Electrolysis Solutions for Class 10 Science ICSE Board (Concise - Selina Publishers)
Free download of step-by-step solutions for class 10 Science (Chemistry) Chapter 6 - Electrolysis of ICSE Board (Concise - Selina Publishers). All exercise questions are solved & explained by an expert teacher and as per ICSE board guidelines.
Access ICSE Selina Solutions for Chemistry Class 10 Chapter 6- Electrolysis
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Powdered sodium chloride (common salt) does not conduct an electric current, but it does so when ____ or when _____.
Ans: Powdered sodium chloride (common salt) does not conduct an electric current, but it does so when electrolyte or when melted .
(b) Molten lead bromide conducts electricity. It is called an____. It is composed of lead ____ and bromide _____. The lead ions are ____charged and are called_____. The bromide ____ are _____ charged and are called ______.
Ans: Molten lead bromide conducts electricity. It is called an electrolyte. It is composed of lead ions and bromide ions. The lead ions are positively charged and are called cations. The bromide ions are negatively charged and are called anions.
(c) Substances which conduct electricity in the solid state are generally ______.
Ans: Substances which conduct electricity in the solid state are generally metals.
(d) The electron releasing tendency of zinc is _____than that of copper.
Ans: The electron releasing tendency of zinc is more than that of copper.
(e) A solution of HCl gas in water conducts electricity because _____, but a solution of HCl gas in toluene does not conduct an electric current because_____.
Ans: A solution of HCl gas in water conducts electricity because it ionizes, but a solution of HCl gas in toluene does not conduct an electric current because it does not ionize into toluene.
(f) Pure water consists entirely of ………….. (ions/molecules).
Ans: Pure water consists entirely of molecules(ions/molecules).
(g) We can expect pure water …………… (will/will not) normally conduct electricity.
Ans: We can expect pure water will not (will/will not) normally conduct electricity.
(h) Electrolysis is the passage of……………. (electricity/electrons) through a liquid or a solution accompanied by a ………….. (physical/chemical) change.
Ans: Electrolysis is the passage of electricity (electricity/electrons) through a liquid or a solution accompanied by a chemical (physical/chemical) change.
2. Define the following terms:
(a) Electrolysis
Ans: It is the process of decomposition of a chemical compound in aqueous solutions or in molten state accompanied by a chemical change using direct electric current.
(b) Non-electrolyte
Ans: It is a compound that neither in solution nor in the molten state allows an electric current to pass through it.
(c) Cation and an anion
Ans: Ions carrying the positive charge are called cations.
Ions carrying the negative charge are called anions.
(d) Weak electrolyte
Ans: Electrolytes that allows small amount of electricity to flow through them and are partially dissociated in aqueous solution are called weak electrolytes.
3. What is the difference between:
(a) Modern explanation and Arrhenius explanation for the theory of electrolysis
Ans:
Modern Theory | Arrhenius Theory |
This theory states that water helps in the ionization of electrolytes. | This theory states that electrolytes are ionic in nature even in solid state, ions are held together by strong electrostatic force of attraction which makes the ions immobile. |
(b) Electrolytic dissociation and ionization
Ionization | Electrolytic dissociation |
It is the formation of positively and negatively charged ions. | It is the separation of ions present in ionic form. |
Polar covalent compounds show ionization. e.g. HCl, H2CO3, NH4OH etc. | Electrovalent compounds show dissociation. e.g. Potassium chloride , lead bromide, etc. |
(c) A cation and an anion
Ans:
Cation | Anion |
It is a positively charged ion. | It is a negatively charged ion. |
During electrolysis, cation moves to the cathode. | During electrolysis, anion moves to anode. |
Gain electrons and become the neutral atom. | Lose electrons and become the neutral atom. |
(d) Electrolytic dissociation and thermal dissociation
Ans:
Electrolytic Dissociation | Thermal Dissociation |
Electrolytic dissociation is the dissociation of an electrovalent compound into ions in the fused state or in aqueous solution state. | Reversible breakdown of a chemical compound into simpler substances by heating it. The splitting of ammonium chloride into ammonia and hydrogen chloride is an example. On cooling, they recombine to form the salt. |
(e) Strong electrolyte and weak electrolyte
Ans:
Strong Electrolyte | Weak Electrolyte |
Strong electrolytes allow large amounts of electricity to pass through it. | Weak electrolytes allow a small amount of electricity to pass through it. |
They are good conductors of electricity. | They are poor conductors of electricity. |
They completely dissociate into ions in aqueous solution. | They partially dissociate into ions. |
They only contain free ions. | They contain free ions as well as molecules. |
4. Name:
(a) A salt which is a weak electrolyte
Ans: Sodium carbonate
(b) A base which is a weak electrolyte
Ans: NH4OH
(c) An inert electrode and an active electrode
Ans: An inert electrode: graphite and Active electrode: silver
(d) A positively charged non-metallic ion
Ans: H+
(e) The electrode at which reduction occurs
Ans: Cathode
(f) A non-metallic element which is a conductor of electricity
Ans: Graphite
5. Electrolysis is a redox process. Explain.
Ans: Redox reactions are reactions where oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously. In the process of electrolysis, cations move to cathode and undergo reduction(gain of electron) while anions move to anode and undergo oxidation(loss of electron).
