




Why Do Haloalkanes Exhibit a Dipole Moment?
Alkyl halides also known as haloalkanes or halogen alkanes are chemical compounds that are derived from alkanes that contain one or more than one halogens. Alkyl halides or haloalkanes are made by substitution or replacement of a hydrogen atom in an open-chain hydrocarbon with halogen atoms (Fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine). Dipole moment depends on the difference between the electronegativity order of carbon and halogen compounds.
Definition of Dipole Moment
Dipole moments occur when there's a separation of charge. When atoms in a molecule share electrons unevenly, a dipole moment is formed. This happens when one atom is more electronegative as compared to a different atom or when one atom includes a lone pair of electrons and also the difference of electronegativity vector points within the same approach.
They can occur between 2 ions in an ionic bond or between atoms in a chemical covalent bond. The higher the difference in electronegativity, the higher the dipole moment. The gap between the charge separation is also a significant factor in the scale of the dipole moment. The dipole moment may be a measure of the polarity of the molecule.
Dipole Moment of Haloalkanes
Dipole moment decreases with a decrease in the electronegativity of the halogen compound. Although Cl is less electronegative than F, the dipole moment of the C-Cl bond is higher than the C-F bond. This is often due to the smaller C-F bond length that dominates the impact of greater electronegativity.
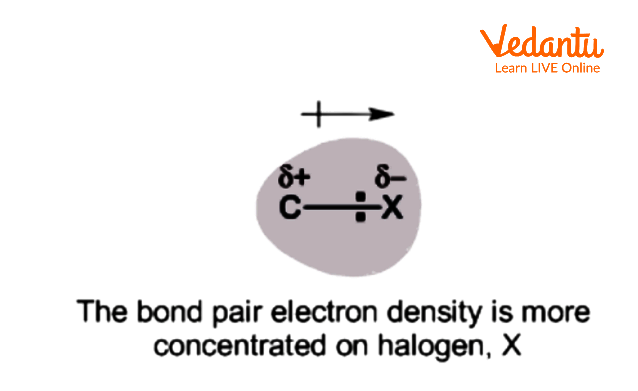
Dipole Moment in Halogen Compounds
Electronegativity of the alkyl halides :
F>Cl>Br>I
Bond length increases with the increase in the size of the halogen group.
C-F<C-Cl<C-Br<C-I
Order for bond dipoles:
\begin{align}
& C-Cl>C-F>C-Br>C-I \\
& 1.56D>1.51D>1.48D>1.29D \\
\end{align}
Molecular dipole depends on the geometry of the molecule.
The Dipole Moment of RX Depends on:
the sizes of the partial charges.
the distance between the charges.
the polarizability of the unshared electrons present on halogen.
Properties of Alkyl Halides
Physical Properties of Haloalkanes
Haloalkanes are colourless, odourless, and hydrophobic.
They are heavier than alkanes.
Density is directly proportional to the mass of the compound, therefore down the homologous series, density will increase, also fluoro derivatives are less dense than chloro derivatives; chloro derivatives are less dense than Bromo derivatives, and so on.
The boiling point of chlorides, bromides, and iodides is relatively more than those of the hydrocarbons of comparable molecular mass. The boiling point reduces with the increase in branching.
Properties of Haloarenes
All halogen compounds are less ignitable than hydrocarbons. The inflammability decreases with a rise in halogen groups.
In haloarenes halogen groups are connected to carbon atoms, hence dipole moment develops between them. The dipole moment will increase because the number of halogen atoms increases.
Due to the double character of the C-X bond in aryl halides, the C-X bond is shorter in length and stronger than in the alkyl halides, hence, their boiling points are more than in alkyl halides. Boiling points will increase because the number of halogen atoms increases in rings.
Density order for halo arenes increases as follows:
Ar-I>Ar-Br>Ar-Cl>Ar-F
Interesting Fact
A large variety of halogen-containing compounds are found in nature and plenty of those are utilised in drugs and technology.
