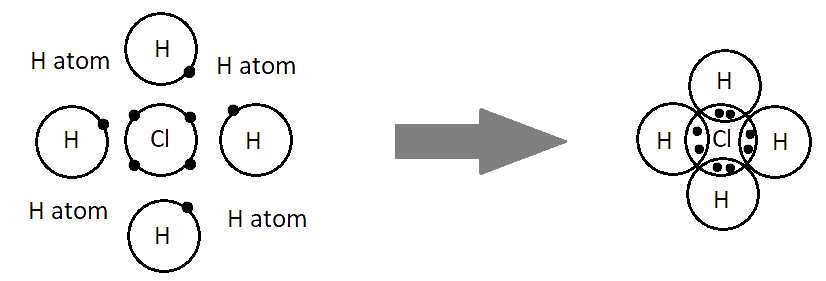
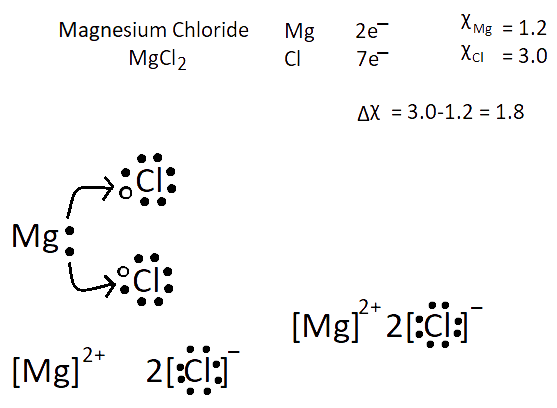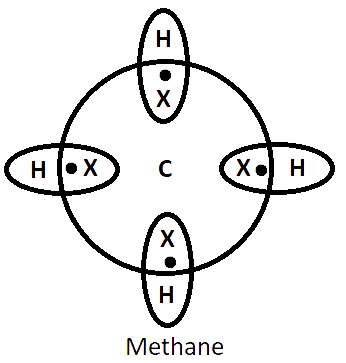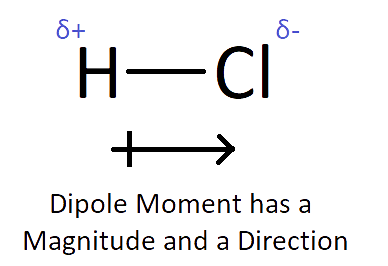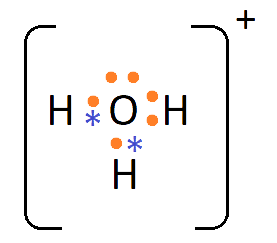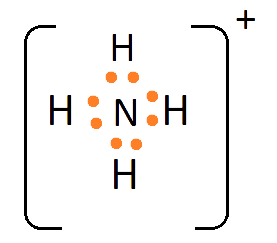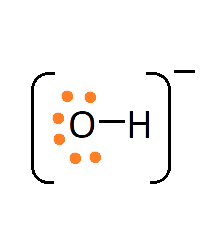Chemical Bonding Solutions for Class 10 Science ICSE Board (Concise - Selina Publishers)