NaCl$\to $ Na+ + Cl-
Cathode : Na+ + e-$\to $ Na(reduction)
Cl-- e-$\to $ Cl(oxidation)
Cl + Cl $\to $Cl2
Overall reaction: 2NaCl $\to $2Na + Cl2
6. Classify the following substances under three headings:
Acetic acid, ammonium chloride, ammonium hydroxide, carbon tetrachloride, dilute hydrochloric acid, sodium acetate, dilute sulphuric acid.
a. strong electrolytes
Ans: dilute hydrochloric acid, dilute sulphuric acid, sodium acetate
b. weak electrolytes
Ans: acetic acid, ammonium hydroxide
c. non-electrolytes
Ans: carbon tetrachloride
7. Explain why:
a. Cu, though a good conductor of electricity, is a nonelectrolyte.
Ans: Copper is a good conductor of electricity due to the presence of free electrons. But copper does not dissociate into its ions in solution so considered to be non electrolyte.
b. Solid sodium chloride does not allow electricity to pass through.
Ans: In solid state, no free Na+ and Cl- ions are present. So sodium chloride will not allow electricity to pass through.
8. Choose A, B, C or D to match the descriptions
(i) to (v) below. Some letters may be repeated.
A. non-electrolyte
B. strong electrolyte
C. weak electrolyte
D. metallic conductor
i. Molten ionic compound
Ans: Strong electrolyte
ii. Carbon tetrachloride
Ans: Non- Electrolyte
iii. An aluminium wire
Ans: Metallic conductor
iv. A solution containing solvent molecules, solute molecules and ions formed by the dissociation of solute molecules.
Ans: Weak electrolyte
v. A sugar solution with sugar molecules and water molecules.
Ans: Non électrolyte
9. An electrolyte which completely dissociates into ions is:
a. Alcohol
b. Carbonic acid
c. Sucrose
d. Sodium hydroxide
Ans: d. Sodium hydroxide
Intext Questions
1. Name two substances in each case:
(a) Contain only molecules
Ans: Glucose, kerosene
(b) Contain only ions
Ans: NaCl and NaOH
(c) Contain ions as well as molecules
Ans: CH3COOH and NH4OH
2. Select the ion in each case that would get selectively discharged from the aqueous mixture of the ions listed below:
a. SO42-, NO3-, and OH-
Ans: OH-
b. Pb2+, Ag+, and Cu2+
Ans: Ag+
3. (a) Among Zn and Cu, which would occur more readily in nature as metal and which as ion?
Ans: Zn is more reactive than copper. Zn has more tendency to release electrons and thus Zn more readily occurs as ion while Cu as metal.
(b) Why cannot we store AgNO3 solution in copper vessels?
Ans: Copper lies above silver in electrochemical series so its Cu is more reactive than silver. So Cu displaces Ag from silver nitrate.
Cu +AgNO3 $\to$ Cu(NO3)2 + 2Ag
(c) Out of Cu and Ag, which is more active?
Ans: Cu is more reactive than Ag, Cu lies above Ag in the electrochemical series.
4. (a) How would you change a metal like Cu into ions?
Ans: By treating its salt with a more reactive metal.
(b) How would you change Cu2+ ions to Cu?
Ans: Cu2++2e-$\to $Cu
5. A solution of caustic soda (NaOH) in water or when fused, conducts an electric current. What is the similarity in these two cases?
Ans: In an aqueous state, the slightly negatively charged oxygen atoms of the polar water molecule pull on the positively charged sodium ions in the aqueous state. The mildly charged hydrogen atoms of water exert a similar force on the negatively charged chloride ions. As a result, the ions in solution become free. These free ions are electrical conductors.
The high temperatures required to melt the solid weaken the link between the particles in the molten state, allowing the ions to escape.
6. During electrolysis of an aqueous solution of sulphuric acid between platinum electrodes, two types of anions migrate towards the anode but only one of them is discharged.
(a) Name the two anions.
Ans: SO42- and OH-
(b) Name the main product of the discharge of anion at the anode and write the anode reaction.
Ans: OH- is discharged at anode and the main product of the discharge of OH- is O2
Reaction is :
OH- $\to $ OH +e-
4OH $\to $ 2H2O + O2
(c) Name the product at the cathode and write the reaction.
Ans: The product formed at cathode is hydrogen. The reaction is :
H+ + e- $\to $ H
H + H $\to $ H2
(d) Do you notice any change in colour? State why?
Ans: No change in colour is observed.
(e) Why is this electrolysis considered as an example of catalysis?
Ans: The breakdown of water molecules into ions is catalysed by dilute sulphuric acid, hence electrolysis of acidified water is an example of catalysis.
7. Copper sulphate solution is electrolysed using a platinum anode. Study the diagram given alongside and answer the following questions:
a. Give the names of the electrodes A and B.
Ans: A = Platinum anode, B = Platinum or copper cathode
b. Which electrode is the oxidising electrode?
Ans: A = Platinum anode
8. To carry out the so-called 'electrolysis of water', sulphuric acid is added to water. How does the addition of sulphuric acid produce a conducting solution?
Ans: Water is dissociated into H+ ions and OH- ions when sulfuric acid is added.
9. Choosing only words from the following list, write down the appropriate words to fill in the blanks (i) to (v) below: Anions , anode, cathode, cations , electrode, electrolyte, nickel , voltameter.
a. The electroplating of an article with nickel requires an (i) ____ which must be a solution containing (ii) ____ ions. The article to be plated is placed as the (iii) ____ of the cell in which the plating is carried out. The (iv) ____ of the cell is made from pure nickel. The ions that are attracted to the negative electrode and discharged are called (v) _____.
Ans:
i. Electrolyte
ii. Nickel
iii. Cathode
iv. Anode
v. Cations
b. When a molten ionic compound is electrolysed, the metal is always formed at …………… and the non-metal is formed at …………..
