




What Is Combustion? Definition, Process, and Real-Life Examples
What is Combustion?
(Image to be added soon)
Combustion is a redox chemical reaction that takes place between fuel and an oxidant to give a mixture of gases and heat and light. Combustion does not always give rise to fire. But when it does, the flames are an indicator of the reaction. Incomplete combustion, the reactants get oxidized or burn in oxygen to give a limited number of byproducts. For Example- when 1 molecule of hydrocarbon burns in oxygen, it gives carbon dioxide and water. Thus, it can be deduced that end product from the burning of an element in oxygen gives the oxides of the same element. Which means, carbon yields carbon dioxide, sulfur yields sulfur dioxide, and so on.
When not, enough oxygen is available for the continuation of chemical reaction or burning of elements in oxygen, it produces more by products. For example- in incomplete combustion of Hydrocarbon, carbon, hydroxide and carbon monoxide are produced.
Combustible and Non-Combustible Substances
Substances that easily catch fire are combustible substances. Example- paper, coal, wood, etc.
Substances that do not catch fire easily are non-combustible substances. Example- water, glass, sand, etc.
Fuel
Fuel is a substance that produces a usable form of energy on combustion. Like fossil fuel, biogas, etc.
The physical state of the fuel may vary. That is, it may be solid, liquid or gas.
Fuels are of two types- Natural and Artificial depending upon the source.
Fire
When chemical combustion takes place between oxygen and fuel, it produces a visible heat and light source- fire. The fire keeps burning until there is enough oxygen and fuel to continue the combustion. The temperature at which a combustible substance catches fire when heated in the presence of oxygen is called ignition temperature. Thus, it’s a necessary parameter for generating fire. Some substances like diesel, petrol have very low ignition temperatures. Which means that they easily catch fire with a flame. These substances are known as inflammable substances.
A Fire Can Only Be Generated If
Fuel or combustible material is present.
A flame or heat source is present to bring the temperature to the ignition temperature of the fuel.
Oxygen is present to sustain combustion.
When any of these factors are removed or controlled, the fire is controlled.
Types of Combustion
Combustion is of Two Types
Rapid Combustion - In rapid combustion, heat and light is released rapidly in a short span of time.
Spontaneous Combustion - It is spontaneous and occurs without the application of heat. In such a type of combustion, the substance catches fire on its own. Forest fires are one of the examples of this type of combustion.
What is Flame?
A flame can be defined as a region where gaseous elements burn, generating heat and light. All combustible materials, whether liquid or gaseous, emit flames as they burn. Both the combustible substance and the combustion's supporter must be gases in order for combustion to result in a flame. For instance, when kerosene is burnt on a stove, it rises with the wick and evaporates before burning with flames. Similar circumstances apply in the case of a candle flame. However, charcoal does not vapourize. They shine rather than burn with a flame.
Structure of Candle Flame
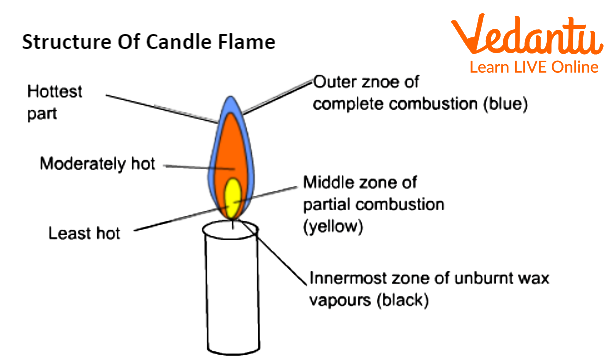
Candle Flame
Three zones can be found in a candle flame:
The Outer Zone:
The outer zone of the Flame is referred to as the zone of full combustion or the non-luminous zone. Complete combustion happens because the wax vapours are able to get enough oxygen from the air. Due to total combustion, this area is completely blue, and anything that comes into touch with it leaves with no residue. It is hardly possible to see the hotter zone. Goldsmiths can benefit greatly from this region of the Flame.
