




Key Functions of the Nucleus: Why It’s Vital in Cells
A nucleus can be referred to as the brain of a cell. It is an essential part of a eukaryotic cell. Now let us learn what is a nucleus? It controls the processes happening inside a cell. The nucleus decides what proteins are formed, what organelles are present in the cell, etc.
The nucleus is the most significant structure inside the animal and plant cells. It is the cell's main control centre.
Nucleus
Where is it Present?
A nucleus is usually present in the centre of the cell but may be pushed to the periphery in some cells for various reasons. The nucleus is not found in all cells, though. It can be seen only in eukaryotic cells. A eukaryotic cell is defined by the presence of a nucleus, whereas a prokaryotic cell is determined by the absence of a nucleus.
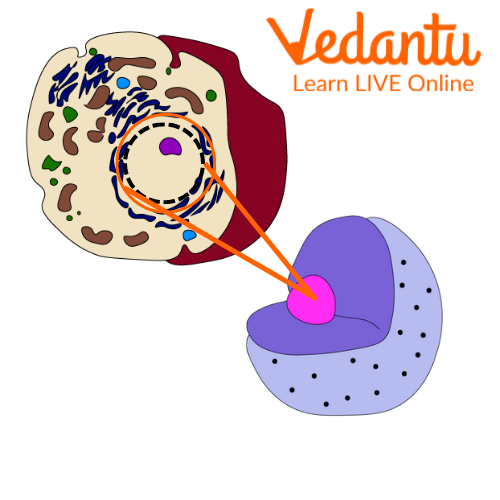
Location of Nucleus
There is usually a single nucleus in the cell, but many cells are seen with multiple nuclei.
Parts of Nucleus
The nucleus is made of many structures, and each of them has different but specific functions. The parts of a nucleus are:
Nuclear Envelope/Membrane: The nuclear envelope consists of two membranes; the outer membrane and the inner membrane. The nucleus is shielded from the rest of the cytoplasm in the cell by the envelope, which prevents specific molecules within the nucleus from escaping.
Nucleolus: The nucleolus is a huge structure in the nucleus that is responsible for the production of ribosomes and RNA.
Chromatin: Proteins and DNA make up chromatin. Before cell division, they assemble into chromosomes.
Nucleopores: Pores are tiny channels that go through the nuclear envelope. They allow tiny molecules, such as messenger RNA molecules, to pass through while keeping larger DNA molecules inside the nucleus.
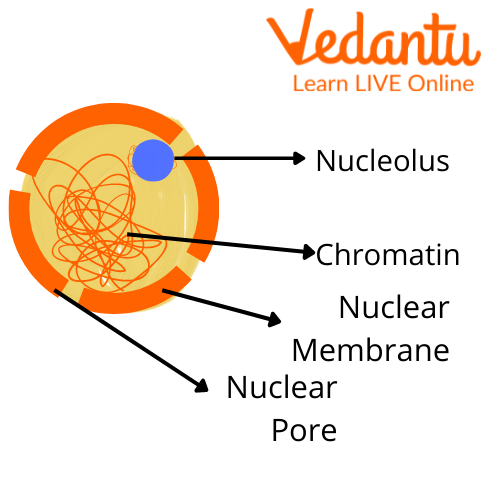
Parts of a Nucleus
Structure of Nucleus
The structure of a nucleus is formed of the parts of a nucleus which constitute the organelle. The nucleus is a globular or round organelle mostly found in the centre of a eukaryotic cell and is formed of a double-walled nuclear membrane. The nuclear membrane controls the exchange of substances within the cell and the nucleus. The ribosomes, genetic material, and other proteins lie in the nucleoplasm. The genetic material, mostly DNA, is packed properly into a chromosome.
Functions of Nucleus
Some of the functions of a nucleus are mentioned below.
DNA, which conveys genetic information, is the genetic substance of a cell that lies in the nucleus.
In the synthesis of RNA and ribosomes, the nucleus is crucial.
It is in charge of the cell's entire biological activity.
By directing gene expression, the nucleus aids in cellular differentiation.
Genetic variants also play a significant role in biological evolution.
Cell division and gene replication are controlled by the nucleus.
Conclusion
A cell's nucleus is sometimes referred to as its brain. It is an organelle that regulates internal cellular activities and is a crucial component of eukaryotic cells. What proteins are made and which organelles are present in the cell are determined by the nucleus. It performs similarly to the brain and is the primary control centre of the cell.
FAQs on What Does the Nucleus Do?
1. What is the nucleus and what is its main role in a cell?
The nucleus is a large, membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells, often described as the cell's "control center" or "brain". Its primary role is to house the cell's genetic material (DNA) and to coordinate all major cellular activities, including growth, metabolism, protein synthesis, and reproduction.
2. What are the key parts that make up the structure of a nucleus?
The nucleus has a complex structure designed to protect the cell's DNA. Its key parts include:
- Nuclear Envelope: A double membrane surrounding the nucleus that separates its contents from the cytoplasm.
- Nuclear Pores: Channels within the nuclear envelope that regulate the transport of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
- Nucleolus: A dense structure inside the nucleus responsible for producing ribosomes.
- Chromatin: The complex of DNA and proteins (histones) that condenses to form chromosomes during cell division.
- Nucleoplasm: The jelly-like substance within the nucleus that cushions the contents.
3. What are the two primary functions of the cell nucleus?
The two most critical functions of the nucleus are:
1. Storing Genetic Information: It contains the cell's entire hereditary material (DNA), which holds the instructions for every cellular process.
2. Controlling Cell Activity: It regulates gene expression, determining which proteins are made and when. This control dictates all cellular activities, from metabolism and growth to cell division.
4. Why is it so important for a cell's DNA to be kept inside the nucleus?
Keeping the DNA safely enclosed within the nucleus is vital for its protection. The nuclear envelope acts as a physical barrier, shielding the DNA from potentially harmful enzymes and chemical reactions occurring in the cytoplasm. This separation prevents damage or mutations to the genetic code, ensuring the long-term stability and integrity of the instructions needed for the cell to function and reproduce correctly.
5. How does the nucleus's position and function compare in plant and animal cells?
The fundamental function of the nucleus is identical in both plant and animal cells: it controls all cellular activities and stores the genetic material. However, its position often differs. In an animal cell, the nucleus is typically found near the center. In a mature plant cell, a large central vacuole fills with water and pushes the nucleus and other organelles to the periphery, against the cell wall.
6. If the nucleus is the cell's "brain," how do organisms like bacteria survive without one?
Organisms like bacteria are prokaryotic cells, which means they do not have a true, membrane-bound nucleus. Instead of being enclosed, their genetic material—a single circular chromosome of DNA—is located in a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid. While they lack the compartmentalisation of a nucleus, their DNA still directs all essential life processes like metabolism and reproduction, allowing them to survive and thrive effectively.
7. What is the importance of the nucleolus, the structure found inside the nucleus?
The importance of the nucleolus lies in its role as the primary site for ribosome synthesis. Ribosomes are the cellular machines responsible for translating genetic information into proteins. By manufacturing and assembling ribosomes, the nucleolus plays an essential, indirect role in controlling all protein production in the cell, making it crucial for growth, repair, and overall function.