Ans: When a molten ionic compound is electrolysed, the metal is always formed at cathode and the non-metal is formed at anode.
c. Electrolysis of acidulated water is an example of ………… (Reduction/ oxidation/ redox reaction/synthesis).
Ans: Electrolysis of acidulated water is an example of redox reaction.
10. Explain the following :
(a) A solution of cane sugar does not conduct electricity, but a solution of sodium chloride is a good conductor.
Ans: Cane sugar is a molecule-only substance that does not contain any ions, even in solution. As a result, it is not an electrical conductor. Sodium chloride solution, on the other hand, has free mobile ions and permits electric current to pass through it. As a result, it is a great conductor of electricity.
(b) Hydrochloric acid is a good conductor of electricity.
Ans: Hydrochloric acid is a powerful electrolyte that totally dissociates in water. Electric current can travel through the solution because it contains free mobile ions. As a result, hydrochloric acid is a strong electrical conductor.
(c) During the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of NaCl, hydrogen ion is reduced at the cathode and not the sodium ion though both Na+ and H+ ions are present in the solution.
Ans: In the electrochemical series, hydrogen is placed lower, while sodium is at the higher position. This is due to the fact that H+ ions discharge more quickly at the cathode during electrolysis than Na+ ions and gain electrons more readily.
As a result, the H+ ion, rather than the Na+ ion, is reduced at the cathode.
(d) On electrolysis of dilute copper (II) sulphate solution, copper is deposited at the cathode but hydrogen gas evolves there. Explain why.
Ans: In the electrochemical series, copper is placed below hydrogen. Cu2+ on reduction is discharged as metallic copper in preference to hydrogen.
(e) When a dilute aqueous solution of sodium chloride is electrolysed between platinum electrodes, hydrogen gas is evolved at the cathode but metallic sodium is not deposited. Why?
Ans: Since hydrogen is much below sodium in the activity series, hydrogen is discharged at the cathode in preference to sodium.
(f) Zinc can produce hydrogen by reacting with acids but copper cannot. Explain.
Ans: Zinc is more reactive than hydrogen, so it displaces hydrogen from acids, but copper is less reactive than hydrogen, so it does not liberate hydrogen from acids.
Exercise Questions
Give reasons for the following:
(a) Electrolysis of molten lead bromide is considered to be a reaction in which oxidation and reduction go side by side i.e, a redox reaction.
Ans: Electrolysis of lead bromide results in the loss of electrons at the anode by the bromine and the gain of electrons at the cathode by the lead. As a result, oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously. Hence its a redox reaction.
PbBr2$\to $Pb2++2Br-
(b) The blue colour of aqueous copper sulphate fades when it is electrolyzed using platinum electrodes.
Ans: The blue colour of copper ions diminishes as Cu2+ ions decrease, and the solution eventually becomes colourless after Cu2+ ions are exhausted.
(c) Lead bromide undergoes electrolytic dissociation in the molten state but is a non-electrolyte in the solid state.
Ans: In the molten state, lead bromide dissociates into ions, but it does not dissociate in the solid state. When lead bromide is molten, the ions become free, but when it is solid, the ions are not free because they are packed tightly together due to electrostatic forces. As a result, in the molten state, lead bromide undergoes electrolytic dissociation.
(d) Aluminium is extracted from its oxide by electrolytic reduction and not by conventional reducing agents.
Ans: Because aluminium has a strong affinity for oxygen, it cannot be reduced by a reducing agent. As a result, electrolytic reduction is used to separate it from its oxide.
(e) The ratio of hydrogen and oxygen formed at the cathode and anode is 2:1 by volume.
Ans: 4H1+ at the cathode and 4OH- at the anode are required for electrolytic reactions, and two molecules of water are generated at the anode. Two molecules of hydrogen at cathode and one molecule of oxygen at anode are liberated for every two molecules of water.
2H2$\to $2H2(cathode)+O2(anode)
(f) In the electrolysis of acidified water, dilute sulphuric acid is preferred to dilute nitric acid for acidification.
Ans: Because HNO3 is volatile
(g) Ammonia is unionized in the gaseous state but in the aqueous solution, it is a weak electrolyte.
Ans: The chemical molecule ammonia is a covalent compound. In the gaseous state, it is unionised, but in aqueous solution, it yields NH4OH, which is a weak electrolyte that dissociates into ions.
(h) A graphite anode is preferred to other inert electrodes during electrolysis of fused lead bromide.
Ans: Graphite is unaffected by bromine vapours
(i) For electroplating with silver, silver nitrate is not used as electrolyte.
Ans: Silver nitrate is not utilised as an electrolyte for silver electroplating because the silver deposition is very fast and hence not very smooth and uniform.
(j) Carbon tetrachloride is a liquid but does not conduct electricity.
Ans: Carbon tetrachloride is a liquid and does not conduct electricity because it is a covalent compound and there are no free ions present and contain only molecules.
(k) Potassium is not extracted by electrolysis of its aqueous salt solution.
Ans: Potassium is not extracted from its aqueous salt solution by electrolysis as it can react with water.
2. a.Copy and complete the following table which refers to two practical applications of electrolysis
Anode | Electrolyte | Cathode | |
Silver plating of a spoon | Solution of potassium argentocyanide | ||
Purification of copper | |||
Extraction of sodium |
Ans:
Anode | Electrolyte | Cathode | |
Silver plating of a spoon | Plate of pure clean silver | Solution of potassium argentocyanide | Article to be electroplated |
Purification of copper | Impure copper | Solution of copper sulphate and dilute sulphuric acid | Thin strip of pure copper |
Extraction of sodium | Nickel | Fused sodium chloride | Iron |
b. Write the equation taking place at the anode for Q. 2(a).
