




Key Parts and Working of the Human Brain for Students
The brain is the largest and most complex organ in the body. It has more than 100 billion neurons or brain cells that form numerous synapses in the body for communication. It acts as a controlling centre and manages our thoughts, emotions, movement, vision, breathing, touch, temperature, hunger, and every vital function. The brain and the spinal cord make the CNS or central nervous system.
Any damage to the brain or spinal cord due to a sudden jerk, accident, trauma, or disease may hamper their functioning and can lead to death in severe cases. Therefore, we have the skull outside the brain, which acts as a shock absorber and protects it from damage.
Human Brain
What is the Human Brain Composed of?
The human brain weighs around 3 pounds (1.4 kilograms) in an average adult. It is composed of organic matter. Two-thirds of the brain is made of fat, and the remaining is a combination of proteins, water, salts, and carbohydrates. It contains nerves and blood vessels.
How does the Brain Work?
The human brain collects and sends electrical and chemical signals throughout the body. Each signal determines a different process, and our brain interprets it. Some make us feel tired, while others may cause pain.
However, the interesting fact is that it keeps some messages within itself, and others are spread throughout the body through nerves. These messages are conveyed by neurons or nerve cells. These are responsible for collecting sensory input from the outer environment and sending commands to muscles to perform functions.
What are the Main Parts of the Brain and their Functions?
The human brain has three main parts; cerebrum, brainstem, and cerebellum. Let us understand these using the brain parts diagram given below.
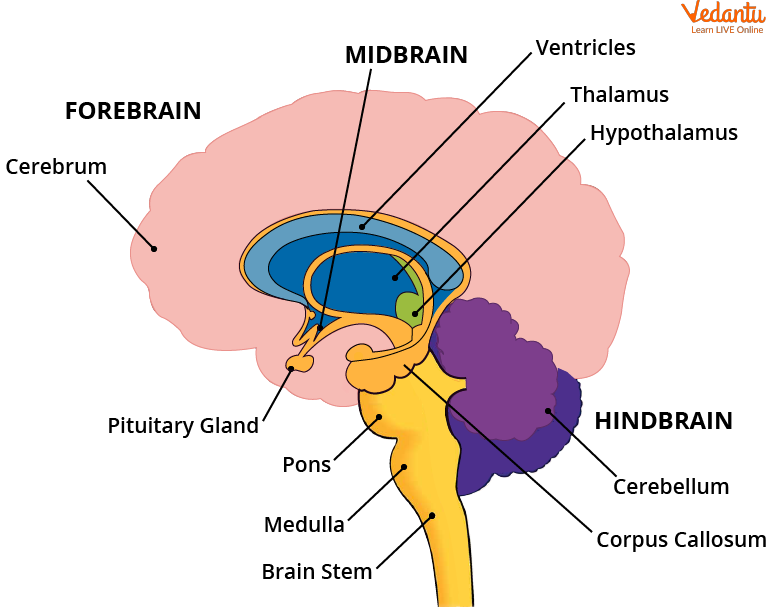
Human Brain Parts
Cerebrum
The cerebrum is the frontal and the largest part of the brain. It regulates temperature and initiates and coordinates movements. Other parts of the cerebrum control speech, problem-solving, reasoning and thinking abilities, judgement, vision, hearing, touch and learning, and emotions.
Refer to the cerebrum diagram for better understanding.
