





E-commerce
Scope of E-Business
Explanation of the scope of e-Business can be listed as hereunder:
There are a large number of people involved in e-commerce, such as the transporter, seller, buyer, intermediary, delivery agency and many more such organisations, which provide a huge base of employment to the various sections of society.
It promotes digitalisation not only in terms of the selling of goods but due to the availability of various modes of payment such as phone pe, Paytm, wallet and many such agencies.
The database is integrated from a centralised system. Hence there is a quick update of the data, which is how faster transactions are processed and reach the customers on time.

Online Shopping
Difference between the E-business and Traditional Business
Directions for the E-Business
There are 4 kinds of direction of E-business
B2B Commerce (Business-to-Business)
In this case, the business provides services or provides manufactured goods to other businesses in order to generate revenue
B2C Commerce (Business-to-Consumer)
B2C commerce directly serves the final consumers by delivering goods directly to the final consumers and eliminating the intermediaries.
B2G Commerce (Business-to-Government)
Here the business enterprise provides goods either to the central government or state government or some local authorities. They may also be provided to the government corporations in the case of B2G Commerce.
C2C Commerce (Consumer-to-Consumer)
Sometimes, one consumer sells goods to another consumer in order to generate income in the form of brokerage or commission. Such a type of direction is known as C2C commerce.
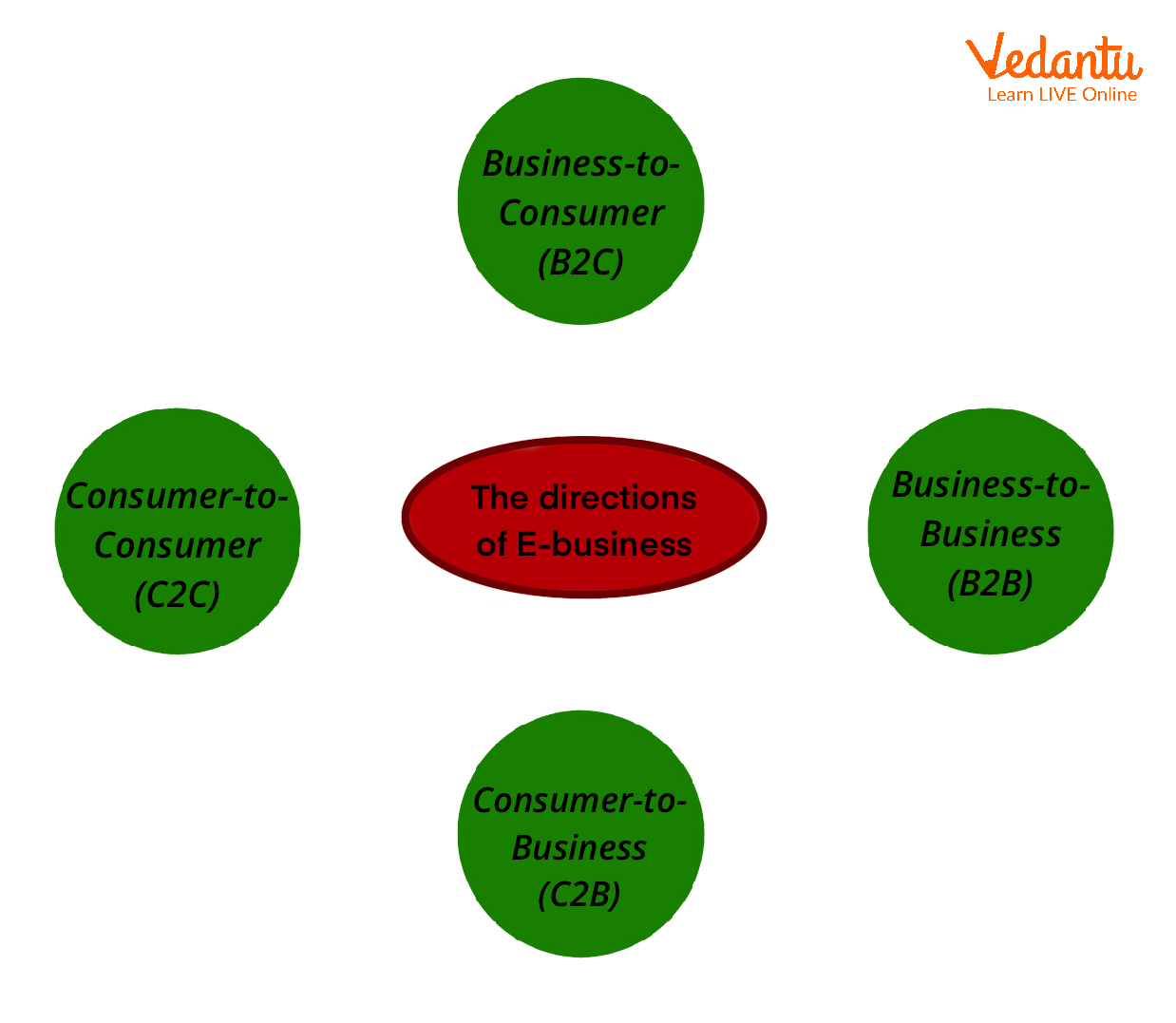
Directions of E-Business
Case Study
Vishal has recently started his business. His friend Nishad insists on him selling goods via an e-commerce platform, but Vishal refuses to do so. So in favour of Nishad, enlist some benefits of e-commerce.
Ans: The benefits available to Vishal are as under
It attracts a large customer base from anywhere in the world.
It brings uniformity to scaled business
The entry is very easier into the e-commerce business
Elimination of time delays in respect of payments and in delivery of goods
Conclusion
E-commerce has eased the life of humans, it now becomes just a click and then done. There is a need to shift every enterprise on e-commerce to beat the competition. Anytime and anywhere is the most important keynote for e-commerce.
FAQs on E-Commerce: Transforming Business in a New Era
1. What is E-commerce and how is it different from traditional commerce?
