




Why Are Ribosomes Essential for Plant Cell Survival?
All living things, plants, animals, and even bacteria, are made up of cells. Thus, the cell is the smallest functional and structural unit of life. Each cell contains many other smaller structures which perform essential life functions. These structures are known as organelles. The nucleus (the brain of the cell) is an example of an organelle.
Ribosomes are essential organelles present in cells. In plant cells, ribosomes are located in the cytoplasm (liquid inside the cell) or attached to the cell membrane (covering of the cell). Let us read ahead to know more about ribosomes and their functions.
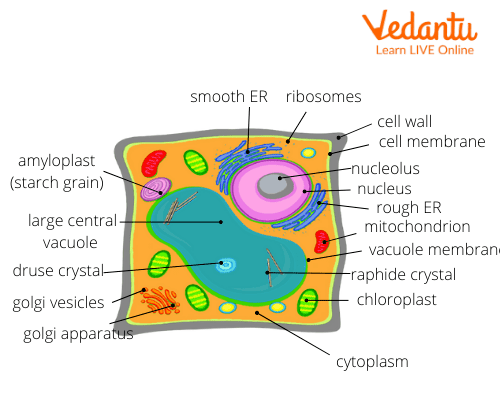
Ribosomes in Plant Cell
Structure of Ribosomes
Ribosomes are composed of a special type of RNA called ribosomal RNA or rRNA. They are circular in appearance under a microscope. They are granular in structure and are made up of two parts - A large subunit and a small subunit.
The ribosomal large subunit is called the 60S in plant cells and contains the area where proteins are made.
The ribosomal small subunit is called the 40S in plant cells and contains the area through which instructions about which proteins to make are received.
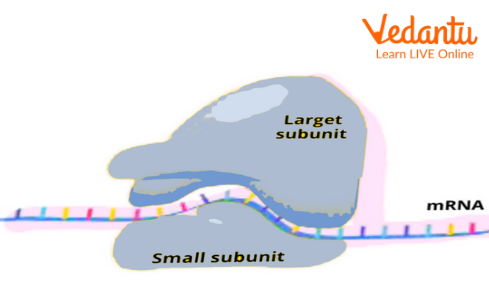
Structure of Ribosomes
Functions of Ribosomes
The primary function of ribosomes is to make proteins in their simplest forms - amino acids. Essentially, they act as factories of the cell. In animal cells, the function of ribosomes remains the same. As many different types of proteins need to be produced, the ribosomes get specific instructions on how to make each protein through Messenger RNA (Ribonucleic acid).
The mRNA carries these instructions in the form of a code only ribosomes understand, and this code acts as an instruction book telling the RNA how to make a specific protein. The production of amino acids begins only once the ribosome receives the start instruction (start codon). Then the ribosome moves down the mRNA reading the instructions on which amino acid to produce until it receives the stop instruction (stop codon)
The Ribosomes also help link these basic forms of proteins to help create more complex proteins. It does so by attaching one amino acid to another in specific ways to create specific proteins (amino acid chains). The way ribosomes are shaped helps them perform these functions. Due to its functions of creating amino acids from mRNA (a process called translation), ribosomes and molecules associated with it are together called the translation apparatus.
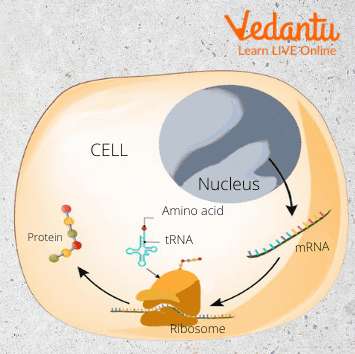
Function of Ribosomes - Translation
Few Interesting Facts about Ribosomes
Ribosomes are one of the only cell organelles found in prokaryotic cells.
Ribosomes get their name from RNA (RiboNucleic Acid).
Unlike other organelles within the cell, ribosomes do not have a protective layer or membrane.
They are produced in the nucleolus within the nucleus of the cell.
They are also found attached to the surface of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum.
They are also called Palade Granules after the scientist who discovered them - George Palade.
Summary
Ribosomes are small circular organelles found in the cell. They have two subparts - 60S and 40S. In simple words, their function is protein synthesis. They act like factories for the cell as they produce specific amino acids as per instructions given to them by mRNA. They also join these amino acids to create complex proteins. This was the discussion about ribosomes. We hope you liked reading about it. You can head to our website to read more about such interesting Science topics.
FAQs on Ribosomes in Plant Cells: Function and Importance
1. What is the primary function and structure of ribosomes in a plant cell?
The primary function of ribosomes in a plant cell is protein synthesis, a process also known as translation. Structurally, a ribosome is a non-membrane-bound organelle made of two main components: ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. It consists of two subunits, a larger one and a smaller one, which come together to read messenger RNA (mRNA) and assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains.
2. Where are ribosomes located within a typical plant cell?
In a plant cell, ribosomes can be found in several locations, which determines the destination of the proteins they synthesise. They are located:
- Freely suspended in the cytoplasm, where they make proteins for use within the cell.
- Attached to the outer surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), where they produce proteins that are exported out of the cell or embedded in cell membranes.
- Inside other organelles, specifically within the mitochondria and chloroplasts.
3. What is the difference between the ribosomes found in a plant cell's cytoplasm and those inside its chloroplasts?
The key difference lies in their size and type. The ribosomes in a plant cell's cytoplasm and on the RER are 80S ribosomes, which are characteristic of eukaryotic cells. In contrast, the ribosomes found within the chloroplasts (and mitochondria) are 70S ribosomes. This smaller 70S type is similar to the ribosomes found in prokaryotic cells and provides strong evidence for the endosymbiotic theory of organelle evolution.
4. How do the two subunits of a ribosome work together to synthesise a protein?
The two subunits of a ribosome have distinct roles that are coordinated during protein synthesis. The process unfolds as follows:
- The small subunit first binds to a molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA).
- The large subunit then joins the small subunit to form a complete, functional ribosome.
- The large subunit contains specific sites (A, P, and E sites) that accommodate transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which carry specific amino acids.
- As the ribosome moves along the mRNA template, it reads the genetic code and catalyses the formation of peptide bonds between the amino acids, building a polypeptide chain.
5. Why are ribosomes considered essential for all living cells, including prokaryotes which lack most other organelles?
Ribosomes are universally essential because they perform the fundamental task of protein synthesis, which is required for all life. Proteins function as enzymes, structural components, and signalling molecules. Unlike organelles such as the nucleus or mitochondria, ribosomes are not enclosed by a membrane. This is why prokaryotic cells, which lack membrane-bound organelles, can still possess ribosomes freely in their cytoplasm to produce the proteins necessary for their survival and metabolic functions.
6. What would be the immediate consequence for a plant cell if its ribosomes stopped functioning?
If a plant cell's ribosomes were to stop functioning, there would be an immediate and complete halt to all protein production. This would be catastrophic for the cell because it would be unable to:
- Produce new enzymes to carry out metabolic reactions like photosynthesis and respiration.
- Create structural proteins needed for cell repair and growth.
- Synthesise proteins required for nutrient transport and cell signalling.