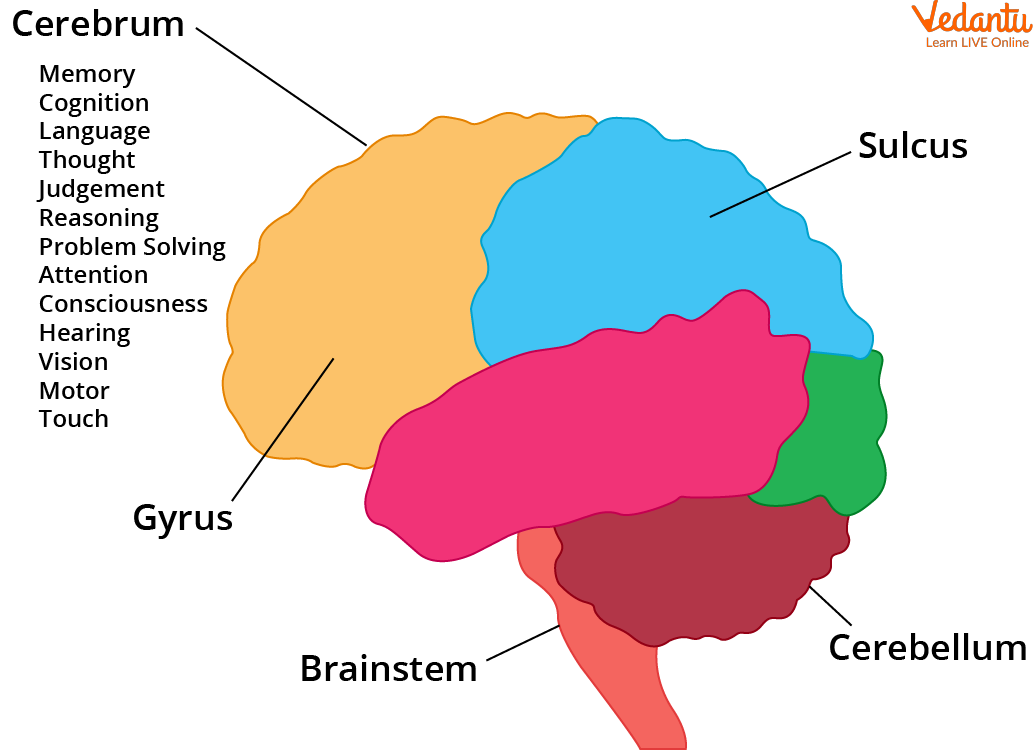
Cerebrum
Brainstem
The brainstem is the middle part of the brain that connects the cerebrum and the spinal cord. The brainstem is classified into the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla as shown in the brainstem diagram.
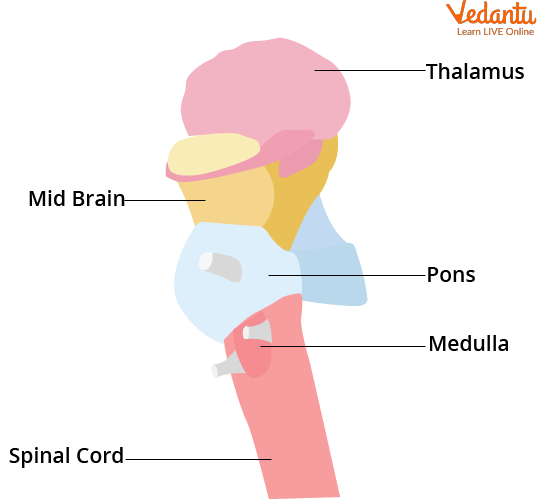
Brainstem
1. Midbrain: The midbrain is a complex structure and has different types of neurons, layers, and other structures. It facilitates functions from movement and hearing to analysing environmental changes and responses.
2. Pons: It is the second-lowest structure of the brainstem and lies above the medulla. It contains nerves that are connected directly to the brain. These nerves are important and help in controlling the senses and various parts of the mouth and face. The pons enables different functions, such as sleep, tear production, blinking, chewing, focusing vision, hearing, pain management and feeling, control and coordination, and facial expressions.
3. Medulla: It is at the bottom of the brainstem. It is the meeting point for the brain and the spinal cord. Functions of the medulla include; managing and controlling heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, carbon dioxide, and oxygen levels. It produces reflexive actions or involuntary movements that occur after exposure to a stimulus. These can include sneezing, coughing, swallowing, and vomiting.
Cerebellum
It is a structure situated at the back of the brain. It is divided into two hemispheres that control muscular activities, such as walking, balance, posture, speech and learning motor behaviours.
The Spinal Cord
The spinal cord runs at the back of the body from the bottom of the medulla through a large opening at the bottom of the skull. It is supported by the vertebral bones, which prevent it from external jerks or damages. It helps in receiving and sending signals to and from the brain to other body parts. It enables reflex actions, balance and coordination, mobility, and sensory functions.
