




What is the Cash Account Format?
Every cash transaction during an accounting cycle is documented in a cash account format that functions as an auxiliary ledger. The cash account is often split in two for more prominent businesses: the cash payments journal for recording cash payments made and the cash receivables journal for recording cash revenues.
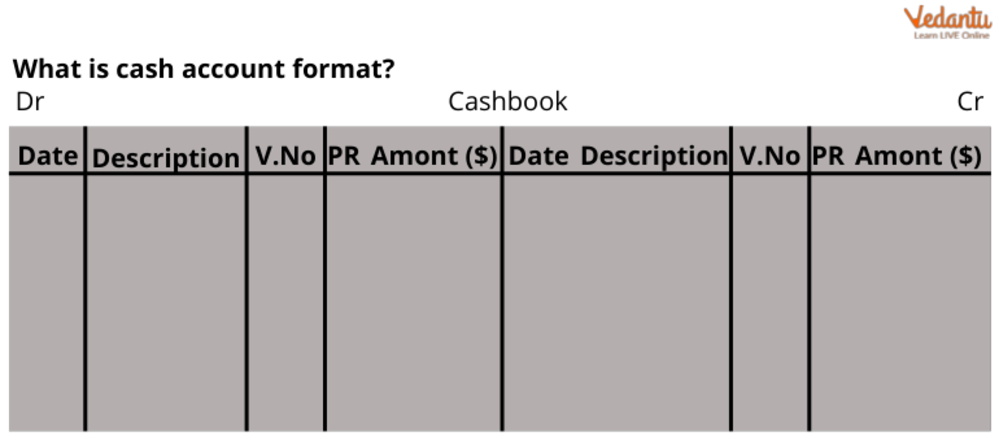
What do you understand about a Cash Book Account?
Let's look at the many structures each of these categories may take.
Single Cash Account Format: There is no need for a separate cash account or complicated journal entries when using an essential line cash book to keep track of money coming in and going out of the business.
Dual Column Cash Account Format: There are two distinct varieties of two-column cash books: those with cash and discounting columns and those with money and bank sections. The double-column cash account is, nevertheless, the standard.
Triple Column Cash Account Format: Cash, financial institution, and discounting sections are condensed into one convenient location in the triple column cash account. All discounts on sales or purchases are noted here, and any cash or bank-related operations.
Features of Double-Column Cash Book Format

Know about the Dual-column Cash Book and its Format
So, both credit and debit sections of the cash account have two separate money sections. Both cash and bank balance account operations should be recorded in their respective columns. Cash and banking transactions are recorded in the company's double-column cash book. However, credit activities are not included when a dual-column cash book is being prepared.
The following are the listed features of double column cash book format:
Cash payments are noted in the Cash-Debt column of the Cash Section.
The Cash section is credited with all cash receipts.
An entry is created in the bank section to the debit column if a consumer uses a bank to make a payment.
If the funds were deposited via check on the same day, the amount would be reflected in the banking section as a debit.
The sum is reported in the cash section when a check is received but not posted on the same day it was written.
The debit entry is made in the banking section, and a credit entry is made in the cash section when the check is collected on the same day as its lodged receipt in the financial institution or bank. The term "contra entry" describes this kind of cash book entry.
Reasons to Keep the Double-Column Cash Book Records
Two columns on every side make up a two-column cash book with the bank, sometimes called a double-column cash book, for keeping track of money and banking activities.
A dual-column cash account allows bookkeepers to track cash and bank transactions in one convenient location. Due to this, keeping track of financial dealings is made much more straightforward. For example, the cash book with one column may be expanded to a cash book with two different columns by inserting a banking column on each page.
The reasons to make the dual-column cash account format are:
Discount-free transactions are recorded in the standard cash book format containing a sole column. The entire value of discount-containing debit entries is credited to the appropriate account.
Credited discount entries are transferred to the debit side of the corresponding account. The sum of the debit side's discounted column is debited from the discount allowable account. The sum of the discount line item on the debit side is credited to the discount earned account.