FAQs on Chemical Bonding Solutions for ICSE Board Class 10 Science
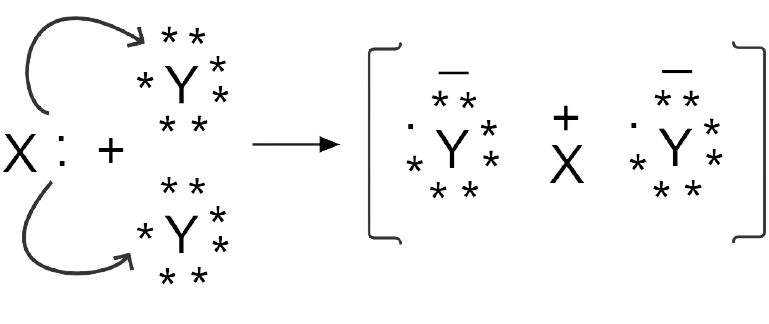
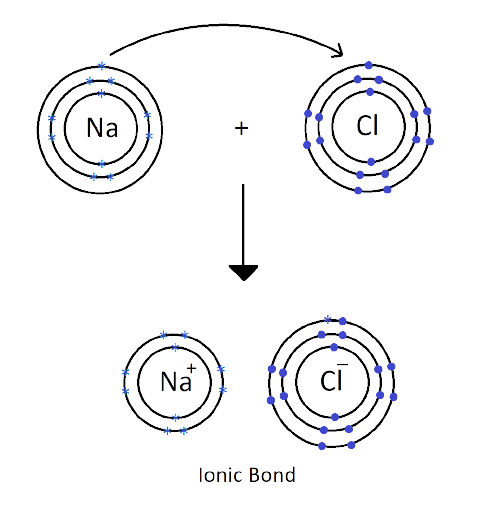
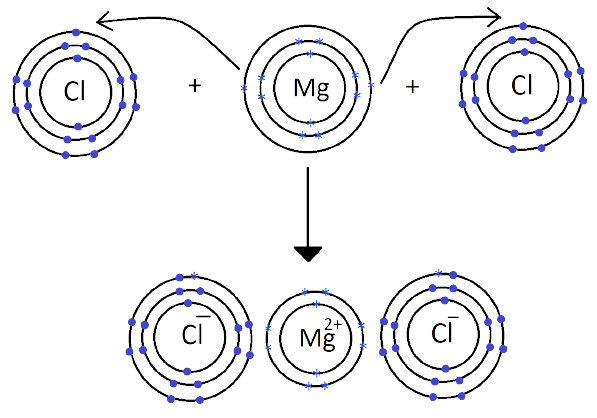
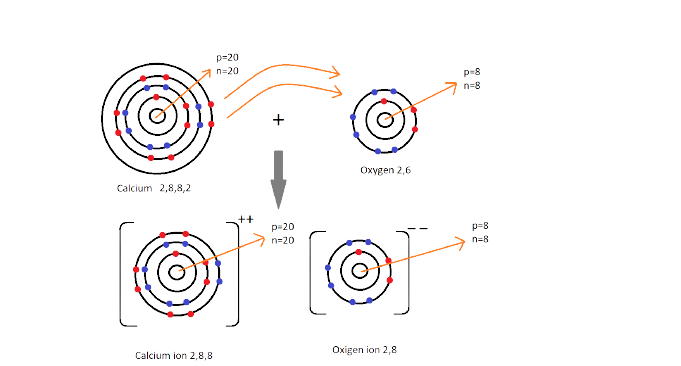
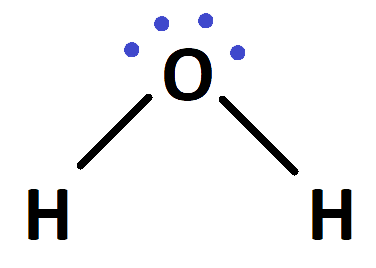
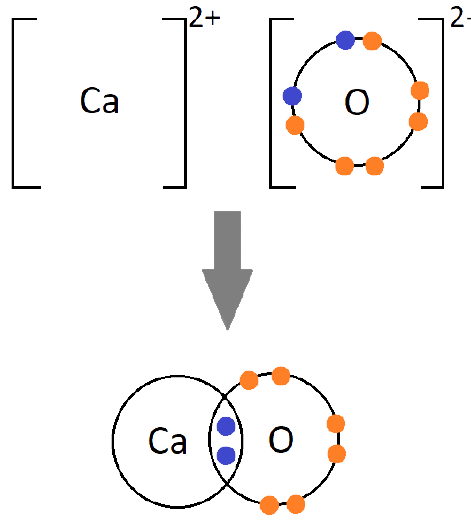
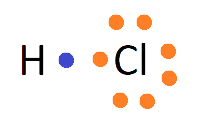
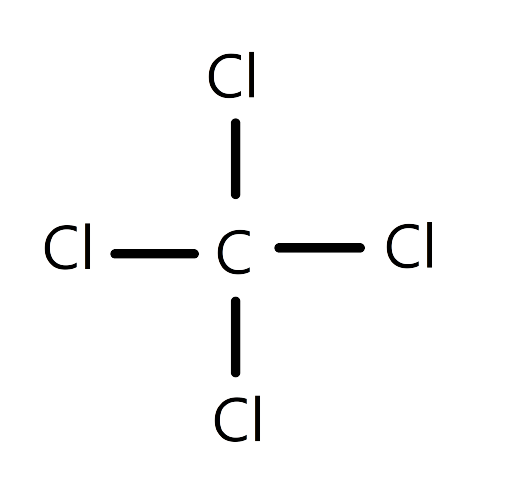
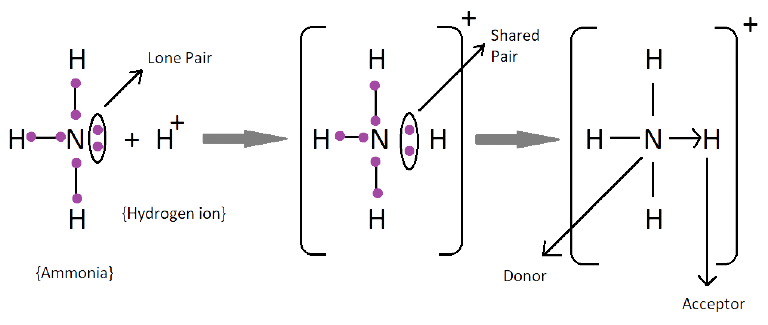
1. What are Ionic or Electrovalent Bonds with Examples?
Ionic bonds are developed by the electrostatic magnet of rudiments with contrary electric charges generated in the following way. Consider as illustration sodium and a chlorine snippet. In their commerce to form an emulsion, these two rudiments will suffer a rearrangement of their electronic configuration analogous to that of a near inert component. Sodium gives up the single electron of its remotest shell, therefore forming an appreciatively charged sodium cation or simply a cation with an electronic structure analogous to that of its nearest inert component neon. Chlorine, on the other hand, is close to the inert element argon, and thus, has to add an electron to its external shell to gain the electronic structure of the ultimate, therefore forming the negatively charged chlorine ion or anion. In this way two ions of contrary charge can be formed by the transfer of one electron from the sodium to the chlorine snippet, performing in the conformation of the electrostatically neutral sodium chloride, NaCl, known as common salt.
2. What is Ligand Field Theory (LFT)?
Ligand field proposition (LFT) describes the cling, orbital arrangement, and other characteristics of collaboration complexes (Schläfer and Gliemann, 1969). It represents an operation of a molecular orbital proposition to transition essence complexes. A transition essence is an element whose snippet has a deficient due-shell, or which can give rise to cations with a deficient d'sub-shell. It has nine valence infinitesimal orbitals, 5 (n)d, 1 (n + 1)s, and 3 (n + 1)p orbitals. These orbitals are of applicable energy to form related commerce with ligands. A ligand is an ion or patch that binds to a central essence snippet to form a collaboration complex. The LFT analysis is largely dependent on the figure of the complex, but utmost explanations begin by describing octahedral complexes, where six ligands coordinate to the essence (Miessler and Tarr, 2003). In alumina, (Al2O3), ionic cling is reported to be 60, while covalent cling is about 40. Similar cases are, thus, called ligand field cases.
3. How is metallic bonding formed?
