
When a capillary tube is immersed vertically in water the capillary rise is 3cm. If the same capillary tube is inclined at an angle of 60 degrees to the vertical, the length of the water column in the capillary tube above that of the outside level is:
A) 6cm
B) 1cm
C) 8cm
D) Zero.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: To choose the correct option you should be familiar with capillary action. Capillary action is the ability of a liquid to flow in a narrow space. For example, if you dip a strip of paper in the water you will find that the water starts to flow in the strip above the water level in which the strip is dipped. This flow occurs because of adhesion, cohesion, and surface tension of the water. But this capillary rise happens to some limited height because of the gravitational force. It cannot flow continuously upwards. Since gravitational force affects the capillary rise then it makes sense that the rise in a capillary tube depends on the density of the liquid. Therefore less radius of the tube means more rise of liquid. If we incline the capillary tube then because of the surface tension the height of the level of rising above that of the outside level will be the same. Then use a simple cosine trigonometric function to calculate the water column length.
Complete step by step solution:
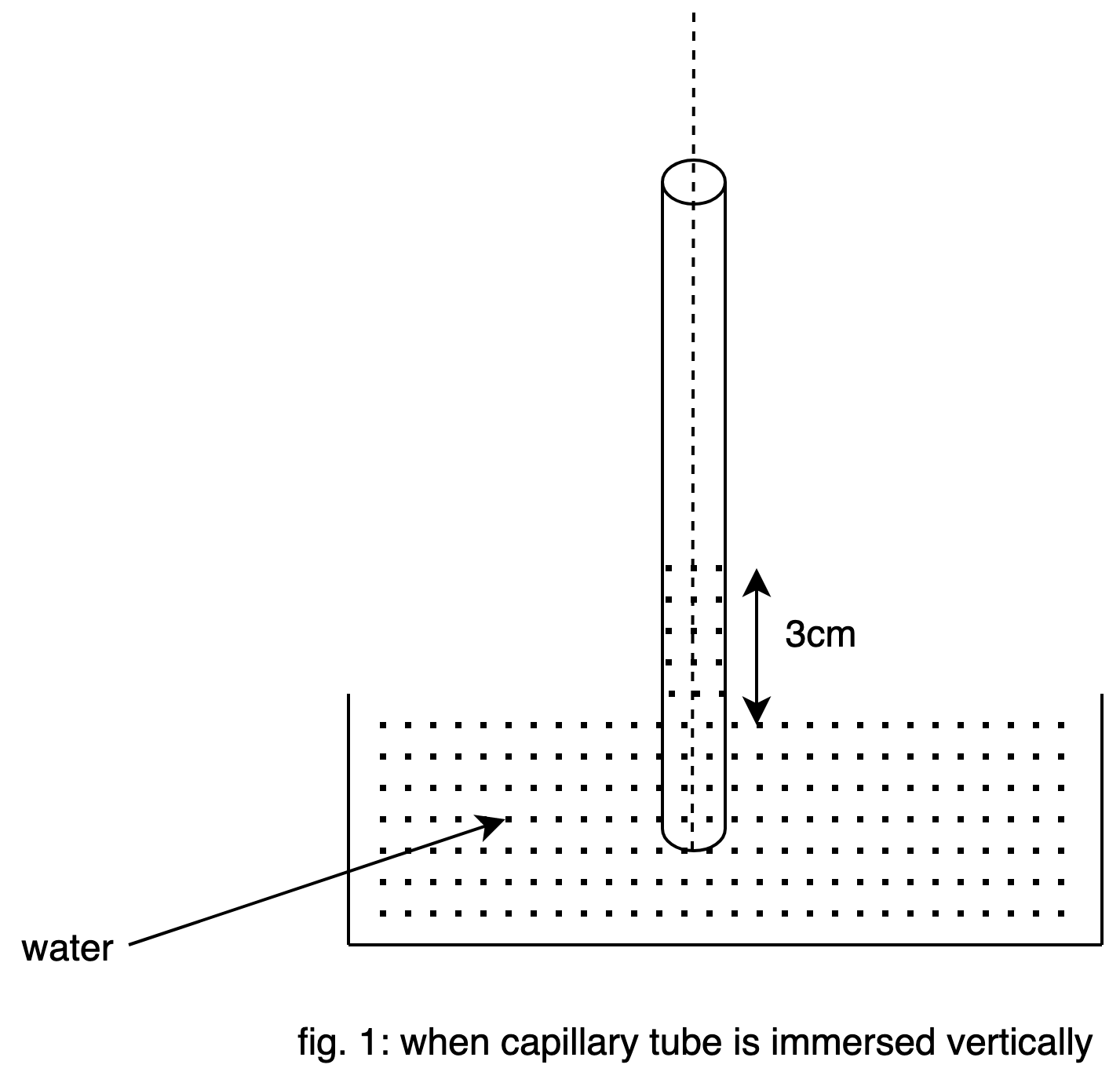
In fig.1 a capillary tube is immersed vertically in the water. The capillary rise is 3cm.
