




Trade Barrier: Introduction
The government imposes trade barriers so that their domestic trade can flourish without any foreign impact. Trade barriers are aimed at protecting domestic jobs. They help in improving trade deficits. They protect infant industries and protect against dumping. And sometimes they are imposed to earn more revenue.
Trade Barrier: Definition and its Types
Trade Barriers are defined as government-induced restrictions on international trade. They are imposed for various reasons, primarily to protect the domestic market and to earn revenue.
Types of Trade Barriers
There are six major types of trade barriers as discussed below.
Voluntary Export Restraints (VERs)
In this type of trade barrier, a nation limits the amount of export and increases the price of the goods and thus the revenue.
Regulatory Trade Barriers
The regulatory trade barriers are some legal barriers which hurdle the import of the products. These regulatory barriers are set by the government and specifically include product, safety, and pollution standards. For example, there are safety ratings for vehicles which need to be passed by the manufacturers to sell their products in the importing country.
Anti-Dumping Duty
Exporters, in order to earn more profit, sell their products below the actual cost in various countries. It is known as dumping. The government, in order to protect the domestic market from these dumped products, imposes the Antidumping Duty.
The Subsidy
Subsidies act as the support provided by the government to the firms manufacturing products to lower their production cost and become more competitive.
The Tariffs
Tariffs are taxes on imports. Tariffs are imposed to increase the price of imported products so that they are not consumed. There are many types of tariff, including ad valorem tax or a specific tax. A tariff diagram explains the effects of tariffs.
The Quota
Quota restricts the quantity of a product that can be imported into a country.
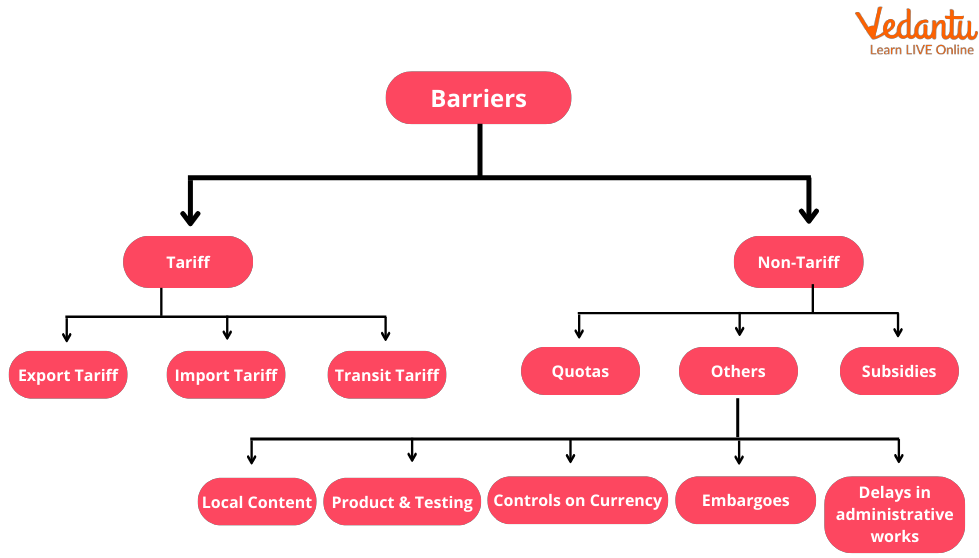
Tariff and Non-Tariff Barriers
A tariff Barrier is imposed by the government of the country importing goods. It has two-fold objectives, one to increase the government revenue and second, to raise the cost of foreign goods so that domestic companies can compete with the foreign goods. Examples of tariff barriers include Export duties, Specific duties, Import duties, Ad - valorem duties, Transit duties, Compound duties, Revenue tariffs, Protective tariffs, Counter - vailing and Antidumping duties, Single - column tariff, Double - column tariff.
Types of Barriers
Non-tariff barriers are defined as non-tax measures adopted by a nation's government to limit imports from foreign countries. These can be in the form of laws, policies, practices, conditions, requirements, etc. and are specified by the government to restrict imports. Examples of non-tariff barriers are Import quotas, Voluntary Export Restraints (VERs), Import licensing, Technical and administrative regulations, Price control, Foreign exchange regulations, Consular formalities, Quantity restrictions, and Pre-shipment inspection and Rules of origin.
Import Tariff and Its Benefits
An import tariff is particularly imposed on the price of imported goods. Import tariff benefits the country importing goods since it generates revenue for the government. Import tariff creates a friendly competitive environment for domestic companies.
Retaliatory Tariff
A country imposes a retaliatory tariff in order to pressurise another country to remove its tariffs or it may be imposed for the purpose of trade concessions.