Metallic bonds are created when the charge is spread over a larger distance as compared to the size of single atoms in solids. Substantially, in the periodic table, left rudiments form metallic bonds, for illustration, zinc and copper. Because cores are solid, their atoms are securely packed in a regular arrangement. They're so adjacent to each other so valence electrons can be moved down from their atoms. An “ ocean” of free, delocalized electrons is formed, girding a chassis of appreciatively charged essence ions. These ions are held by powerful attractive forces to mobile electrons.
4. What is a Metallic Bond?
The metallic bond can be described in an analogous manner as the covalent bond. The main contrast between these two bond types is that the ionization energy for electrons enwrapping the external orbitals of the metallic rudiments is much lower. In typical essence, like the alkali essence, these external orbitals are globular s-orbitals allowing lapping with over to 12 farther s-orbitals of the girding atoms. Therefore, the well-defined electron localization in bonds connecting pairs of atoms with each other loses its meaning.
Quantum-mechanical computations show that in large agglomerations of essence atoms the delocalized cling electrons enthral lower energy situations than in the free atoms; this would not be true for insulated “ essence motes”. The metallic bond in typical essence is non-directional, favouring structures corresponding to closest paddings of spheres. With adding localization of valence electrons, covalent relations beget diversions from spherically symmetric cling, leading to more complicated structures.
5. What is the role of Thermally Grown Oxide (TGO)?
The TGO plays a critical part in binding the ceramic subcaste to the metallic bond fleece deposited on the substrate. The composition of the TGO, as bandied before, is generally α-Al2O3 for alumina-forming bond fleeces. For NiCoCrAlY bond fleeces, minor quantities of spinels (Ni, Co) (Al, Cr) 2O4, and sometimes NiO, is also planted, particularly in the region of the TGO closer to the bond fleece. The growth rate of the TGO is affected by the eventual spallation of the TBC when it's cycled to high temperatures in an oxidizing terrain. Experimental as well as field data from aircraft gas turbine machines suggest that typical TGO consistency at TBC spallation is in the 6 to 7 μm range and clearly below 10 µm. Grounded on electron bitsy characterization, the general microstructural features of the TGO formed on overlay coatings of MCrAlY composition have been modelled by Lelait et al. (1992) .