Ans: i. Ag - e- → Ag+
ii. Cu - e-→ Cu2+
iii. Cl- - e- → Cl
Cl + Cl → Cl2
3. (a) Draw a labeled diagram to show how iron is electroplated with copper.
Ans:
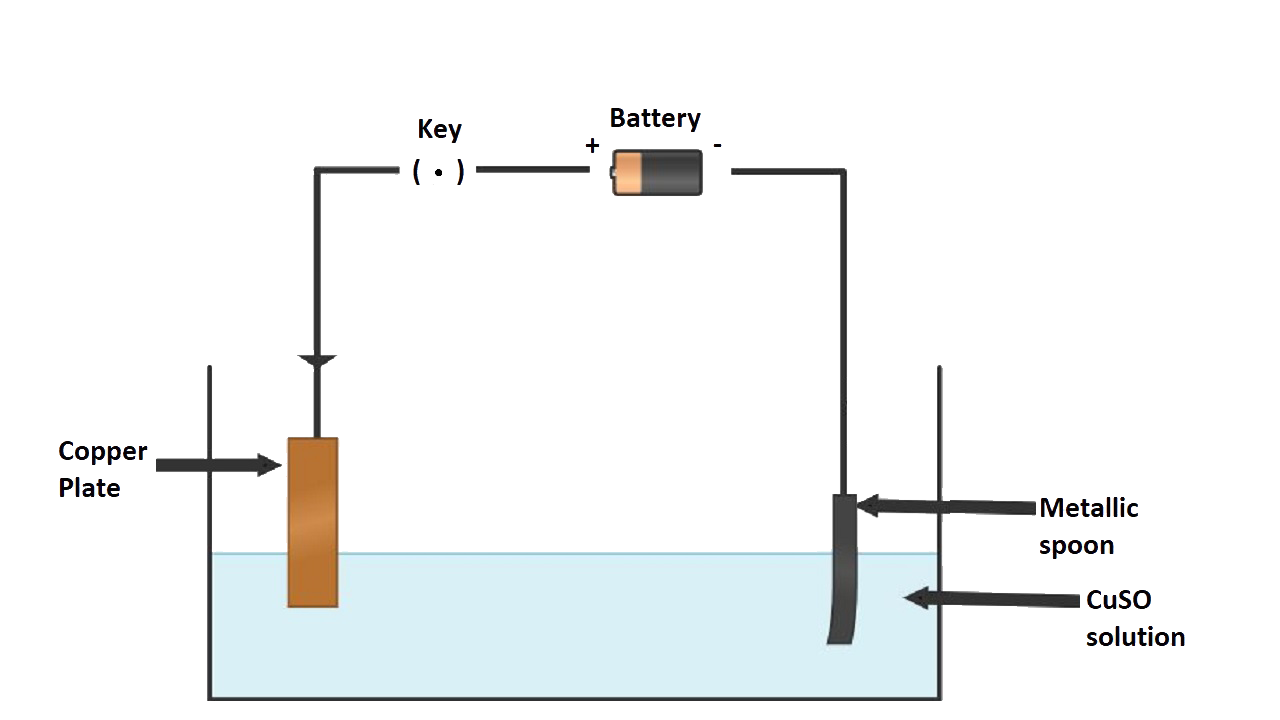
(b) Which solution is preferred as electrolyte, CuSO4 or FeSO4?
Ans: CuSO4 is preferred as an electrolyte.
(c) Describe what happens to the iron object and the copper rod.
Ans: The copper anode continuously dissolves as ions in solution and is replaced periodically. The electrolyte dissociates into Cu2+ ions which migrate towards the iron object taken as the cathode and are deposited as neutral copper atoms on the cathode.
Electrolyte: Aqueous solution of nickel sulphate
Dissociation: CuSO4 $\rightleftharpoons$ Cu2+ + SO42- H2O $\rightleftharpoons$ H+ + OH-
Electrodes:
Cathode: Article to be electroplated
Anode: Block of pure copper
Electrode reactions:
Reaction at cathode: Cu2+ + 2e-$\to$ Cu (deposited)
Reaction at anode: Cu - 2e- $\to$ Cu2+
4. Element X is a metal with a valency 2. Element Y is a non-metal with a valency 3.
(a) Write equations to show how X and Y form ions?
Ans: X $\to$ X2+ +2e-
Y + 3e- $\to$ Y3-
(b) If Y is a diatomic gas, write the equation for the direct combination of X and Y to form a compound.
Ans: Y2 + 3X $\to$ X3Y2
(c) If the compound formed between X and Y is melted and an electric current passed through the molten compound, the element X will be obtained at the _____ and Y at the _________of the electrolytic cell.(Provide the missing words)
Ans: Cathode , Anode
5. Write two applications of electrolysis in which the anode diminishes in mass.
Ans: i. Electroplating of metals
ii. Electrorefining of metals
6. (a) What kind of particles will be found in a liquid compound which is a non- electrolyte?
Ans: Non-electrolyte contains molecules.
(b) If HX is a weak acid, what particles will be present in its dilute solution apart from those of water?
Ans: Molecules of HX and H+ and X- ions.
(c) Cations are formed by ____ (loss/gain) of electrons and anions are formed by _________(loss/gain) of electrons. (Choose the correct word to fill in blank)
Ans: Loss
(d) What ions must be present in a solution used for electroplating a particular metal?
