




What Are Lipids? Structure, Types, and Their Importance
A chemical substance known as a lipid can be found in living things. It's waxy or oily. Lipid molecules are the building blocks of fat. Lipid comes from various sources, including algae, seeds, pork, cheese, butter, and fish. As the foundation of many cell membranes, lipid bilayers serve an essential biological purpose. Lipids can also be used as a source of backup energy.
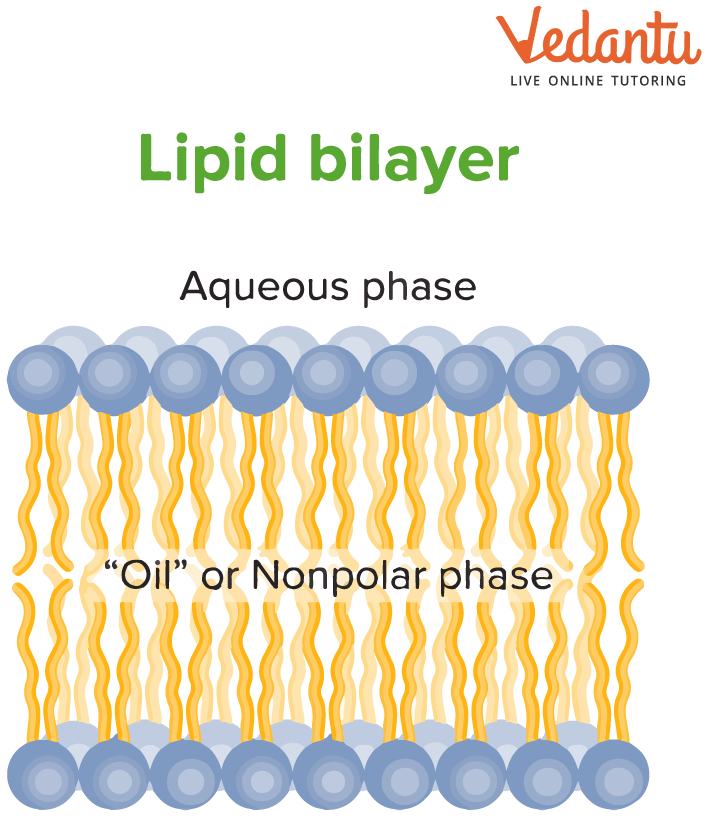
A class of naturally occurring compounds known as lipids includes fats, waxes, sterols, glycerides, phospholipids, and fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E, and K). Lipids serve various biological purposes, chief among them the storage and transmission of signals and the construction of cell membranes.
What are Lipids?
As per lipids definition biology, lipids are one of the four main types of organic molecules. The other three are proteins, nucleic acids (DNA), and carbohydrates (sugars). Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are the parts that make up carbs and lipids. Lipids, on the other hand, have a lot more hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats, steroids, phospholipids, and waxes are all types of lipids. Lipids don't dissolve in water, one of their most important traits.
Types of Lipids
Many important types of lipids fall into these two main groups. These are fatty acids, triglycerides, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, and steroids. In a broad sense, these are divided into simple lipids and complex lipids.
Fats: Esters are made up of glycerol and fatty acids. Oils are fats that are in a liquid form.
Waxes: Esters of fatty acids with monohydric alcohols with a higher molecular weight. They have more than just alcohol and fatty acid in them.
Phospholipids are lipids with a phosphate group, fatty acids, and alcohol. They often have bases with nitrogen and other parts. For example, the alcohol in glycerophospholipids is glycerol; in sphingophospholipids, it is sphingosine.
Glycolipids (glycosphingolipids): Lipids with fatty acids, sphingosine, and carbohydrates.
Other complex lipids: Some types of lipids are sulfolipids and amino lipids. Lipoproteins could also fit into this group.
Functions of Lipids
Lipids are a part of the structure of the cell membrane. They help keep the cell membrane fluid and flexible.
It keeps the body from getting too hot or too cold and helps keep the temperature inside the body stable.
Adipose tissue is a type of tissue in the body that stores extra energy from food.
Fats are essential for storing energy, keeping the body's temperature steady, protecting vital organs, regulating hormones, sending nerve impulses, and moving fat-soluble nutrients around the body.
Fats in food give you a concentrated source of energy, make food taste and feel better, and help you feel full.
Characteristics of Lipids
In this portion of the article, we will look at various examples and characteristics of lipids.
There are four main categories of organic compounds: lipids, proteins, nucleic acids (comprise the genetic material), and carbohydrates (sugars). Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are the main constituents that make up a lipid compound. This means lipids are composed of the same basic components as any carbohydrate. But lipid elements often have a lot more hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms.
Wax, phospholipids, steroids, and fats are major examples of lipids. Lipids don't dissipate in water, which is one of their primary characteristics.
In living things, lipids play many crucial roles from energy storage and hormone production to being the major component of cell membranes.
Lipid Examples in Biology
Various types of fats are found in living organisms. Therefore in this part of the article, we will look at those types and lipid examples from Biology. Types of lipids are as follows:
1. Fats
A fat unit is made up of three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule. Fat particles, like other lipids, are composed of hydrocarbons. In our bodies, fat serves as a form of stored energy. There are two major divisions of fats, namely- saturated and unsaturated fats.
Saturated Fats
They are found as a solid at normal room temperature and pressure.
They are also called bad fats.
If consumed can cause various health hazards like blockage of arteries, cancer, etc.
Unsaturated Fats
They are Found in a liquid state at room temperature and pressure.
