




Why Every Student Should Learn Periodic Table Facts
The ordered arrangement of all chemical elements in order of increasing atomic number—that is, the total number of protons in the atomic nucleus—is known as the periodic table or the full periodic table of the elements.
The "periodic law," which describes a recurring pattern in which elements in the same column (group) have comparable properties, is present when the chemical elements are grouped in this way. Dmitry I. Mendeleyev's original discovery, which was made in the middle of the 19th century, has had immeasurable significance for the advancement of Chemistry.
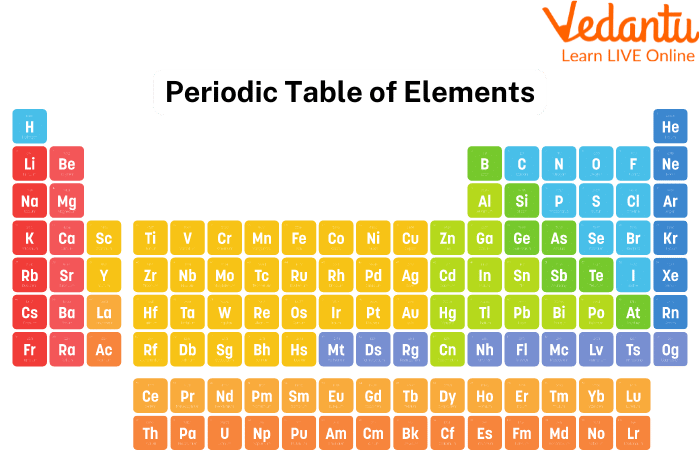
Periodic Table Elements
Significance of the Atomic Number
An atomic number is equal to the total number of protons in an atom. The fact that the order of elements in the periodic system is determined by their atomic numbers, the integers of which is equivalent to the positive electrical charges of the atomic nuclei represented in electronic units, was not truly understood until the second decade of the 20th century.
Better Knowledge about Periodic Table
In the years that followed, significant advancements were achieved in our understanding of how the electrical structure of atoms and molecules relates to the periodic law. The legislation, which stated the only relationship between the elements that were known at the time it was written, has gained more importance as a result of its clarification and is still widely used today.
The skill of differentiating between chemical substances saw rapid development in the early 19th century, which led to the accumulation of a great body of information about the chemical and physical characteristics of both elements and compounds.

Oxygen Atom
Facts about Periodic Table
The Periodic table now contains a total of 118 elements. Here are some facts about the periodic table.
Hydrogen (H) is the first element and oganesson (O) is the last element (Og).
The first Periodic Table was produced by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev. The contemporary Periodic Table groups elements with increasing atomic numbers as opposed to Mendeleev's table, which arranges elements according to their rising atomic weight.
The Periodic Table is controlled by the International Union of Pure Applied Chemistry IUPAC.
The element that is most prevalent in the universe is hydrogen (H). It accounts for roughly 75% of the entire observable cosmos.
The second most prevalent element in the universe is helium. Over 99% of the observable universe is made up of hydrogen and helium.
The first element to be created artificially was technetium (Tc). In 1937, it was first synthesised.
All the periodic table element symbols are missing one letter: J.
The most recent names of the four elements are 113, 115, 117, and 118. Nihonium (Nh), Moscovium (Mc), Tennessine (Ts), and Oganesson were authorised as the names and symbols for these elements by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry on November 28, 2016. (Og).
The systematised literature of Chemistry as well as the laboratory arts by which chemistry is transmitted as a living science from one generation of chemists to another are based on the classification of chemical knowledge, which soon became necessary due to the rapid expansion of chemical knowledge.
Which superhero is your favourite? Thor, the Nordic god of thunder, is the name of the element thorium (Th).

Thor and Thorium
Conclusion
The periodic table appears to be incredibly complicated at first. In actuality, it is a huge grid that contains every element that exists. By atomic number, the elements are organised in descending order. The number of protons in an atom's nucleus is known as the atomic number.
The elements are arranged in such a way that those with comparable qualities (properties) are grouped. The periodic table features columns that run up and down and rows that run left to right, just like any other grid. The columns are known as groups, and the rows are known as periods.
FAQs on Fascinating Facts About the Periodic Table
1. What is the modern periodic law, and why is it important?
The modern periodic law states that the physical and chemical properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number. This is critically important because it provides a logical and highly predictable framework for organising all known elements. This arrangement allows scientists to understand the relationships between different elements and even predict the characteristics of elements that have not yet been discovered.
2. What is the main significance of an element's atomic number in the periodic table?
The atomic number (Z) of an element is its defining characteristic. It represents the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, which is unique to that element. The entire periodic table is arranged in increasing order of atomic number, which directly determines the element's position and, consequently, its electron configuration and chemical behaviour. It is the fundamental organising principle of the modern table.
3. What are some interesting facts about the periodic table's structure?
Here are a few key structural facts about the periodic table:
The horizontal rows are called periods, and elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
The vertical columns are called groups. Elements in the same group typically share similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons.
The letter 'J' is the only letter in the alphabet that does not appear as an element symbol on the periodic table.
The vast majority of elements are metals, which are located on the left side and in the centre of the table.
4. Are all elements on the periodic table found in nature?
No, not all elements are natural. Elements with atomic numbers 1 (Hydrogen) through 94 (Plutonium) occur naturally, although some are found only in extremely trace amounts. Elements with atomic numbers greater than 94 are known as synthetic elements. These are created artificially in particle accelerators and are generally highly radioactive and unstable, with very short half-lives.
5. What is the rarest naturally occurring element on Earth?
The rarest naturally occurring element in the Earth's crust is Astatine (At), with atomic number 85. It is a halogen and is extremely radioactive. It is estimated that less than one gram of astatine exists on the entire planet at any given moment because it is only produced through the decay of heavier elements and it decays very quickly itself.
6. How can you predict an element's basic properties just by its position in the periodic table?
An element's position reveals key information about its properties. Its group number often indicates its number of valence electrons, which governs its chemical reactivity and bonding behaviour. Its period number tells you the principal energy level of its outermost electrons. For example, any element in Group 1 (like Lithium or Sodium) will be a highly reactive alkali metal, while any element in Group 18 (like Helium or Argon) will be a very unreactive noble gas.
7. If Mendeleev's original table was based on atomic mass, why was it so successful?
Mendeleev's table was remarkably successful because, for most elements, atomic mass increases in the same general order as atomic number. His true genius, however, was in prioritising periodic properties over strict mass order. When the properties of an element didn't fit, he was bold enough to leave a gap or even reverse the order of elements (like Tellurium and Iodine) to keep elements with similar behaviours in the same group. This focus on chemical patterns allowed him to correctly predict the existence and properties of undiscovered elements.
8. Why is it so difficult for scientists to create element 119 and add it to the table?
Creating element 119 pushes the boundaries of current technology because superheavy elements are incredibly unstable. The process requires smashing lighter atomic nuclei together with immense energy, hoping they will fuse. The probability of a successful fusion event decreases dramatically as the target element gets heavier. Furthermore, any atoms of element 119 that might form are predicted to have extremely short half-lives, likely decaying in microseconds, which makes detecting and confirming their existence an enormous scientific challenge.









