




What do You Know About Growth?
As we start learning about growth in plants we first need to ask ourselves about what we already know about growth in general.
One can define growth in several ways such as increase in the number of cells in our body or increase in the size or girth of a tree. The growth pattern differs in us humans from that seen in plants. Unlike humans plants continue to grow throughout their life. In this article we will study a little in detail about the growth pattern seen in plants.
Growth is a size expansion. A living object keeps expanding in numerous ways throughout its lifespan. One cell in a living creature becomes two identical cells through the process of cell division. Then, those cells can also divide. As the process progresses, the living thing grows.
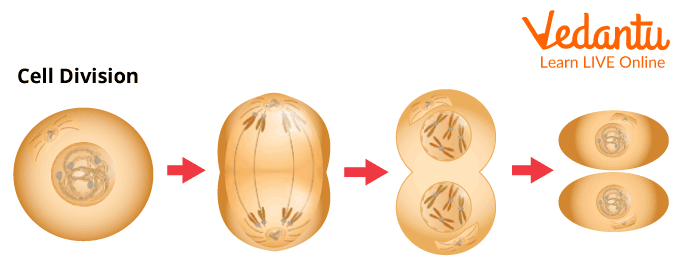
Cell Division Process
Growth in Animals
Growth is a natural process in any living being including animals. Growth in animals happens when the cells inside the organism start to divide and multiply. The speediest cell division occurs in an unborn newborn mammal. The animal's cells continue to divide after birth, causing it to grow larger.
An animal's cell division slows down as it ages. Cell division mostly takes place in mature animals to replace aged and dead cells. After birth, several animal organ systems experience minimal cell division or development. For instance, the brain's nerve cells are produced long before an animal is born. Animals' other organs develop during the course of a lifetime. For instance, the liver can create new cells whenever it wants.
Growth Cycle in A Cat
Growth in Plants
The division of cells is necessary for plant growth. A little plant begins to split its cells while it is still inside its seed. Cell division stops in specific parts of the developing plant as soon as the root tip, shoot tip, and small leaves appear. At the tip of the shoot, brand-new cells enable the development of stems and leaves. New cells can continue to divide in places like the root and shoot tip. Some plant tissues also go through cell division. These tissues aid in transporting moisture from the earth to the leaves. In addition, they aid in the movement of sugar from the leaves to the remainder of the plant.
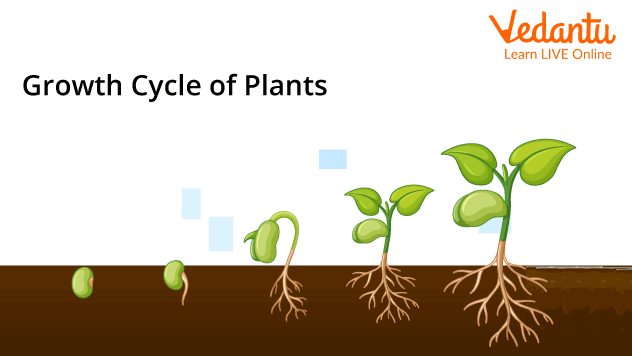
Growth Cycle of a Plant
What are the Different Factors Affecting Growth?
1. Environment
The surroundings or environment of a living thing might impact its growth. For example, temperature and light are environmental factors that can either hinder or accelerate development.
2. Genes
Each plant and animal has a specific growth strategy. Growth seldom happens by accident. Genes, the fundamental building blocks of heredity, govern how big and how shaped plants and animals are. They convey data about a living object, including details about its characteristics. Within each of the cells that make up, a living creature is genes.
3. Hormones
Hormones are produced by almost all living things that have more than one cell. Chemicals called hormones instruct cells and other body components to carry out certain tasks.
Solved Questions
1. At what stage of animal life is the growth at its fastest rate?
Ans: The speediest cell division occurs in an unborn newborn mammal. The animal's cells continue to divide after birth, causing it to grow larger.
2. Name the factors affecting the growth process.
Ans: The factors affecting the growth process are:
Genes
Hormones
Environment
3. How does growth in plants take place?
Ans: A little plant begins to split its cells while it is still inside its seed. Cell division stops in specific parts of the developing plant as soon as the root tip, shoot tip, and small leaves appear. New cells can continue to divide in places like the root and shoot tip.
Summary
A growing organism's growth in size and changes in shape are dependent on the individual's increased quantity and amount of cells. Growth is a size expansion. A living entity grows as the size and quantity of its cells increase. The animal's cells continue to divide after birth, causing it to grow larger. An animal's cell division slows down as it ages.
Cell division mostly takes place in mature animals to replace aged and dead cells. After birth, several animal organ systems experience minimal cell division or development. The division of cells is necessary for plant growth. A little plant begins to split its cells while it is still inside its seed. Cell division stops in specific parts of the developing plant as soon as the root tip, shoot tip, and small leaves appear.
FAQs on Growth in Animals and Plants: How Do They Grow?
1. How does plant growth vary from animal growth?
Animals grow differently from plants in terms of how they do. All body parts of juvenile animals develop as they get older until they reach a size that is genetically predetermined for each species. On the opposite hand, plant growth is limited to specific meristematic tissue regions and persists throughout the life of the plant.
2. What is necessary for growth in plants?
The division of cells is necessary for plant development. A little plant begins to split its cells while it is still inside its seed.
3. What is cell division?
Cell division is the process through which a living cell divides and forms two daughter cells. It is a very important process as it helps in maintaining the cells in our bodies. In our body cell division is used for both repairing and replacing the damaging cells in our body and also for generating new cells, as cells in our body also have a limited life span after which they die so it is important for our body to make new cells periodically to replace them.