Ans: The electrolyte used for the purpose must contain the ions of metal which is to be electroplated on the article.
7. A strip of copper is placed in four different colourless salt solutions. They are KNO3, AgNO3, Zn(NO3)2 and Ca(NO3)2. Which one of the solutions will finally turn blue?
Ans: AgNO3 solution
2008
(a) Here is an electrode reaction :
Cu $\to $Cu+2 +2e-
At which electrode (anode or cathode) would such a reaction take place? Is this an example of oxidation or reduction?
Ans: The reaction takes place at anode. This is an example of oxidation
(b) A solution contains magnesium ions (Mg2+), iron (II) ions (Fe2+) and copper ions (Cu2+ ). On passing an electric current through this solution, which ions will be first to be discharged at the cathode? Write the equation for the cathode reaction.
Ans: Cu+2 will discharge easily at cathode.
Reaction at cathode:
Cu+2 +2e- $\to $Cu
(c) Why is carbon tetrachloride, which is a liquid, a non-electrolyte?
Ans: Carbon tetrachloride is a non-electrolyte because it is a covalent compound. It does not ionize and hence does not conduct electricity.
(d) During the electrolysis of molten lead bromide, which of the following takes place?
A. Bromine is released at the cathode
B. Lead is deposited at the anode
C. Bromine ions gain electrons
D. Lead is deposited at the cathode
Ans: D. Lead is deposited at cathode.
2009
a. Select the correct answer: The aqueous solution of the compound which contains both ions and molecules is
A. H2SO4
B. HCl
C. HNO3
D. CH3COOH
Ans: D. CH3COOH
b. Correct the following statement: Lead bromide conducts electricity.
Ans: Molten lead bromide conducts electricity.
c. A metal article is to be electroplated with silver. The electrolyte selected is sodium argentocyanide.
i. What kind of salt is sodium argentocyanide?
Ans: Complex salt
ii. Why is it preferred to silver nitrate as an electrolyte?
Ans: On using silver nitrate, the deposition of silver on the cathode is very fast and hence not very smooth and uniform because it is a strong electrolyte.
iii. State one condition to ensure that the deposit is smooth, firm and long lasting.
Ans: A long current for a longer time should be used.
iv. Write the reaction taking place at the cathode.
Ans: Ag+ + e- $\to$ Ag
v. Write the reaction taking place at the anode.
Ans: Ag - e- $\to$ Ag+
2010
Select the correct answer: A compound which during electrolysis in its molten state liberates a reddish brown gas at the anode.
i. Sodium chloride
ii. Copper (II) oxide
iii. Copper (II) sulphate
iv. Lead (II) bromide
Ans: iv. Lead (II) bromide
During electroplating of an article with nickel,
i. Name
A. The electrolyte
Ans: Aqueous solution of nickel sulphate with few drops of dil. sulphuric acid.
B. The cathode
Ans: Article
C. The anode
Ans: Pure nickel
ii. Give the reaction of electrolysis at
A. The cathode
Ans: Ni2+ + 2e- $\to$ Ni
B. The anode
Ans: Ni $\to$ Ni2+ + 2e-
c. A, B and C are three electrolytic cells connected in different circuits. Cell 'A' contains NaCl solution. And the bulb in the circuit glows brightly when the circuit is completed. Cell 'B' contains acetic acid and the bulb glows dimly. Cell 'C' contains sugar solution, and the bulb does not glow. Give reason for each observation.
Ans: Cell A contains sodium chloride solution which is a strong electrolyte and contains only ions. So, it conducts electricity and the bulb glows brightly.
Cell B contains both ions and molecules. So, there are very few ions to conduct electricity and the bulb glows dimly.
Cell C contains sugar solution which is a non-electrolyte and does not contain ions. So, it is a bad conductor of electricity and the bulb does not glow.
2011
a. Give reason: The electrolysis of acidulated water is considered to be an example of catalysis.
Ans: Dissociation is catalysed by dilute sulphuric acid, so electrolysis of acidified water is considered an example of catalysis.
b. During the electrolysis of copper (H) sulphate solution using platinum as a cathode and carbon as an anode,
i. State what you observe at the cathode and at the anode.
Ans: Red shiny metal deposits at the cathode.
ii. State the change noticed in the electrolyte.
Ans: The electrolyte colour changes gradually from blue to colourless.
iii. Write the reactions at the cathode and at the anode.
Ans: At the cathode:
Cu2+ + 2e- $\to$ Cu
Reaction at the anode:
OH- $\to$ OH + e-
4OH $\to$ 2H2O + O2
c. Differentiate between electrical conductivity of copper sulphate solution and that of copper metal.
2012
a. Identify the weak electrolyte from the following:
i. Sodium chloride solution
ii. Dilute hydrochloric acid
iii. Dilute sulphuric acid
iv. Aq. acetic acid
Ans: iv. Aq. acetic acid
b. Match the following in Column A with the correct answer from the choices given in Column B:
Column A | Column B |
1. Ammonium hydroxide solution | (i) Contains only ions |
2. Dilute hydrochloric acid | (ii) Contains only molecules |
3. Carbon tetrachloride | (iii) Contains ions and molecules |
Ans: Ammonium hydroxide solution - Contains ions and molecules
Dilute hydrochloric acid - Contains only ions
Carbon tetrachloride - Contains only molecules
c. Give reason: An aqueous solution of sodium chloride conducts electricity.