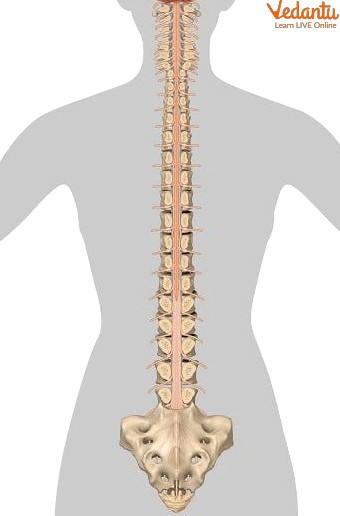
Spinal Cord
Sample Questions
State whether the statements mentioned below are correctly stated or not:
1.The cerebrum is divided into two hemispheres by a deep groove.
Ans: True.
2.The cerebellum is the main part of the forebrain.
Ans: False, the cerebrum is the main part of the forebrain.
3.The brain is protected inside the skull.
Ans: True
4.The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord.
Ans: True
Learn by Doing
Complete the the statements that follow by filling in the blanks:
1.The forebrain is classified into ________ lobes.
Ans: four
2.The brain is covered by a ______ layered meninges.
Ans: three
Segregate the given parts of the brain into the given categories:
Forebrain
Midbrain
Hindbrain
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Thalamus
Pons
Medulla
Hypothalamus
Lobes for vision
Lobes for hearing
Ans: Forebrain: cerebrum, thalamus, hypothalamus
Midbrain: lobes for vision, lobes for hearing
Hindbrain: cerebellum, pons, medulla.
Summary
The brain is the vital organ of the human body. It is like an intelligent machine that controls different functions ranging from managing movements to sensory activities. It consists of billions of neural cells that help in receiving and processing information.
FAQs on Understanding the Human Brain
1. What are the three main sections of the human brain and what is the function of each?
The human brain is primarily divided into three main sections: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brainstem. Each plays a vital role:
- Cerebrum: This is the largest part of the brain and is responsible for higher-level functions like thinking, learning, memory, and emotions. It also processes information from our senses.
- Cerebellum: Located at the back of the brain, the cerebellum's main job is to control balance, movement, and coordination. It helps us perform smooth, precise actions.
- Brainstem: This part connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls essential life functions that we don't think about, such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
2. What is the importance of the four lobes of the cerebrum?
The cerebrum is divided into four lobes, each specialising in different tasks:
- The Frontal Lobe is crucial for problem-solving, planning, and personality.
- The Parietal Lobe manages sensations like touch, temperature, and pain.
- The Temporal Lobe is responsible for hearing, language comprehension, and memory.
- The Occipital Lobe is dedicated to processing and interpreting everything we see.
3. How does the brain send and receive messages from the rest of the body?
The brain communicates with the body through the nervous system. The brainstem acts as a relay station, connecting the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord. The spinal cord is a long bundle of nerves that runs down the back, sending motor commands from the brain to the muscles and carrying sensory information from the body back to the brain.
4. Why is the cerebellum so important for everyday activities like playing sports or writing?
The cerebellum is vital for these activities because it controls fine motor skills, balance, and coordination. When you play a sport or write, your cerebellum is constantly making tiny adjustments to your muscle movements to ensure they are smooth and accurate. Without it, actions would be clumsy, shaky, and uncoordinated.
5. Is it true that humans only use 10% of their brain?
No, this is a popular myth. Brain scans show that we use virtually every part of our brain, and that most of the brain is active almost all the time. While you might only use a specific part for a certain task, like talking or listening, you use all of your brain over the course of a day for different functions.
6. What is the key difference between a voluntary action and a reflex action?
The main difference lies in conscious control. A voluntary action, like picking up a book, is a deliberate choice controlled by the cerebrum (the thinking part of your brain). In contrast, a reflex action, like pulling your hand away from a hot object, is an automatic and incredibly fast response that is processed by the spinal cord to protect the body from harm, without involving the brain for the initial decision.
7. How does understanding the human brain help with studying and learning?
Understanding how the brain works helps you learn more effectively. For example, knowing that the brain forms stronger connections through repetition explains why revision is important. Understanding that the brain needs rest to consolidate memories shows why getting enough sleep after studying is crucial for remembering information for exams.
8. What are some simple examples of how different parts of the brain work together?
Think about catching a ball. Your occipital lobe processes the visual information of the ball coming towards you. Your cerebellum calculates its path and coordinates your hand and body movements. Your frontal lobe makes the decision to catch it. All these parts work together in an instant to complete the action.