Some haloalkanes (those containing Cl or bromine) have negative effects on the surroundings like ozone depletion. The foremost widely renowned family among this group is the chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
Important Questions
1. Arrange propane, 1-chloropropane, and isopropyl chloride in order of increasing boiling points.
Ans: First, calculate the molecular masses of the given compounds :
\begin{align}
& MolecularMas{{s}_{\left( C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}} \right)}}=\left( 12\times 3+8\times 1 \right)=44 \\
& MolecularMas{{s}_{\left( C{{H}_{3}}CH\left( Cl \right)C{{H}_{3}} \right)}}=\left( 12\times 3+7\times 1+1\times 35.5 \right)=78.5 \\
& MolecularMas{{s}_{\left( C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}Cl \right)}}=\left( 12\times 3+7\times 1+1\times 35.5 \right)=78.5 \\
\end{align}
Since the boiling point will increase with a rise in molecular mass, propane has the lowest boiling point among them. Further, the boiling point decreases with branching; thus, isopropyl chloride contains a lower boiling point than 1-chloropropane.
CH3CH2CH3<CH3CH(Cl)CH3<CH3CH2CH2Cl
2. Para-Dichlorobenzene has a higher melting point than those of o- and m-isomers. Explain.
Ans: The para-isomer is more symmetrical and fits closely within the crystal lattice. This results in stronger intermolecular forces of attraction than those of ortho- and meta-isomers. Thus, a larger value of energy is needed to melt the para-isomer than the corresponding ortho- and meta-isomers.
Summary
Halogens are group 17 components within the periodic table and are electronegative (F, Cl, Br, I, At). Fluorine (F) is the most electronegative element. The group 17 components need only 1 electron to complete their outer shell. The dipole moment of alkyl halides and aryl halides varies according to the electronegativity order of halide compounds. Down the group, the electronegativity of halogen compounds decreases, and therefore the dipole moment also decreases.
FAQs on Dipole Moment of Haloalkanes Explained
1. As per the CBSE 2025-26 syllabus, why does p-dichlorobenzene have a significantly higher melting point than its ortho- and meta-isomers? (2 marks)
The para-isomer (p-dichlorobenzene) has a highly symmetrical structure. This symmetry allows its molecules to fit more closely and orderly into the crystal lattice. As a result, the intermolecular forces of attraction are much stronger in the para-isomer compared to the less symmetrical ortho- and meta-isomers. Overcoming these stronger forces requires more energy, which is why p-dichlorobenzene has a higher melting point.
2. Arrange propane, 1-chloropropane, and isopropyl chloride in increasing order of their boiling points. Provide a justification for this important trend. (2 marks)
The increasing order of boiling points is: Propane < Isopropyl chloride < 1-chloropropane. The justification is as follows:
- Propane has the lowest boiling point because it has the lowest molecular mass and only weak van der Waals forces.
- Both 1-chloropropane and isopropyl chloride have the same molecular mass, which is higher than propane, but 1-chloropropane has a higher boiling point. This is because it is a straight-chain molecule with a larger surface area, leading to stronger intermolecular van der Waals forces. Isopropyl chloride is branched, resulting in a more compact, spherical shape with a smaller surface area and weaker forces.
3. Explain why haloarenes are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions than haloalkanes. (3 marks)
Haloarenes are considerably less reactive than haloalkanes towards nucleophilic substitution for the following key reasons:
- Resonance Effect: The electron pairs on the halogen atom are in conjugation with the π-electrons of the benzene ring. This results in the C-Cl bond acquiring a partial double bond character, making it stronger and more difficult to break compared to the pure single C-X bond in haloalkanes.
- Difference in Hybridisation: In haloarenes, the carbon atom attached to the halogen is sp² hybridised, which is more electronegative than the sp³ hybridised carbon in haloalkanes. The sp² hybridised carbon holds the electron pair of the C-X bond more tightly, reducing its polarity and bond length.