Stating the Cash Book in Accounting in a Detailed Manner
To maintain accurate books, cash dealings, the most common form of payment in most businesses, must be documented. Overdrafts, payment orders, and deposit accounts are all instances of money transfers that qualify as current assets.
To keep track of the organisation's cash flow, cash inflows (which are recorded on the debit column) and outflows (which are recorded on the credit column) are recorded in a cash book. The cash book serves as the firm's first and last accounting record. You may get double-column cash book questions with solutions online.
The cashbook may be considered a ledger that records cash activities immediately, saving time and effort compared to entering cash activities available. It's a valuable tool for keeping track of money. Frequent cash account balancing is anti-free differences, and apparent differences become apparent and may be resolved.
Conclusion
The cash account is distinct from the cash book to which journal entries are posted since it is the book of accounts in which the firm's cash dealings for a particular day are recorded, unlike the account, where one must transfer the whole amount towards the goal needed to be. The appropriate general ledger is updated with the new entries. Every cash collection is entered on the right-hand side of the cash account, and vice versa.
FAQs on Cash Account Format: Everything You Need to Know
1. What is a cash account and what is its primary purpose in bookkeeping?
A cash account is a ledger account that exclusively records all cash transactions of a business in chronological order. Its primary purpose is to provide a detailed summary of all cash receipts (inflows) and cash payments (outflows) over a period, making it easy to determine the cash balance at any given time.
2. What are the main types of cash books used in accounting?
There are four main types of cash books, each serving different levels of transactional complexity:
- Single-Column Cash Book: Records only cash receipts and payments.
- Double-Column Cash Book: Has two amount columns on each side, typically for cash and discount, or cash and bank transactions.
- Triple-Column Cash Book: Includes three amount columns for cash, bank, and discount transactions.
- Petty Cash Book: Used for recording small, miscellaneous expenses like stationery, postage, or snacks.
3. What is the standard format of a single-column cash account?
A single-column cash account follows a 'T-account' format with two sides. The left side is the Debit (Dr.) side for recording all cash receipts, and the right side is the Credit (Cr.) side for all cash payments. Each side contains columns for the Date, Particulars, Ledger Folio (L.F.), and Amount.
4. What is the key difference between a single-column and a double-column cash book?
The key difference lies in the number of amount columns. A single-column cash book has only one amount column on each side to record cash transactions. In contrast, a double-column cash book has two amount columns on each side. The second column is typically used to record either bank transactions or discount allowed/received, allowing the business to track two accounts simultaneously within one book.
5. How are transactions recorded in a cash account using 'Debit' (Dr.) and 'Credit' (Cr.)?
The recording follows the golden rule of accounting for real accounts: "Debit what comes in, and Credit what goes out." Therefore:
- All cash receipts (inflows), such as cash sales or money received from debtors, are recorded on the Debit (Dr.) side.
- All cash payments (outflows), such as payments for expenses or purchases, are recorded on the Credit (Cr.) side.
6. Why can a cash account never show a credit balance?
A cash account represents a physical asset (cash in hand). A credit balance would imply that the business has paid out more cash than it possesses, which is physically impossible. You cannot spend money you do not have. Therefore, the balance of a cash account can either be a debit balance (indicating cash is available) or a nil balance (zero cash), but it can never be negative or credit.
7. What is a 'contra entry' and why is it important in a double-column cash book format?
A contra entry is a transaction that affects both the cash and bank columns of a double-column cash book, essentially moving funds between these two accounts. Examples include depositing cash into the bank or withdrawing cash for office use. It is recorded on both the debit and credit sides of the cash book. It is marked with the letter 'C' in the L.F. column to signify that no further ledger posting is required, as the debit and credit aspects are settled within the cash book itself.
8. How does maintaining a proper cash account format help in business management?
Maintaining a proper cash account format is crucial for effective business management. It provides a clear, up-to-date record of the company's liquidity, helping with cash flow management and budgeting. Furthermore, by regularly comparing the book balance with the actual physical cash, it acts as an essential internal control mechanism to quickly detect clerical errors, prevent unauthorised payments, and reduce the risk of fraud.























