} \right) $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric addition identities for the cosine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=Cos\alpha +Cos\beta +Cos\gamma +Cos\left( \alpha +\beta +\gamma \right) $
$ =2\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2} \right).\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha -\beta }{2} \right)+2\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha +\beta +\gamma +\gamma }{2} \right).\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha +\beta +\gamma -\gamma }{2} \right) $
$ =2\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2} \right).\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha -\beta }{2} \right)+2\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2} \right).\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha +\beta +2\gamma }{2} \right) $
$ =2\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2} \right)\left[ \operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha -\beta }{2} \right)+\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha +\beta +2\gamma }{2} \right) \right] $
$ =2\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2} \right)\left[ 2\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\dfrac{\alpha -\beta }{2}+\dfrac{\alpha +\beta +2\gamma }{2}}{2} \right).\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\dfrac{\alpha +\beta +2\gamma }{2}-\dfrac{\alpha -\beta }{2}}{2} \right) \right] $
$ =2\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2} \right)\left[ 2\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha +\gamma }{2} \right).\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\beta +\gamma }{2} \right) \right] $
$ =4\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2} \right).\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\beta +\gamma }{2} \right).\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{\gamma +\alpha }{2} \right) $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
5. Prove that $ \operatorname{Sin}3x+\operatorname{Sin}2x-\operatorname{Sin}2x=4\operatorname{Sin}x.\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{x}{2}.\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{3x}{2} $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric addition identity for the sine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\sin 3x+\sin x-\sin 2x $
$ =2\cos \left( \dfrac{3x+x}{2} \right).\operatorname{Sin}\left( \dfrac{3x+x}{2} \right)+\operatorname{Sin}2x $
$ =2\cos 2x.\sin x+\sin 2x $
$ =2\cos 2x.\sin x+2\sin x\cos x $
$ =2\sin x[\cos 2x+\cos x] $
$ =2\sin x\left[ 2\cos x\dfrac{3x}{2}.\cos \dfrac{x}{2} \right] $
$ =4\sin x\cos x\dfrac{3x}{2}\cos \dfrac{x}{2} $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
6. Prove that $ 2\cos \dfrac{\pi }{13}.\cos \dfrac{9\pi }{13}+\cos \dfrac{3\pi }{13}+\cos \dfrac{5\pi }{13}=0 $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side using the trigonometric addition identities for the cosine and sine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=2\cos \dfrac{\pi }{13}.\cos \dfrac{9\pi }{13}+\cos \dfrac{3\pi }{13}+\cos \dfrac{5\pi }{13} $
$ =\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{13}+\dfrac{9\pi }{13} \right)+\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{13}-\dfrac{9\pi }{13} \right)+\cos \dfrac{3\pi }{13}+\cos \dfrac{5\pi }{13} $
$ =\cos \dfrac{10\pi }{13}+\cos \dfrac{18\pi }{13}+\cos \dfrac{3\pi }{13}+\cos \dfrac{5\pi }{13} $
$ =\cos \left( \pi -\dfrac{3\pi }{13} \right)+\cos \left( \pi -\dfrac{5\pi }{13} \right)+\cos \dfrac{3\pi }{13}+\cos \dfrac{5\pi }{13} $
$ =-\cos \dfrac{3\pi }{13}-\cos \dfrac{5\pi }{13}+\dfrac{3\pi }{13}+\cos \dfrac{5\pi }{13} $
$ =0 $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
7. Find the value of $ \tan (\alpha +\beta ) $ given that $ \cot \alpha =\dfrac{1}{2},\alpha \in \left( \pi ,\dfrac{3\pi }{2} \right) $ and $ \operatorname{Sec}\beta =-\dfrac{5}{3},\beta \in \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2},\pi \right) $
Ans-
We know that,
$ \tan \left( \alpha +\beta \right)=\dfrac{\tan \alpha +\tan \beta }{1-\tan \alpha \tan \beta } $
Given,
$ Cot\alpha =\dfrac{1}{2} $
$ \tan \alpha =2 $
Now, let us find $ \tan \beta $
$ 1+{{\tan }^{2}}\beta ={{\operatorname{Sec}}^{2}}\beta $