E-commerce, or electronic commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet. It involves conducting business activities electronically. The primary difference from traditional commerce lies in the medium and operational model. Traditional commerce relies on physical, face-to-face interactions in a specific location, while e-commerce operates in a digital marketplace without geographical boundaries. Key differences include:
- Reach: Traditional commerce is limited to a local area, whereas e-commerce provides a global reach.
- Availability: E-commerce businesses can operate 24/7, unlike traditional stores with fixed working hours.
- Cost: E-commerce often involves lower overhead costs related to rent, utilities, and staffing compared to physical stores.
- Interaction: Traditional commerce offers direct personal interaction, while e-commerce relies on digital interfaces, customer reviews, and online support.
2. How has e-commerce transformed the way modern businesses operate?
E-commerce has fundamentally transformed modern business operations by breaking down geographical barriers and enhancing efficiency. It allows businesses to reach a global customer base with minimal investment in physical infrastructure. Key transformations include data-driven decision-making by analysing customer behaviour online, personalised marketing to target specific demographics, and streamlined supply chain management through automated inventory and logistics systems. Furthermore, it has lowered the barrier to entry for new entrepreneurs, enabling small businesses to compete with larger corporations on a digital platform.
3. What are the main types of e-commerce models? Please provide examples.
The main e-commerce models are categorised based on the nature of the participants involved in the transaction. The primary types are:
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C): This is the most common model, where businesses sell directly to individual consumers. Examples include shopping for clothes on Myntra or electronics on Amazon.
- Business-to-Business (B2B): Here, businesses sell products or services to other businesses. This often involves bulk orders and customised pricing. An example is a company buying software from Salesforce or raw materials through IndiaMART.
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C): This model facilitates transactions between individual consumers. Platforms like OLX or eBay are classic examples, where one person sells a used item to another.
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B): In this model, individuals offer products or services to companies. A freelance photographer offering their images to a stock photo agency like Shutterstock is an example of C2B.