Ans: An aqueous solution of sodium chloride consists of free sodium and chloride ions which are responsible for conducting electricity.
d. Select the correct answer from the list in brackets:
i. An aqueous electrolyte consists of the ions mentioned in the list. The ion which could be discharged most readily during electrolysis... (Fe2+, Cu2+, Pb2+, H+)
Ans: Cu2+
ii. The metallic electrode which does not take part in an electrolytic reaction... (Cu, Ag, Pt, Ni)
Ans: Pt
iii. The ion which is discharged at the anode during the electrolysis of copper sulphate solution using copper electrodes as anode and cathode… (Cu2+, OH-, SO42-, H+)
Ans: Cu2+
iv. When dilute sodium chloride is electrolysed using graphite electrodes, the cation which is discharged at the cathode most readily... (Na+, OH_, H+, Cl-)
Ans: H+
v. During silver plating of an article using potassium argentocyanide as an electrolyte, the anode material should be... (Cu, Ag, Pt, Fe)
Ans: Ag
2013
a. State one appropriate observation for: Electricity is passed through molten lead bromide.
Ans: Dark red brown fumes of bromine release at the anode and greyish white metal lead is formed on the cathode.
b. State which of these will act as a non-electrolyte:
i. Liquid carbon tetrachloride
ii. Acetic acid
iii. Sodium hydroxide aqueous solution
iv. Potassium chloride aqueous solution
Ans: i. Liquid carbon tetrachloride
c. Copper sulphate soln. is electrolysed using copper electrodes.
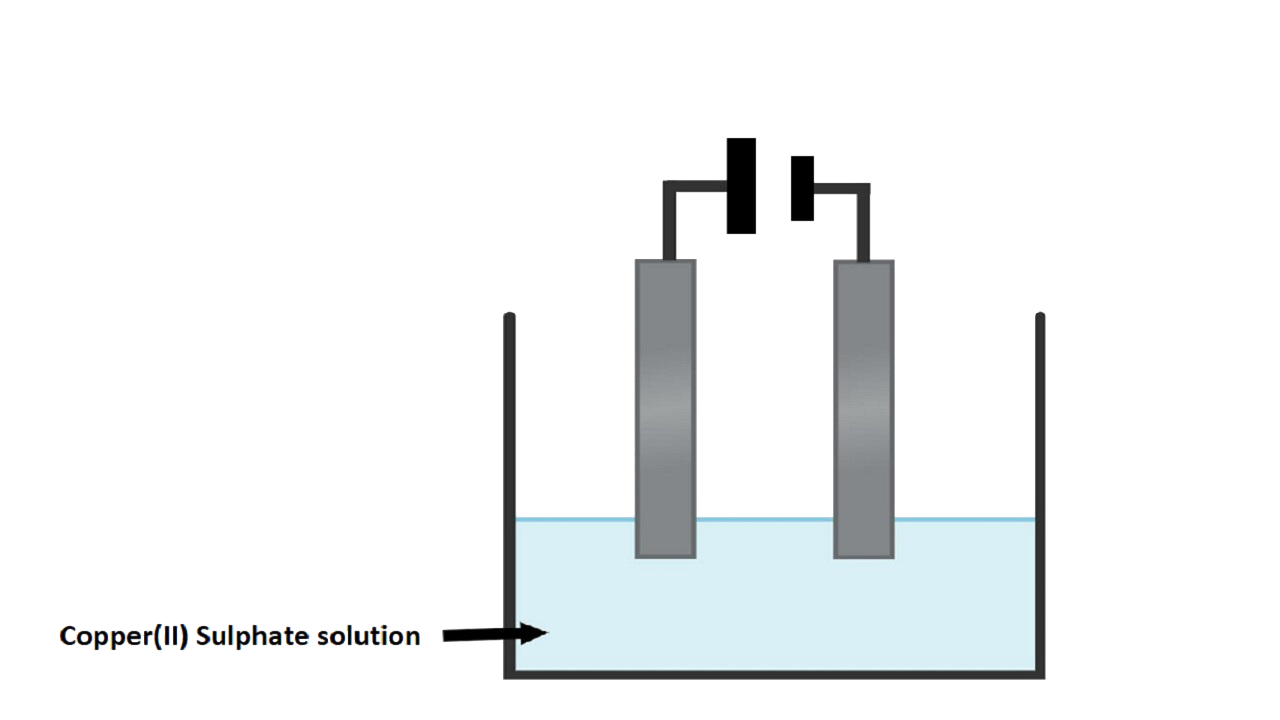
i. Which electrode to your left or right is known as the oxidising electrode and why?
Ans: The right electrode is the anode and oxidising electrode. Cu $\to$ Cu2+ + 2e- losing electrode.
ii. Write the equation representing the reaction that occurs.
Ans: Reaction at the anode: Cu $\to$ Cu2+ + 2e-
Reaction at the cathode: Cu2+ + 2e-$\to$ Cu
iii. State two appropriate observations for the above electrolysis reaction.
Ans: The anode dissolves and anode mud containing precious metal is recovered.
d. Identify: A gas which does not conduct electricity in the liquid state but conducts electricity when dissolved in water.
Ans: Hydrogen chloride
2014
The observation seen when fused lead bromide is electrolysed is
i. A silver grey deposit at anode and a reddish brown deposit at cathode.
ii. A silver grey deposit at cathode and a reddish brown deposit at anode.
iii. A silver grey deposit at cathode and reddish brown fumes at anode.
iv. Silver grey fumes at anode and reddish brown fumes at cathode.
Ans: iii. A silver grey deposit at cathode and reddish brown fumes at anode.
b. During electroplating an article with silver, the electrolyte used is
i. Silver nitrate solution
ii. Silver cyanide solution
iii. Sodium argentocyanide solution
iv. Nickel sulphate solution
Ans: iii. Sodium argentocyanide solution
c. Give one word or phrase for: Electrolytic deposition of a superior metal on a baser metal.