These are extracted from natural and healthy sources like nuts.
They are termed good fats.
2. Wax
They are similar in composition to fats, however are only composed of only one long fatty acid chain. These are usually produced as a source of protection by animals and plants. Wax is also produced by humans from the ear as a source of protection against dust and germs.
3. Steroids
Another important category of lipids is steroids. Cholesterol in the human body, plant pigment chlorophyll, and various hormones are examples of steroids. Hormones like testosterone, the male hormones, and estrogen, the female hormone, are produced by our bodies using cholesterol. Moreover, Plants need chlorophyll to capture light for the process of photosynthesis.
4. Phospholipids
The fourth main category of lipids is phospholipids. In terms of chemical composition, they resemble fats a lot. One of the primary structural elements of cell membranes in various organisms is phospholipids.
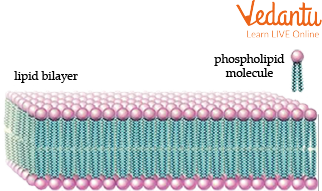
Phospholipid Layer in Cell Membranes
Fun Facts About Lipids
Honeybees use wax to create their honeycombs, shielding them from rain.
For absorption and to stay in our bodies, several vitamins require lipids. A, D, E, and K are a few of these vitamins.
If we mix fats and water, they float in the water rather than dissolve in it.
The fats can be dissolved in water if added alkali, such as dish soap.
All commonplace products, such as chewing gum, polishes, and candles, use wax.
Lipids are "hydrophobic" because they do not dissolve in water.
Without lipids, digestion and absorption of food would not be possible.
Conclusion
Lipids are crucial in our lives, and we cannot live without lipids. Some are core components of cell membranes, which enclose cells. The body requires fats to cushion its organs, store energy, and regulate body temperature. Fats also aid in the absorption of vitamins.
FAQs on Key Facts About Lipids Every Student Should Know
1. What are some common examples of lipids in our daily life?
Lipids are found in many foods and products we use every day. Common examples include cooking oils (like olive oil and sunflower oil), butter, ghee, cheese, and the fat present in meat and fish. They are also abundant in nuts, seeds, and avocados. Other types of lipids include waxes, such as beeswax, and cholesterol.
2. Are all fats bad for you?
No, not all fats are bad. In fact, our bodies require healthy fats to function correctly. Unsaturated fats, found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, are beneficial for heart health. However, saturated fats (found in butter and red meat) should be consumed in moderation, and trans fats (often in processed snacks) are generally considered unhealthy as they can increase the risk of heart disease. You can learn more about the different sources and types of fats.
3. What makes lipids unique compared to other biomolecules like carbohydrates and proteins?
The most unique property of lipids is that they are hydrophobic, which means they do not dissolve in water. While other major biomolecules like carbohydrates and proteins are defined by their specific monomer structures (forming long polymer chains), lipids are grouped together primarily based on this shared physical property of water insolubility. This characteristic is essential for their role in forming cell membranes.
4. What are the main functions of lipids in the human body?
Lipids have several vital functions in the body, including:
- Energy Storage: They are the body's most concentrated source of long-term energy.
- Insulation: A layer of fat under the skin helps to maintain body temperature.
- Protection: Lipids cushion vital organs like the heart and kidneys from injury.
- Cell Structure: They are the primary components of all cell membranes.
- Hormone Production: They are used to synthesize important steroid hormones.
5. Why are lipids, especially fats, crucial for brain development in children?
The human brain is remarkably rich in fat, consisting of nearly 60% lipids. These lipids are not just for energy; they are fundamental building blocks for brain cells (neurons) and nerve tissues. Essential fatty acids, like omega-3 and omega-6, are critical for the formation of cell membranes and myelin sheaths, which insulate nerves and allow for rapid communication. Therefore, a sufficient intake of healthy fats during childhood is directly linked to proper cognitive function, learning, and memory development.
6. How are lipids structured?
Unlike proteins or carbohydrates, lipids do not have a single, uniform structure. However, the most common type, triglycerides (fats and oils), are made from two basic components: a glycerol molecule and three fatty acid chains. The fatty acids are long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms. The properties of a lipid, such as whether it's a solid fat or a liquid oil, depend on the length and chemical structure of these fatty acid chains.
7. What is the difference between a fat and an oil?
Both fats and oils are types of lipids, specifically triglycerides. The main distinction is their physical state at room temperature.
- Fats are typically solid at room temperature. They are usually derived from animal sources and contain a higher proportion of saturated fatty acids. Example: Butter.
- Oils are liquid at room temperature. They are commonly sourced from plants and have a higher proportion of unsaturated fatty acids. Example: Olive oil. You can read more about the chemical difference between fats and oils here.
8. How do lipids help our body absorb certain vitamins?
Certain vitamins, known as fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), cannot dissolve in the watery environment of our blood. For the body to absorb these essential nutrients from the food we eat, they must be dissolved in fat. Dietary lipids act as carriers, packaging these vitamins and helping them pass through the wall of the small intestine into the bloodstream, where they can be transported to various parts of the body.
9. Where are lipids made inside a cell, and what is their role in the cell membrane?
Within a eukaryotic cell, most lipids are synthesized in an organelle called the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER). Their role in the cell membrane is crucial for life. The membrane is primarily a lipid bilayer made of phospholipids. These molecules have a 'water-loving' head and a 'water-fearing' tail, causing them to arrange into a two-layered sheet that forms a flexible and selective barrier. This structure, explained by the Fluid Mosaic Model, controls everything that enters and exits the cell.