$ 1+{{\tan }^{2}}\beta ={{\left( \dfrac{-5}{3} \right)}^{2}}\left[ \because \operatorname{Sec}\beta =\dfrac{-5}{3} \right] $
$ \tan \beta =\pm \dfrac{4}{3} $
$ \tan \beta =-\dfrac{4}{3}\left[ \because \beta \in \left( \dfrac{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}{x} \right) \right] $
Therefore, we have that
$ \tan \left( \alpha +\beta \right)=\dfrac{2-\dfrac{4}{3}}{1-2\left( \dfrac{-4}{3} \right)} $
$ =\dfrac{2}{11} $
Prove that $ \dfrac{\operatorname{Sec}8A-1}{\operatorname{Sec}4A-1}=\dfrac{\tan 8A}{\tan 2A} $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric elementary identities of the cosine function and sine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\dfrac{\sec 8A-1}{\sec 4A-1} $
$ =\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{\operatorname{Cos}8A}-1}{\dfrac{1}{\operatorname{Cos}4A}-1} $
$ =\dfrac{1-\operatorname{Cos}8A}{1-\operatorname{Cos}4A}\times \dfrac{\operatorname{Cos}4A}{\operatorname{Cos}8A} $
$ =\dfrac{2{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}4A}{2{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}2A}.\dfrac{\operatorname{Cos}4A}{\operatorname{Cos}8A} $
$ =\dfrac{(2\operatorname{Sin}4A.\operatorname{Cos}4A).\operatorname{Sin}4A}{2{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}2A.\operatorname{Cos}8A} $
$ =\dfrac{\operatorname{Sin}8A(2\operatorname{Sin}2A.\operatorname{Cos}2A)}{2{{\operatorname{Sin}}^{2}}2A.\operatorname{Cos}8A} $
$ =\dfrac{\operatorname{Sin}8A\operatorname{Cos}2A}{\operatorname{Sin}2A.\operatorname{Cos}2A} $
$ =\dfrac{\tan 8A}{\tan 2A} $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
Prove that $ {{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}x+{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}\left( x+\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)+{{\operatorname{Cos}}^{2}}\left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)=\dfrac{3}{2} $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using trigonometric addition identities of the cosine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\dfrac{1+\operatorname{Cos}2x}{2}+\dfrac{1+\operatorname{Cos}\left( 2x+\dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)}{2}+\dfrac{1+\operatorname{Cos}\left( 2x-\dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)}{2} $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 1+1+1+\operatorname{Cos}2x+\operatorname{Cos}\left( 2x+\dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+\operatorname{Cos}\left( 2x-\dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right) \right] $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 3+\operatorname{Cos}2x+\operatorname{Cos}\left( 2x+\dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)+\operatorname{Cos}\left( 2x-\dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right) \right] $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 3+\operatorname{Cos}2x+2\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{2x+\dfrac{2\pi }{3}+2x-\dfrac{2\pi }{3}}{2} \right).\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{2x+\dfrac{2\pi }{3}-2x+\dfrac{2\pi }{3}}{2} \right) \right] $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 3+\operatorname{Cos}2x+2\operatorname{Cos}2x.\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{4\pi }{6} \right] $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 3+\operatorname{Cos}2x+2\operatorname{Cos}2x.\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right] $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 3+\operatorname{Cos}2x+2\operatorname{Cos}2x.\operatorname{Cos}\left( \pi -\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right) \right] $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 3+\operatorname{Cos}2x+2\operatorname{Cos}2x.\left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right) \right] $
$ =\dfrac{3}{2} $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
