
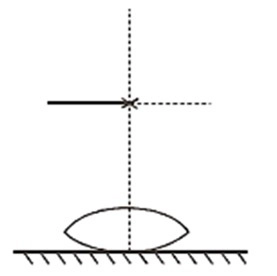
A symmetric biconvex lens of radius of curvature R and made of glass of refractive index 1.5 is placed on a layer of liquid placed on top of a plane mirror as shown in the figure. An optical needle with its tip on the principal axis of the lens is moved along the axis until its real inverted image coincides with the needle itself. The distance of the needle from the lens is measured in x. On removing the liquid layer and repeating the experiment the distance is found to be y. Obtain the expression for the refractive index of the liquid in terms of x and y.
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: We should know that the other name of convex lens is converging lens. This is known as so because the ray of light when passing through this lens converges and is always found to be parallel to the principal axis. The distance between the two foci points of a convex lens is known as the focal length. To answer this, it is required to consider each focal length as a specific variable and then solve it using the lens maker equation.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that when a liquid is placed on the top of a plane mirror and a convex lens over it then this entire system would be a combination of convex lens of glass and plano convex lens of the liquid. This is shown in the figure.
Let us consider that the focal length of the convex lens is ${{f}_{1}}$
And the focal length of the plano convex liquid lens is given as ${{f}_{2}}$
The combined focal length can be written as: F
Now we can say that in both the cases the image will coincide with the needle and hence the ray is normal to the plane mirror. So, the needle position is the focal lengths of the convex lens and also the system combined together.
Now, according to the question,
${{\text{f}}_{\text{1}}}\text{= y unit}$
And, \[\text{F = x unit}\]
We also know that for the combination of two lenses we can write the expression as:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{F}=\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{f}_{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{F}-\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{1}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{f}_{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}$
Thus, ${{f}_{2}}=\dfrac{xy}{y-x}$
Now for the glass lens, let us consider that ${{R}_{1}}=R$ and ${{R}_{2}}=-R$.
Now, from the lens maker formula we can write:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=(n-1)(1/R-(1/R))$
$\Rightarrow 1/y=(1.5-1)(1/R+1/R)$
$\Rightarrow 1/y=1/R$
$\Rightarrow R = y$ $unit$
Now for the liquid plano concave lens
$\Rightarrow {{R}_{1}}=-R$ and ${{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}\text{= infinity}$
Now, for the lens maker formula, we can write that:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{f}_{2}}}=\left( {{n}_{1}}-1 \right)\left( -\dfrac{1}{R}-\dfrac{1}{\infty } \right)$
$\Rightarrow 1-{{n}_{1}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{y-x}{x}$
$\Rightarrow {{n}_{1}}=\dfrac{1-y-x}{x}$
$\Rightarrow {{n}_{1}}=\dfrac{x-y+z}{x}$
$\Rightarrow {{n}_{1}}=\dfrac{2x-y}{x}$
Note: We know that an image coincides with the object only when light falls normal to mirror. Also, this can happen only when the light arrives from infinity to the normal to plane mirror i.e. it was placed at the focal length. Therefore, we can consider both x and y as focuses of the respective frames.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that when a liquid is placed on the top of a plane mirror and a convex lens over it then this entire system would be a combination of convex lens of glass and plano convex lens of the liquid. This is shown in the figure.
Let us consider that the focal length of the convex lens is ${{f}_{1}}$
And the focal length of the plano convex liquid lens is given as ${{f}_{2}}$
The combined focal length can be written as: F
Now we can say that in both the cases the image will coincide with the needle and hence the ray is normal to the plane mirror. So, the needle position is the focal lengths of the convex lens and also the system combined together.
Now, according to the question,
${{\text{f}}_{\text{1}}}\text{= y unit}$
And, \[\text{F = x unit}\]
We also know that for the combination of two lenses we can write the expression as:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{F}=\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{f}_{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{F}-\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{1}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{f}_{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}$
Thus, ${{f}_{2}}=\dfrac{xy}{y-x}$
Now for the glass lens, let us consider that ${{R}_{1}}=R$ and ${{R}_{2}}=-R$.
Now, from the lens maker formula we can write:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=(n-1)(1/R-(1/R))$
$\Rightarrow 1/y=(1.5-1)(1/R+1/R)$
$\Rightarrow 1/y=1/R$
$\Rightarrow R = y$ $unit$
Now for the liquid plano concave lens
$\Rightarrow {{R}_{1}}=-R$ and ${{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}\text{= infinity}$
Now, for the lens maker formula, we can write that:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{f}_{2}}}=\left( {{n}_{1}}-1 \right)\left( -\dfrac{1}{R}-\dfrac{1}{\infty } \right)$
$\Rightarrow 1-{{n}_{1}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{y-x}{x}$
$\Rightarrow {{n}_{1}}=\dfrac{1-y-x}{x}$
$\Rightarrow {{n}_{1}}=\dfrac{x-y+z}{x}$
$\Rightarrow {{n}_{1}}=\dfrac{2x-y}{x}$
Note: We know that an image coincides with the object only when light falls normal to mirror. Also, this can happen only when the light arrives from infinity to the normal to plane mirror i.e. it was placed at the focal length. Therefore, we can consider both x and y as focuses of the respective frames.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry




