




What is Economic Capital?
Economic capital is a capital-based way to express risk. For instance, the amount of capital required to maintain financial stability at a certain degree of confidence and time horizon could be a concern for a bank. In contrast to Regulatory Capital required measurements, EC may be thought of as the amount of risk capital from the standpoint of the banks. Economic capital is primarily intended to support business choices, whereas regulatory capital (RC) is meant to establish minimum capital needs against all risks in a bank, following various regulatory laws and guidelines.
There is currently no standard definition of economic capital domestically or internationally because it is more of a bank-specific or internal measure of available capital. Additionally, there are a few components that many banks share when defining economic capital. Grade 1, Grade 2, Grade 3, or classifications used by rating agencies and other forms of capital, such as expected earnings, unrealised profit, or an implied government guarantee, may all encompass EC projections.
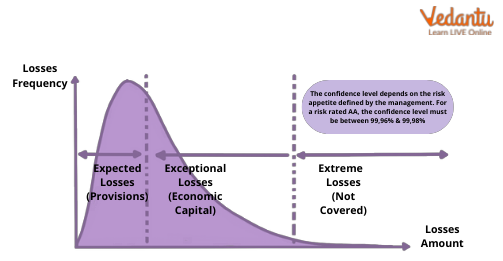
Economic Capital
Economic Capital vs Regulatory Capital
EC is particularly significant since it may give critical answers to specific business choices or for analysing a bank's various business segments. It also serves as a tool for comparing RC.
The management of a bank can utilise EC estimations to distribute capital across business streams, favouring those that yield a desirable profit per unit of risk. Return on risk-adjusted capital (RORAC), risk-adjusted return on capital (RAROC), and economic value added are examples of performance measurements that use EC (EVA).
Economic Risk Capital
Economic capital is a capital-based measure of risk. More specifically, it is the amount of capital required by a corporation (typically in the financial services industry) to be solvent given its risk profile.
Internally, the corporation calculates economic capital, sometimes using proprietary methods. The resulting figure is also the amount of capital that the firm should have to sustain any risks that it takes.
The long-term future uncertainties that banks and other financial institutions must take into account. The Basel Accords were developed in this context to enhance the risk management capabilities of significant financial institutions. Basel, I, Basel II, and Basel III are the three sets of laws that make up the agreements, which are guidelines for the banking sector.
Basel II offers worldwide guidelines on the required minimum capital that banks must keep to protect themselves against risks including counterparty risk, credit risk, market risk, operational risk, and pension risk, among others. In addition, Basel II outlines regulatory guidelines and requirements for modelling regulatory capital and encourages companies to utilise economic capital models. Although the idea of EC and its use as a risk indicator are not new, banks and other financial institutions are quickly adopting it as a crucial metric.
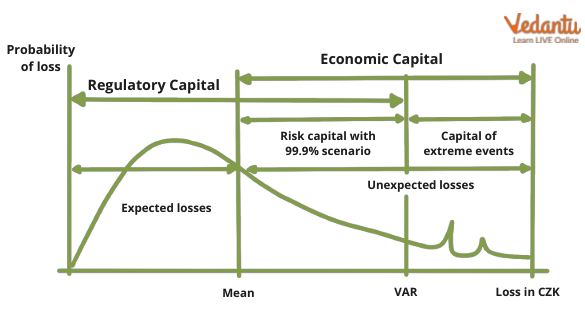
Economic Risk Capital
Economic Capital Framework
The term "economic capital framework" refers to the risk capital required by the central bank while accounting for various hazards. The economic capital framework reflects the capital that an institution needs or must keep as a hedge against future risks, occurrences, or losses.
India's Economic Capital Structure
Section 47 of the RBI Act specifies that the RBI's profits are to be remitted to the government after making allowances "often given by bankers."
In 2013-14, the RBI established a Technical Committee chaired by Y. H. Malegam to assess the RBI's internal reserves level and sufficiency, as well as its surplus distribution strategy.
The RBI implemented a draught Economic Capital Framework in 2015 in response to the above committee's recommendations.
Risks to the balance sheet and contingent risks were both attempted to be covered.
Why Does it Require Fixing?
The existing economic capital framework, which governs the RBI's capital requirements and terms for transferring its surplus to the government, is based on the central bank's conservative risk assessment, and a review of the framework would result in excess capital being released, which the RBI could then share with the government.
The government thinks that the RBI has far more reserves than is required to weather any financial problems that India may confront.
Some central banks throughout the world (such as the United States and the United Kingdom) hold 13% to 14% of their assets as reserves, compared to the RBI's 27% and some (such as Russia) keep even more.
Economists have previously advocated for the RBI to release "excess" capital that the government can put to productive use. In 2013, the Malegam Committee estimated the excess to be Rs 1.49 lakh crore.
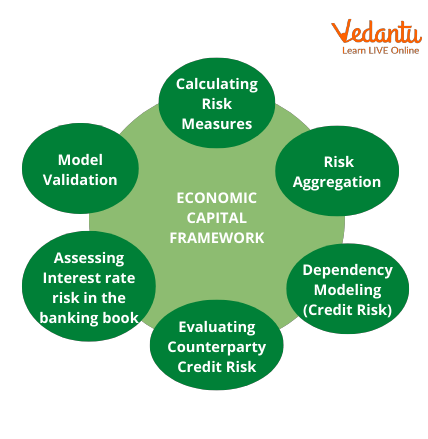
Economic Capital Framework
How Does Economic Capital Operate?
In the corporate sector, there are three primary categories of economic capital:
Debt
Equity
Specialty
Each form of funding source is unique, yet they may all support business expansion.
Conclusion
A bank's risk capital is quantified by its EC. Although it is not a brand-new idea, banks and other financial organisations are quickly adopting it as a crucial step. For business-based choices, EC offers a beneficial complement to RC. Banks' use of EC frameworks is growing, and it is expected to do so in the future. The pertinent query could be whether the need for regulatory capital might ever be replaced by economic capital.
FAQs on Economic Capital
1. What attributes does capital in economics have?
The following are some crucial traits that capital possesses:
An inactive factor is capital.
Man-made capital.
Capital is not inexhaustible.
Capital is very mobile.
Elastic Capital Capital Depreciates
Capital is useful.
Capital is transient. Capital is prospective.
Capital is referred to as Past Savings.
Capital is more than just money; it also includes tools and equipment, infrastructure, technology, and many other things. Capital has the highest degree of mobility among all the production elements. While labour has the least mobility and the land is immovable, capital enjoys both "place mobility" and "occupational mobility."
2. Why is money not capital in the economy?
Money is not capital, as defined by economists, because it is not a resource that can be used to produce goods. Even though capital may be acquired with money, the production of products and services is done with the help of capital goods (items like equipment and tools). Capital assets are generally the assets of a firm that may be seen on the balance sheet's current or long-term component. Capital is more than just money; it also includes tools and equipment, infrastructure, technology, and many other things.
3. How is economic capital determined?
Typically, economic capital is calculated by determining the amount of capital the firm needs to ensure that its realistic balance sheet stays solvent over a certain period with a pre-specified probability. Therefore, economic capital is often calculated as a value at risk. In this scenario, the balance sheet would be constructed with the market value (as opposed to book value) of the assets and liabilities. The goal for businesses and financial services authorities should then be to hold risk capital that is at least equivalent to economic capital.