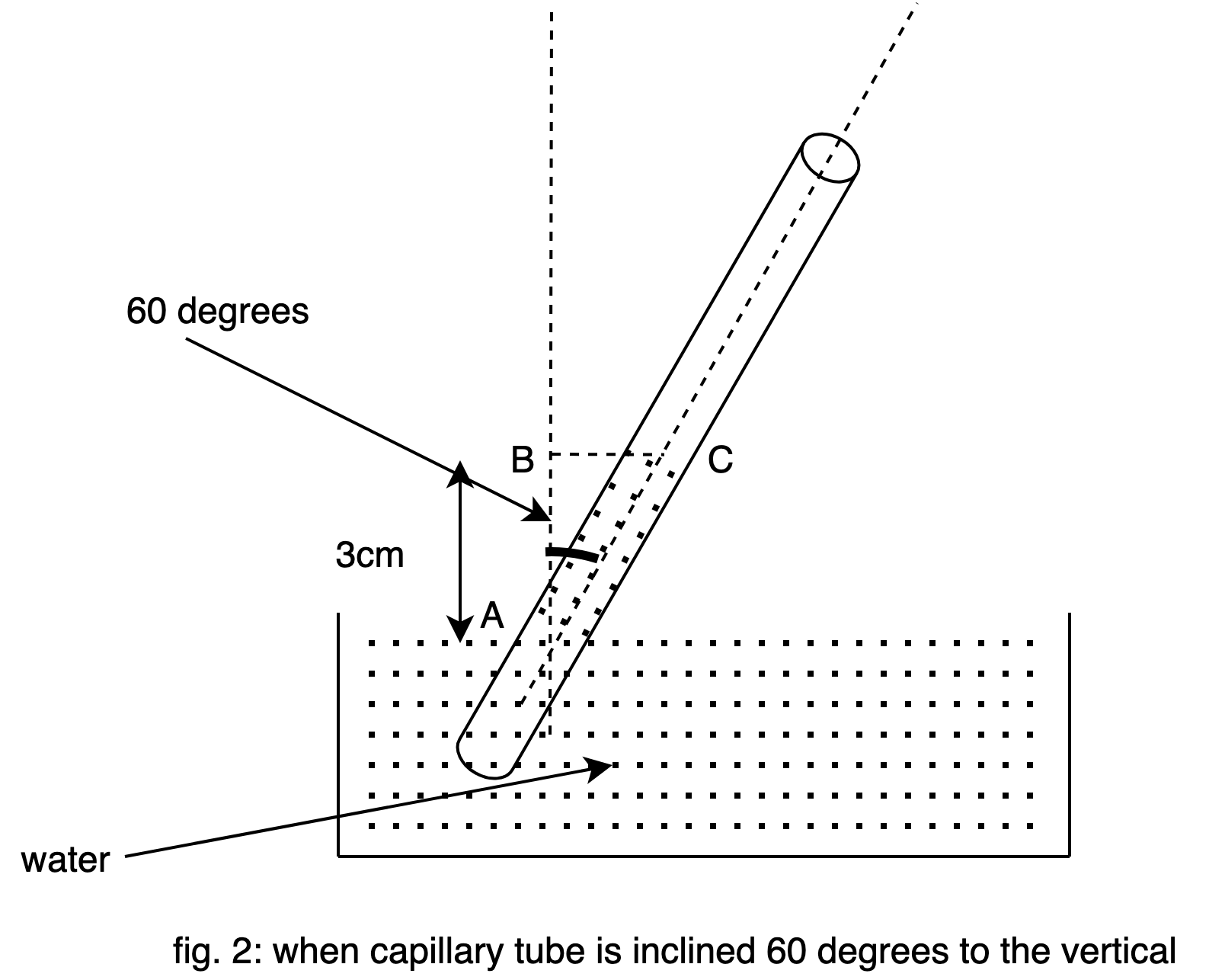
In fig.2 the capillary tube is inclined 60 degrees to the vertical. Since the height of the raised water level will be the same when the capillary tube is inclined. Therefore AB is 3cm. Let us assume the length of AC is $l$ .
Now in right triangle ABC we can wright
$\cos 60 = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}$
Substitute the values, 3 for $AB$ and $l$ for $AC$
$\therefore \cos 60 = \dfrac{3}{l}$
now put $\cos 60 = \dfrac{1}{2}$
$\therefore \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{3}{l}$
$ \Rightarrow l = 2 \times 3$
$ \Rightarrow l = 6$
Therefore the correct option is option A.
Note: The height of water level in the capillary tube from the level of water in which the tube is dipped does not depend on the angle with which the capillary tube is inclined. But the length of water-rise in the capillary tube changes as the angle changes to the vertical.
Complete step by step solution:

In fig.1 a capillary tube is immersed vertically in the water. The capillary rise is 3cm.

In fig.2 the capillary tube is inclined 60 degrees to the vertical. Since the height of the raised water level will be the same when the capillary tube is inclined. Therefore AB is 3cm. Let us assume the length of AC is $l$ .
Now in right triangle ABC we can wright
$\cos 60 = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}$
Substitute the values, 3 for $AB$ and $l$ for $AC$
$\therefore \cos 60 = \dfrac{3}{l}$
now put $\cos 60 = \dfrac{1}{2}$
$\therefore \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{3}{l}$
$ \Rightarrow l = 2 \times 3$
$ \Rightarrow l = 6$
Therefore the correct option is option A.
Note: The height of water level in the capillary tube from the level of water in which the tube is dipped does not depend on the angle with which the capillary tube is inclined. But the length of water-rise in the capillary tube changes as the angle changes to the vertical.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




