




Overview of Tree
We all know what a tree looks like because they are everywhere, but what exactly makes a tree a tree? A tree has a long and thick woody bark with leaves and fruits in some. So we can say that a plant is a tree if it has a woody stem, is perennial(a plant that exists for several years), and grows to be more than 10 feet tall. Trees provide us with many things, from the air to food, shelter, and many more.
The upper part of the tree is known as a shoot which includes branches, fruits, and leaves and the lower part is the root. There are more than 80,000 different types of trees in the world! Examples of trees include Apple, Mango, Palm, etc. Here, we are going to learn more about the uses of trees for kids.

Parts of a Tree
What is a Tree?
A tree is a plant with a tall structure consisting of a stem and branches to support leaves and a root system that anchors the stem as well as procures and stores essential growth elements such as water and nutrients. Trees are unique from other plants because they can and usually do live for decades and up to several millennia (the oldest known single-stem tree is a baobab in South Africa measured to be 6000 years old), grow successive layers of woody vascular tissue that is added from growth just under the bark to develop woody stems, and in most parts of the Earth grow taller than surface vegetation, ranging in height from several meters up to 115.55 meters (the tallest recorded tree is a giant redwood in northern California).
How do Trees Grow?
When the seed falls on the ground it starts its journey to becoming a tree. It needs water to sprout and break through the soil so that it can start growing roots. Older trees expand in height, width, and depth. By generating new cells at the terminals of their branches, trees increase in height. They develop deeper into the earth as roots that draw water and nutrients from the soil. Like the tips of the branches, the roots also grow. Additionally, the trunks and branches of trees enlarge. The cambium, which is the outer layer, is where this growth occurs. Tree trunks form rings because the cambium's growth ceases in the colder months. A year of growth is represented by each ring. By counting the rings on a tree, we may determine its age.
Types of Trees
1. Conifers and Evergreens Trees
Scales or needles are the names for the stiff, slender leaves on coniferous plants. The majority of them are evergreen, which means that their leaves don't change color and fall off in the fall but instead remain green all year round. Conifers are named after the cones that contain their seed. Coniferous trees include, among others, cypresses, pines, cedars, firs, and redwoods. The tallest and biggest types of life are said to inhabit conifer trees. These are enormous redwood or sequoia trees.

Conifers and Evergreen
2. Deciduous and Broadleaf Trees
The broadleaf tree is another kind of tree. The majority of broadleaf trees shed their leaves every fall because they are deciduous. Unlike conifers, which have narrow needles, broadleaf plants have broad leaves, hence the name. Flowers are also produced by these plants. Flowers can occasionally take the shape of foods we can eat, like fruit or nuts. Oaks, beeches, maples, elms, and birches are a few examples of broadleaf trees.

