




About Rainwater
Rain is a very important part of our lives. It is the primary source of water for all of us. It helps maintain the water cycle and provides fresh water for everyone. However, rain does not only provide us with water. It also has a very calming and refreshing effect on us. The sound of raindrops can be very relaxing, and the smell of rain is very pleasant.
How Rain Helps Us?
There are many reasons why people prefer to use rainwater in houses and even for drinking. Uses of Rainwater can bring many benefits. We can use rainwater for various purposes. There are 10 Uses of Rainwater given below:
Drinking
Bathing
Cooking
Washing clothes
Watering plants
Washing vehicles and other equipment.
Rising vegetables
Cleaning floors
Irrigation
Fountain or fish pond refills

Rainwater
Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is a process of storing and collecting rainwater for human use. Every drop of rain on earth is like a blessing from God for the people. It is helpful for many purposes like domestic work, field irrigation, agriculture, animal husbandry, etc.
On a small scale, rainwater harvesting systems use simple rain barrels to store rainwater, while heavy pumps, large tanks, and refining techniques are used for large-scale storage.
It is a long-lasting and renewable process that helps conserve water for future needs. Today's water crisis is a matter of serious concern. Rainwater harvesting is a convenient way of conserving water.
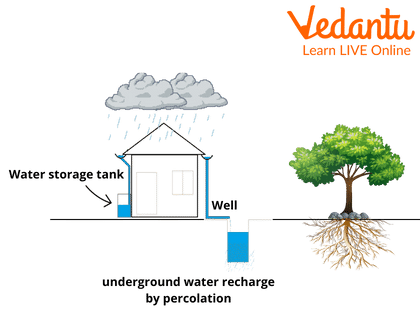
Rainwater Harvesting System at Home
Applications of Rainwater Harvesting
Maximum water can be saved for household work, and this water can be used for cleaning clothes, cooking, cleaning the house and bathing.
Huge amounts of water are wasted using clean water in the factory. In such a situation, storing rainwater and using it is a great way to save water.
There are some cities and villages where there is a lot of water scarcity. In such a situation. Harvesting water in such a place during the rainy month can reduce the water loss in the summer months by a few per cent.
Through rainwater harvesting, more and more rainwater can be collected so that farmers can use that water for agricultural purposes during the summer months for free and save water expenditure.
Why is Rain Important for Agriculture?
A good balance of rain and proper irrigation can lead to faster-growing plants, which can reduce germination times and the length of time between planting and harvesting. Crops depend on water during their entire life cycle to survive and thrive.
Rainwater Helps in Agriculture
Solved Questions
Write two uses of rainwater.
Ans: Uses of rainwater are:
Drinking
Washing clothes
Name the best method of collecting and storing rainwater.
Ans: Rainwater harvesting is the best method of collecting rainwater.
Learning by Doing
Write True or False.
Rainwater harvesting is a technique of collecting and storing rainwater.
We only use water for cooking food.
Rainwater is a secondary source of water.
Rain is the liquid form of water.
Summary
Rainwater is the most important and primary source of water. It is essential for everyone. As we have already studied in this chapter, we know how rainwater helps us and have seen various uses of rainwater in our daily life. We have also learnt about Rainwater harvesting, which is the most convenient and effective way to save rainwater.
FAQs on Uses of Rains
1. What is rain?
The water that rains from the clouds in the sky is called rain. Water evaporates from the surface of the earth and then cools down and falls in the form of water droplets which we call rain.
2. What is acid rain?
Rain washes dust and dirt from the air. But the rain is not always pure. Sometimes polluting chemicals from cars, factories and power plants get trapped in clouds. They contain harmful chemicals in the rain of these clouds. This polluted rain, known as acid rain, can cause damage to plants, animals, people and property.
3. What are the objectives of rainwater harvesting?
The following are the objectives of rainwater harvesting:
(1) To reduce the runoff loss.
(2) To avoid flooding the roads.
(3) To meet the increasing water demand.
(4) To raise the water level by recharging the groundwater.
(5) To reduce groundwater pollution.
(6) To supplement the groundwater supply during weak seasons.