Prove that $ \operatorname{Cos}2x.\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{x}{2}-\operatorname{Cos}3x.\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{9x}{2}=\operatorname{Sin}5x\operatorname{Sin}\dfrac{5x}{2} $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using trigonometric addition identities for the cosine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 2\operatorname{Cos}2x.\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{x}{2}-2\operatorname{Cos}3x.\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{9x}{2} \right] $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ \operatorname{Cos}\left( 2x+\dfrac{x}{2} \right)+\operatorname{Cos}\left( 2x-\dfrac{x}{2} \right)-\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{9x}{2}+3x \right)-\operatorname{Cos}\left( \dfrac{9x}{2}-3x \right) \right] $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ \operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{5x}{2}+\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{3x}{2}-\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{15x}{2}-\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{3x}{2} \right] $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ \operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{5x}{2}-\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{15x}{2} \right] $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ -2\operatorname{Sin}\left( \dfrac{\dfrac{5x}{2}+\dfrac{15x}{2}}{2} \right).\operatorname{Sin}\left( \dfrac{\dfrac{5x}{2}-\dfrac{15x}{2}}{2} \right) \right] $
$ =-\operatorname{Sin}5x.\operatorname{Sin}\left( \dfrac{-5x}{2} \right) $
$ =\operatorname{Sin}5x.\operatorname{Sin}\dfrac{5x}{2} $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
Prove that $ \operatorname{Cos}20{}^\circ .\operatorname{Cos}40{}^\circ .\operatorname{Cos}60{}^\circ .\operatorname{Cos}80{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{16} $
Ans-
Starting with the left-hand side and using the trigonometric addition identities of the cosine function, we obtain
$ \text{L}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.}=\operatorname{Cos}{{20}^{{}^\circ }}.\operatorname{Cos}{{40}^{{}^\circ }}.\operatorname{Cos}{{60}^{{}^\circ }}.\operatorname{Cos}{{80}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ =\operatorname{Cos}{{60}^{{}^\circ }}.\operatorname{Cos}{{20}^{{}^\circ }}.\operatorname{Cos}{{40}^{{}^\circ }}.\operatorname{Cos}{{80}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ =\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{1}{2}\operatorname{Cos}{{40}^{{}^\circ }}\left( 2\operatorname{Cos}{{20}^{{}^\circ }}.\operatorname{Cos}{{80}^{{}^\circ }} \right) $
$ =\dfrac{1}{4}\operatorname{Cos}{{40}^{{}^\circ }}\left[ \operatorname{Cos}(80+20)+\operatorname{Cos}(80-20) \right] $
$ =\dfrac{1}{4}\operatorname{Cos}{{40}^{{}^\circ }}\left[ \operatorname{Cos}{{100}^{{}^\circ }}+\operatorname{Cos}{{60}^{{}^\circ }} \right] $
$ =\dfrac{1}{4}\operatorname{Cos}{{40}^{{}^\circ }}\left[ \operatorname{Cos}{{100}^{{}^\circ }}+\dfrac{1}{2} \right] $
$ =\dfrac{1}{8}(2\operatorname{Cos}{{100}^{{}^\circ }}\operatorname{Cos}{{40}^{{}^\circ }})+\dfrac{1}{8}\operatorname{Cos}{{40}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ =\dfrac{1}{8}\left[ \operatorname{Cos}{{(100+40)}^{{}^\circ }}+\operatorname{Cos}{{(100-40)}^{{}^\circ }} \right]+\dfrac{1}{8}\operatorname{Cos}{{40}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ =\dfrac{1}{8}\left[ \operatorname{Cos}{{140}^{{}^\circ }}+\operatorname{Cos}{{60}^{{}^\circ }} \right]+\dfrac{1}{8}\operatorname{Cos}{{40}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ =\dfrac{1}{8}\left[ \operatorname{Cos}{{140}^{{}^\circ }}+\dfrac{1}{2} \right]+\dfrac{1}{8}\operatorname{Cos}{{40}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ =\dfrac{1}{8}\operatorname{Cos}{{(180-40)}^{{}^\circ }}+\dfrac{1}{16}+\dfrac{1}{8}\operatorname{Cos}{{40}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ =-\dfrac{1}{8}\operatorname{Cos}{{40}^{{}^\circ }}+\dfrac{1}{16}+\dfrac{1}{8}\operatorname{Cos}{{40}^{{}^\circ }} $
$ =\dfrac{1}{16} $
$ =\text{R}\text{.H}\text{.S}\text{.} $
If $ \tan x=\dfrac{3}{4},\pi <x<\dfrac{3\pi }{2}, $ Find the value of $ \operatorname{Sin}\dfrac{x}{2},\operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{x}{2} $ and $ \tan \dfrac{x}{2} $
Ans-
Given that
$ \pi <x<\dfrac{3\pi }{2} $ implying that $ x $ is in the third quadrant
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{2}<\dfrac{x}{2}<\dfrac{3\pi }{2} $
Therefore, we have that $ \operatorname{Sin}\dfrac{x}{2} $ is positive and $ \operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{x}{2} $ is negative.
