




Unregulated Market: An Overview
Markets that are not regulated by a specific regulator are governed by existing agreements between the parties involved; however, the offering process is typically regulated so that it adheres to a set of established rules and principles. They are also known as private items or private offers because the method of offering is usually private.
As they are a substitute for goods sold in public markets, they are also known as alternative market items. Section 21 of the Capital Markets (Securities) (Public Offers, Listings, and Disclosures) Regulation, 2002 outlines a list of nine requirements that must be met before issuing a private offer in Kenya.

Unregulated Market
Impact of Deregulation
Small businesses are more likely to be squeezed out of the market by larger, more established enterprises if there are no restrictions in place. Larger corporations can form monopolies and grab market dominance.
Consumers' interests may not always be served by deregulation. Banking regulations, for example, require banks to retain a certain amount of cash on hand, which helps clients who need to withdraw money.
Companies in a deregulated sector are not compelled to inform the public about how they conduct their activities. Financial industry regulations, for example, outline how publicly traded companies must publish financial statements so that investors may evaluate the business and make investment decisions.
Without government restrictions and oversight, businesses can commit fraud more easily, putting customers at risk.
Pros of Unregulated Market or Free Market Economy
Opportunity for high profit; if the market is deregulated, you can charge whatever you want for your goods. Furthermore, if your product is unique, you may gain market exclusivity. You have complete control over the market's entry and exit.
You can avoid paying taxes if the government does not monitor the market or if the market is uncontrolled. There is no tax on water, commercial real estate, or the environment. However, the local legal system determines whether it is unusual or not.
If a company does not follow government regulations, low-cost labour is available. Consider skipping ESI, PF, and other benefits to provide workers with as little money as possible.
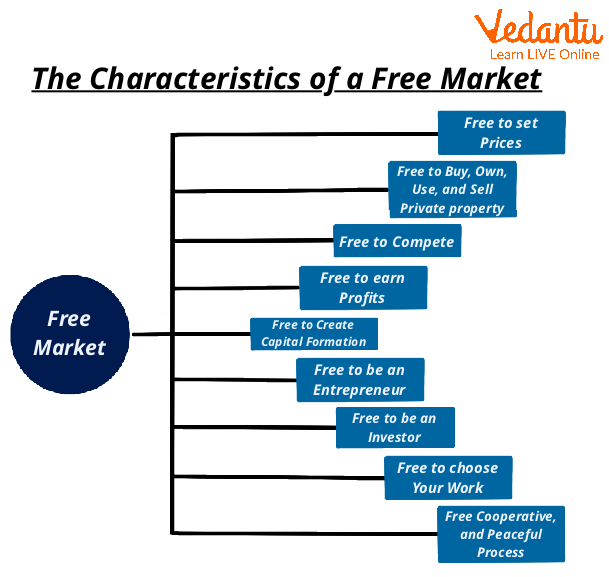
Advantages of Free Market Economy
Free Market Economy Disadvantages
1. It is a Free Market Economy.
Profit is advantageous to business. On the other hand, companies so focused on making a profit frequently overlook the bigger picture: people are working hard to create a product. Businesses will sometimes disregard their employees to gain an advantage. Employers frequently disregard their employees' health because they must provide a high-quality product to generate more revenue.
2. When it Fails, The Consequences are Disastrous.
When a market fails, serious consequences follow. We can look no further than history for proof; two prime examples are the 2008 real estate crash and the 1930s Great Depression. The entire world was affected, not just one country. People lost their homes as well as their jobs. Some people have been able to recover, while others have required more time to heal.
Case Study
How do free market economies work? Explain with the examples.
Ans: The majority of countries' economies are mixed, with both private and public sectors. Different countries have varying degrees of government involvement, private-sector regulation, and social programmes that encourage widespread participation in the market economy.
A command economy, which is a type of planned economy in which resources are distributed and centralised, differs from a free-market economy. People with more resources typically have more influence in these types of economies because they have government officials' ears (and often the control).
Unquestionably, some consumer data must be controlled to protect consumers from misleading advertising. However, this should not be interpreted as a complete prohibition on product marketing. Advertising is critical for ensuring transparency and preventing producers from covering up problems.

Free Market Economy
Conclusion
Before deciding whether to invest in or avoid unregulated products, investors must understand their investment purpose, risk tolerance, and available investment products. We strongly advise you to consult a financial advisor before investing in either of the two types of investments.
We must abandon the notion that all financial products must be regulated to advance our capital markets. Instead, we must clearly distinguish between a private and a public offer and allow both to coexist.
FAQs on Unregulated Market: Definition and Characteristics
1. What is an unregulated market in economics?
An unregulated market is an economic system where the prices of goods and services are determined purely by the forces of supply and demand, with minimal or no government intervention. In such a market, there are no government-imposed price controls, quality standards, or licensing requirements, allowing for free competition among producers and sellers.
2. What are the key characteristics of an unregulated market?
The main characteristics of an unregulated market include:
- Free Entry and Exit: Businesses can start or stop operating in the market without significant government barriers.
- Price Determination by Market Forces: Prices are set by the interaction of buyers and sellers, not by a regulatory authority.
- Absence of Government Controls: There are typically no price ceilings, price floors, or mandatory quality checks imposed by the government.
- High Level of Competition: The ease of entry often leads to a large number of sellers competing for customers, which can drive prices down.
3. How does a regulated market differ from an unregulated one?
The primary difference lies in the level of government oversight. An unregulated market operates on principles of free competition with minimal government rules. In contrast, a regulated market is subject to significant government control. This includes setting price caps (like MRP), enforcing quality standards (e.g., FSSAI for food), requiring licenses for operation, and implementing laws to protect consumers from fraud and ensure fair practices.
4. Can you provide some real-world examples of unregulated markets?
Examples of unregulated or minimally regulated markets are common in the informal sector. These include local weekly markets (haats), many street food vendors, and certain online freelance platforms. The global market for cryptocurrencies is another prominent example where regulation is still evolving and often minimal compared to traditional financial markets like stock exchanges.
5. What are the potential dangers or defects for consumers in an unregulated market?
While they can offer competitive prices, unregulated markets pose several risks to consumers. Key defects include the high risk of fraud and scams, the potential for poor or unsafe product quality due to the lack of mandatory standards, and the possibility of price gouging during periods of high demand. Consumers may also suffer from information asymmetry, where sellers know more about the product than buyers, leading to unfair transactions.
6. If unregulated markets have risks, why do governments allow them to exist?
Governments often allow unregulated markets to exist to foster innovation, entrepreneurship, and competition. The absence of strict rules lowers the barrier to entry for new businesses, which can lead to economic growth and job creation. It allows new products and industries (like early e-commerce) to develop without being stifled by heavy bureaucracy. It represents a trade-off between promoting economic freedom and ensuring complete consumer protection.
7. How does the absence of regulation in a market affect pricing and quality?
The effect can be twofold. For pricing, intense competition can lead to lower prices for consumers. However, it can also cause price instability or allow for exploitation if a few sellers gain control. For quality, competition can motivate sellers to improve their products to attract customers. Conversely, some sellers may be tempted to cut corners and reduce quality to lower their costs, especially when consumers cannot easily assess the product's true value before purchase.