Ans: Galvanisation
d. State your observation seen: At the cathode when acidified aqueous copper sulphate solution is electrolysed with copper electrodes.
Ans: Acidified aqueous copper sulphate solution is electrolysed with copper electrodes by electrolysis. The electrolysis of an aqueous solution of copper sulphate using copper electrodes (i.e. using active electrodes) results in transfer of copper metal from the anode to the cathode during electrolysis. The copper sulphate is ionised in the aqueous solution.
Copper sulphate solution is ionised by the following chemical equation:
CuSO4 $\to$ Cu2+ + SO42-
The positively charged copper ions migrate to the cathode, where each gains two electrons to become copper atoms which are deposited on the cathode.
Cu2+ + 2e-$\to$ Cu
Hence, the colour of copper sulphate changes from
blue to colourless.
e. State which electrode: anode or cathode is the oxidising electrode. Give a reason for the same.
Ans: Cathode (Reducing electrode): At the cathode, the cations gain electrons to form neutral atoms. As electrons are gained, the ion is said to be reduced.
Anode (Oxidising electrode): At the anode, the anions lose electrons to form neutral atoms. As electrons are lost, the ion is said to be oxidised.
f. Name the kind of particles present in
i. Sodium hydroxide solution
Ans: Positive sodium ions and negative hydroxide ions
ii. Carbonic acid
Ans: Hydrogen ions and carbonate ions
iii. Sugar solution
Ans: Glucose, fructose and galactose
g. M2O is the oxide of a metal 'M' which is above hydrogen in the activity series. M2O when dissolved in water forms the corresponding hydroxide which is a good conductor of electricity.
i. State the reaction taking place at the cathode
Ans: M+ + 1e- $\to$ M
ii. Name the product at the anode
Ans: Oxygen gas
2015
State the observation at the anode when aqueous copper sulphate solution is electrolysed using copper electrodes.
a. Copper anode itself ionises to give Cu2+ ions.
Ans: Cu - 2e- $\to$ Cu2+
b. During electrolysis of molten lead bromide, graphite anode is preferred to other electrodes. Give a reason.
Ans: During the electrolysis of molten lead bromide, a graphite anode is preferred because graphite remains unaffected by the reactive bromine vapours which are released at the anode.
c. Electrolysis of molten lead bromide is considered to be a redox reaction. Give a reason.
Ans: In the electrolysis of molten lead bromide, the following reactions take place:
At the cathode: Pb2+ (l) + 2e- $\to$ Pb(l)
At the anode: 2Br- (l) $\to$ Br2 (g) + 2e-
Lead (II) ions (Pb2+) are attracted to the negative electrode, and the Pb2+ ions are forced to accept two electrons. Pb2+ ions are reduced. Bromide ions (Br-) are attracted to the positive electrode, and the bromide ions are forced to give away their extra electrons to form bromine atoms. Thus, bromide ions are oxidised. So, electrolysis of molten lead bromide is a redox reaction.
2016
Give reasons why :
(a) Sodium Chloride will conduct electricity only in fused or aqueous solution state.
Ans: Electrostatic forces of attraction between ions in the solid state are very strong. These forces weaken in the fused or solution state. Hence, ions become mobile.
(b) In the electroplating of an article with silver, the electrolyte sodium argentocyanide solution is preferred over silver nitrate solution.
Ans: If silver nitrate solution is used directly instead of double cyanide of silver and sodium, silver will deposit very fast and its deposition will not be smooth and uniform.
(c) Although copper is a good conductor of electricity, it is a non-electrolyte.
Ans: Copper has no mobile electrons in the solid state and an electrolyte should dissociate into oppositely charged ions to conduct electricity.
Hence, copper is a non-electrolyte.
Free Download of Solutions for Class 10 Science (Chemistry) Chapter 6
Electrolysis is an interesting chapter in the Selina textbook for class 10 chemistry. The chapter explains what electrolysis is, and students will learn how the process works in different situations or from different perspectives.Students will also learn about electrolysis products and reactions in this chapter.Because there are many questions that can be asked about this topic, we are providing free concise Chemistry class 10 ICSE Solutions for chapter 6 here.
What Exactly is Electrolysis?
The process of breaking down ionic compounds into their constituent elements by passing a direct electric current through the compound in a fluid state is known as electrolysis. The cathode reduces cations, while the anode oxidizes anions. An electrolyte, electrodes, and some form of external power source are the main components required for conducting electrolysis. A partition, such as an ion-exchange membrane or a salt bridge, may also be used, but this is optional. These are primarily used to prevent the products from diffusing near the opposing electrode.
Bypassing an electric current through acidified or salt-containing water, the original elements hydrogen and oxygen can be decomposed. Sodium and chlorine atoms can be separated from molten sodium chloride.
Electrolysis is typically performed in a vessel known as an 'electrolytic cell,' which contains two electrodes (cathode and anode) connected to a direct current source and an electrolyte, which is an ionic compound in decomposition, either molten or dissolved in a suitable solvent. Electrodes made of metal, graphite, and semiconductor materials are commonly used. However, the selection of an appropriate electrode is based on the chemical reactivity of the electrode and electrolyte, as well as the manufacturing cost.
The Electrolytic Method
Electrolysis involves the exchange of ions and atoms caused by the addition or removal of electrons from the external circuit. Essentially, as current flows, cations move to the cathode, take electrons from the cathode (provided by the supply source battery), and discharge into the neutral atom. If the neutral atom is solid, it is deposited on the cathode; if it is gas, it moves upwards. The cation is reduced at the cathode during this reduction process.
