




What Makes Iguanas Unique: Habitat, Diet, and Cool Adaptations
Native to tropical regions of Mexico, Central America, South America, and the Caribbean, iguanas are a genus of herbivorous lizards. The genus was first described in 1768 in Specimen Medicum, Exhibens Synopsin Reptilium Emendatam cum Experimentis circa Venena by Austrian naturist Josephus Nicolaus Laurenti. The green iguana, which is common across its range and a well-liked pet, and the Lesser Antillean iguana, which is indigenous to the Lesser Antilles, are both included in the genus. The green iguana may be a complex of several species, some of which have only recently been described, according to genetic studies, although the Reptile Database classifies all of these as subspecies of the green iguana. Let’s now see Iguana Habitat, images of Iguanas and much more.
Where does Iguana Live?
Mexico, Central and South America, the Galápagos Islands, various Caribbean islands, Fiji, and Madagascar are among the places where these lizards can be found. According to the San Diego Zoo, they typically inhabit tropical and subtropical woods, deserts, and beaches. The rain forests of southern Brazil, the Caribbean Islands, northern Mexico, and Central America make up the vast range of the green iguana. They rarely descend to the ground to mate, lay eggs, or shift trees instead of spending most of their time in the canopy.
Iguanas inhabit a range of habitats, including lowlands, rocky areas, marshes, and deserts, depending on the species. In all of Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean Islands, and southern Brazil, green iguanas can be found. The term "rock iguanas" refers to all of the iguana species that live on the Caribbean islands. Southwest U.S. and Mexico are home to desert iguanas while the Galapagos Islands are home to two genera of marine iguanas. This is about Iguana Habitat.

Iguanas
Iguana Facts
Iguana food habits
Some facts about Iguanas are as follows:
Iguanidae is the family name.
Typical Names: Typical Iguana (for green iguana)
Order: Squamate
Group of Basic Animals: Reptile
Size ranges from 5 to 7 feet (green iguana) to 5 to 39 inches (spiny-tailed iguana).
Weight: Up to 30 pounds (blue iguana)
Life Span: depends on the species, 4 to 40 years on average.
Diet: Fruits, flowers, leaves, insects, and snails
Habitat: Rainforests, lowlands, swamps, deserts
Population: About 13,000 Fiji iguanas, 3,000 to 5,000 spiny-tailed iguanas, and 13,000 to 15,000 green iguanas make up each species.
Protection Level: Least Concern (green iguana), Endangered (Fiji iguanas), Critically Endangered (Fiji crested iguana).
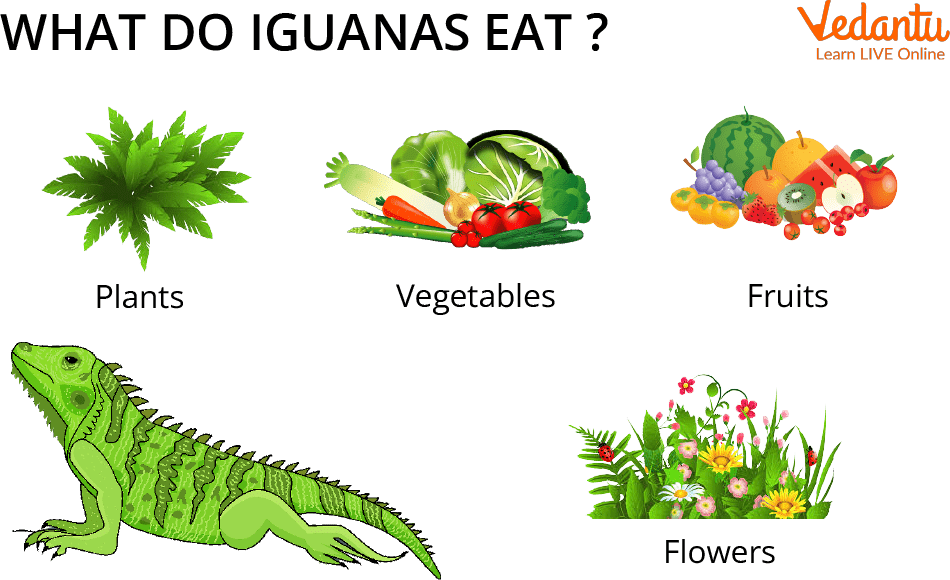
What do Iguanas Eat?