Tariff v/s Non-Tariff Barriers
Tariff Barrier includes taxes or duties which the government imposes, whereas non - tariff barrier includes all the restrictions except taxes imposed by the government. Tariff barriers are explicit in nature, whereas non-tariff barriers are implicit. The tariff barrier leads to revenue generation for the government, whereas no revenue is received due to non-tariff barriers. A tariff barrier affects the price of imported products, whereas non - a tariff barrier affects the quantity, price, or both of the imported products.
Types of Non - Tariff Barriers
Summary
Tariff barriers make a nation self-sufficient and also reduce dependency on foreign goods. Non-tariff barriers act as hindrances to international trade, and these can be legal or bureaucratic. Reasons for imposing tariff and non-tariff barriers are multifold, including national security, retaliation, protection of domestic jobs, protection of startups, etc.
FAQs on Trade Barriers: Hurdles in International Trade Explained
1. What are trade barriers in the context of international trade?
Trade barriers are government-imposed policies or regulations that restrict, limit, or discourage the flow of goods and services between countries. The primary goal of these barriers is to make imported products or services less competitive than domestic ones, thereby protecting local industries. They act as hurdles to free international trade by increasing the cost or limiting the quantity of imported goods.
2. What are the main types of trade barriers with examples?
Trade barriers are broadly classified into two main categories:
Tariff Barriers: These are taxes or duties imposed on imported goods, making them more expensive. Examples include:
Ad Valorem Tariffs: A percentage of the value of the imported goods (e.g., 10% tax on the value of an imported car).
Specific Tariffs: A fixed fee per unit of the imported product (e.g., ₹1000 per imported smartphone).
Non-Tariff Barriers (NTBs): These are restrictions that do not involve a direct tax. Examples include:
Import Quotas: A limit on the quantity of a specific good that can be imported.
Embargoes: A complete ban on trade with a particular country.
Subsidies: Financial aid provided by the government to domestic producers to make their goods cheaper than imported ones.
Licensing Requirements: The need for a special license to import certain goods, which can be difficult to obtain.
3. What is the primary importance of imposing trade barriers for a country?
Governments impose trade barriers for several key reasons, the importance of which can be seen in their economic objectives:
Protecting Domestic Industries: This is the most common reason, especially for 'infant industries' that are new and not yet able to compete with established foreign companies.
Generating Government Revenue: Tariffs on imported goods can be a significant source of income for the government.
National Security: Countries may restrict the import or export of goods vital for national defence and security.
Protecting Domestic Jobs: By discouraging imports, trade barriers can protect jobs in domestic industries that would otherwise struggle against foreign competition.
Retaliation: A country might impose barriers in response to trade restrictions imposed by another country, leading to a trade war.
4. What is the main difference between a tariff and a quota as trade barriers?
The main difference lies in how they restrict trade and the revenue they generate. A tariff is a tax on imports which increases their price, but it does not directly limit the quantity that can be imported; as long as importers are willing to pay the tax, they can bring in more goods. Tariffs also generate revenue for the government. In contrast, a quota is a direct physical limit on the quantity of a good that can be imported, regardless of price. It does not generate revenue for the government but creates a guaranteed market share for domestic producers once the quota is reached.
5. How do trade barriers like tariffs affect a country's domestic consumers?
Trade barriers generally have a negative impact on domestic consumers. By making imported goods more expensive or limiting their availability, barriers lead to:
Higher Prices: Consumers have to pay more for imported goods due to tariffs, and domestic producers may also raise their prices due to a lack of foreign competition.
Reduced Choice: Quotas and embargoes directly limit the variety of products available in the market, reducing consumer choice.
Lower Quality: With less competition from foreign companies, domestic firms may have less incentive to innovate and improve the quality of their products.
6. Why might a government prefer using non-tariff barriers (NTBs) instead of tariffs?
A government might prefer non-tariff barriers over tariffs for several strategic reasons. NTBs like product standards, licensing, or complex customs procedures can be more subtle and less likely to provoke direct retaliation from other countries compared to a straightforward tax (tariff). They can also be tailored to target specific industries or issues without being a blanket tax. Furthermore, since international trade agreements often focus on reducing tariffs, NTBs can be a way to protect domestic industries without explicitly violating the terms of these agreements.
7. Are trade barriers always harmful to an economy?
While free trade is generally seen as beneficial, trade barriers are not always considered harmful, especially in specific contexts. The 'infant industry' argument suggests that new industries in developing countries need temporary protection from established international competitors to grow and become efficient. In such cases, carefully applied barriers can be beneficial in the short term. However, most economists agree that if these barriers are kept for too long, they can lead to inefficiency, lack of innovation, and higher costs for consumers, ultimately harming the economy in the long run.





