Simultaneously, anions surrender their extra electrons to the anode and are oxidized to neutral atoms at the anode. Electrons released by anions travel across the electrical circuit and complete the circuit by reaching the cathode. Electrolysis involves a simultaneous oxidation and reduction reaction at the anode and cathode.
For example, when an electric current is passed through molten sodium chloride, the cathode attracts the sodium ion, which then takes an electrode and becomes a sodium atom.
Chloride ion reaches the anode, gives up its electron, and transforms into a chlorine atom, which then forms a chlorine molecule.
Na+ (in electrolyte) + e– (from cathode) Na....
Cl–(from electrolyte) e– + Cl Cl2.... At the Anode
While the electrolysis process is useful for directly obtaining elemental forms from compounds, it can also be used indirectly in the metallurgy of alkali and alkaline earth metals, metal purification, and metal refining.
The Voltage or Cell Potential
The minimum potential required for electrolysis is determined by the ability of individual ions to absorb or release electrons. It is also known as decomposition potential or decomposition voltage, and it is the minimum voltage (difference in electrode potential) between the anode and cathode of an electrolytic cell that allows electrolysis to occur.
The voltage at which electrolysis is thermodynamically preferred is calculated using the Nernst equation as the difference of the electrode potentials. Overpotential, or the application of additional voltage, can increase the rate of reaction and is frequently required above the thermodynamic value. It is especially important in electrolysis reactions that involve gases like oxygen, hydrogen, or chlorine.
This capability is measured as the electrode potential of the ions in the electrolytic cell. The sum of the potentials required for the reduction and oxidation reactions is the cell potential. The standard reduction potential is available in the literature and is involved in various redox reactions.
According to thermodynamic Gibbs free energy, only reactions with positive redox cell potentials will be possible (or standard potential). Electrolysis is generally thermodynamically controlled.
A potential equal to or slightly greater than that is applied externally in electrolysis. Ions that are stable and do not react are made to react in the presence of an externally applied potential. As a result of the external potential, an unfavorable reaction occurs. Because chemical bonds connecting atoms are formed or broken during electrolysis, electrolysis involves the conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy.
Electrolysis Byproduct
Direct electrolysis occurs when only two ions (cation and anion) are present in a single electrolyte. Electrolysis will generate products that are already present in the compound. When there are multiple cations and anions present, each ion competes for reduction and oxidation. Reactions with higher positive redox potentials will be reduced or oxidized over others.
So, despite the presence of multiple redox couples, only one can be reduced or oxidized. The ions that are reduced or oxidized may vary depending on their relative amount. In other words, the redox reaction and electrolysis can be controlled kinetically. In such cases, the analysis product may differ depending on the relative concentration of the various ions present in the electrolyte.
For example, electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride can result in a variety of products-
Hydrogen and chlorine, oxygen and hydrogen, and chlorine, oxygen, and hydrogen.
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 6 Electrolysis is covered in detail by Vedantu. Selina Concise Chemistry ICSE Solutions for Class 10 are available for free PDF download. All questions in Selina Publishers Concise Chemistry for Class 10 ICSE Solutions are solved and explained by expert teachers in accordance with ICSE board guidelines.
FAQs on Electrolysis Solutions for ICSE Board Class 10 Science
1. Give three distinctions between a sodium atom and a sodium ion.
(i) In nature, sodium atoms are neutral, whereas sodium ions are positively charged particles.
(ii) A sodium atom vigorously reacts with water to liberate hydrogen gas, whereas a sodium ion does not.
(iii) In the outermost shell, a sodium atom tends to lose an electron to form a sodium ion with a complete octet.
2. Explain what a redox reaction is and how electrolysis is an example of one.
Redox reactions are known as simultaneous oxidation-reduction reactions. Positively charged ions (cations) accept electrons from the cathode to form neutral atoms in electrode reactions, i.e., cathode reduction occurs. Anode oxidation occurs when negatively charged ions (anions) lose electrons to form neutral atoms at the anode. As a result, electrode reactions also represent oxidation-reduction reactions. As a result, they are also known as Redox reactions.
3. M, for example, does not liberate hydrogen from dilute sulphuric acid but instead displaces copper from aqueous copper (II) sulphate. Indicate the metal's most likely position in the electrochemical series.
The activity series is obtained by investigating the replacement of one metal ion from its solution by another metal. In the activity series, the metal (M) that displaces copper from aqueous copper (II) sulphate is placed higher than copper.
4. How to study the chapter Electrolysis for Class 10 Science ICSE Board effectively?
Students can study the Electrolysis Solutions for Class 10 Science ICSE Board effectively with the help of Electrolysis Solutions for Class 10 Science ICSE Board Concise Selina Publishers. They can help students to learn every topic in an easier way. Vedantu provides these study materials for students free of cost and helps them study in a better manner.
5. How is a silver spoon electroplated?
In a beaker, a silver nitrate solution is taken. The solution is used to dip silver wire and a spoon to be plated with silver. The positive terminal of the battery is connected to the silver wire, which acts as an anode, and the negative terminal of the battery is connected to the spoon, which acts as a cathode.
When an electric current is passed through a silver nitrate solution, electrolysis occurs, and silver is deposited on the surface of the spoon as a fine thin film. The spoon is silver-plated and appears to be a silver spoon.






