4. Why is a robust payment gateway crucial for the success of an e-commerce business?
A robust payment gateway is crucial because it acts as the digital cash register for an online store, directly impacting customer trust and sales conversion. Its importance extends beyond simply processing payments. A secure gateway encrypts sensitive customer data (like credit card details), protecting both the customer and the business from fraud. It builds credibility and user confidence, which is vital for online transactions. Furthermore, offering multiple payment options (UPI, credit/debit cards, net banking, wallets) through a reliable gateway reduces cart abandonment and ensures a smooth, successful checkout experience, which is essential for retaining customers.
5. What are the key benefits for a business to shift from a physical store to an e-commerce platform?
Shifting from a physical store to an e-commerce platform offers several significant benefits that can drive growth and efficiency. The most important advantages include:
- Wider Market Access: An online store is not limited by geography, allowing a business to attract customers from across the country and even globally.
- Lower Operational Costs: E-commerce reduces expenses related to rent for prime locations, store staff, and utilities, leading to higher profit margins.
- Improved Customer Data: Online platforms can track user behaviour, purchase history, and preferences, enabling personalised marketing and product recommendations.
- Scalability: It is easier and cheaper to scale an e-commerce business by adding new products or handling more customers than it is to open new physical branches.
- 24/7 Availability: The business is always open, allowing customers to shop at their convenience, which can significantly increase sales opportunities.
6. How does e-commerce impact Business-to-Business (B2B) transactions differently than Business-to-Consumer (B2C) ones?
E-commerce impacts B2B and B2C transactions differently due to their distinct objectives and transaction characteristics. In B2C, the focus is on creating an emotional connection, brand appeal, and a seamless user experience to drive individual purchases, which are typically smaller in value but higher in volume. In contrast, B2B e-commerce is driven by logic, efficiency, and long-term relationships. It involves larger order values, complex logistics, and negotiated pricing. The transformation in B2B is about streamlining the procurement process, managing supply chains more effectively, and reducing administrative overhead, rather than impulse buying.
7. What are the common security threats in e-commerce, and how can a business protect its customers' data?
Common security threats in e-commerce include phishing attacks (tricking users into revealing sensitive information), malware, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks that crash a website, and data breaches that expose customer information. To protect customer data, a business must implement multiple layers of security. Key measures include:
- Using an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate to encrypt data transmitted between the customer and the server.
- Adhering to PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliance for handling card information.
- Implementing two-factor authentication (2FA) for customer accounts.
- Regularly updating software and conducting security audits to identify vulnerabilities.
- Having a clear privacy policy that informs customers how their data is used and protected.
8. Beyond just selling online, what other business functions are transformed by e-commerce technology?
E-commerce technology transforms far more than just the sales function. It revolutionises several core business operations:
- Marketing and Advertising: Businesses can use digital marketing, SEO, and social media to execute highly targeted and measurable campaigns.
- Supply Chain Management: Automation in inventory management, order fulfilment, and logistics tracking makes the entire supply chain more efficient and transparent.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): E-commerce enables businesses to collect valuable customer data, which can be used to provide personalised support, run loyalty programs, and build long-term relationships through tools like chatbots and automated email follow-ups.
- Finance and Accounting: Digital transactions and automated invoicing simplify financial reconciliation and cash flow management.
9. What potential limitations or challenges might a business face when adopting an e-commerce model?
While e-commerce offers many advantages, businesses also face significant challenges. A primary limitation is the lack of personal touch, as customers cannot physically inspect products, which can lead to higher return rates. Other challenges include:
- Intense Competition: The online marketplace is crowded, making it difficult for new businesses to stand out without a strong marketing strategy.
- Technological Costs: Setting up and maintaining a secure, user-friendly website, along with costs for digital marketing and payment gateways, can be substantial.
- Security Risks: Businesses are responsible for protecting customer data from cyberattacks, which requires constant vigilance and investment in security.
- Logistics and Fulfilment: Managing shipping, returns, and inventory across wide geographical areas can be complex and expensive.