Let us find for $ \tan \dfrac{x}{2} $
We know
$ 1+{{\tan }^{2}}x={{\operatorname{Sec}}^{2}}x\dfrac{5}{4} $
$ 1+{{\left( \dfrac{3}{4} \right)}^{2}}={{\operatorname{Sec}}^{2}}x $
$ {{\operatorname{Sec}}^{2}}x=\pm \dfrac{25}{16} $
$ \operatorname{Cos}x=\pm \dfrac{4}{5} $
$ \operatorname{Cos}x=-\dfrac{4}{5}\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left[ \because \pi <x<\dfrac{3\pi }{2} \right] $
Let us find the required values
$ \operatorname{Sin}\dfrac{x}{2}=\sqrt{\dfrac{1-\operatorname{Cos}x}{2}} $
$ =\sqrt{\dfrac{1+\dfrac{4}{5}}{2}} $
$ =\sqrt{\dfrac{9}{10}} $
$ =\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{10}} $
$ \operatorname{Cos}\dfrac{x}{2}=-\sqrt{\dfrac{1-\operatorname{Cos}x}{2}} $
$ =-\sqrt{\dfrac{1-\dfrac{4}{5}}{2}} $
$ =-\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{10}} $
$ =\dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{10}} $
$ \tan \dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{10}}}{\dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{10}}} $
$ =-3 $
The Formula for Function of Trigonometric Ratios
Formulas for Angle θ | Reciprocal Identities |
sin θ = Opposite Side/Hypotenuse | sin θ = 1/cosec θ |
cos θ = Adjacent Side/Hypotenuse | cos θ = 1/sec θ |
sec θ = Hypotenuse/Adjacent Side | sec θ = 1/cos θ |
cosec θ = Hypotenuse/Opposite | cosec θ = 1/sin θ |
tan θ = Opposite Side/Adjacent | tan θ = 1/cot θ |
cot θ = Adjacent Side/Opposite | cot θ = 1/tan θ |
Trigonometric Table
Trigonometric Ratios/ angle= θ in degrees | 0 ° | 30 ° | 45 ° | 60 ° | 90 ° |
Sin θ | 0 | 1/2 | 1/√2 | √3/2 | 1 |
Cos θ | 1 | √3/2 | 1/√2 | 1/2 | 0 |
Sec θ | 1 | 2/√3 | √2 | 2 | ∞ |
Cosec θ | ∞ | 2 | √2 | 2/√3 | 1 |
Tan θ | 0 | 1/√3 | 1 | √3 | ∞ |
Cot θ | ∞ | √3 | 1 | 1/√3 | 0 |
Important Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Based on Exercise
Q. An engine produces 360 revolutions in one minute. Through how many radians will it turn in one second?
Solution:
Provided,
The total number of revolutions made by an engine in one minute = 360
1 minute = 60 seconds
Therefore, number of revolutions in 1 second = 360/60 = 6
Angle formed in 1 revolution = 360°
Angles formed in 6 revolutions = 6 × 360°
Radian measure of the angle in a total of six revolutions = 6 × 360 × π/180
= 6 × 2 × π
= 12π
So, the engine turns 12π radians in one second.
Practice Questions
Prove that:
(sin 5x + sin 3x)/(cos 5x + cos 3x) = tan 4xFind the value of tan 765° cot 675° + tan 225° cot 405°
Solve the equation: tan² θ + cot² θ = 2
Write the value of 2sin 75° sin 15°
Show that:
tan 4A = (cos8Acos5A - cos12Acos9A) / (sin8Acos5A + cos12Asin9A)Find the general solution of the following equation:
tan2θ +(1 – √3) tan θ – √3 = 0Prove that:
3sinπ/6secπ/3 - 4sin5π/6cotπ/4 = 1Find the value:
cos4π/8 + cos43π/8 + cos45π/8 + cos47π/8Show that:
tan 15° + cot 15° = 4Find the most general value of θ satisfying the equation tan θ = -1 and cos θ = 1/√2
Advantages of Opting Vedantu for Important Questions of Class 11 Maths: Chapter 3 Trigonometric
Vedantu offers several benefits to students using their platform for the "Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 - Trigonometric Functions (2025-26)":
Comprehensive Coverage: Vedantu's important questions are curated to cover a wide spectrum of topics within the chapter, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of trigonometric functions.
Strategic Exam Preparation: These questions are strategically selected to align with the CBSE curriculum and examination patterns, preparing students effectively for their exams.
Conceptual Clarity: Vedantu's platform emphasizes conceptual clarity by providing in-depth explanations and solutions for each question, helping students grasp the underlying principles.
Variety of Problem Types: The diverse range of questions offered by Vedantu challenges students to apply trigonometric concepts in various problem-solving scenarios, enhancing their problem-solving skills.
Self-Assessment and Practice: Students can use these questions for self-assessment and regular practice, enabling them to gauge their progress and identify areas that need improvement.
Flexibility and Convenience: Vedantu's platform allows students to access these questions anytime, anywhere, providing flexibility in their study routine.
Conclusion
Trigonometric Functions is an important chapter in Class 11 Maths that helps build a strong foundation for advanced topics in calculus and geometry. Practising important questions from this chapter allows students to understand concepts like trigonometric identities, inverse functions, and their applications more clearly. The free PDF provides a variety of problems, making it easier for students to prepare effectively, boost their confidence, and perform well in exams. Regular practice of these questions ensures a better understanding of the topic and helps in scoring good marks.