Iguanas are herbivorous, or plant-eating, creatures because they are folivores or leaf eaters. In the wild, iguanas primarily consume fruits, flowers, and a few fruits and vine leaves. Iguanas shouldn't consume meat or insects. Stick to plant-based foods like fruits, leaves, and flowers. If Iguanas are fed an excessive number of other foods, they may become unhealthy. As an example, let's look at two typical greens that are on most reptile keepers' lists of foods.
Summary
To conclude all the conceptual understanding regarding Iguanas in this article, we can say that native to tropical regions of Mexico, Central America, South America, and the Caribbean, iguanas are a genus of herbivorous lizards. Iguanas are lizards distinguished by their stocky build, sagging throat skin, and spines that stick out from their heads, necks, backs, and tails. Iguanas make popular pets and, with the right care, can survive for 15 to 20 years. We hope you enjoyed reading this article, in case of any other doubts, feel free to ask in the comments.
FAQs on Fascinating Facts About Iguanas Every Student Should Know
1. What exactly is an iguana?
An iguana is a type of large lizard native to the tropical regions of Central America, South America, and the Caribbean. They belong to the family Iguanidae and are known for their distinctive appearance, including a dewlap (a flap of skin under the chin), a row of spines along their back, and a long, powerful tail.
2. What makes iguanas unique compared to other lizards?
Iguanas have several unique features that set them apart. Key characteristics include:
- Parietal Eye: Often called a 'third eye,' this is a light-sensitive spot on top of their head that helps them detect predators from above.
- Herbivorous Diet: Unlike many lizards that eat insects, most iguanas are herbivores, primarily eating leaves, flowers, and fruits.
- Powerful Tails: Their tail is not just for balance; it can be used as a sharp whip to defend against threats.
- Size: Green iguanas can grow up to 6 feet long, making them one of the largest lizards in the Americas.
3. Are iguanas friendly and can they be kept as pets?
While some people keep iguanas as pets, they are not naturally friendly or affectionate animals. They generally do not enjoy being handled or petted and can become stressed. With proper care and patience, an iguana might learn to recognise its owner, but they require large, specific habitats and a specialised diet to stay healthy, making them a challenging pet for beginners.
4. What do iguanas eat in the wild?
In their natural habitat, iguanas are primarily herbivores. Their diet consists mainly of plant matter. They eat a wide variety of leaves from trees and vines, as well as flowers, fruits, and young shoots. Their sharp, serrated teeth are perfectly adapted for tearing through tough plant material.
5. How do iguanas defend themselves from predators?
Iguanas have several clever defence mechanisms. Their first instinct is to flee by running or diving into water, as they are excellent swimmers. If cornered, they will puff up their bodies to appear larger, hiss loudly, and bob their heads. For physical defence, an iguana can deliver a painful bite with its sharp teeth and, most effectively, use its long, muscular tail as a powerful whip to strike attackers.
6. Why are iguanas often seen basking in the sun?
Iguanas bask in the sun because they are ectothermic, or 'cold-blooded'. This means they cannot produce their own body heat and rely on external sources like the sun to regulate their body temperature. Basking helps them warm up, which is essential for digestion, energy, and overall activity.
7. Can an iguana's tail grow back if it breaks off?
Yes, like many other lizards, iguanas can detach a part of their tail to escape a predator. This process is called autotomy. While the tail can grow back, the regenerated one is often shorter, darker in colour, and not as functional as the original, as it is made of cartilage instead of bone.
8. What happens if an iguana bites a person?
An iguana bite can be quite serious. They have powerful jaws and dozens of razor-sharp teeth designed to tear plants, which can cause deep cuts in human skin. Because their teeth can sometimes break off in the wound, there is a significant risk of infection. It's important to seek medical attention if bitten to properly clean the wound and prevent complications.