The Middle Zone:
The bright zone, also known as the zone of incomplete combustion, is the pale-yellow zone. The Flame's middle region is just moderately hot. Here, there isn't enough oxygen for the wax vapours to totally burn. Carbon monoxide and some carbon particles are produced during partial combustion. Additionally, some carbon atoms are not completely burnt. Unburned carbon atoms heat up to a white-hot state and cause the flame to become yellow. On things that come into touch with this zone, black soot or carbon particles are left behind.
The Innermost Zone:
The region around the wick is known as the dark zone or the zone of no combustion. This region is black in colour, thus the name. Because it is the innermost zone of the Flame, there is no oxygen available for combustion in this zone, hence there is no combustion. Vaporised wax makes up the majority of it.
Classification of Flame
Flames can be categorised into two groups. Namely,
Diffusion flames, also known as non-premixed flames: candle flames.
Premixed Flames: Laminar premixed flames and turbulent premixed flames are the two forms of premixed flames. Example: a Bunsen burner, an LPG stove, etc.
Candle Flame
An illumination (light) source is a candle. It is made up of a solid fuel block with a built-in wick. Beeswax, soy wax, and other plant-based waxes can also be used to make candles.
Today's candles are often constructed of paraffin. Paraffin and plastic are combined to make gel candles. When you light a candle, a little quantity of wax is melted and vaporised by the match's heat.
It combines after being vaporised. Once it has evaporated, it combines with atmospheric oxygen to produce a flame. This Flame generates sufficient heat to maintain the candle's flame through a self-sustaining sequence of actions:
The solid fuel's top end melts due to the heat of the flame.
Through the wick, the liquid fuel then rises.
The evaporated fuel is then burned inside the flame of the candle.
Premixed Flame and its Structure
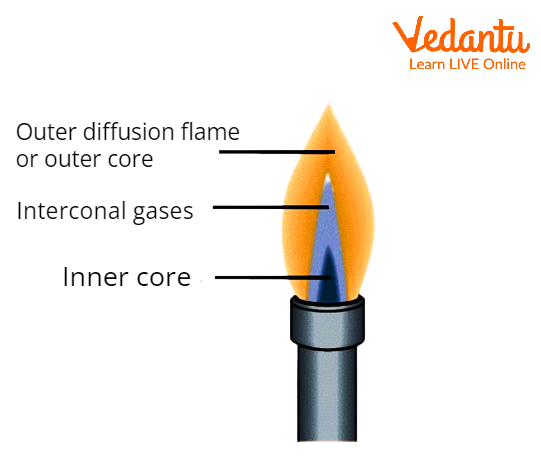
Structure of the Premixed Flame
Due to atmospheric oxygen diffusion, a diffusion flame arises in addition to the flame zone when a premixed flame burns in the open air with an excess of fuel.
For instance, the flow of a Bunsen flame generated by a burner with a controlled air intake can be changed from an extremely hot flux in which the majority of the fuel gases are oxidised to carbon dioxide and water to a low-temperature flux in which the majority of the fuel gases are only partially oxidised.
These flames consist of two zones, known as the reducing and oxidising zones, that are separated by an inner cone and an outer cone. The extra oxygen in the outer cone is what causes it to oxidise.
Important Questions
1. What are the different zones present in a candle flame?
Ans: There are three distinct zones present in a candle flame, namely the outer zone, the middle zone, and the innermost zone.
2. What is the definition of flame?
Ans: A flame is a region where gaseous components burn, releasing heat and light in the process.
Summary
A flame is a region where gaseous elements burn, creating heat and light in the process. Every combustible material, including liquids and gases, burns with a flame. A source of light is a candle. It consists of a block of solid fuel with an inserted wick. There are three zones in the candle flame. Specifically, the hotter zones are the outside zone, also known as the non-luminous zone, the middle zone, also known as the luminous zone, and the innermost zone, also known as the dark zone, which does not experience combustion.
FAQs on Combustion and Flames: Complete Guide for Students
1. What is combustion?
Combustion is a chemical process where a substance reacts rapidly with an oxidant, usually oxygen, to produce heat and light. The substance that undergoes this process is known as a combustible substance or a fuel. For example, when you burn wood or LPG, you are initiating a combustion reaction.