Deciduous and Broadleaf Trees
Functions of Trees
Now, let’s understand more about the functions trees in our lives:
A tree's leaves are essential for capturing sunlight for photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is a process that occurs when green pigment chlorophyll in leaves captures light and uses it to make sugars which then release oxygen.
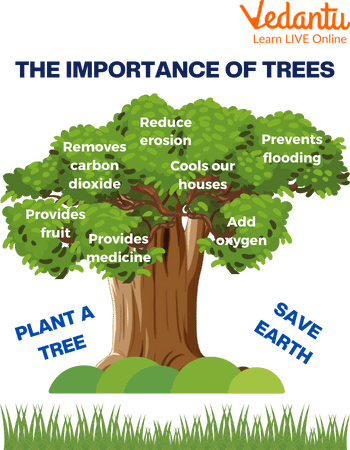
Trees give us oxygen, timber for buildings and fuel, and wood to make furniture and paper.
They also provide shade in the summertime, fixing atmospheric greenhouse gasses.
The trees help in preventing soil erosion with the help of their roots.
They also help in decreasing pollution by absorbing harmful emissions and filtering out the gasses.
They play a role in balancing the ecosystem by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
In addition, they also act as housing for different types of insects.
They absorb carbon dioxide emissions and decrease global warming.
Without trees, we would not have gasoline or paper which are very essential things.
Trees also make the environment stress-free.
Uses of Trees for Kids
A great source of fuel for cooking and stoking fires has historically been trees. A large portion of our food, including fruit and nuts, is also gathered from trees. But trees are also crucial to the environment. The main source of oxygen is trees. They take in air, which they then use to release oxygen and reduce carbon dioxide. Without trees, we couldn't survive. Additionally, trees offer us beauty and shade.
Importance of Trees
Summary
A plant or shrub that grows above ground with a trunk fixed firmly in the earth by its roots answers the question: what is a tree? From the article, tree for kids, we have also learned about trees, their features, types, and functions of trees. There are many different types of trees on Earth. Trees are of utmost importance for Humans and our environment. They provide the oxygen that we need to survive and also maintain carbon dioxide levels. Trees prevent soil erosion as the roots of trees strongly hold the soil and do not allow them to flow. Trees' natural changes have given them countless ways of helping the environment and are subject to multiple threats.
FAQs on Tree for Kids
1. How would you describe a tree in simple words for a child?
A tree is a very tall and strong plant that can live for a very long time. It has a main woody stem called a trunk, branches that spread out like arms, leaves that soak up the sun, and roots that hold it firmly in the ground.
2. What are the main parts of a tree and what do they do?
A tree has several important parts, and each one has a special job to do:
- Roots: They grow under the ground to hold the tree tight and drink water and nutrients from the soil.
- Trunk: This is the strong, woody main stem that supports the tree and carries water up to the leaves.
- Branches: These grow out from the trunk and hold the leaves, flowers, and fruits.
- Leaves: They are usually green and make food for the tree using sunlight, air, and water. This process is called photosynthesis.
- Flowers: Some trees have flowers which are colourful and can turn into fruits.
3. In what ways are trees important for people and animals?
Trees are very important for all living beings. They give us oxygen to breathe, which is essential for life. They also provide us with delicious fruits to eat, wood for making furniture, and shade to rest under on a hot day. For animals like birds and squirrels, trees are a home and a safe place to live.
4. What is the main difference between big trees and small plants like herbs or shrubs?
The main difference is their stem and size. A tree has a single, thick, hard, and woody stem called a trunk, and it is very tall. Small plants like shrubs have many smaller woody stems starting from the ground, while herbs have soft, green stems. Trees are much bigger and live longer than most small plants.
5. How do the roots of a tree help the land and soil?
Tree roots act like a strong net under the ground. They hold the soil together tightly, which stops it from being washed away by rain or blown away by the wind. This is called preventing soil erosion. The roots also help the ground absorb rainwater, which is good for the land.
6. How do trees help in keeping the air clean?
Trees work like natural air purifiers. They breathe in a gas called carbon dioxide, which is what we breathe out and what can make the air dirty in large amounts. In return, trees release fresh oxygen, which is the gas we need to breathe to stay alive. This amazing exchange helps keep our air healthy and clean.
7. If a tree loses all its leaves in winter, does that mean it is no longer alive?
No, the tree is not dead! Some trees, called deciduous trees, lose their leaves in winter to save energy and water. It's like they are taking a long nap or resting. When spring arrives with more sunlight and warmth, they wake up and grow new leaves, flowers, and branches. Other trees, called evergreen trees, keep their leaves all year round.
8. Why do some trees, like mango trees, give us fruit while others, like pine trees, do not?
This is because different types of trees reproduce in different ways. Trees like mango and apple trees grow flowers, and after pollination, these flowers develop into fruits that contain seeds. Other trees, like pine and fir trees, do not have flowers. Instead, they produce their seeds in woody cones. So, only flowering trees can produce what we call fruits.
9. As students, what are some simple ways we can help protect trees?
Even as students, we can do a lot to help protect trees! Here are a few simple ideas:
- Water them: Give water to young plants in your school or neighbourhood, especially during hot weather.
- Don't harm them: Avoid peeling their bark or breaking their branches.
- Plant more trees: Participate in tree plantation drives with your family or school.
- Spread awareness: Tell your friends and family about the importance of trees and why we need to save them.
10. What are some examples of trees that are commonly seen in India?
India has many beautiful and useful trees. Some of the most common ones you might see are the Banyan tree, which is our national tree and has hanging roots; the Neem tree, known for its medicinal properties; the Mango tree, famous for its sweet fruits; and the Peepal tree, which is considered sacred and gives a lot of oxygen.