- Instability of Phenyl Cation: In case of a self-ionisation reaction, the resulting phenyl cation is highly unstable and will not be formed.
4. Compare the SN1 and SN2 reaction mechanisms for haloalkanes based on the substrate and nature of the nucleophile. (3 marks)
The choice between SN1 and SN2 mechanisms is a critical concept and depends heavily on these factors:
- Substrate: The SN1 mechanism is favoured by bulky substrates, with the order of reactivity being tertiary (3°) > secondary (2°) > primary (1°). This is due to the stability of the intermediate carbocation formed. The SN2 mechanism is favoured by less sterically hindered substrates, with the reactivity order being primary (1°) > secondary (2°) > tertiary (3°), as the nucleophile needs to attack the carbon atom directly.
- Nucleophile: The SN1 reaction is typically favoured by weak nucleophiles (e.g., H₂O, ROH) because the rate-determining step does not involve the nucleophile. In contrast, the SN2 reaction requires a strong nucleophile (e.g., OH⁻, CN⁻) as it is directly involved in the single, rate-determining step.
5. How is a Grignard reagent prepared? Why is it essential to use strictly anhydrous (dry) conditions during its preparation? (3 marks)
A Grignard reagent is prepared by reacting a haloalkane with magnesium metal in the presence of dry ether. The general reaction is: R-X + Mg → R-Mg-X.
Using anhydrous conditions is absolutely critical because Grignard reagents are highly reactive. They are strong bases and will react with any source of a proton, such as water. If moisture is present, the Grignard reagent will react with water to form an alkane, destroying the reagent and rendering the intended reaction unsuccessful.
R-Mg-X + H₂O → R-H (Alkane) + Mg(OH)X
6. An alkyl halide C₄H₉Cl (A) reacts with alcoholic KOH to give an alkene (B), which on ozonolysis gives only ethanal (CH₃CHO). What are the structures of (A) and (B)? (HOTS Question)
This is a high-order thinking question that requires working backwards from the products:
- Ozonolysis of an alkene (B) gives only one product, ethanal (CH₃CHO), which has two carbon atoms. This indicates that the alkene (B) is symmetrical and has a double bond at the centre of a four-carbon chain. Therefore, alkene (B) is But-2-ene (CH₃-CH=CH-CH₃).
- Alkene (B) is formed by the dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halide (A) with alcoholic KOH. To get But-2-ene, the chlorine atom in (A) must be on the second carbon. Therefore, the structure of alkyl halide (A) is 2-Chlorobutane (CH₃-CHCl-CH₂-CH₃).
7. Distinguish between Finkelstein and Swarts reactions, which are commonly asked in board exams. What is their primary utility in organic synthesis? (3 marks)
Both are important halogen exchange reactions:
- Finkelstein Reaction: This reaction is used to prepare iodoalkanes. An alkyl chloride or bromide is treated with sodium iodide (NaI) in dry acetone. The sodium chloride or bromide formed is insoluble in acetone and precipitates, driving the reaction forward according to Le Chatelier's principle.
Example: CH₃Cl + NaI → CH₃I + NaCl (s) - Swarts Reaction: This reaction is used to prepare fluoroalkanes. An alkyl chloride or bromide is heated in the presence of a metallic fluoride such as AgF, Hg₂F₂, or SbF₃.
Example: CH₃Br + AgF → CH₃F + AgBr
8. Although chlorine is an electron-withdrawing group, it is ortho, para-directing in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Why? (HOTS)
This is a frequently asked question that tests the understanding of competing electronic effects. The explanation involves two opposing factors:
- Inductive Effect (-I): Being electronegative, the chlorine atom withdraws electron density from the benzene ring, deactivating it towards electrophilic substitution. This effect is dominant and makes chlorobenzene less reactive than benzene.
- Resonance Effect (+R): Through resonance, the lone pair of electrons on the chlorine atom can be delocalised into the benzene ring. This increases the electron density, particularly at the ortho and para positions.
