2. What are the three essential conditions required for combustion to take place?
For any combustion to occur, three conditions, often called the 'fire triangle,' must be met simultaneously:
Presence of a Fuel: There must be a combustible substance to burn.
Supply of Oxygen: There must be a continuous supply of an oxidiser, typically oxygen from the air.
Attainment of Ignition Temperature: The fuel must be heated to its ignition temperature, which is the minimum temperature at which it catches fire.
3. What is the difference between complete and incomplete combustion?
The primary difference is the availability of oxygen. Complete combustion occurs with a sufficient supply of oxygen, producing carbon dioxide (CO₂), water, and a large amount of energy, often with a clean, blue flame. In contrast, incomplete combustion occurs when the oxygen supply is limited. It produces harmful carbon monoxide (CO), soot (unburnt carbon), water, and less energy, typically with a yellow, sooty flame.
4. Why does a piece of paper catch fire easily, but a log of wood does not?
This is due to the difference in their ignition temperatures. The ignition temperature is the lowest temperature at which a substance will spontaneously ignite in a normal atmosphere. Paper has a very low ignition temperature, so the small amount of heat from a matchstick is enough to make it burn. A log of wood, being much denser and thicker, has a significantly higher ignition temperature and requires more prolonged heating to reach the point of combustion.
5. Can you explain the different zones of a candle flame?
A typical candle flame consists of three distinct zones:
Innermost Zone: This is the dark area directly around the wick. It is the least hot part as it contains unburnt wax vapours and has a poor supply of oxygen.
Middle Zone: This is the bright yellow, luminous part of the flame. Incomplete combustion occurs here, producing tiny carbon particles that glow, creating the yellow light.
Outermost Zone: This is a faint blue, non-luminous zone. It is the hottest part of the flame because complete combustion takes place here due to an ample supply of oxygen from the air.
6. Why do goldsmiths use the outermost part of a flame for melting gold and silver?
Goldsmiths use the outermost zone of a flame because it is the hottest part. In this zone, complete combustion of the fuel gas occurs, releasing the maximum amount of heat energy. Since gold and silver have high melting points, this intense heat from the outermost zone is required to melt them efficiently and quickly.
7. How does a carbon dioxide (CO₂) fire extinguisher work to put out a fire?
A carbon dioxide fire extinguisher works on two main principles. Firstly, CO₂ is much heavier than oxygen, so when sprayed on a fire, it displaces the oxygen and forms a protective layer, effectively cutting off the oxygen supply to the fuel. Secondly, as the pressurised CO₂ is released, it expands rapidly and cools down, which helps to lower the temperature of the combustible material below its ignition point. This dual action makes it very effective.
8. What is meant by the 'calorific value' of a fuel, and why is it important?
The calorific value of a fuel is the amount of heat energy produced upon the complete combustion of 1 kilogram of that fuel. It is expressed in units of kilojoules per kilogram (kJ/kg). This value is a crucial measure of a fuel's efficiency. A fuel with a higher calorific value is considered better because it can produce more energy per unit mass.
9. What are the major harmful environmental effects caused by burning fuels?
The burning of fuels, particularly fossil fuels, releases several harmful products into the environment:
Air Pollution: Unburnt carbon particles (soot) are released, which can cause respiratory problems like asthma.
Global Warming: An increased concentration of carbon dioxide (CO₂) in the atmosphere traps heat, leading to a rise in the Earth's average temperature.
Acid Rain: Burning coal and diesel releases oxides of sulphur and nitrogen. These gases dissolve in rainwater to form acids, resulting in acid rain that damages buildings, soil, and forests.
Toxic Gas: Incomplete combustion produces carbon monoxide (CO), which is a highly poisonous gas.
10. What is the key difference between rapid combustion and spontaneous combustion?
The main difference lies in the trigger or cause. Rapid combustion requires an external agent to initiate it, such as lighting an LPG stove with a lighter. The substance burns quickly, producing a large amount of heat and light in a short time. In contrast, spontaneous combustion occurs without any apparent external cause. The substance ignites on its own as its temperature rises to the ignition point due to slow oxidation or internal heat generation, such as in coal mines or haystacks.
