Important Study Materials for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
S. No | CBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Other Study Materials |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | CBSE Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions RD Sharma Solutions |
5 | CBSE Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions RS Aggarwal Solutions |
6 | CBSE Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions NCERT Exemplar Solutions |
CBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter-wise Important Questions
CBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter-wise Important Questions and Answers cover topics from all 14 chapters, helping students prepare thoroughly by focusing on key topics for easier revision.
S. No | Chapter-wise Important Questions for Class 11 Maths |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | Chapter 4 - Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Questions |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 | Chapter 11 - Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry Questions |
11 | |
12 | |
13 |
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 11 Maths
S.No. | Important Study Material for Maths Class 11 |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 |
FAQs on CBSE Important Questions for Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions - 2025-26
1. What are the most important topics to focus on in Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 for the 2025-26 exams?
Based on the CBSE 2025-26 syllabus trends, students should prioritise:
- Proving complex trigonometric identities.
- Finding the general and principal solutions of trigonometric equations.
- Applying sum, difference, and product formulas (e.g., sin(A±B), 2sinAcosB).
- Questions involving the domain, range, and graphs of trigonometric functions.
- Solving problems that require converting between radians and degrees.
2. What type of questions from Trigonometric Functions are typically asked for 3 or 5 marks?
In the Class 11 final exams, the marks distribution is usually as follows:
- 3-mark questions often test your ability to prove standard identities or find the general solution of a straightforward trigonometric equation.
- 5-mark questions are more complex, often involving multi-step proofs, the application of multiple formulas (like sum-to-product combined with double-angle formulas), or solving challenging trigonometric equations that require simplification first. These are often HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills) questions.
3. What is the conceptual difference between a principal solution and a general solution, and why is it important for scoring full marks?
The principal solution refers to the values of the angle that lie within the primary range of the function, typically [0, 2π). In contrast, the general solution provides a formula that represents all possible solutions by incorporating the periodic nature of the function, usually involving the integer 'n'. Forgetting to write the general solution when asked is a common error that can lead to a loss of marks, as examiners check for the complete set of solutions.
4. How can I master proving trigonometric identities for the Class 11 exams?
To master identity proofs, first, memorise all fundamental identities (Pythagorean, sum/difference, double/triple angle, etc.). When solving a problem, always start from the more complex side (LHS or RHS) and simplify it. A key strategy is to convert all functions like tan, cot, sec, and cosec into their basic sine and cosine forms. Consistent practice helps you recognise patterns and apply the correct identity quickly under exam pressure.
5. How are sum and difference formulas, like sin(A±B) and cos(A±B), used in 5-mark important questions?
In high-value 5-mark questions, sum and difference formulas are rarely used in isolation. They are typically part of a multi-step problem where you might need to use them to expand or simplify an expression. For instance, you might need to prove an identity by expanding terms like cos(π/4 + x) or find the value of expressions like tan(15°) by writing it as tan(45° - 30°). These formulas are often combined with other identities to test your overall command of the chapter.
6. Are questions based on the graphs of trigonometric functions important for the 2025-26 exam?
Yes, questions on graphs are important as they test your conceptual understanding beyond formula manipulation. For the 2025-26 exams, you should be able to identify the graphs of sin x, cos x, and tan x and understand their key properties like domain, range, and period. You may also face questions on how transformations, such as y = A sin(Bx + C), affect the amplitude, period, and phase shift of the graph.
7. Why is understanding the domain and range of trigonometric functions crucial for solving HOTS questions?
Understanding domain and range is critical for HOTS questions because it helps you validate or reject potential solutions. For example, knowing the range of sin x and cos x is [-1, 1] immediately tells you that an equation like cos x = 3 has no real solution. This prevents you from wasting time. HOTS problems often create scenarios where an algebraic solution appears valid but is impossible within the function's defined range, testing your fundamental knowledge.
8. What is a common mistake students make in trigonometry that leads to losing marks in exams?
A very frequent and costly mistake is incorrect sign application in different quadrants. Students often misapply the ASTC (All-Sin-Tan-Cos) rule when dealing with angles greater than 90° or negative angles. Another common error is mixing up degrees and radians; always ensure your calculator is in the correct mode and that you use the correct conversion (π radians = 180°).
9. Why is it so beneficial to practise a curated list of important questions for this chapter?
Practising a specific set of important questions is beneficial because it aligns your preparation directly with exam expectations. It helps you understand the question patterns, identify high-weightage topics, and master the types of problems frequently asked in past CBSE papers. This focused practice builds problem-solving speed and confidence, ensuring you are well-prepared for the actual exam scenario as per the latest 2025-26 syllabus.

























