




EDTA Full Form - Definition, Uses & Importance in Chemistry
EDTA's full form is Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid. It is a powerful chelating agent that binds metal ions, preventing their harmful effects. EDTA is widely used in medicine, water treatment, food preservation, and laboratory research. It helps remove heavy metals from the body, prevents blood clotting in medical tests, and stabilises medicines.
Know The Chemical Structure of EDTA
EDTA is an amino polycarboxylic acid with four carboxyl (-COOH) groups and two amine (-NH₂) groups, allowing it to bind metal ions tightly. It is commonly found in its sodium salt form as disodium EDTA or tetrasodium EDTA in different applications.
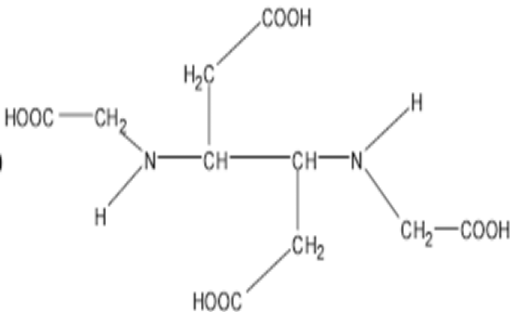
Main Function of EDTA
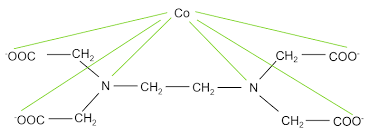
EDTA’s primary function is to act as a chelating agent, meaning it binds to metal ions and prevents them from interfering with chemical and biological processes. This property makes EDTA widely used in several field applications.
Here's How EDTA chelate with Metal Ion
What are the Uses of EDTA?
1. Medical Applications
Used in chelation therapy to treat heavy metal poisoning by binding lead, mercury, and other toxic metals for removal from the body.
Acts as an anticoagulant in blood sample collection to prevent clotting.
Used in dentistry to remove calcium deposits in root canal treatments.
2. Industrial Applications
Helps in water treatment by removing metal ions that cause scaling and corrosion.
Used in cosmetics and skin care products to stabilise formulations.
Added in food preservation to prevent oxidation and maintain freshness.
3. Laboratory & Research Uses
Used in buffer solutions to maintain metal-free conditions in biochemical experiments.
Commonly used in DNA and RNA extraction to prevent degradation caused by metal-dependent enzymes.
Must Know Safety & Side Effects While Dealing With EDTA
While EDTA is widely used, excessive exposure can cause low calcium levels, kidney problems, or allergic reactions. Medical use should always be under supervision.
Conclusion
EDTA is a powerful chelating agent with diverse applications in medicine, industry, and laboratories. Its ability to bind metal ions makes it essential in treatments, research, and manufacturing. Understanding EDTA’s role helps in appreciating its widespread importance in daily life and scientific advancements.
FAQs on EDTA Full Form- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid
1. What is the main function of EDTA?
EDTA primarily functions as a chelating agent, binding to metal ions to prevent unwanted chemical reactions.
2. How does EDTA work as a chelating agent?
EDTA surrounds and traps metal ions, preventing them from interfering with biological and chemical processes.
3. Why is EDTA used in medicine?
It is used in chelation therapy to remove toxic heavy metals like lead, mercury, and arsenic from the body.
4. What role does EDTA play in blood preservation?
EDTA binds calcium ions, preventing blood from clotting in laboratory tests and blood storage.
5. How does EDTA help in water treatment?
It removes metal impurities like iron, magnesium, and calcium, preventing scaling in pipes and machinery.
6. Why is EDTA added to food products?
EDTA prevents oxidation and spoilage by binding metal ions that cause food deterioration.
7. What is the use of EDTA in cosmetics and skincare?
It stabilises formulations by preventing metal ions from degrading creams, shampoos, and lotions.
8. Can EDTA be used for cleaning purposes?
Yes, EDTA is present in household and industrial cleaning agents to improve effectiveness by neutralising metal ions.
9. Is EDTA safe for human consumption?
In regulated amounts, EDTA is considered safe by food and health authorities, but excessive intake can lead to side effects.
10. Does EDTA have any impact on the environment?
EDTA is slow to degrade in nature, and its widespread use has raised concerns about its accumulation in water systems.



































